
Muscle-Like Soft Actuation for Motor-Less Robotic Exoskeletons
Julian D. Colorado
1 a
, John E. Bermeo
1 b
, Fredy A. Cuellar
1 c
Catalina Alvarado-Rojas
1 d
,
Diego Mendez
1 e
, Angela M. Iragorri
2 f
and Ivan F. Mondragon
1 g
1
School of Engineering, Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Bogota, 110231, Colombia
2
Neurology, School of Medicine, Hospital Universitario San Ignacio, Bogota, 110231, Colombia
Keywords:
Shape Memory Alloys, Exoskeletons, Soft Actuation, Rehabilitation Robotics.
Abstract:
Shape Memory Alloys (SMAs) have opened new alternatives upon conventional actuation technologies used
in robotics. SMA-based actuators are also known as muscle-like actuation mechanisms, in which Nickel
titanium (Nitinol) fibers operate as artificial tendons for soft actuation. This paper explores the use and limits
of tendon-like SMA actuation for a robotic exoskeleton to actively support hand motion rehabilitation.
1 INTRODUCTION
Actuation technology based on smart materials has
opened new alternatives in robotics systems. Piezo-
electric fiber composites (Mishra, 2022), electro-
active polymers (Hodgins, 2014) and shape memory
alloys (Guo, 2015; Bhatt, 2022) are being adopted
to replace classical servomotor actuators, enabling a
new generation of soft robotic applications (Jeong,
2023; Jin, 2016).
In particular, shape memory alloys (SMA) are an
interesting alternative to developing bio-inspired ac-
tuation mechanisms, by mimicking the way how mus-
cles generate motion in several biological organisms,
with the advantage of reducing the size and weight of
the system, while obtaining higher force-weight ra-
tio and precise sensing capabilities. In this regard,
SMAs have opened new alternatives and the potential
of building lighter and smaller soft robotic systems
for motor rehabilitation (Stano, 2021; Wang, 2020).
In this arena, robotic exoskeletons are being ac-
tively applied to support the activities of daily living
(ADLs) for patients with motion impairments. In this
regard, SMAs have been used in exoskeletons for re-
habilitation, by applying additive manufacturing ap-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6925-0126
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7183-4027
c
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-2261-1654
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2315-5692
e
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9866-4416
f
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0249-4951
g
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7828-6681
proaches (Stano, 2021). Additionally, bio-mimetic
systems using SMAs (Wang, 2020) are playing an im-
portant role for modeling and controlling human hand
kinematics without the restrictions of rigid mechan-
ical joints, while having an entire deformable body
with limitless points of actuation (Wang, 2022). In
this regard, closed-loop position and velocity con-
trollers can be developed to regulate SMA operation
precisely (Ruth, 2022; Singh, 2022; Khan, 2022).
However, issues such as the power consumption and
control bandwidth are the main limits of this technol-
ogy.
This paper proposes the application of tendon-
like SMA actuation for a robotic exoskeleton me-
chanics model developed in prior work reported in
(Castiblanco, 2021). The ultimate goal is to migrate
our current heavy and bulky rigid-body mechanism
to a softer and lighter prototype, by including these
muscle-like SMA actuators. Here, we demonstrate
the functionality and accuracy of this technology ap-
plied to our exoskeleton model, allowing to conclude
on the future research directions to be tackled in order
to overcome the inherent drawbacks when using bio-
inspired soft actuation for robotic-aided rehabilitation
tasks.
2 METHODS
SMA wires can be mechanically connected to a joint
to generate rotational motion during the contraction of
the NiTi alloys upon heating. In order to achieve two-
Colorado, J., Bermeo, J., Cuellar, F., Alvarado-Rojas, C., Mendez, D., Iragorri, A. and Mondragon, I.
Muscle-Like Soft Actuation for Motor-Less Robotic Exoskeletons.
