
Identifying Student Profiles in CSCL Systems for Programming
Learning Using Quality in Use Analysis
Rafael Duque
1a
, Miguel Ángel Redondo
2b
, Manuel Ortega
2c
, Sergio Salomón
3d
and Ana Isabel Molina
2e
1
Departamento de Matemáticas, Estadística y Computación, Universidad de Cantabria, Avenida de los Castros S/N,
Santander, Spain
2
Departmento de Tecnologías y Sistemas de Información, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Ciudad Real, Spain
3
Departmento de Inteligencia Artificial, Axpe Consulting, Maliaño, Spain
Keywords: User Profiles, Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning, Programming Learning, Quality in Use.
Abstract: In the digital age, computer programming skills are in high demand, and collaborative learning is essential
for its development. Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL) systems enable real-time
collaboration among students, regardless of their location, by offering resources and tools for programming
tasks. To optimize the learning experience in CSCL systems, user profiling can be used to tailor educational
content, adapt learning activities, provide personalized feedback, and facilitate targeted interventions based
on individual learners' needs, preferences, and performance patterns. This paper describes a framework that
can be applied to profile students of CSCL systems. By analysing log files, computational models, and quality
measures, the framework captures various dimensions of the learning process and generates user profiles
based on the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality. The work also conducts a case study that
applies this framework to COLLECE 2.0, a CSCL system that supports programming learning.
1 INTRODUCTION
Computer-Supported Collaborative Learning (CSCL)
systems are learning environments that use computer
technology to support collaboration among students
in educational activities. To facilitate the teaching and
learning processes of computer programming, CSCL
systems can be considered particularly useful as they
replicate the professional context in which multiple
programmers participate in the same work processes
(Silva et al., 2020)
CSCL systems for programming learning provide
students with an interactive learning environment that
allows them to work together in real-time, regardless
of their physical location. They can share knowledge
and receive feedback from their peers and teachers.
These systems can offer a variety of resources and
tools such as tutorials, source code examples, and
shared editors. Furthermore, these resources and tools
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8636-3213
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5809-3412
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0194-7744
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4052-0556
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3449-2539
facilitate the teaching and learning of programming
based on a problem-solving paradigm (Dolog et al.,
2016). In this paradigm, students work in teams to
address a problem that involves identifying a solution
which they must then implement by writing the
source code and verifying it by executing the
program.
The quality of the learning experience with CSCL
systems can be optimized by considering the student
profiles (De Backer et al., 2022). For instance, the
student profile can be used to propose tasks, configure
working groups, and provide tutoring that aligns with
the specific needs of the learner. At this point, the
challenge arises to establish frameworks to identify
the student profiles who use CSCL systems that
support computer programming. This article
approaches this challenge using the concept of quality
in use (ISO/IEC 25010:2011, 2011), which is the
capability of the software product to enable specified
286
Duque, R., Redondo, M., Ortega, M., Salomón, S. and Molina, A.
Identifying Student Profiles in CSCL Systems for Programming Learning Using Quality in Use Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0012181800003584
In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2023), pages 286-293
ISBN: 978-989-758-672-9; ISSN: 2184-3252
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

users to achieve specified goals with effectiveness,
productivity, safety, and satisfaction in specified
contexts of use. More specifically, the article seeks
to assess the quality in use from the individual
perspective of each student, with the aim of
subsequently identifying user profiles based on the
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality
(Myers, 1962). For this purpose, this work describes
a framework that process log files, computational
models that represents several dimensions of the
learning process (features of the CSCL system, tasks
to be solved, etc.) and measures of the quality in use
of the CSCL system used by the learner. This
framework has been applied to COLLECE 2.0
(Lacave et al., 2019), a CSCL system that supports
programming learning.
The article includes 4 additional sections. Section
2 reviews works related with the generation of student
profiles interacting with CSCL systems. Section 3
describes the framework for generating students’
profile. Section 4 describes a case study in which the
applicability of the framework to the COLLECE 2.0
system is studied. Section 5 analyses the conclusions
of the work carried out and the new lines of research
that will be undertaken in the future.
2 BACKGROUND
This section begins with a review of works in the field
of generating user profiles of CSCL systems in
support of programming learning. Subsequently, the
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality is
analysed. Finally, the section explores how software
quality in use can be measured.
2.1 Learner Profiles
Learner profiles in CSCL systems for computer
programming learning aim to capture and represent
various aspects of learners, including their
programming skills, problem-solving strategies,
learning preferences, and social interactions within
the collaborative environment (Muehlenbrock, 2006).
