
The 12th Player: Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Football:
Conceptualisation, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions
Andria Procopiou and Andriani Piki
School of Sciences, University of Central Lancashire Cyprus, Larnaca, Cyprus
Keywords:
Explainable Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, Deep Learning, Football Analytics, Injury Prediction,
Rehabilitation, Football Tactical Analysis, Human Factors, Human-Centred AI.
Abstract:
Artificial intelligence (AI) has demonstrated tremendous progress in many domains, especially with the vast
deployment of machine and deep learning. Recently, AI has been introduced to the sports domain including
the football (soccer) industry with applications in injury prediction and tactical analysis. However, the fact
remains that the more complex an AI model is, the less explainable it becomes. Its black-box nature makes it
difficult for human operators to understand its results, interpret its decisions and ultimately trust the model it-
self. This problem is magnified when the decisions and results suggested by an AI model affect the functioning
of complex and multi-layered systems and entities, with a football club being such an example. Explainable
artificial intelligence (XAI) has emerged for making an AI model more explainable, understandable and in-
terpretable, thus assisting the creation of human-centered AI models. This paper discusses how XAI could be
applied in the football domain to benefit both the players and the club.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the last decade the advances in artificial in-
telligence (AI) have been significant to the world.
Machine and deep learning (perhaps the most popu-
lar subsets of AI) have been integrated in numerous
technology-enabled sectors (Russell, 2010) forming a
vital part in their operations. Beyond the corporate
sector, AI became a vital part in people’s lives, im-
proving their everyday tasks and quality of life. Ex-
amples include voice recognition, self-driving cars,
and recommendation systems (Gupta et al., 2021),
(Bharati et al., 2020a), (Mondal et al., 2021), (Bharati
et al., 2020b). AI is also being deployed in the sports
industry including football (Moustakidis et al., 2023).
The main goal of utilising AI is to improve the de-
cision making in numerous areas. Notable exam-
ples include improving individual players’ and the
team’s performance and development (Moustakidis
et al., 2023), assisting in scouting, identifying poten-
tial talents from the youth academies, enhancing ana-
lytics and tactics, predicting and potentially prevent-
ing injuries and optimising rehabilitation periods for
injured players (Rathi et al., 2020).
The sophisticated learning, reasoning, and adap-
tation capabilities of AI models have proved to be
pivotal in all of the areas it has been utilised, includ-
ing the sports industry, and require little or no hu-
man intervention (Arrieta et al., 2020). However, the
fact that machine and deep learning algorithms follow
a black-box approach (Arrieta et al., 2020) presents
challenges in explaining a model’s decisions and pre-
dictions. AI models do not provide sufficient justifica-
tion, explainability, and interpretability on their over-
all behaviour (Gunning et al., 2019). Evidently, clear
and precise explanations are vital towards demys-
tifying how AI operates, especially when deployed
in complex and multi-layered domains such as foot-
ball, where the decisions and predictions may affect
a team’s performance and even more importantly a
player’s health.
Gaining an in-depth understanding of how AI sys-
tems function and achieve their results is needed,
especially when critical decisions need to be made
(Goodman and Flaxman, 2017). In the sports indus-
try, especially football, decisions are made on a daily
basis with regards to multiple operations of a club, in-
cluding scouting procedures, team tactics, opposition
analysis, players’ personal fitness/rehabilitation pro-
grammes and injury prevention procedures. Even a
small miscalculation can be proven financially costly
for the club. In addition, the players’ physical and
mental health and overall wellbeing can be negatively
impacted. Therefore, there is need for improved ex-
Procopiou, A. and Piki, A.
The 12th Player: Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Football: Conceptualisation, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions.
DOI: 10.5220/0012233800003587
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support (icSPORTS 2023), pages 213-220
ISBN: 978-989-758-673-6; ISSN: 2184-3201
Copyright © 2023 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
213

plainability and interpreatability of AI models. Fur-
thermore, there is need for human experts to reas-
sure both themselves and relevant stakeholders that
AI solutions are transparent, unbiased, and trustwor-
thy, by essentially minimising its black-box nature
(Miller, 2019). Explainable Artificial Intelligence
(XAI) emerged to make AI systems’ reasoning, out-
puts and overall results more understandable and clear
to human experts (Chazette et al., 2021), (K
¨
ohl et al.,
2019), (Langer et al., 2021b), (P
´
aez, 2019).
Motivated by the eminent concerns and opportuni-
ties observed, we discuss how XAI could be utilised
in the football industry, focusing in various operations
impacting both the team and individual stakehold-
ers (players, coaches, sports analysts, etc.). Firstly,
we provide the necessary background knowledge dis-
cussing key concepts of XAI, including definitions,
the characteristics an XAI model should exhibit, and
how XAI could become more human-centred. Sub-
sequently, we discuss in-depth how XAI could be
utilised in various aspects of the football industry,
including scouting, tactical analysis, player develop-
ment and performance optimisation, injury prediction
and prevention and finally, rehabilitation. We con-
clude by summarising our insights and provide future
directions on XAI applied in the football industry.