DOI: 10.5220/0012194200003543
In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO 2023) - Volume 1, pages 683-688
ISBN: 978-989-758-670-5; ISSN: 2184-2809
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
683
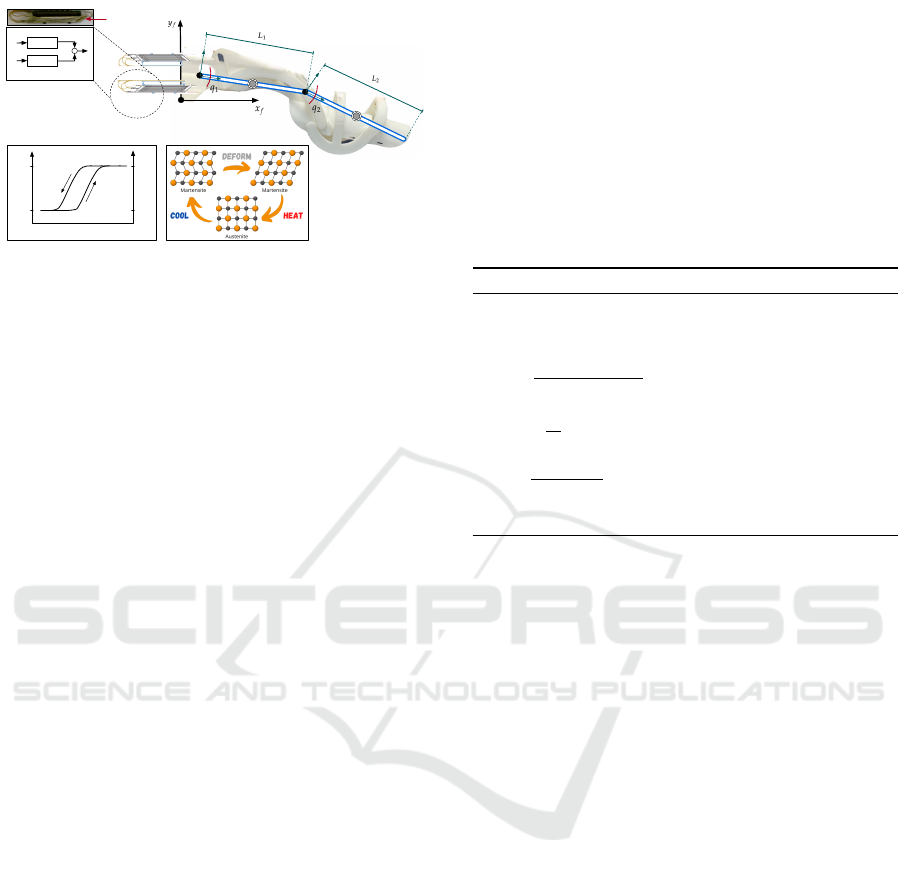
SMA 1
SMA 2
SMA_1
SMA_2
-
+
I1 Fsma-1
Fsma-2
Ƭdif
I2
SMA antagonistic model
NiTi wires
SMA muscle
Fsma-1
Fsma-2
Temperature
Mf
Af
As
Ms
cooling
heating
0
100
100
0
% Austenite
% Martensite
Theoretical SMA curve
Figure 1: SMA-driven exoskeleton finger testbed. Artifi-
cial muscles are placed by following an antagonistic con-
figuration. Each finger is modeled as a serial chain com-
posed by 2 DoF links. The joint q
1
is directly actuated by
the SMA actuators, according to the pull forces F
sma1
and
F
sma2
, whereas q
2
is an underactuated joint. The insets be-
low elucidate the theoretical curve of SMA NiTi alloys for
each phase transformation: Austenite and Martensite.
way rotational motion, a biasing returning force must
induced. To this purpose, we propose an antagonistic
arrangement of SMA actuators, as shown in Fig 1.
We used the commercial nanomuscle model NM706-
Super manufactured by MigaMotors, consisting of 6
Nickel titanium (NiTi) wires stacked in parallel, with
an overall mass of 1.1g and stroke of 4mm.
In this paper, we present how to use SMA thermo-
mechanical phenomenological equations to elucidate
the martensitic transformation between the high tem-
perature austenite phase and the low temperature
martensite stage of the NiTi alloys. This allows to
evaluate and explore the limits of SMA operation in
terms of actuation frequency and output range of mo-
tion, by keeping the input power below the limits of
SMA wire overheating. Figure 1 introduces the pro-
posed muscle-like SMA driven exoskeleton.
2.1 SMA-Driven Muscle-Like Actuation
The exoskeleton can assist in both open and close
finger gestures, since both directions can be actively
controlled. However, it is crucial to have an under-
standing of the SMA hysteresis curve, in order to
evaluate the proposed antagonistic configuration.
Tanaka in (Tanaka, 1986) presented one of the
first approaches to study NiTi SMA behavior, by us-
ing a dimensional thermo-mechanical model based
on a stress-induced input. Elahinia et al. (Elahinia,
2005), complemented Tanaka’s model by extending
the equations to support electrical stimulation, and
by connecting the effects of electrical current input
with alloy temperature and stress, while taking into
account the two-way shape memory effect. In our
application, the exoskeleton mechanics and the pa-
tient’s hand will impose a significant external payload
to the SMA actuation system, requiring characteriza-
tion to determine the limits of SMA operation. In pre-
vious work reported in (Colorado, 2012; Coral, 2012),
SMAs were experimentally characterized in terms of
the power-to-force ratio, using muscle-like actuation
to drive a bio-inspired fish robot and bat-like aerial
vehicle with morphing wings. Here, we used simi-
lar approaches for both modeling and control, by ap-
plying the Elahinia’s SMA model, which consists in
several equations described in Algorithm 1.
Algorithm 1: SMA thermo-mechanical computation.
