
Emotional Stability and Psychological Well Being of Investors: Role
of Stock Market Swings
Tarika Singh Sikarwar
*
, Harshita Mathur, Archana Kaushal, and Anubha Tripathi
Prestige Institute of Management & Research, Gwalior, India
Keywords: Social Analytics, Psychology, Behavioral Finance, Emotional Stability
Abstract: This research aimed to examine and validate the elements influencing investors' emotional steadiness and
psychological wellbeing during stock market fluctuations. It took into account the variables that affect
investor’s emotional steadiness and psychological health, and then utilized confirmatory factor analysis to
authenticate these determinants. The author has incorporated past research on behavioral finance to develop
society's comprehension of emotions, psychological well-being, and investment behavior. The report suggests
that policymakers and financial firms should pay greater attention to these aspects when devising promotional
strategies. This research can help investors understand the changes in price so they can make a wise decision
when investing in the stock market.
1 INTRODUCTION
Price fluctuation is defined as the variation in price
levels from one period to the next or the variation
between a stock's daily starting and closing prices.
Share prices fluctuate on the stock market every
second, and these variations are generated by supply
and demand for a certain share, similar to other market
product price fluctuations. Several prior studies show
that the stock market has a direct impact on human
psyche. Stock market movements have an impact on
people's behaviour, health, and personal lives. It can
produce a variety of issues such as anxiety, panic
disorder, or severe depression, as well as unhealthy
habits like as smoking and drinking alcohol. In certain
cases, an investor who consistently loses money may
resort to illicit actions. Individuals all throughout the
world are affected by stock market swings, whether
they are in India or another foreign nation. Stock price
fluctuations have an almost direct impact on investors'
physical health, with sharp price drops increasing
hospitalizations within the next two days. The effect is
especially strong for situations associated with mental
health, such as anxiety, implying that concern about
the future, as well as current, consumption shocks,
influence an investor's immediate perception of well-
being Another research, done in the United States in
2008, looked at how a stock market crash affected life
*
Corresponding author
satisfaction, mental discomfort, and elderly health
habits. According to the data, a market collapse had a
detrimental influence on hospitalisations, child
reported medical condition, sick days from school,
and emotional issues. Psychology has also been used
to better understand the decisions of traders. Early in
the 1970s, Kahneman and Tversky (1979) reexamined
how attitudes, emotions, and behavioral biases
generally affected the choices made by investors. One
of the most recent advancements includes the
application of psychology to explore how emotions
and sentiments influence the utility function choice
and perception of the environment as a whole.
According to this new development, affect rather than
logical calculation now controls behavior. Decision-
making must take into account feelings and
sentiments, Thaler (1993) further establishes that
psychological factors influence asset prices. Damasio
(1994) demonstrated the very next year how
individuals who have lost the use of the emotional part
of their brains may find it extremely difficult to make
decisions. Furthermore, Forgas (1995) demonstrates
that the calculations necessary to make investment
decisions are frequently intricate, abstract, and risky.
These characteristics are thought to lead people to
make decisions based more on emotion than reason.
Financial crises have also been explained in terms of
emotions (Tuckett and Taffler, 2008).
Sikarwar, T., Mathur, H., Kaushal, A. and Tripathi, A.
Emotional Stability and Psychological Well Being of Investors: Role of Stock Market Swings.
DOI: 10.5220/0012493800003792
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR 2023), pages 557-562
ISBN: 978-989-758-687-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
557

1.1 Stock Market Fluctuations
For decades, stock markets have been the hub of
economies. Any instability or crisis that occurs in
these markets affects the economy either generally or
partially (Demir, 2019). The value of stocks and
debentures in the stock market may vary over time,
which can be seen by the differences in their values
between one period and the next or the gap between a
stock's opening and closing prices on a single day.
The price of stocks, just like any other commodity, is
determined by supply and demand. Prices increase
when the number of available shares is insufficient to
fulfill investor demand; they decline whenever few
investors are interested in purchasing stocks. Futher
(Al-Rimawi and Kaddumi, 2021) in their research
tried to explore the determinants of stock market
volatility, the findings of their study revealed that
foreign investments, interest rates, economic growth
rate and inflation are the major macroeconomic
factors influencing stock prices.
1.2 Emotions and Investors
The majority of decisions individuals make in
various facets of their lives are influenced by feelings,
many psychology experts now believe that feelings &
emotions are, for good or worse, the primary force
behind the majority of important life decisions.
Emotion is a person's reaction to an external
stimulation that influences their judgment and
conduct and contains both physical and psychological
components (Aren and Hamamci, 2020). In the
context of finance, Standard finance theories presume
that investors in stock markets typically act
"rationally." The rational behavior hypothesis states
that investors' decision-making entails gathering
relevant details from business financial statements
and other sources and objectively evaluating them
using time-tested investing techniques and models.
