
Text Mining for Customer Experience Mobile Banking Analysis
Helmi Adiningtyas
1
and Aishananda Shavira Auliani
2
1
Magister Management, School of Economics and Business, Telkom Univesity,
Jl. Gegerkalong Hilir No. 47 Bandung, 40152, Jawa Barat, Indonesia
2
Magister Management, School of Economics and Business, Padjadjaran Univesity,
Jl. Dipati Ukur No.23, Lebakgede, Kecamatan Coblong, Kota Bandung, 40132, Jawa Barat, Indonesia
Keywords:
Text Mining, Customer Experience, Mobile Banking.
Abstract:
Improvements in information and communication technology have resulted in several innovative changes to
reach consumers. The use of online financial transactions is increasing due to the convenience and security
provided. The changed habit of customer transaction from traditional payment into digital or online payment
creating a new need of customers and company new ways to fulfilled new mission of succession, to fulfill
it company needs to providing good service that been customize to their customer’s needs. In this study,
we examined the mobile banking customer experience through customer perception on Google Play Store,
and we used BCA Mobile, one of Indonesia’s mobile banking services, as our case study. Sentiment analysis
methods to assess customer satisfaction and topic modeling methods to extract key customer issues within each
sentiment class. This research aims to provide an evaluation and valuable insight into customer experience
in mobile banking. As a result of this research, BCA Mobile customers are dissatisfied with the app service.
Consumers consider transactions with the most recent version of BCA mobile to be risky because it does not
use pins or onetime passwords (OTP). This discovery may help BCA Mobile pay more attention to other app
features to better understand the needs of their customers
1 INTRODUCTION
The proliferation of the internet and mobile phone
users, as well as the advancement of information and
communication technology, have modified service de-
livery methods. Therefore, companies have utilized
a variety of innovative channels to reach consumers
(Jebarajakirthy and Shankar, 2021). Likewise, banks
offer banking services via technologically oriented
platforms such as mobile banking (m-banking) (Mul-
lan et al., 2017). M-banking is primarily utilized
by bank customers to interact ubiquitously and in-
stantaneously with the bank through mobile devices
such as telephones, smartphones, and tablets (Kwa-
teng et al., 2019)(Ver
´
ıssimo, 2016). M-banking func-
tionalities provide customers with access to a variety
of information, such as bank statement requests, bal-
ance checks, and ATM locations. This cutting-edge
technology also enables real-time and secure financial
transactions such as bill payments and money trans-
fers (Jadil et al., 2021). Global adoption of mobile
banking has increased significantly in recent years
(Arcand et al., 2017). Currently, 2.4 billion people
use m-banking services worldwide in 2020, with the
number expected to reach 3.6 billion by 2024 (Re-
search, 2020). In Indonesia, the use of m-banking has
also increased dramatically, as indicated by a Bank
Indonesia report stating that the volume of m-banking
transactions reached 3.2 billion from January to May
2022. This value increased by 67.87% from the same
point last year, when it was 1.90 billion transactions.
In addition, the research indicated that the value of
m-banking transactions between January to May of
2022 reached IDR 3,888.09 trillion, a rise of 43.76%
compared to the same period last year (Kontancoid,
2022). BCA Mobile is currently one of the most pop-
ular mobile banking services in Indonesia. Accord-
ing to the Populix survey titled ”Consumer Preference
Towards Banking and e-Wallet Apps,” conducted on-
line on 1,000 respondents aged 18-55 in several major
cities in Indonesia, BCA Mobile will be the most pop-
ular m-banking service among Indonesians in 2022,
with a market share of up to 60% (Angelia, 2022).
The implementation of m-banking has also shifted
the fulfillment of customer needs, and the impor-
tant factor to a company’s success lies not just in
the quality of its products/services, but also in ef-
forts to meet the needs of its customers, followed by
162
Adiningtyas, H. and Auliani, A.
Text Mining for Customer Experience Mobile Banking Analysis.