1. Compute SMA temperature rate:
˙
T ← m
−1
sma
c
−1
p
(i
2
R
sma
− h
c
A
c
(T − T
o
))
2. Calculate the SMA stress rate upon heating:
˙
σ ←
θ
s
−Ω(A
f
−A
s
)
−1
1−Ω(A
f
−A
s
)
−1
C
m
˙
T
3. Calculate phase transformation rate:
˙
ξ ← −
ξ
m
2
sin(a
A
(T − A
s
) + b
A
σ) + (a
A
˙
T + b
A
˙
σ)
4. Compute SMA strain rate upon heating:
˙
ε ←
˙
σ−θ
s
˙
T −Ω
˙
ξ
E
A
6. Integrate
˙
ε
7. Return ε
The step 1 computes the temperature rate (
˙
T )
based on the current input i. It allows for the eval-
uation of overheating when the SMAs are subject to
high values of input power. The term m
sma
is the mass
of the wires, A
c
is the circumferential area of the wire,
c
p
is the specific heat, R
sma
is the electrical resistance
and h
c
is the heat coefficient.
During step 2 the stress rate
˙
σ is calculated. The
equation allows us to observe stress effects caused
by overheating the wires, thus identifying an upper
threshold for the input current i. The term θ
s
is the
thermal expansion factor of the wire, Ω is the phase
transformation factor, A
f
, A
s
are the Austenite border
condition upon temperature and C
m
is the stress coef-
ficient. Based on that, the changes between transfor-
mation phases (hysteresis curve) are calculated during
step 3, where
˙
ξ is the phase transformation rate that
describes the phase transformation from martensite to
austenite. Finally, step 4 calculates the SMA strain
due to the contraction. More details on the model’s
parameters can be found in (Elahinia, 2005).
2.2 Exoskekelton’s Equations of Motion
In Fig 1 we proposed a 2 Degree-of-Freedom (DoF)
serial link model to represent the exoskeleton me-
chanics of the finger. Also, each finger is treated sep-
arately, as a branched of rigid bodies connected to the
same fixed-based.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
684
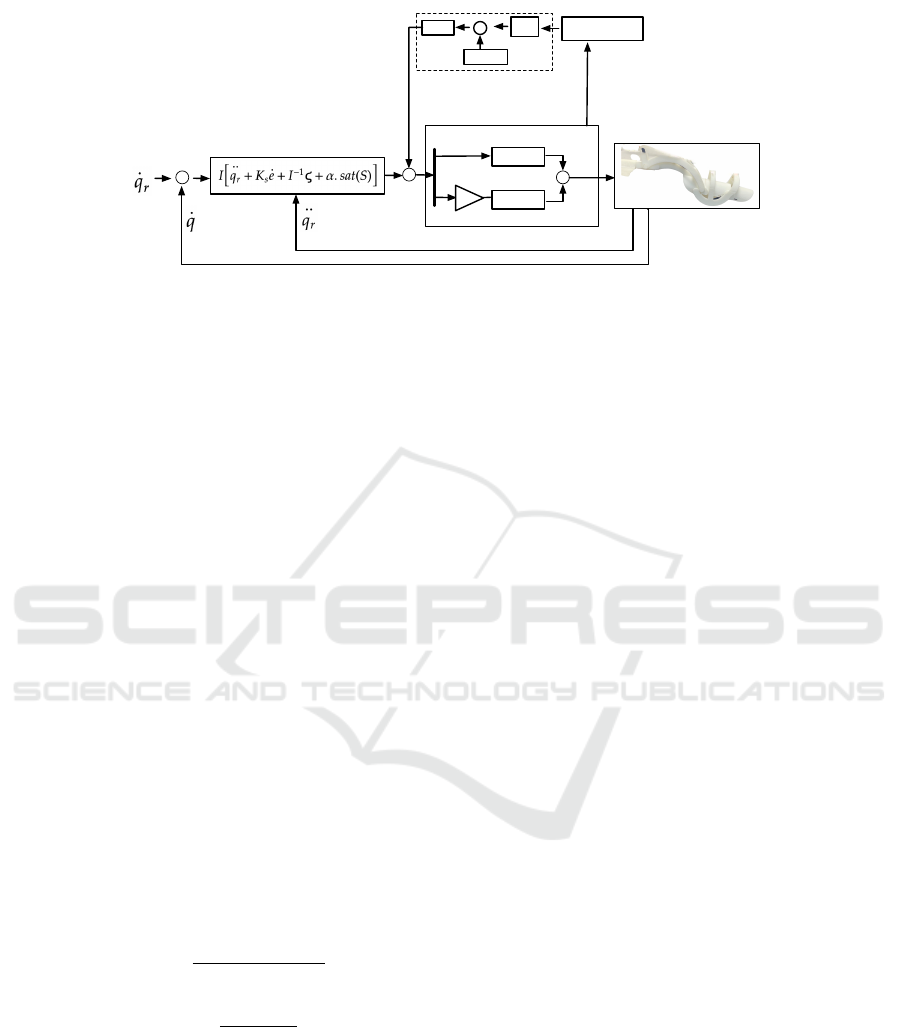
-
+
Fsma_1
Fsma_2
-1
-
+
SMC
Antagonistic mechanism
u
heating
τ
dif
SMA_1
SMA_2
SMA actuation
(thermomechanical model)
Euler-Lagrange EoM
Exoskeleton testbed
MIN
-
+
0.3W
0.95
anti-slack loop
+
+
u_low
P
sma
= I
sma
2
R
sma
SMA power
Figure 2: SMA control architecture.