These profiles are typically created by collecting and
analysing data generated during students' interactions
with the CSCL system, such as their programming
code, communication logs, and problem-solving
actions.
The integration of learner profiles in CSCL
systems offers numerous benefits. Firstly, it enables
the identification of students who may be struggling
or excelling in certain programming concepts,
allowing educators to provide targeted support or
challenge accordingly (Villanueva et al, 2018).
Secondly, learner profiles facilitate the formation of
heterogeneous or homogeneous groups based on
students' skills and preferences, promoting effective
collaboration and knowledge sharing among peers
(Duque et al., 2015). Additionally, learner profiles
can contribute to the development of intelligent
tutoring systems, adaptive learning environments,
and recommendation systems, enhancing the overall
learning experience for students (Kukla et el., 2003).
Despite the advancements made in the field of
learner profiles in CSCL systems for computer
programming learning, several challenges and
opportunities remain. There have been numerous
research proposals aimed at identifying student
profiles as users of CSCL systems. However, it is
commonly observed that measures of quality in use
are not frequently utilized as criteria for establishing
these profiles. The focus often remains on factors
such as demographic information, academic
performance, or behavioural patterns, rather than
considering the quality of the user experience during
CSCL system usage.
2.2 Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a
psychological assessment tool used to understand a
person's preferences and personality traits. It is based
on Carl Jung's theories of psychological types. The
MBTI classifies individuals into four binary
dimensions, resulting in 16 possible personality
types. These dimensions are:
• Extraversion (E) vs. Introversion (I): It refers to
a person's source of energy. Extroverts tend to
derive energy from interacting with others and
the external world, while introverts draw energy
from internal reflection and solitude.
• Sensing (S) vs. Intuition (N): It relates to how a
person prefers to gather information. Individuals
who prefer sensing rely on tangible and concrete
information through their senses, while those
who prefer intuition rely on patterns,
possibilities, and abstract connections.
• Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F): It pertains to how
a person makes decisions and values
information. Those who prefer thinking tend to
be logical, objective, and focused on principles
and consistency, while those who prefer feeling
tend to be empathetic, consider personal values,
and focus on interpersonal harmony.
• Judging (J) vs. Perceiving (P): It relates to
lifestyle and how a person approaches the
Identifying Student Profiles in CSCL Systems for Programming Learning Using Quality in Use Analysis
287

external world. Those who prefer judging tend
to be structured, organized, and prefer planning,
while those who prefer perceiving tend to be
flexible, spontaneous, and adaptable.
By combining preferences in these four
dimensions, the MBTI yields 16 personality types,
such as INFP (Introverted, Intuitive, Feeling,
Perceiving) or ESTJ (Extraverted, Sensing, Thinking,
Judging). These personality types provide insights
into a person's general tendencies and preferences
regarding social interaction, decision-making,
information acquisition, and lifestyle.
2.3 Quality in Use
The ISO 25010:2011 standard introduces the concept
of quality in use as the degree to which a product or
system can be used by specific users to meet their
needs and achieve specific objectives effectively,
efficiently, without risks, and with satisfaction in
specific contexts of use. The ISO 25010:2011
standard defines a quality in use model with the
following set of software characteristics and sub-
characteristics that provide a generic framework for
evaluation.
According to ISO 25010:2011 standard,
efficiency refers to the resources used to achieve
objectives. Resource measurement is done by
quantifying the amount of time to complete tasks, as
well as the number of actions and spaces used.
The risk mitigation characteristic is defined in
ISO 25010:2011 standard as the degree to which a
system mitigates potential risk to economic status,
human life, health, or the environment. The quality in
use measures associated with this characteristic
quantify the system's responses to mitigate these
risks.
The satisfaction characteristic is defined as the
degree to which user needs are met when using a
system in a specific context of use. This characteristic
is represented in the ISO 25010:2011 quality model
by the following sub-characteristics:
• Usefulness: It is the degree to which a user is
satisfied by perceiving that they achieve their
goals pragmatically, including the results and
consequences of system use. The associated
measures evaluate the extent to which the user
finds the actions and spaces available in the
system useful for achieving their goals.
• Trust: It is the degree to which a user or other
stakeholder has confidence that a product or
system will behave as expected. These measures
assess whether the user takes actions related to
risks and responses from other collaborators,
relying on a satisfactory response from the
system and other participants.