DOI: 10.5220/0012445800003848
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development (ICAISD 2023), pages 162-165
ISBN: 978-989-758-678-1
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
providing good and friendly service to convert them
into loyal customers. To get it all, every company
must understand the customer’s needs. Customer
information can assist a company in making major
decisions regarding business reorganization, market-
ing, service offerings, and other strategies (Alamsyah
et al., 2020). Customer information can provide a
company with specific information about what a cus-
tomer wants and needs, or it can provide something
are of how customers feel about a particular aspect of
the company’s business (Anderson and Kerr, 2002).
Technological advancements have made it possible
for businesses to manage customer relationships and
create enhanced customer experiences more effec-
tively (Peppers and Rogers, 2017). In accordance
with this, BCA Mobile can analyze by understand-
ing customer perceptions of their service and identi-
fying the issues that satisfy and disappoint their cus-
tomers. In this study, we analyzed customer experi-
ence towards BCA Mobile using customer perception
on Google Play Store. However, the large volume
and unstructured data cause the process of process-
ing data into more useful information to require spe-
cial techniques and methods (Khan et al., 2019). To
overcome this, we use sentiment analysis and topic
modeling methods. The level of customer satisfaction
was determined using sentiment analysis, while key
customer issues were extracted using topic modeling
within each sentiment class.
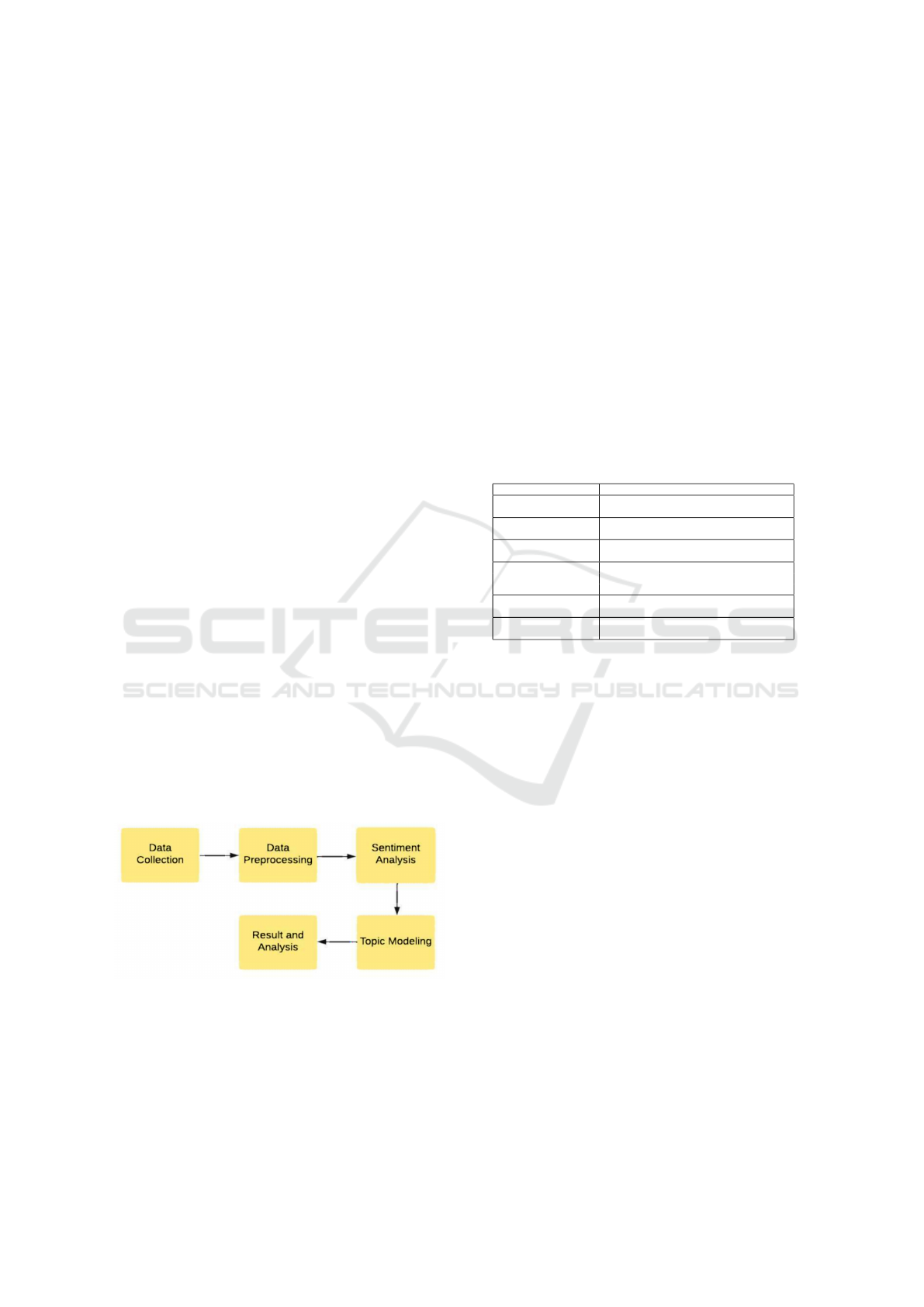
2 METHODS
The research is divided into five stages: data collec-
tion, pre-processing, sentiment analysis, topic model-
ing, and results and analysis. The steps process of this
research is shown in the following figure:
Figure 1: Research Workflow.