2 RESEARCH BACKGROUND
2.1 XAI Definitions
Numerous definitions have been proposed to capture
the meaning of XAI. The most notable ones define
XAI, in general terms, as one of AI’s sub-fields that
is responsible for accompanying an AI model with in-
telligible explanations to the end users and stakehold-
ers by constructing effective and accurate approaches
(Van Lent et al., 2004) (Biran and Cotton, 2017),
(Miller, 2019), (Mittelstadt et al., 2019). More specif-
ically, XAI has been defined as the set of features
that assist users understanding how an AI model con-
structs its predictions (Arrieta et al., 2020), (Nazar
et al., 2021). To this end, XAI should highlight the
most influential factors contributing to the prediction
process (Viton et al., 2020), hence allowing more ef-
ficient pre-processing to be conducted.
Making an AI model more understandable and ex-
plainable does not directly guarantee its interpreata-
bility, especially when it is used by multiple types of
users with different levels of expertise and knowledge
and varying degrees of experience. This issue was
correctly raised by (Bharati et al., 2023). Specifically,
it is argued that explainability focuses on the ’why’
behind a decision and not on the ’how’, while in-
tepretability deals with making the users understand
the rationale behind its decision (Vishwarupe et al.,
2022), (Miller, 2019).
An important factor to consider when it comes
to XAI is the need for reassuring the human ex-
perts/users that the AI model constructed is neither
biased nor discriminating (Duell et al., 2021). XAI
plays a pivotal role in strengthening trust between hu-
man experts and AI models and assisting in better
collaboration between the two (Adadi and Berrada,
2018). In conclusion, the authors in (Gunning et al.,
2019) effectively stated that XAI should be heavily in-
fluenced by the social sciences (Miller, 2019), specif-
ically the psychology of explanation, and should aim
to make machine and deep learning algorithms:
• More explainable and socially aware, while also
maintaining their high levels of accuracy.
• Human-centred, by assisting in creating and
maintaining trust between human experts and AI.
2.2 XAI Characteristics and Goals
According to (Arrieta et al., 2020), the main proper-
ties an XAI model include:
• Understandability (also called Intelligibility):
An AI model should make its functioning and
decision-making more understandable to humans.
Low-level details such as its inner structure and
algorithmic training procedure should be omitted.
• Comprehensibility: An AI model should provide
human-readable explanations regarding its learnt
knowledge. In that way, its complexity becomes
more approachable to human operators.
• Interpretability: An AI model should describe re-
sults in a human-meaningful way.
• Explainability: An AI model should provide
meaningful explanations about the results to assist
human experts in their decisions.
• Transparency: An AI model should be fair, unbi-
ased, and transparent without leaving any details
or knowledge hidden, vague or ambiguous to hu-
man experts.
2.3 User-Centred XAI
The most important objective of XAI is to pro-
vide substantial support to the various types of users
in accurate, effective and correct decision-making
(Nadeem et al., 2022), thus demystifying AI’s black-
box nature. We proceed with discussing a set of com-
mon practices with which XAI can be realised in prac-
tice based on previous work by (Nadeem et al., 2022).
icSPORTS 2023 - 11th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
214

2.3.1 XAI Enabled by Visualisation
The construction of visualisations is the most popu-
lar and straightforward way of providing explainabil-
ity and understandability of how an AI model oper-
ates. This is due to human cognition being in favour
of visual information instead of text when it comes
to decision making (Padilla et al., 2018). There are
multiple parts of an AI model that can be visualised.
One approach is to visualise how an AI model pro-
ceeds to make a decision. Visualisations work par-
ticularly well with tree-based machine learning algo-
rithms such as decision trees and random forests (An-
gelini et al., 2017), (Sopan et al., 2018), (Nadeem
et al., 2021). Other approaches include providing vi-
sual analytics regarding the data input, so that human
experts can perform manual investigation in further
(Angelini et al., 2017), or presenting additional visual
information selectively based on the human expert’s
trust levels (Anjomshoae et al., 2019).
2.3.2 XAI Enabled by Usability Testing
When it comes to effective, accurate, and correct de-
cision making by human experts, usability becomes
a priority. Complex visualisations could overwhelm
human experts rather than assisting them (Nadeem
et al., 2022). Therefore, the explanations provided by
an XAI model must be as clear, precise, and simplistic
as possible so human experts can effectively and effi-
ciently utilise them (Antwarg et al., 2021), (Panigutti
et al., 2022). There is a also a need to eliminate the
misconception that explainability automatically pro-
vides interpretability (Nadeem et al., 2022). Inter-
pretability can improve decision making since it can
identify bias in the training data and can also ensure
that the variables involved meaningfully contribute to
the results of the AI model (Arrieta et al., 2020).