• Pleasure: It is the degree to which the user feels
a pleasurable experience when fulfilling their
requirements. The measures for this sub-
characteristic evaluate whether the person
acquires new capabilities beyond those initially
established in the user model after using the
system in different work sessions.
• Comfort: It is the degree to which the user is
satisfied with the physical comfort of the device.
These measures assess the workload density of
each space and evaluate the use of interaction
paradigms based on implicit actions and
Augmented/Virtual Reality, which may be more
comfortable for the user.
The context coverage defines the degree to which
a system can be used while fulfilling the other
characteristics (effectiveness, efficiency, risk
mitigation, and satisfaction) in relation to the context
of use. The ISO 25010:2011 standard defines two
sub-characteristics for context coverage:
completeness and flexibility. Completeness implies
that quality in use is evaluated in a set of intended
usage contexts. Flexibility implies that the system is
used by users in contexts that were not initially
considered.
3 FAQUIS
FAQuiS (Framework for Assessing Quality-in-use of
Software) is a framework for calculating quality-in-
use measures (Salomón et al., 2022). FAQuiS does
not use questionnaires or user interviews, but it allows
complementing these methods with computational
support to automate the measurement of quality-in-
use by processing log files and the following three
computational models: (i) task model, (ii) context
model, and (iii) user model.
The task model in FAQuiS (see Figure 1) is based
on the following concepts:
• Task: A process that enabling the user to achieve
a goal with the support of the system. Tasks are
categorized into four types (Li et al., 2010): (i)
user tasks, which are exclusively performed by
the user without interacting with the system; (ii)
cognitive tasks, which are solely the
responsibility of the user and do not involve
interaction with the system; (iii) system tasks,
WEBIST 2023 - 19th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
288

performed by the application itself and do not
require direct user intervention; (iv) interactive
tasks, which involve active participation by the
user interacting with the system; (v) abstract
tasks, which are decomposed into a set of
smaller and more specific subtasks to facilitate
their execution and monitoring.
• Artifact: It refers to the products, results, or
outputs that users produce when performing a
task using a computer system (e.g., source code,
compilation or execution results).
• User action: The unit of user interaction with the
system, which is stored in a log repository. Each
action is classified as follows (Duque et al.,
2011): cognitive action, interacts with an artifact
but does not alter its state; communicative
action, allows the exchange of messages
between users (e.g., sending messages through
chat, forums, email, etc.); instrumental action,
modifies a construction artifact (e.g., changes in
source code); protocol-based action, allows
coordinating the collaborative process without
establishing dialogue between users (e.g.,
requesting access to a shared editor, voting on a
proposal, etc.).
Additionally, each action can have associated
risks (economic, health-related, etc.) whose
frequency needs to be estimated and quantified,
considering how the system mitigates their impact.
User actions allow the user to interact with the system
through an interaction paradigm (ubiquitous
computing, augmented/virtual reality, etc.).
The context model (see Figure 1) includes
information such as the user's location, social
relationships, and whether they are engaged in
synchronous or asynchronous collaboration. Finally,
the context model includes a technological dimension
that specifies the software and hardware support
available to the user.
The user model (see Figure 1) represents
information about the profile of the person interacting
with the system (age range, gender, nationality, etc.),
interests in certain types of tasks, role (student,
teacher, etc.), and other traits that can influence the
interaction with the system such as the MBTI (see
Subsection 2.2). Additionally, a specification of the
user's technical and language skills is established.
The log file is a repository of actions executed by
the user or the system. This file includes an identifier
for the actions collected in the task model that are
executed, who performs them, when they are carried
out, and the system space that supports those actions.
This space can be any user interface element defined
in the system.
FAQuiS uses these models and log file to generate
a set of measurements associated with each of the
characteristics and sub-characteristics of the ISO
25010:2011 standard. Section 4 describes what these
measures are and how they can be used to establish
user profiles in a case study.
4 CASE STUDY
COLLECE 2.0 (COLLaborative Edition,
Compilation and Execution of programs) is an
Eclipse plugin for group programming, which
features a customizable user interface. This interface
(see Figure 2) includes a project file tree, a panel of
connected users, tele-cursors to identify who is
editing and where in the code they are doing it, a
shared code editor, functionalities for locking code
regions so that a student can prohibit modifications to
a code snippet by other peers, a control panel for
locked regions to show which code is blocked and
who restricted it, chat functionality, and the problem
statement to be solved. All these elements are
designed to enable synchronous distributed
collaboration among students for problem-solving in
the field of computer programming. Furthermore,
COLLECE 2.0 uses version control systems to
maintain the persistent state of code projects
associated with sessions.