a Data Collection
This study scrapped customer perception of BCA
mobile on the Google Play Store. The data collec-
tion period runs from June 1, 2022, to November 5,
2022, with a total of 2.000 data points collected.
b Data Preprocessing
Data preprocessing is a critical step before data
analysis, as it transforms data samples into
more meaningful information (Angiani et al.,
2016)(Haddi et al., 2013). Data preprocessing
starts in several steps. Converting uppercase
to lowercase letters (transform case). Cleaning
and removing non-alphabetic characters from the
dataset, such as numbers, and symbols. Divide the
input data format, which exists a long text, into
small units known as tokens. In the context of
a document, a token could be a word, a number,
or punctuation (Tokenize). Eliminate unnecessary
words (Stop word removal), convert words in sen-
tences to their root words, and eliminate word addi-
tions (Stemming). Table 1 shows examples of each
process in the data preprocessing procedure.
Table 1: Preprocessing Procedure.
Procedure Data Text
Raw data Pelayanan super bak dan sempurna. Sukses
terus buat BCA mobile dan semua jajaran nya.
Transform Case pelayanan super baik dan sempurna. sukses
terus buat bca mobile dan semua jajarannya
Cleaning pelayanan super baik dan sempurna sukses
terus buat bca mobile dan semua jajarannya
Tokenize ∥pelayanan∥∥super∥∥baik∥∥dan∥∥sempurna
∥∥sukses∥∥terus∥∥buat∥∥bca∥∥mobile∥
∥dan∥∥semua∥∥ ja jarannya∥
Stopword Removal Pelayanan super baik sempurna sukses bca mo-
bile semua jajarannya
Stemming Pelayanan super baik sempurna sukses bca mo-
bile semua jajaran
c Sentiment Analysis
To classify text in the sentiment dimension, we
implement the machine learning principle and the
Naive Bayes algorithm. We classify the data as 70
percent training data and 30 percent testing data.
For the training data, the text should be labeled with
a sentiment class.