Additionally, achieving understandability in-
volves ensuring multiple usability factors that are
evaluated through effective user testing (Doshi-Velez
and Kim, 2017). Hence, it is essential for an XAI
model to be user-centric and multiple rounds of user
and usability testing to be conducted (Doshi-Velez
and Kim, 2017). Sepcifically, before an XAI model
is deployed on top of the AI system in place, in-depth
usability testing must be conducted. In this way, en-
lightening feedback will be received from the users
and all the necessary changes will be made. Essen-
tially, an XAI model should be designed and evalu-
ated based on the feedback from the users involved.
2.3.3 XAI Enabled by Different Stakeholders
The results generated by an AI model are essen-
tial for effective decision-making procedures by var-
ious types of stakeholders exhibiting different back-
ground knowledge, expertise, experience, needs, and
motivates. Hence, each stakeholder will potentially
require different understandability, comprehensibil-
ity, interpretability, explainability, and transparency
approaches, tailored and adapted to their individual
needs (Blumreiter et al., 2019).
3 XAI IN FOOTBALL
XAI aims to support in accurate, effective and correct
decision making (Nadeem et al., 2022). In football in-
dustry, there are multiple types of users/stakeholders
involved in order for a team to be fully functional.
Examples include managers, assistant managers, fit-
ness/conditioning coaches, chief sports analysts, nu-
tritionists, physiotherapists, and scouters. Every user
comes from a different scientific background, with
different levels of experience and expertise, respon-
sibilities and roles in the team. In practice, an XAI
model should help each of these users understand how
AI models were constructed, function, what the re-
sults reveal, and provide useful insights and conclu-
sions about the input data it received, tailored to their
needs, level of experience and knowledge (Nadeem
et al., 2022). We proceed by discussing how XAI
could be integrated in various football aspects, high-
lighting which of the characteristics and goals defined
in the previous section are vital for its effective utili-
sation. Our guidelines and recommendations are also
summarised in Table 1.
3.1 XAI in Scouting
Recruiting/scouting is one of the most important pro-
cesses for football clubs. Most of the clubs have a
combination of human scouting experts physically at-
tending games and watching the potential players to
be signed and also using AI tools to assess a potential
player’s suitability for the team.
Several stages in scouting can enhanced by AI.
The first stage consists of the AI model identifying
which positions in the team require new/additional
players for maximised performance and effective
player-rotating. The second stage is collecting the rel-
evant data for accurate comparison between the play-
ers the team is interested in recruiting. This includes
performance statistics for each player, such as passes
(short/long/dangerous) completed, successful assists,
The 12th Player: Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Football: Conceptualisation, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions
215
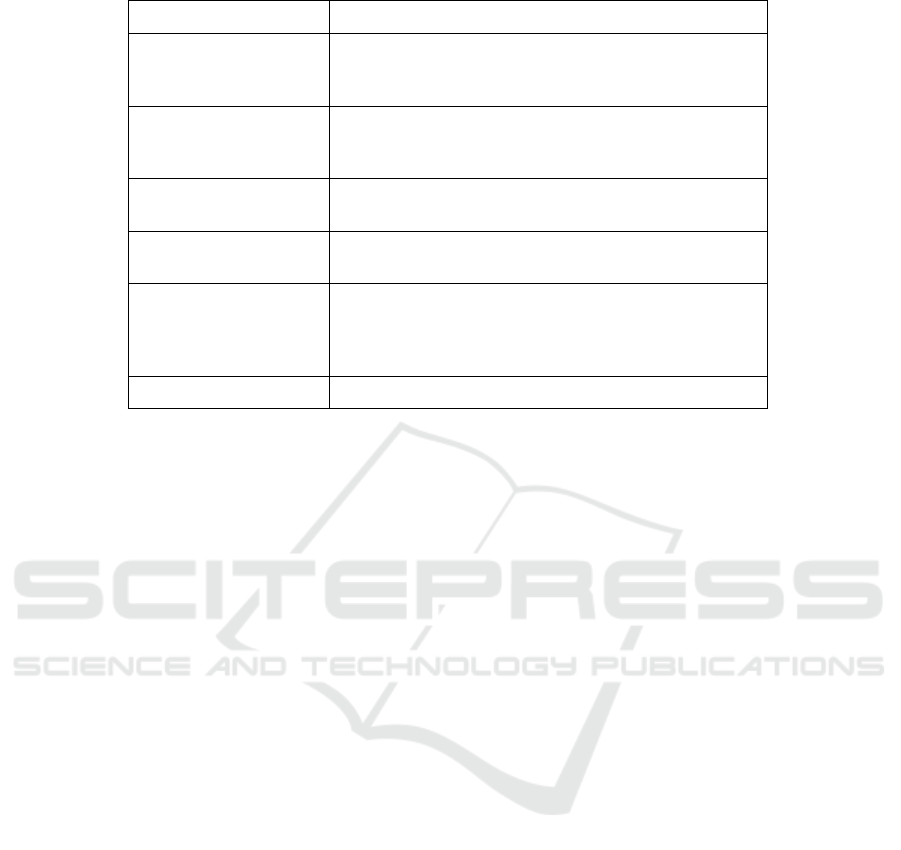
Table 1: Summary of XAI utilisation to the Football Industry.