COLLECE 2.0 also includes a space that
leverages the Augmented Reality (AR) paradigm,
where students can visualize the behavior of the
program they are constructing using the ANGELA
notation (notation of road signs to facilitate the
Learning of progrAmming). This notation is based on
a metaphor of roads and traffic signs represented by
3D graphics. These visual representations allow for
an intuitive visualization of the program's execution
flow, as students are familiar with these roads and
signs in their daily lives. Such graphical
visualizations can be automatically generated from
the source code of the programs. The ANGELA
notation enables both static and dynamic
visualization of the implemented algorithms. In the
case of static visualization, the goal is to facilitate
understanding of the statements that compose the
program. On the other hand, dynamic visualization
allows for tracking the program's execution,
functioning as a simulator of the program's trace.
Identifying Student Profiles in CSCL Systems for Programming Learning Using Quality in Use Analysis
289
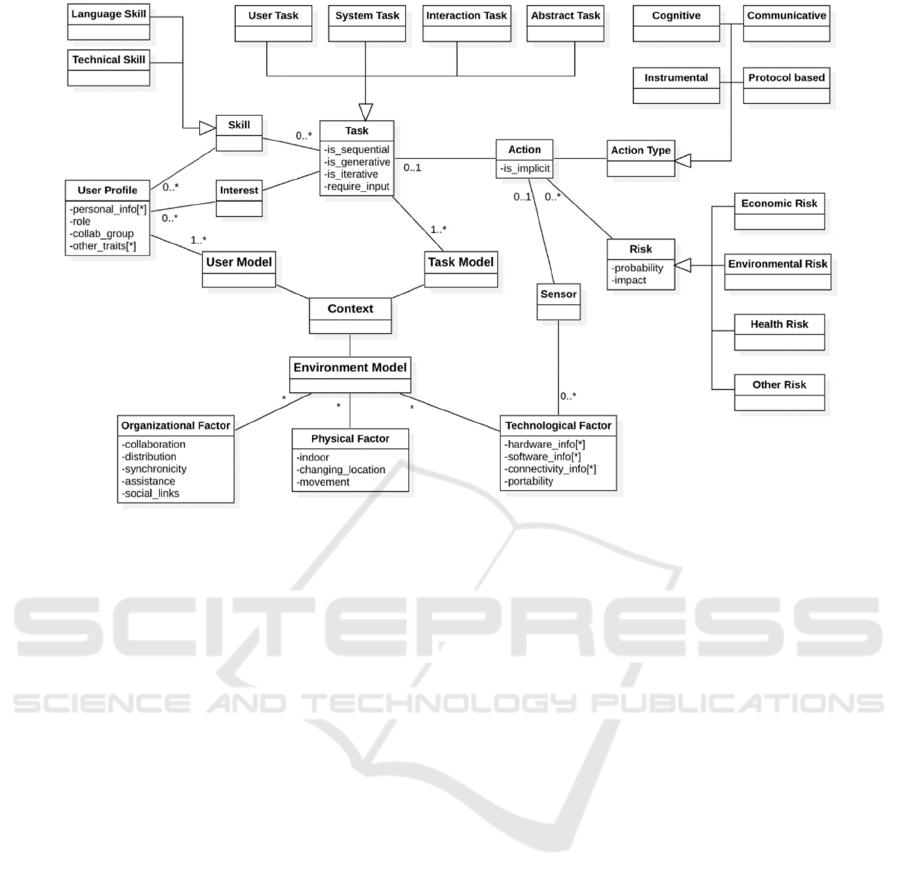
Figure 1: Metamodel of FAQuiS (Salomón et al., 2022).
Table 1 synthesizes how the actions collected in
the log file and the processing of the three models
managed by FAQuiS (task model, context model, and
user model) allow evaluating the quality in use of
COLLECE 2.0 as a learning tool for programming
through a problem-based approach.
The effectiveness of the problem-solving process
is measured through the impact of instrumental
actions in the shared editor, as they allow building an
artifact that solves the problem posed by the system,
the results obtained in the console after compilation
and execution actions, and the degree of adherence to
the patterns specified in the task model (see Table 1).