The joint q
1
is directly driven by the SMA an-
tagonistic pair of artificial muscles, while the joint
q
2
is under-actuated, i.e, kinematically coupled to the
former joint. Here, we apply the well-known Euler-
Lagrange formalism to determine the corresponding
Equations of Motion (EoM). First, we derive the ve-
locities of each body, such as:
˙x
1
= −L
c1
sin(q
1
) ˙q
1
˙y
1
= L
c1
cos(q
1
) ˙q
1
˙x
2
= −L
1
sin(q
1
) ˙q
1
− L
c2
sin(q
1
+ q
2
)( ˙q
1
+ ˙q
2
)
˙y
2
= L
1
cos(q
1
) ˙q
1
− L
c2
cos(q
1
+ q
2
)( ˙q
1
+ ˙q
2
)
(1)
where [ ˙x
1
, ˙y
1
] and [˙x
2
, ˙y
2
] describe the components
of the center of mass velocity for each body of the
exoskeleton, according to the diagram in Fig 1. Hav-
ing the velocity, the kinetic energy can be calculated,
while the potential energy is neglected, since gravity
will be compensated by a closed-loop control law. In
this regard, the Lagrangian operator (L) is defined as:
L(q, ˙q) = 0.5
m
1
L
2
c1
˙q
2
1
+ m
2
L
2
1
˙q
2
1
+ L
2
c2
( ˙q
1
+ ˙q
2
)
2
(2)
Applying the Euler-Lagrange formulation, the
state-variable EoM are defined as follows:
˙
X
1
= X
2
˙
X
2
= ¨q
1
=
τ
1
−m
2
L
2
c2
¨q
2
m
1
L
2
c1
+m
2
L
2
1
+m
2
L
2
c2
˙
X
3
= X
4
˙
X
4
= ¨q
2
=
τ
2
−m
2
L
2
c2
¨q
1
m
2
L
2
c2
(3)
2.3 SMA Control
Figure 2 introduces the closed-loop control architec-
ture for the exoskeleton. This control scheme is com-
posed by three loops: i) an inner loop to feedback
joint accelerations ( ¨q
r
) based on the EoM defined in
Eq. 3, ii) an outer loop to regulate the exoskeleton’s
angular position (q) or velocity ( ˙q) according to the
rehabilitation reference trajectory, and iii) an upper
loop in charge of supervising the SMA’s power con-
sumption (P
sma
), as function of the measured electri-
cal current (I
sma
) and the known electrical resistance
(R
sma
) of the SMA wires.
As detailed in Fig 2, the input torques τ
1
and τ
2
are both functions of the generated pull-force driven
by the SMA antagonistic mechanism, being τ
di f
=
F
sma1
− F
sma2
. Thanks to the aforementioned up-
per loop, the SMA wires do not cool entirely, while
maintaining a minimum threshold for the input cur-
rent i = u
heating
injected by the control law. This
setup avoids wire slack, while tacking advantage of
the pseudo-elasticity phenomenon presented in NiTi
alloys, resulting in a more precise operation of the
antagonistic mechanism. Based on this, a non-linear
control method based on the sliding-mode technique
(SMC) is proposed as follows:
• A sliding surface of the form S = ˙e + K
′
s
e defines
the dynamics that governs the system behavior
while sliding, with gain K
′
s
> 0.
• The SMC control law (u
heating
) is designed ac-
cording to a Lyapunov function of the form: V =
0.5S
T
, S > 0.
• The sliding control is chosen such as
˙
V = S
T
S < 0,
or −αS
T
sgn(S).
• The sliding condition is
˙
S = −αsgn(s).
By differentiating S = ˙e+K
′
s
e with respect to time:
˙
S = ¨q
r
− ¨q + K
′
s
˙e
(4)
In Eq. (4) the term ¨q
r
represents the forward dy-
namics solution in canonical form:
¨q
r
=
I
−1
(F − ξ )
,
(5)
where F is the applied force, ξ is the Coriolis term
and I is the moments of inertia. By substituting Eq.