Stakeholders XAI Application in Football
Players
-Injury prediction and prevention
-Personalised rehabilitation programmes
-Personal training programme
Managers
Assistant Managers
- Decision making at player and team level
- Exploration of alternative tactics
- Player position changes for improved team performance
Coaches
Fitness/Training Experts
- Youth/Pro Players monitoring and development
- Performance optimisation
Sports Analysts
Chief Sports Analysts
-Tactical/Opposition analysis
-Gameplay patterns
Nutritionists
Physiotherapists
Healthcare Specialists
Medical Team
- Injury risk monitoring and Targeted interventions
-Rehabilitation monitoring and adjustments
-Wellbeing and fatigue level monitoring
-Physical and mental health monitoring
Scouters - Talent identification
on and off target shots, successful dribbles, successful
aerial battles won, successful interceptions/tackles,
successful saves (goalkeepers), and so on. The AI-
informed scouting team can subsequently go and ac-
tually watch the players in-action to gather subjec-
tive evidence, beyond statistics (Ryan Beal and Ram-
churn, 2019). Examples include but not limited to
off-the-ball movement abilities, positioning, bravery
in pursuing challenges, team responsibility, stamina,
concentration, good communication and good re-
flexes. Once all the necessary data is gathered and
based on the available budget, optimal decisions can
be taken. This is essentially an AI-optimised prob-
lem, meaning getting the most highly-rated players
with the least budget. There are also other factors to
consider, such as squad sizes and player wage caps.
As the literature suggest (Ryan Beal and Ramchurn,
2019), scouting is a process that can involve both hu-
man experts and AI models, each bringing their own
skills in the formula.
XAI could assist in the scouting process by firstly
identifying the best players for the required posi-
tions, why these players were selected and based on
which factors (understandability and explainability),
and how these factors contributed to their selection
(interpretability). Moreover, the XAI model, based on
the observations and feedback provided by the human
experts (scouters), can visually quantify which play-
ers are the most suitable and why (understandability
and explainability) and what requirements they sat-
isfy (interpretability). Finally, XAI could suggest on
alternative players, based on available budget.
3.2 XAI in Tactical Analysis
Unarguably, football is one of the most complex
sports and one of the most challenging to analyse due
to the large number of players involved and their var-
ied roles. AI can model the behaviour of players and
identify team gameplay patterns (Moustakidis et al.,
2023), in an attempt to provide sufficient information
on which players are the most influential on the pitch,
the most reliable when it comes to goal scoring, the
most successful in stopping counter-attacks, with the
highest number of dangerous passes, and so on.
XAI could assist in explaining how different for-
mations of the squad could contribute to the play-
ers’/team’s improved performance (understandabil-
ity), thus explaining why certain players perform bet-
ter under certain circumstances (different position,
opponent, cooperation) (explainability and compre-
hensability) and what factors (features) have con-
tributed to it, as well as how these factors were han-
dled from the AI model (interpretability). Moreover,
based on what the manager and assistant managers
would like to try out, XAI could be used to suggest
alternative positions for certain players and different
formations, where their performance is maximised. In
addition, XAI could similarly used to analyse the op-
position team. In that way, the manager and the assis-
tant manager can gain valuable and insights on what
they are up against and make improvements to their
team and/or construct alternative strategies.
icSPORTS 2023 - 11th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
216

3.3 XAI in Player Development and
Performance Optimisation
Football clubs around the world invest a lot on their
youth academies. Therefore, the appropriate develop-
ment of youth players is essential for becoming suc-
cessful candidates for joining the first team squad.
AI systems can assist and optimise this process in
numerous stages. Firstly, AI can provide informa-
tion on the players’ performance both during practice
and game days. Input data can be performance re-
lated (e.g., successful shots/assists, passes completed,
tackles/interventions, etc.) or physical data captured
from GPS vests (e.g., total distance, high intensity
distance, sprint distance, top speeds, etc.) (Ryan Beal
and Ramchurn, 2019). Moreover, AI can be vi-
tal in personalising the training programme for each
footballer, according to their skills and capabilities
and the needs of the team. AI could also assist in
decisions relating to assigning a player to a higher
level team or a smaller club for gaining more expe-
rience and playing minutes. More specifically, an
AI model could map players (youth/professional) to
specific strength/conditioning programmes based on
their physical characteristics and objectives set by the
coaching team. XAI could assist in visually quanti-
fying the performance of players (understandability),
thus explaining why a player is performing in a spe-
cific way (explainability and comprehensability) and
what factors contributed, as well as how these factors
were handled from the AI model (interpretability).