Measures related to efficiency (see Table 1)
compute the amount of time the student spends
resolving the problem by interacting and performing
actions in all areas of the system. Specifically, the
time spend working with the editor and console of
COLLECE 2.0 and the number artifacts generated are
computed.
The evaluation of risk mitigation relies on
indications within the task model, which delineates
actions potentially associated with risk. In this case,
the system's actions that successfully prevent
modifying a locked code fragment by another student
are computed (see Table 1).
For each of the satisfaction sub-characteristics
(usefulness, trust, pleasure, comfort), specific
measures are established. Therefore, usefulness
measures (see Table 1) process all the actions in the
log repository to identify those specified in the task
model that are not executed (compilation actions,
execution, sending messages in the chat, etc.) and the
underutilized areas of the system (console, region
locking panel, etc.).
User trust in the system is gauged using a set of
values designed to identify situations in which a
student might not receive responses from peers in the
chat, avoids executing protocol actions for code
locking, leaves problem-solving tasks incomplete
from previous sessions, or refrains from utilizing the
AR paradigm (see Table 1). Such behaviours may
imply reduced confidence in the system's
functionality (see Table 1).
The pleasure sub-characteristic has associated
measures (see Table 1) that depend on the problem
statement and the user model to assess the extent to
which the collaboration process enables the students
to acquire new skills. These measures assess whether
the student is able to solve problems that require new
skills and does so in work sessions that demand less
effort over time as the required competencies are
consolidated.
Comfort measures (see Table 1) are related to the
number of actions supported within a single interface
space, which can hinder its usability. The use of the
AR paradigm is also considered, estimating that it
may provide greater comfort for the student in
performing their tasks.
WEBIST 2023 - 19th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
290
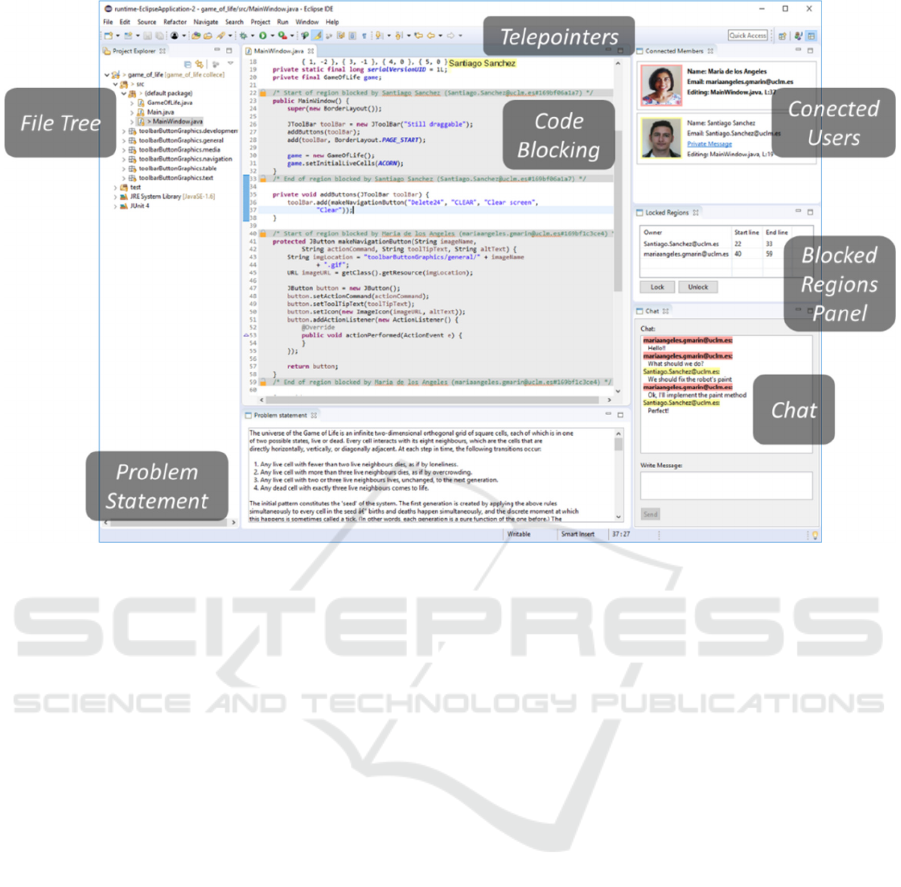
Figure 2: User interface of COLLECE.