(5) into (4):
˙
S = ¨q
r
−
I
−1
(F − ξ )
+ K
′
s
˙e
(6)
Muscle-Like Soft Actuation for Motor-Less Robotic Exoskeletons
685
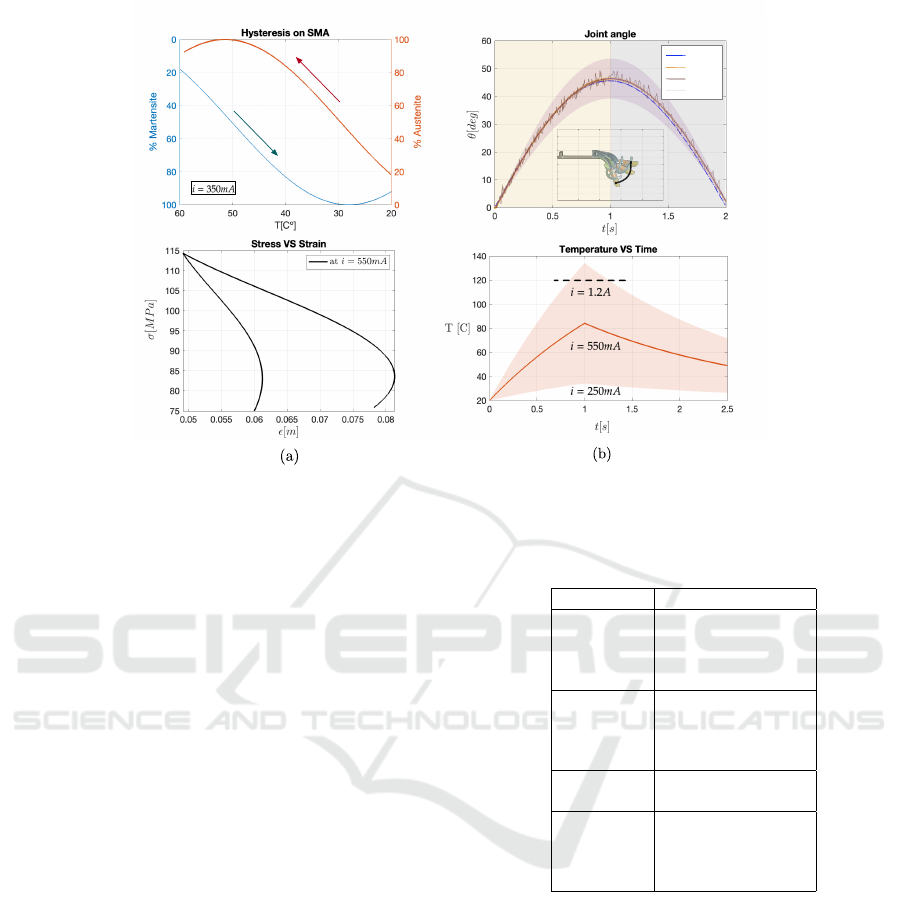
SMA heating
SMA cooling
overheating - SMA damage
reference
no-load
with-load
variance
SMA 1 SMA 2
-
+
Fsma_1
Fsma_2
-1
-
+
SMC
Antagonistic mechanism
u
heating
τ
dif
SMA_1
SMA_2
SMA actuation
(thermomechanical model)
Euler-Lagrange EoM
Exoskeleton testbed
S=0
MIN
-
+
0.3W
0.95
anti-slack loop
+
+
u_low
P
sma
= I
sma
2
R
sma
SMA power
anti-slack
-
+
Fsma_1
Fsma_2
-1
-
+
SMC
Antagonistic mechanism
u
heating
τ
dif
SMA_1
SMA_2
SMA actuation
(thermomechanical model)
Euler-Lagrange EoM
Exoskeleton testbed
S=0
MIN
-
+
0.3W
0.95
anti-slack loop
+
+
u_low
P
sma
= I
sma
2
R
sma
SMA power
anti-slack
Figure 3: SMC-driven SMA actuation for joint position control. (a) Simulation results of SMA hysteresis, stress and strain by
following the thermo-mechanical model described in Algorithm 1. (b) SMA-driven exoskeleton motion tracking by combining
the dynamics model presented in Eq. 3 and the actuation law described in Eq. 8.
By equaling Eq. (6) with the sliding condition
˙
S =
−αsgn(s), and then isolating F, yields:
−αsgn(s) = ¨q
r
−
I
−1
(F − ξ )
+ K
′
s
˙e
F = I[ ¨q
r
+ K
s
′
˙e + I
−1
ξ + αsgn(s)]
(7)
By renaming u
heating
= F, the sliding control law
is derived from Eq. (7), as:
u
heating
= I[ ¨q
r
+ K
′
s
˙e + I
−1
ξ + αsgn(s)]
(8)
The control gains K
′
s
and α must be positive.
3 RESULTS
The results reported in this section are oriented to de-
termine the limits of SMA operation. To this purpose,
three operation modes for the SMA actuators were de-
fined in terms of the driven electrical current injected
by the SMC controller: i) low (i = 250mA), ii) nomi-
nal (i = 550mA), and iii) overheating (i > 1200mA).
Using Algorithm 1, thermo-mechanical equations
are computed, in order to evaluate SMA stress, tem-
perature, hysteresis, strain and the range of motion,
according to the operations modes previously defined.