In this way, the ”weak points” of a player can
be identified allowing the personnel involved to take
informed action. In case a footballer needs to be-
come physically stronger, the strength and condition-
ing team can re-construct their fitness programme
along with the nutritionist who can improve their diet
plan. If the footballer needs to work on improving
their technique and/or specific actions (e.g. passing
accuracy), the manager/coaching personnel could use
re-construct their individual practice programme, so
they can improve. In addition, XAI could suggest
alternative positions for certain players (especially
youth players), based on their performance and phys-
ical characteristics (understandability, explainability
and comprehensability) and how certain factors con-
tribute to the alternative position (interpretability).
Managers and assistants could use this information to
improve their team tactics/strategies and rotation sys-
tems, coaches could differentiate their personal pro-
grammes, while the conditioning team could make the
necessary changes to their exercise programme based
on their role on the pitch.
3.4 XAI in Injury Prediction/Prevention
Injuries in football can be severe and many times sea-
son ending. Certain types of injuries may be avoided
or at least their magnitude and impact may be signif-
icantly minimised. AI could be used as an injury pre-
diction and prevention tool by monitoring the players’
overall movement to identify poor body posture, in-
correct form or overexertion, allowing potential risks
of injury to be identified. The AI model could make
insightful suggestions to readjust posture or to pre-
vent an injury, such as specific exercise programmes
to strengthen certain muscle groups. XAI could be
used to identify the types of injuries each player is at
risk of experiencing, visualising the factors contribut-
ing to this risk (understandability and explainability)
and how these factors can impact the players’ health
and wellbeing (interpretability) through visual quan-
tification of these risks. The results obtained can help
the coaching and medical teams understand what ad-
justments need to be made and how, hence creating
personalised exercise programmes to ensure the play-
ers’ health, safety, and improved performance.
In addition, the game minutes could be analysed
by the AI model, to estimate which players are poten-
tially at risk of injuring themselves based on the num-
ber games played and their resting periods between
games. Once again, the XAI model could provide ac-
curate visualisations on the potential ”fatigue” levels
of the players and how these are constructed. Such
results can assist the managers into constructing an
optimised and safer player-rotation system.
3.5 XAI in Rehabilitation
Inevitably, most footballers will suffer from injuries
during their career. Some of these injuries may be
long-term and require one or more surgeries. Hence,
proper rehabilitation is essential for effective recov-
ery. Undeniably, every footballer is different and
therefore, every injury in manifested differently. AI
could assist in personalising the rehabilitation pro-
gramme for each player based on the type and sever-
ity of injury, their biomechanics and how each player
corresponds to the rehabilitation programme to max-
imise the probability of a successful recovery. In de-
tail, the AI model could take a closer look to each
player’s biomechanics so it can spot any weaknesses
or imbalances that may contribute to their slower re-
habilitation. In addition, AI could estimate approxi-
mate recovery timelines based on the current progress
made by the player as well as similar previous cases.
Finally, AI could track players’ movements in real-
time and provide effective feedback to maximise their
The 12th Player: Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Football: Conceptualisation, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions
217

progress and minimise the risk of re-injury.
Through XAI, medical/healthcare special-
ists (sports injury rehabilitation, physiother-
apy/conditioning team) can understand the purpose of
a specific rehabilitation programme (understandabil-
ity, explainability) and what factors contributed to its
selection. Examples of important factors include the
type/severity of injury, medical intervention (if any),
whether it is a recurrent injury, player’s biological
characteristics (e.g., age, height, weight, BMI),
biomechanics (e.g. muscle imbalances) and perfor-
mance results (e.g., stamina levels). In addition, XAI
could explain why certain movements put the player
at risk of re-injury by visualising how they currently
move and how they should move correctly to avoid
putting additional physical stress to the injured area.
XAI should also assist in presenting similar past
cases (similar injuries/recovery) to illustrate common
points between them and the current case to support
its decision (Comprehensability). Interpretablity
could provide more information on how these factors
are used by AI and how influential and important
they were when choosing the specific rehabilitation.
Additionally, managers and assistant managers
can keep track of their players’ progress and get an
estimation on their possible return date. In addition,
nutritionists could be informed though the XAI model
on the players’ current exercise programme and its
physical requirements, so they could construct a cor-
responding diet plan based on their bodies needs. Fi-
nally, transparency should be considered so that every
player is treated fairly with regards to their condition,
receives clear instructions on what is required from
them throughout the different stages of the rehabilita-
tion programme and what improvements can be made
from their side to maximise results.
4 CHALLENGES AND FUTURE
DIRECTIONS
XAI is an interdisciplinary research field in the
realm of AI (Brunotte et al., 2022),(Langer et al.,
2021a),(Langer et al., 2021b). Hence, several chal-
lenges emerge when attempting to provide sufficient
explanations on its functioning. Firstly, providing
clear, precise, and sufficient explanations is more
complex than it seems. It is essentially a sociologi-
cal issue (Miller, 2019), which ultimately refers to the
following question: how can we evaluate the qual-
ity of an explanation? (Longo et al., 2020). Ulti-
mately, there is no single correct answer as it can have
multifaceted implications for different stakeholders.