d Topic Modeling
To model the topic, we split the results of senti-
ment analysis into two files (positive and negative)
to represent the entire topic in the dataset.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Figure 2 illustrates the results of the sentiment analy-
sis on BCA mobile, with 65.75 percent of customers
expressing a negative sentiment or equal to 1315 data,
and the remaining 34.25 percent expressing a positive
sentiment or as many as 685 data
Text Mining for Customer Experience Mobile Banking Analysis
163
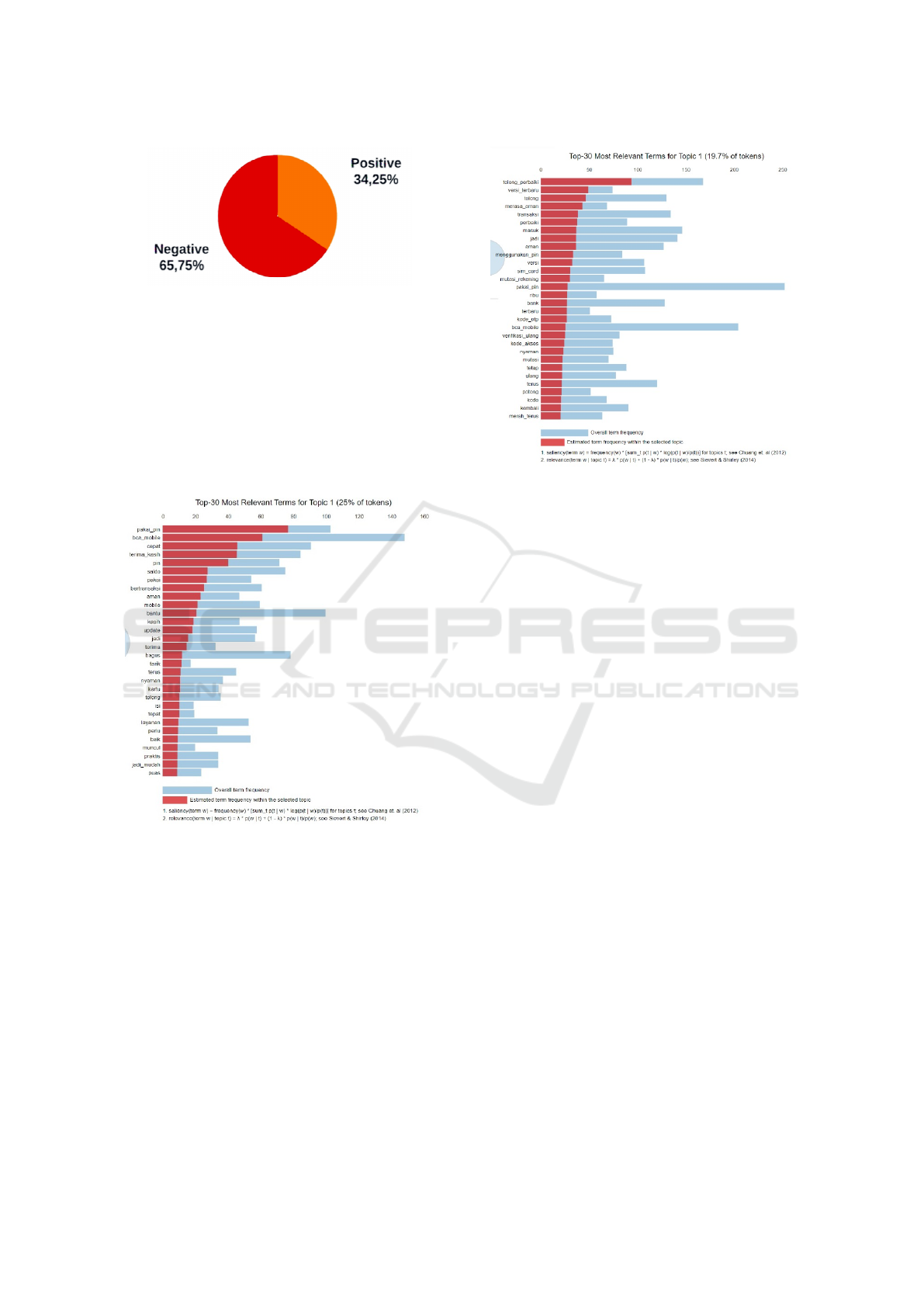
Figure 2: Sentiment Analysis Result.
The sentiment analysis result is divided into two
files for modeling the topic in the dataset (positive
and negative). Figure 3 illustrates two distinct colors,
the red color represents the estimated term frequency
within the document’s selected topic, while the light
blue color indicates the overall term frequency. As
shown in Figures 3 and 4, each word has a red and
light blue color, indicating that each word appears in
more than one topic.
Figure 3: The positive Topic of BCA Mobile.
As shown in Figure 3, the highest frequency topic
in the positive sentiment document is the customer
talking regarding BCA Mobile app features such as
the fast and comfortable service they felt when mak-
ing transactions at BCA Mobile.