Completeness is a sub-characteristic of contextual
coverage that is quantified through the rest of the
measures to determine if changes in the context
model (synchronous or asynchronous collaboration,
composition of the working group, etc.) influence the
other quality of use characteristics (see Table 1).
Flexibility applies the previously calculated metrics
for the other quality of use characteristics to analyse
situations that were not initially identified in the
context model (see Table 1).
Quality in use measurements are useful for
updating the user model of FQuiS using the MBTI.
These measurements can contribute to discriminating
which of the 16 possible personalities corresponds to
the student in the following way (see Table 1):
• Extraversion vs. Introversion: Students who are
more closely related to the extraversion
indicator obtain quality in use measurements
that tend to use communicative and protocol-
based actions. On the other hand, students who
lean towards introversion shy away from these
actions, and these measurements quantify it.
• Sensing vs. Intuition: Quality in use
measurements can be applied to identify
students who are closer to the sensing indicator
because they prefer to use spaces based on AR
to have a visual representation of the program
they are constructing. Conversely, students who
align with the intuition indicator have an
abstract thinking ability that allows them to use
other types of spaces, such as the editor with
source code.
• Thinking (T) vs. Feeling (F): In this case,
students who can be characterized with the
thinking indicator are those who are highly
effective and make full use of all system spaces.
Measurements related to pleasure can be useful
for identifying students close to the feeling
indicator.
• Judging vs. Perceiving: Quality in use
measurements also provide information to
identify students with a judging profile as they
are consistent, highly efficient in their
performance, but their nature prevents them
from taking actions involving risk. On the other
hand, students with the perceiving indicator tend
to exhibit a more anarchic performance.
Identifying Student Profiles in CSCL Systems for Programming Learning Using Quality in Use Analysis
291
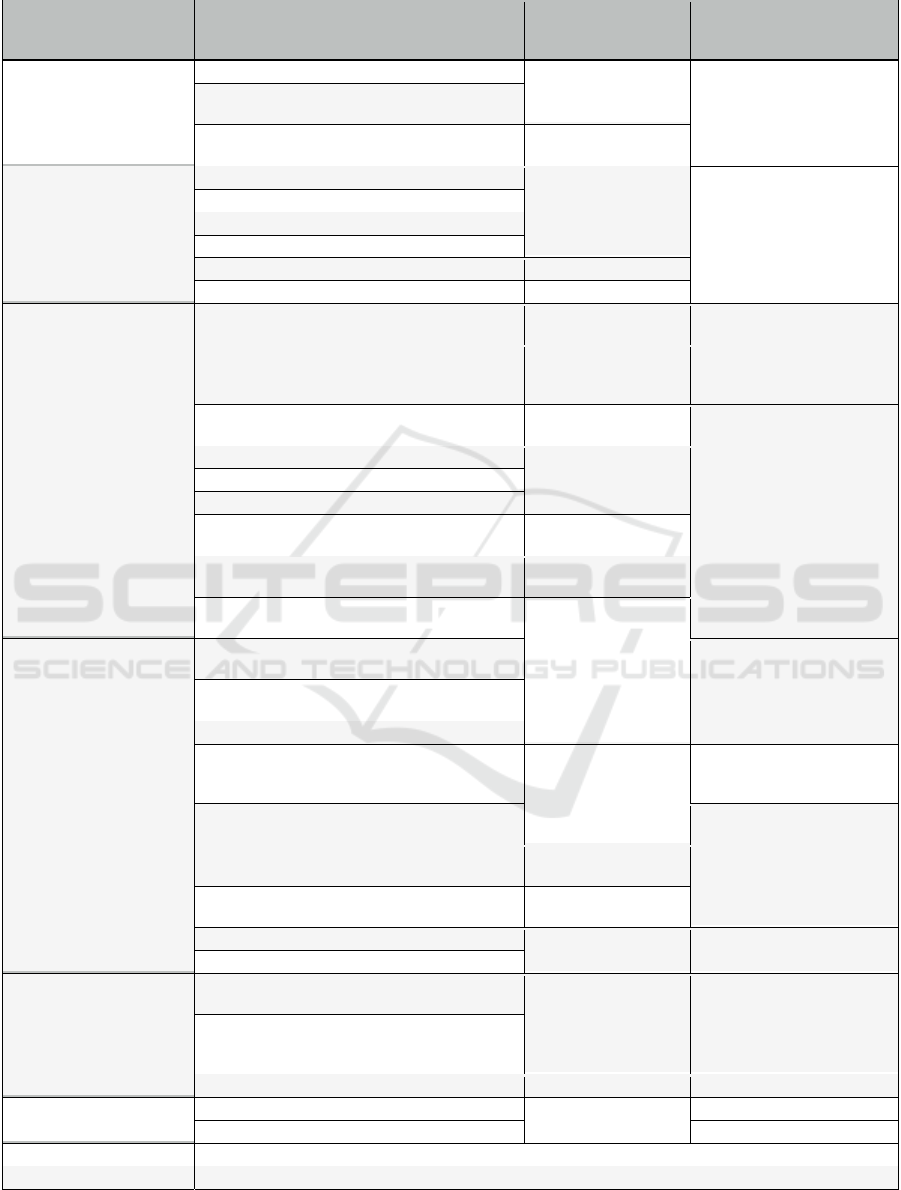
Table 1: Quality in use measures and MBTI.