Also, Table 1 summarizes the parameters used for the
models.
Figure 3 presents the results of controlling the ex-
oskeleton’s testbed by regulating joint positions. Plots
3(a) depict the transformation phases exhibited by the
Table 1: Parameters for SMA thermo-mechanical model.
Parameters Values [unit]
m
sma
, R
sma
1.14 × 10
−4
[Kg], 8.5 [Ω]
A
c
1.76 × 10
−8
m
2
h
c
150
Jm
−2◦
C
−1
s
−1
C
p
0.2
KcalKg
−1◦
C
−1
Ω −1.12[GP
a
]
θ
s
0.55
MP
◦
a
C
−1
C
m
,C
a
10.3
MP
◦
a
C
−1
A
s
, A
f
, M
s
, M
f
68, 78, 52, 42 [
◦
C]
E
A
75[GP
a
]
E
M
28[GP
a
]
ξ
m
, ξ
a
1, 0 [dimensionless]
a
A
0.31
◦
C
−1
a
M
0.31
◦
C
−1
b
A
, b
M
−0.03
◦
C
−1
SMA actuator, including the stress and strain over the
alloys during deformation upon heating. The results
were obtained by applying the thermo-mechanical
model described in Algorithm 1. We applied several
input electrical currents to the SMA actuator, ranging
from 250mA up to 1.2A. With these input parameters,
the SMA actuator contracts from 1mm up to 4mm.
As expected, the linear contraction of the muscle-like
mechanism yields an angular motion ranging between
40 to 52 degrees in rotational motion, as shown by the
upper plot of Fig 3(b). As mentioned, the SMC con-
trol law described in Eq. 8 injects power to the SMA
pair of artificial muscles, where u
heating
is the driven
electrical current.
The lower plot of Fig 3(b) describes the alloy tem-
perature range according to the input current for low,
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
686
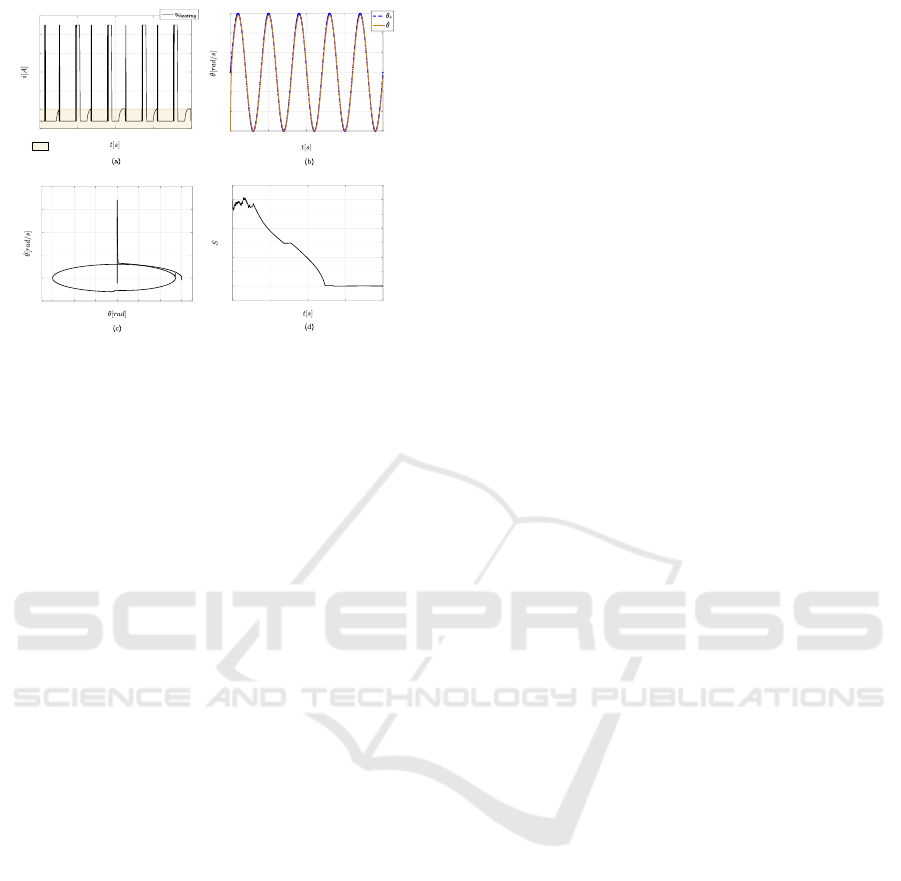
02468
0
0.5
1
1.5
2
2.5
3
Joint velocity
02468
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
SMC output to SMA
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
-5
0
5
10
15
20
Phase plane of the sliding surface (S)
02468
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
Sliding surface (S)
S=0
anti-slack
Figure 4: SMC-driven SMA actuation for joint velocity
control.
nominal and overheating operation modes. As ob-
served, applying a nominal value of 550mA to the
SMA actuator allows the exoskeleton to follow the
corresponding opening and closing gesture trajectory
of reference. Note in the inset of the upper plot in
3(b), that the resultant range of motion corresponds
to the fingertip cartesian point of the exoskeleton,
whereas the antagonistic configuration is differenti-
ated for each SMA actuator driving both open and
close gestures independently.