Therefore, in-depth cognitive experiments should be
conducted to decide on the presentation of explana-
tions (Longo et al., 2020). This is demonstrated in the
football case study presented, as multiple stakehold-
ers are involved with different background knowl-
edge, expertise, experience, motives, goals, and re-
sponsibilities. Therefore, what comprises an explain-
able set of information can vary for each stakeholder.
A possible approach towards simplified and straight-
forward explainability would be to use abstractions
(Gunning et al., 2019). In addition, an XAI model
should be able to explain to human experts about
not only its decisions but also its skills and capabil-
ities (Gunning et al., 2019). Even the most sophisti-
cated AI systems have their own blind spots and may
have cases which they might not have the perfect an-
swer. An XAI model should harmonically co-exist
with human experts to develop cross-disciplinary in-
sights and common baselines, helping both human ex-
perts and other AI agents learn, and improving their
own knowledge by using past knowledge and experi-
ence to accelerate discovery. This re-emphasises the
human aspects of AI.
Furthermore, one should consider the legal impli-
cations and the factor of accountability when it comes
to XAI. If an XAI model provides an incorrect sug-
gestion, what are the legal implications? Who is af-
fected? What are the consequences? What are the
socio-economical, health and safety implications? In
addition, we should consider whether XAI explana-
tions could negatively impact the safety and privacy
of individuals (et. al., 2023). Some important ques-
tions to ask are: How can XAI impact privacy and
safety? Which human factors should be considered?
Such questions are especially important when sensi-
tive information is involved. In the present case study,
this may relate to the players’ injuries records, per-
formance and medical data. Even an accidental leak-
age, could lead to great consequences to individuals
and teams. A possible countermeasure would be to
anonymise data and partially release anonymised sen-
sitive data as a baseline to collect more intelligence
about the individuals involved (Cai et al., 2016).
Moreover, XAI should be human-centred to facili-
tate usable and beneficial interactions between human
experts and AI (Amershi et al., 2019). Beyond the rel-
evant HCI-related principles that should definitely be
considered when designing an XAI-enabled interface,
multiple iterations of user testing and usability studies
should be conducted. In addition, important questions
should be discussed before proceeding with designing
the XAI-enabled interface (Bush et al., 1945), such as
whether XAI should include additional explanations
on particular users who may lack relevant knowledge,
and how explanations can become more interactive to
icSPORTS 2023 - 11th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
218

keep human users engaged while assisting them in un-
derstanding difficult concepts more efficiently. In the
case study presented, it is clear that deploying a one-
fit-for-all XAI system is not sufficient and that the ap-
proach should be differentiated based on the individ-
ual’s knowledge, skills, experience and duties.
In addition, XAI should contribute towards more
responsible AI. It is no secret that an AI system au-
tomates multiple and complex tasks simultaneously.
Although its capabilities are remarkable with how fast
and accurate considerable amounts of data can be
handled, the fact remains that errors and miscalcula-
tions will be made. In such cases, it should be clear
and precise on how such mistakes are handled, who is
responsible to identify and respond to any mistakes,
who should be held accountable (et. al., 2023).
5 CONCLUDING REMARKS
The effective and correct conceptualisation and utili-
sation of XAI is still a work in progress. This holds
especially true for the football (soccer) sector, and
the sports industry in general, as to the best of our
knowledge no substantial research has been made for
it yet. Hence, in this paper we aimed to discuss how
XAI could be applied in various domains of a foot-
ball club to benefit all the relevant stakeholders. In
particular, we have discussed how XAI is defined and
what its characteristics are and the need for XAI to be
user-centred. We explored the domains of the foot-
ball industry (focusing on the footballers-related pro-
cedures) where XAI can be utilised and how can this
be beneficial for the diverse target groups involved.
Finally, since XAI is a relatively recent area of re-
search, there is still plenty of improvement and work
to be done. Hence, we discuss what challenges XAI
faces, focusing on the case presented. In the future,
it is essential for XAI experts to address these chal-
lenges so XAI can be deployed alongside AI. Without
a doubt, XAI is going to be one of the most important
components an AI system should possess. As the field
of AI expands its application areas and obtains a more
substantial social role, it is essential to remain in-sync
to the needs of human users.
REFERENCES
Adadi, A. and Berrada, M. (2018). Peeking inside the
black-box: a survey on explainable artificial intelli-
gence (xai). IEEE access, 6:52138–52160.
Amershi, S., Weld, D., Vorvoreanu, M., Fourney, A., Nushi,
B., Collisson, P., Suh, J., Iqbal, S., Bennett, P. N.,
Inkpen, K., et al. (2019). Guidelines for human-ai in-
teraction. In Proceedings of the 2019 chi conference
on human factors in computing systems, pages 1–13.