For the negative sentiment as shown in Figure 4,
the highest frequency topic is the customer complaint
that the latest version of BCA Mobile is less secure
because it no longer uses pins to access applications
or OTP codes for transactions. They prefer the previ-
ous version because pins and OTP codes make trans-
actions safer
Figure 4: The Negative Topic of BCA Mobile.
4 CONCLUSION
The text mining method was successfully used in this
study to classify and conclude two thousand customer
reviews about BCA Mobile in the Google Play Store
platform to analyze the customer experience in the
BCA Mobile Apps. The Na
¨
ıve Bayes algorithm uti-
lized in this study classifies the sentiment dimension
excellently. According to the results, most BCA Mo-
bile customers are dissatisfied with BCA Mobile’s
service because most customer complaint that the lat-
est version of BCA Mobile is less secure because it no
longer uses pins to access applications or OTP codes
for transactions. They prefer the previous version be-
cause pins and OTP codes make transactions safer.
Therefore, BCA Mobile must be more attentive to
consumer perception to provide a satisfying customer
experience. So that it can generate future consumer
loyalty
REFERENCES
Alamsyah, A., Ramadhani, D., Saputra, M., and Amran, A.
(2020). Analyzing e-commerce customer experience
using text mining: Case study of paperlust.co. Digital
Economy for Customer Benefit and Business Fairness,
page 40–45.
Anderson, K. and Kerr, C. (2002). Customer Relationship
Management. McGraw-Hill Education.
Angelia, D. (2022). Aplikasi mobile banking paling banyak
digunakan masyarakat indonesia 2022 - goodstats.
Goodstats.id.
ICAISD 2023 - International Conference on Advanced Information Scientific Development
164

Angiani, G., Ferrari, L., Fontanini, T., Fornacciari, P., Iotti,
E., Magliani, F., and Manicardi, S. (2016). A compar-
ison between preprocessing techniques for sentiment
analysis in twitter. KDWEB.
Arcand, M., PromTep, S., Brun, I., and Rajaobelina, L.
(2017). Mobile banking service quality and customer
relationships. International Journal of Bank Market-
ing, 35:1066–1087.
Haddi, E., Liu, X., and Shi, Y. (2013). The role of text pre-
processing in sentiment analysis. Procedia Computer
Science, 17:26–32.
Jadil, Y., Rana, N., and Dwivedi, Y. (2021). A meta-analysis
of the utaut model in the mobile banking literature:
The moderating role of sample size and culture. Jour-
nal of Business Research, 132:354–372.
Jebarajakirthy, C. and Shankar, A. (2021). Impact of online
convenience on mobile banking adoption intention: A
moderated mediation approach. Journal of Retailing
and Consumer Services, 58:102323.
Khan, J., Alam, A., Hussain, J., and Lee, Y. (2019).
Enswf: effective features extraction and selection in
conjunction with ensemble learning methods for doc-
ument sentiment classification. Applied Intelligence,
49:3123–3145.
Kontancoid (2022). Bi catat transaksi mobile banking tem-
bus rp 3.888,09 triliun hingga mei 2022. Kontan.co.id.
Kwateng, K., Atiemo, K., and Appiah, C. (2019). Accep-
tance and use of mobile banking: an application of
utaut2. Journal of Enterprise Information Manage-
ment, 32:118–151.
Mullan, J., Bradley, L., and Loane, S. (2017). Bank
adoption of mobile banking: stakeholder perspec-
tive. International Journal of Bank Marketing,
35:1152–1172.
Peppers, D. and Rogers, A. (2017). Managing Customer
Experience and Relationships: A Strategic Frame-
work. John Wiley & Sons.
Research, J. (2020). Digital banking users to exceed 3.6
billion globally by 2024.
Ver
´
ıssimo, J. (2016). Enablers and restrictors of mobile
banking app use: A fuzzy set qualitative compara-
tive analysis (fsqca. Journal of Business Research,
69:5456–5460.
Text Mining for Customer Experience Mobile Banking Analysis
165