Under this scenario, SMA contraction and exten-
sion is achieved in 2s, with a maximum SMA strain
of 4mm. As observed, the SMC-based position con-
troller is not achieving the expected accuracy and pre-
cision during the reference tracking, concretely for
the opening gesture driven by the antagonistic pair
(SMA 2). The inertial load cannot be counteracted
with the position feedback, yielding larger tracking
errors compared against the closing gesture driven by
the SMA 1. This outcome could be associated to
the fact that the control law in Eq. 8 was defined to
smoothly regulate velocity references rather than po-
sitions, since the contraction rate of the SMA actuator
is linearly dependant to the changes of the inner elec-
trical resistance of the alloys.
In order to improve on tracking accuracy and pre-
cision, the reference trajectory was changed from an-
gular position to velocity (as a function of the SMA
contraction rate). Figure 4 presents the results. Plot
4(a) shows the electrical current (u
heating
) applied to
each SMA actuator. Thanks to the anti-slack upper-
loop shown in Fig 2, note how the electrical cur-
rent maintains a minimum threshold value of 50mA,
avoiding the SMA alloys of completely cooling af-
ter contraction, which increase bandwidth control and
actuation frequency. Also, the term u
heating
was satu-
rated to operate at a nominal value of 550mA, avoid-
ing the limits of overheating at > 1200mA, since
higher electrical currents will result in alloy temper-
atures > 120
o
C, causing irreversible damage to the
one-way shape memory effect.
Under this scenario, the SMC control law was able
to properly regulate the joint velocity, maintaining a
precise tracking of the trajectory, as depicted in plot
4(b). Controlling the contraction rate rather than the
specific position of the SMA actuator allows the SMC
method to smoothly track the desired motion, since
the control law is strictly dependent on the dynamics
model of the exoskeleton, as denoted by the term ¨q
r
in Eq. 8. This model-dependent controller counter-
acts the inertial loads more accurately, since the slid-
ing surface S = ˙e + K
′
s
e, governs both the tracking er-
ror (e) and error dynamics rate ˙e. Plots 4(c,d) detail
how the sliding surface goes to zero, fulfilling with
the Lyapunov function condition.
4 CONCLUSIONS
We have demonstrated the feasibility of the use of
muscle-like SMA actuators for the soft control of
the exoskeleton testbed presented in Fig 1. A com-
prehensive thermo-mechanical model for NiTi SMA
wires allowed us to analyze the limits of this actua-
tion technology in terms of power consumption, con-
trol bandwidth, and motion range. The SMA actu-
ator can operate with input electrical currents rang-
ing from 250mA up to 1.2A and generating an out-
put motion range from 40 to 52 degrees in rotation,
which coincides with the average range of motion of
a normal grip movement at the metacarpophalangeal
(MP) joint with an average of 44 degrees (Shimawaki,
2019). Unfortunately, this outcome still does not
work to achieve full opening and closing of the hand,
since the SMA alloys exhibited a maximum stroke of
4mm. We need to increase the contraction length of
the wires, by adding artificial tendons connecting the
SMA muscles directly to both joints, specially to the
second joint (q
2
) of the exoskeleton.
In terms of control bandwidth, we achieved an ac-
tuation frequency of 1.5Hz, being sufficient to fur-
ther assist the patient according to the rehabilitation
gestures. Furthermore, the proposed sliding-mode
control technique (SMC) obtained accurate results in
tracking the desired angular velocity, mostly due to
the incorporation of the exoskeleton inertial model
contained in the terms I and ¨q
r
of Eq. 8, allowing the
SMC controller to counteract the loads more precise
and smooth. Overall, we believe that the actuation
based on SMAs could be an alternative in robotic-
assisted rehabilitation of the hand. Upcoming work
Muscle-Like Soft Actuation for Motor-Less Robotic Exoskeletons
687

is oriented towards the measurement and characteri-
zation of the SMA pull-force, in order to determine
the maximum loads supported by the soft actuation
mechanism presented herein.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the project “iREHAB: Sis-
tema inteligente de Rehabilitaci
´
on usando un Ex-
oesqueleto para recuperar Habilidad motora en dis-
capacidades post-ACV, usando se
˜
nales Biol
´
ogicas
del paciente” sponsored by The Ministry of Science
Technology and Innovation (MinCiencias), program
918-2022 under GRANT CTO: 622-2022, Award ID:
91805.