Characteristics and sub-
characteristics of ISO
25010:2011
Description of the measures proposed in
FAQuiS
Source of information MBTI
Effectiveness
Percentage of problems resolved satisfactorily.
Editor and console
Thinking vs. Feeling
The number of artifacts successfully generated
during the job process.
Similarity between user interaction patterns and
those of the tas
k
model.
All system spaces and
tas
k
model
Efficiency
Numbe
r
of spaces used.
All system spaces
Judging vs. Perceiving
Time to complete tasks.
Numbe
r
of actions executed.
Actions executed pe
r
uni
t
of time.
Numbe
r
of completed tasks. Edito
r
and console
Artifacts generated pe
r
uni
t
of time. Edito
r
Risk mitigation
System actions that prevent modification of
b
locked source code
User interactions to
locked code
Extraversion vs. Introversion
Usefulness
Number of tasks that include actions with risks
or of an instrumental type and are repeated in
differen
t
sessions.
Editor and task model Judging vs. Perceiving
Patterns with a successful AR interaction
response
RA space and task
model
Sensing vs. Intuition
Percentage of completed tasks.
All system spaces and
task model
Thinking vs. Feeling
Percentage of shares used.
Percentage of spaces used.
Percentage of user actions with respect to those
tha
t
imply help feedbac
k
from the system.
Console and RA
Percentage of tasks completed successfully by
the use
r
with system suppor
t
Console
Percentage of tasks performed successfully by
the use
r
with protocol suppor
t
Code lock
Extraversion vs. Introversion
Trust
Number of tasks associated with risks and that
the use
r
avoids executing.
Judging vs. Perceiving Actions associated with risks and that the user
executes repeatedly.
Times executing tasks associated with risks.
Patterns of actions that do not follow the
expected sequence of actions due to an
unexpected response from the system.
All system elements
and task model
Thinking vs. Feeling
Percentage of completed tasks compared to
started in all wor
k
sessions.
Judging vs. Perceiving
Actions executed that require a response from
anothe
r
user.
Chat
Extraversion vs. Introversion
Time spent on actions that require a response
from anothe
r
user.
Chat
Numbe
r
of actions in the RA paradigm
RA space Sensing vs. Intuition
Time spen
t
on AR interactions
Pleasure
Successfully solved problems that require new
skills
User model, all system
spaces and task model
Thinking vs. Feeling
Variation in the execution time, that is, in
different sessions, of the tasks that demand new
skills.
Tendency to resume interrupted wor
k
sessions. All system spaces Judging vs. Perceiving
Comfort
Wor
k
density in each space
Task model
Thinking vs. Feeling
Degree of RA interactions Sensing vs. Intuition
Completeness The above measures fo
r
each contex
t
of intended use
Flexibility The above measures (excep
t
completeness) fo
r
each contex
t
of unintended use
WEBIST 2023 - 19th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
292

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents FQuiS, a framework used to
profile students in Computer-Supported Collabora-
tive Learning (CSCL) systems, with a specific focus
on programming learning. The framework utilizes log
files, computational models, and quality measures to
capture different aspects of the learning process. By
integrating the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI)
personality assessment, user profiles are generated,
allowing for personalized educational content,
adaptive learning activities, tailored feedback, and
targeted interventions.
The application of the framework to COLLECE
2.0, a CSCL system that supports programming
learning, was also analysed through a case study. The
results showcased the feasibility of applying this
framework to capture students' preferences, needs,
and performance patterns based on their MBTI
personality types.