Angelini, M., Aniello, L., Lenti, S., Santucci, G., and Ucci,
D. (2017). The goods, the bads and the uglies: Sup-
porting decisions in malware detection through visual
analytics. In 2017 IEEE Symposium on Visualization
for Cyber Security (VizSec), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Anjomshoae, S., Najjar, A., Calvaresi, D., and Fr
¨
amling,
K. (2019). Explainable agents and robots: Results
from a systematic literature review. In 18th Interna-
tional Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multia-
gent Systems (AAMAS 2019), Montreal, Canada, May
13–17, 2019, pages 1078–1088. International Founda-
tion for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems.
Antwarg, L., Miller, R. M., Shapira, B., and Rokach, L.
(2021). Explaining anomalies detected by autoen-
coders using shapley additive explanations. Expert
systems with applications, 186:115736.
Arrieta, A. B., D
´
ıaz-Rodr
´
ıguez, N., Del Ser, J., Bennetot,
A., Tabik, S., Barbado, A., Garc
´
ıa, S., Gil-L
´
opez, S.,
Molina, D., Benjamins, R., et al. (2020). Explainable
artificial intelligence (xai): Concepts, taxonomies, op-
portunities and challenges toward responsible ai. In-
formation fusion, 58:82–115.
Bharati, S., Mondal, M. R. H., and Podder, P. (2023). A re-
view on explainable artificial intelligence for health-
care: Why, how, and when? IEEE Transactions on
Artificial Intelligence.
Bharati, S., Podder, P., and Mondal, M. (2020a). Artificial
neural network based breast cancer screening: a com-
prehensive review. arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.01767.
Bharati, S., Podder, P., and Mondal, M. R. H. (2020b). Hy-
brid deep learning for detecting lung diseases from
x-ray images. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked,
20:100391.
Biran, O. and Cotton, C. (2017). Explanation and justifi-
cation in machine learning: A survey. In IJCAI-17
workshop on explainable AI (XAI), volume 8, pages
8–13.
Blumreiter, M., Greenyer, J., Garcia, F. J. C., Kl
¨
os, V.,
Schwammberger, M., Sommer, C., Vogelsang, A.,
and Wortmann, A. (2019). Towards self-explainable
cyber-physical systems. In 2019 ACM/IEEE 22nd In-
ternational Conference on Model Driven Engineer-
ing Languages and Systems Companion (MODELS-
C), pages 543–548. IEEE.
Brunotte, W., Chazette, L., Kl
¨
os, V., and Speith, T. (2022).
Quo vadis, explainability?–a research roadmap for ex-
plainability engineering. In International Working
Conference on Requirements Engineering: Founda-
tion for Software Quality, pages 26–32. Springer.
Bush, V. et al. (1945). As we may think. The atlantic
monthly, 176(1):101–108.
Cai, Z., He, Z., Guan, X., and Li, Y. (2016). Collective data-
sanitization for preventing sensitive information infer-
ence attacks in social networks. IEEE Transactions on
Dependable and Secure Computing, 15(4):577–590.
Chazette, L., Brunotte, W., and Speith, T. (2021). Exploring
explainability: a definition, a model, and a knowledge
The 12th Player: Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) in Football: Conceptualisation, Applications, Challenges and Future Directions
219

catalogue. In 2021 IEEE 29th international require-
ments engineering conference (RE), pages 197–208.
IEEE.
Doshi-Velez, F. and Kim, B. (2017). Towards a rigorous sci-
ence of interpretable machine learning. arXiv preprint
arXiv:1702.08608.
Duell, J., Fan, X., Burnett, B., Aarts, G., and Zhou, S.-M.
(2021). A comparison of explanations given by ex-
plainable artificial intelligence methods on analysing
electronic health records. In 2021 IEEE EMBS Inter-
national Conference on Biomedical and Health Infor-
matics (BHI), pages 1–4. IEEE.
et. al., O. G. (2023). Six human-centered artificial intel-
ligence grand challenges. International journal of
human-computer interaction, 39(3):391–437.
Goodman, B. and Flaxman, S. (2017). European union reg-
ulations on algorithmic decision-making and a “right
to explanation”. AI magazine, 38(3):50–57.
Gunning, D., Stefik, M., Choi, J., Miller, T., Stumpf, S.,
and Yang, G.-Z. (2019). Xai—explainable artificial
intelligence. Science robotics, 4(37):eaay7120.
Gupta, A., Anpalagan, A., Guan, L., and Khwaja, A. S.
(2021). Deep learning for object detection and scene
perception in self-driving cars: Survey, challenges,
and open issues. Array, 10:100057.
K
¨
ohl, M. A., Baum, K., Langer, M., Oster, D., Speith, T.,
and Bohlender, D. (2019). Explainability as a non-
functional requirement. In 2019 IEEE 27th Inter-
national Requirements Engineering Conference (RE),
pages 363–368. IEEE.