REFERENCES
A. K. Mishra, V. S. Janani Kavi Priya, K. Pradeep, J. Sai
Vaishnav, and G. Kabhilesh, “Smart materials for ul-
trasonic piezoelectric composite transducer: A short
review,” Mater Today Proc, vol. 62, pp. 2064–2069,
Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.02.514
M. Hodgins, G. Rizzello, D. Naso, A. York, and S. Se-
elecke, “An electro-mechanically coupled model for
the dynamic behavior of a dielectric electro-active
polymer actuator,” Smart Mater Struct, vol. 23, no. 10,
Oct. 2014, doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/23/10/104006
Z. Guo, Y. Pan, L. B. Wee, and H. Yu, “Design and control
of a novel compliant differential shape memory alloy
actuator,” Sens Actuators A Phys, vol. 225, pp. 71–80,
Apr. 2015, doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2015.01.016.
N. Bhatt, S. Soni, and A. Singla, “Analyzing the
effect of parametric variations on the perfor-
mance of antagonistic SMA spring actuator,”
Mater Today Commun, vol. 31, Jun. 2022, doi:
10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103728.
H. Jeong and W. D. Wang, “Self-adaptive detachable
pneumatic soft actuators using uniformly distributed
temporary-bonding-fasteners for wearable applica-
tions,” Sens Actuators A Phys, vol. 349, Jan. 2023,
doi: 10.1016/j.sna.2022.114083.
H. Jin, E. Dong, M. Xu, C. Liu, G. Alici, and Y. Jie, “Soft
and smart modular structures actuated by shape mem-
ory alloy (SMA) wires as tentacles of soft robots,”
Smart Mater Struct, vol. 25, no. 8, Jul. 2016, doi:
10.1088/0964-1726/25/8/085026.
G. Stano and G. Percoco, “Additive manufacturing aimed to
soft robots fabrication: A review,” Extreme Mechan-
ics Letters, vol. 42. Elsevier Ltd, Jan. 01, 2021. doi:
10.1016/j.eml.2020.101079.
Y. Wang, S. Zheng, Z. Song, J. Pang, and J. Li, “A Coupling
Dynamic Model for Studying the Physical Interaction
between a Finger Exoskeleton and a Human Finger,”
IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 125412–125422, 2020, doi:
10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007799.
Ruth, D.J.S.; Sohn, J.-W.; Dhanalakshmi, K.; Choi,
S.-B. Control Aspects of Shape Memory Al-
loys in Robotics Applications: A Review over
the Last Decade. Sensors 2022, 22, 4860.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s22134860
D. Singh, R. Choudhury, M. Mukherjee, and Y. Singh,
“Development of non-linear models to evaluate the
NiTi SMA spring actuator”, JMES, vol. 16, no. 1, pp.
8754–8769, Mar. 2022.
Abdul Manan Khan, Youngshik Kim, Buhyun Shin, Mah-
yar Hasanzadeh Moghadam, Nader A. Mansour, Mod-
eling and control analysis of an arc-shaped SMA actu-
ator using PID, sliding and integral sliding mode con-
trollers, Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, Vol 340,
2022, 113523.
Castiblanco, J.C.; Mondragon, I.F.; Alvarado-Rojas,
C.; Colorado, J.D. Assist As Needed Exoskele-
ton for Hand Joint Rehabilitation Based on Mus-
cle Effort Detection. Sensors 2021, 21, 4372.
https://doi.org/10.3390/s21134372
K. Zuo, B. Wang, and Y. Wang, “Research on exoskele-
ton structure design of hand function rehabilitation
robot,” in 2022 12th International Conference on CY-
BER Technology in Automation, Control, and Intelli-
gent Systems, CYBER 2022, 2022, pp. 812–816. doi:
10.1109/CYBER55403.2022.9907104.
Mohammad H Elahinia and Mehdi Ahmadian 2005. An en-
hanced SMA phenomenological model: I. The short-
comings of the existing models. Smart Mater. Struct.
14 1297, 10.1088/0964-1726/14/6/022
Tanaka K 1986 A thermomechanical sketch of shape mem-
ory effect: one-dimensional tensile behavior Res.
Mech., Int. J. Struct. Mach. Mater. Sci. 18 251-63.
Shimawaki, S., Murai, T., Nakabayashi, M., Sugimoto,
H. (2019). Measurement of flexion angle of the fin-
ger joint during cylinder gripping using a three-
dimensional bone model built by X-ray computed to-
mography. Applied bionics and biomechanics, 2019.
Colorado J. (2012). BaTboT: a biologically in-
spired flapping and morphing bat robot actu-
ated by SMA-based artificial muscles. The-
sis (Doctoral), E.T.S.I. Industriales (UPM).
https://doi.org/10.20868/UPM.thesis.14657.
W. Coral, C. Rossi, J. Colorado, D. Lemus, and A. Bar-
rientos, SMA-Based Muscle-Like Actuation in Bio-
logically Inspired Robots: A State of the Art Re-
view, Smart Actuation and Sensing Systems - Re-
cent Advances and Future Challenges, Oct. 2012, doi:
10.5772/50209.
ICINCO 2023 - 20th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
688