Future work will focus on further experimentation
and refinement of the framework. This includes
exploring the integration of additional personality
assessment tools and psychological indicators to gain
a more comprehensive understanding of students'
learning characteristics. Additionally, evaluating the
effectiveness of the personalized interventions and
adaptive features enabled by the user profiling
framework through controlled studies will be a future
work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is partially supported by the European
Union through the project No. 2021-1-DE01-KA220-
HED-000032031 of the Erasmus+ programme, and
the CODIFICA project, ref. PID2021-125122OB-
100, funded by MCIN/AEI/10.13039/501100011033
and the European Regional Development Fund
(ERDF) "A way to make Europe". The University of
Cantabria is also partially supporting this work
through the project titled “Utilización de las TIC para
monitorizar y gestionar actividades colaborativas
orientadas a resolver tareas de programación de
algoritmos en el Grado en Ingeniería Informática”.
REFERENCES
De Backer, L., Van Keer, H., De Smedt, F., Merchie, E., &
Valcke, M. (2022). Identifying regulation profiles during
computer-supported collaborative learning and
examining their relation with students’ performance,
motivation, and self-efficacy for learning. Computers &
Education, 179, 104421. doi:10.1016/j.compedu.20
21.104421
Dolog, P., Thomsen, L. L., & Thomsen, B. (2016). Assessing
Problem-Based Learning in a Software Engineering
Curriculum Using Bloom’s Taxonomy and the IEEE
Software Engineering Body of Knowledge. ACM Trans.
Comput. Educ., 16(3). doi:10.1145/ 2845091
Duque, R., Bravo, C., & Ortega, M. (2011). A model-based
framework to automate the analysis of users’ activity in
collaborative systems. Journal of Network and Computer
Applications, 34(4), 1200–1209. doi:10.1016/j.jnca.20
11.01.005
Duque, R., Gómez-Pérez, D., Nieto-Reyes, A., & Bravo, C.
(2015). Analyzing collaboration and interaction in
learning environments to form learner groups.
Computers in Human Behavior, 47, 42–49.
doi:10.1016/j.chb.2014.07.012
ISO/IEC 25010:2011. (2011) ‘Systems and software
engineering. Systems and software Quality
Requirements and Evaluation (SQuaRE). System and
software quality models’.
Kukla, E., Nguyen, N.T., Sobecki, J., Danilowicz, C.,&
Lenar, M. (2003). A Model Conception for Learner
Profile Construction and Determination of Optimal
Scenario in Intelligent Learning Systems. In: Palade, V.,
Howlett, R.J., Jain, L. (eds) Knowledge-Based Intelligent
Information and Engineering Systems. KES 2003.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 2774. Springer,
Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-
45226-3_165
Lacave, C., García, M. A., Molina, A. I., Sánchez, S.,
Redondo, M. A., & Ortega, M. (2019). COLLECE-2.0:
A real-time collaborative programming system on
Eclipse. 2019 International Symposium on Computers in
Education (SIIE), 1–6. doi:10.1109/SIIE48397.20
19.8970132
Li, J., Liying, F., Qing, X., Shi, Z., & Yiliu, X. (2010).
Interface generation technology based on Concur Task
Tree. 2010 International Conference on Information,
Networking and Automation (ICINA), 2, V2-350-V2-
354. doi:10.1109/ICINA.2010.5636493
Myers, I. B. (1962). The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator:
Manual (1962). Consulting Psychologists Press.
https://doi.org/10.1037/14404-000
Muehlenbrock, M. (2006). Learning Group Formation Based
on Learner Profile and Context. International Journal on
E-Learning, 5(1), 19–24. Retrieved from
https://www.learntechlib.org/p/21767
Salomón, S., Duque, R., Montaña, J., & Tenés, L. (2022).
Towards automatic evaluation of the Quality-in-Use in
context-aware software systems. Journal of Ambient
Intelligence and Humanized Computing.
doi:10.1007/s12652-021-03693-w
Silva, L., Mendes, A. J., & Gomes, A. (2020). Computer-
supported Collaborative Learning in Programming
Education: A Systematic Literature Review. 2020 IEEE
Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON),
1086–1095. doi:10.1109/EDUCON45650.2020.9125237.
Villanueva, M. G., Taylor, J., Therrien, W., & Hand, B.
(2012). Science education for students with special
needs. Studies in Science Education, 48(2), 187–215.
doi:10.1080/14703297.2012.737117
Identifying Student Profiles in CSCL Systems for Programming Learning Using Quality in Use Analysis
293