Langer, M., Baum, K., Hartmann, K., Hessel, S., Speith,
T., and Wahl, J. (2021a). Explainability audit-
ing for intelligent systems: a rationale for multi-
disciplinary perspectives. In 2021 IEEE 29th inter-
national requirements engineering conference work-
shops (REW), pages 164–168. IEEE.
Langer, M., Oster, D., Speith, T., Hermanns, H., K
¨
astner,
L., Schmidt, E., Sesing, A., and Baum, K. (2021b).
What do we want from explainable artificial intel-
ligence (xai)?–a stakeholder perspective on xai and
a conceptual model guiding interdisciplinary xai re-
search. Artificial Intelligence, 296:103473.
Longo, L., Goebel, R., Lecue, F., Kieseberg, P., and
Holzinger, A. (2020). Explainable artificial intelli-
gence: Concepts, applications, research challenges
and visions. In International cross-domain conference
for machine learning and knowledge extraction, pages
1–16. Springer.
Miller, T. (2019). Explanation in artificial intelligence: In-
sights from the social sciences. Artificial intelligence,
267:1–38.
Mittelstadt, B., Russell, C., and Wachter, S. (2019). Ex-
plaining explanations in ai. In Proceedings of the con-
ference on fairness, accountability, and transparency,
pages 279–288.
Mondal, M. R. H., Bharati, S., and Podder, P. (2021). Co-
irv2: Optimized inceptionresnetv2 for covid-19 detec-
tion from chest ct images. PloS one, 16(10):e0259179.
Moustakidis, S., Plakias, S., Kokkotis, C., Tsatalas, T.,
and Tsaopoulos, D. (2023). Predicting football team
performance with explainable ai: Leveraging shap to
identify key team-level performance metrics. Future
Internet, 5(5):174.
Nadeem, A., Verwer, S., Moskal, S., and Yang, S. J.
(2021). Alert-driven attack graph generation using s-
pdfa. IEEE Transactions on Dependable and Secure
Computing, 19(2):731–746.
Nadeem, A., Vos, D., Cao, C., Pajola, L., Dieck, S., Baum-
gartner, R., and Verwer, S. (2022). Sok: Explainable
machine learning for computer security applications.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.10605.
Nazar, M., Alam, M. M., Yafi, E., and Su’ud, M. M. (2021).
A systematic review of human–computer interaction
and explainable artificial intelligence in healthcare
with artificial intelligence techniques. IEEE Access,
9:153316–153348.
Padilla, L. M., Creem-Regehr, S. H., Hegarty, M., and Ste-
fanucci, J. K. (2018). Decision making with visualiza-
tions: a cognitive framework across disciplines. Cog-
nitive research: principles and implications, 3(1):1–
25.
P
´
aez, A. (2019). The pragmatic turn in explainable artificial
intelligence (xai). Minds and Machines, 29(3):441–
459.
Panigutti, C., Beretta, A., Giannotti, F., and Pedreschi, D.
(2022). Understanding the impact of explanations on
advice-taking: a user study for ai-based clinical deci-
sion support systems. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI
Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems,
pages 1–9.
Rathi, K., Somani, P., Koul, A. V., and Manu, K. (2020).
Applications of artificial intelligence in the game of
football: The global perspective. Researchers World,
11(2):18–29.
Russell, S. J. (2010). Artificial intelligence a modern ap-
proach. Pearson Education, Inc.
Ryan Beal, T. J. N. and Ramchurn, S. D. (2019). Artificial
intelligence for team sports: a survey. The Knowledge
Engineering Review, 34:1–40.
Sopan, A., Berninger, M., Mulakaluri, M., and Katakam,
R. (2018). Building a machine learning model for the
soc, by the input from the soc, and analyzing it for the
soc. In 2018 IEEE Symposium on Visualization for
Cyber Security (VizSec), pages 1–8. IEEE.
Van Lent, M., Fisher, W., and Mancuso, M. (2004). An ex-
plainable artificial intelligence system for small-unit
tactical behavior. In Proceedings of the national con-
ference on artificial intelligence, pages 900–907. Cite-
seer.
Vishwarupe, V., Joshi, P. M., Mathias, N., Maheshwari, S.,
Mhaisalkar, S., and Pawar, V. (2022). Explainable ai
and interpretable machine learning: A case study in
perspective. Procedia Computer Science, 204:869–
876.
Viton, F., Elbattah, M., Gu
´
erin, J.-L., and Dequen, G.
(2020). Heatmaps for visual explainability of cnn-
based predictions for multivariate time series with ap-
plication to healthcare. In 2020 IEEE International
Conference on Healthcare Informatics (ICHI), pages
1–8. IEEE.
icSPORTS 2023 - 11th International Conference on Sport Sciences Research and Technology Support
220