However, over the past few decades, it has been
repeatedly demonstrated that human "emotions" are
just as crucial as reasoning in making educated
investing decisions (Saxena and Yadav, 2017).
2 PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL
BEING
In recent decades, both the scientific and general
literatures have shown a strong interest in the idea of
well-being. The term "psychological well-being"
refers to both intra- and inter-individual levels of
beneficial functioning, such as “interpersonal
connectivity” and “self-referential attitudes” such as
self-mastery and personal development (Burns,
2017). Consequently, Hasnain et al. (2014) defined
psychological well-being as a mental state devoid of
mental diseases. From the standpoint of positive
psychology, this may include a person's capability to
live a good life and create a balance amid living
activities and efforts to acquire psychological
resilience. Psychological well-being is crucial in
terms of how we operate and adapt, as well as whether
or not our lives are fulfilling and productive.
Psychological well-being is how people assess their
life, these judgments, according to (Diener and Suh,
1997) might take the shape of cognitions or feelings.
3 RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
EMOTIONAL STABILITY AND
PSYCHOLOGICAL WELL
BEING
(Frijter et al., 2014) conducted a study that looked
into the influence of stock market movements on the
subjective well-being and health of Australians and
found that stock market improvements yielded a
substantial yet moderate increase in life satisfaction
and mental health. In the similar context (Sarwar et
al., 2016) investigated investors of the London Stock
Exchange and determined that there was no strong
association between gender and investment decisions,
yet found a significant correlation between monthly
salary level and investment and concluded that
psychological factors have a more significant
influence than economic factors. Further Gayar et al.
(2021) investigated the effects of investor sentiments
and herding on the volatility of the stock market in
Egypt and found that investor sentiment indicators
have a direct and indirect influence on stock market
volatility, mediated by herding behavior. In the
similar Context (Naseem et al., 2021) in their research
examined the investor’s psychology and stock market
behavior amid covid-19 pandemic, as generally the
psychological attitude of investor’s both favorable
and unfavorable with regards to the stock market can
alter the way economy is perceived, they particularly
employed principal component analysis to identify
the same, the overall findings revealed that
psychology of investor’s was found to be adversely
linked to the stock market, fear and anxiety and
pessimism cause companies to draw out their
investments from the share market, resulting in lower
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
558

share market returns. Based on the reviews done
following objectives were formulated:
4 OBJECTIVES
1. Analyze and confirm the factors that
contribute to psychological well-being.
2. Analyze and confirm the factors that
contribute to emotional stability.
5 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The investigation was exploratory in character. The
population of the study targeted investors from
Gwalior region. An individual investor was chosen as
the sampling element and data was collected from
200 respondents through a non-probability sampling
technique.
Tools Used of Data Analysis. The exploratory Factor
Analysis was employed to investigate the various
elements influencing Emotional stability and
Psychological Well-being, while Confirmatory
Factor Analysis was utilized to corroborate the factors
affecting both variables.
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
a) Reliability Analysis
The Cronbach alpha value for all variables being
greater than or almost equal to 0.7 shows that the
questionnaire was highly reliable and can be used for
further investigations.
b) Sample Adequacy
The KMO Measure of Sampling Adequacy values for
individuals' emotional stability and psychological
well- being were 0.832 and 0.812, suggesting that the
sample size was adequate for conducting exploratory
factor analysis.
c) Description of factors Emotional Stability
1. Overconfidence: This determinant came out as
the most crucial determinant accounting for
37.281 % of variances in the research.
2. Optimism: This determinant emerged as the
second most influential factor, accounting for
10.971 percent of total variances.
3. Self-Image: The third most significant factor
in explaining a total variance of 9.285 is Self-
Image.
d) Describing Factors of Psychological
Well-Being
1. Healthy & Energetic: This emerged as most
important factor in explaining 30.800 percent
of the total variance.
2. Anxiety: This attribute has been identified as
the second most significant determinant,
accounting for 18.994 percent of the total
variance.
3. Stressed: This attribute has been identified as
the third most important determinant
explaining total variance of 9.468 percent.
4. Depressed: Depression has been identified as
the fourth most influential factor in
explaining 6.787% of the total variance.
e) Confirmation of Factors
e.1) Emotional Stability: Confirmatory factor
analysis was used on both variables of the study to
confirm the factors that emerged from EFA.
Emotional Stability was measured using a 12 items
instrument. Further Exploratory Factor Analysis
resulted into three factors for Emotional Stability,
these factors were further confirmed using CFA
which resulted in 6 model out of which 6
th
model was
found to have good fit.
Final Model of Emotional Stability.
Model 6 gave
an excellent match as indicated by the results of the
first-order confirmatory test. The χ2 statistic was
4.650 (degrees of freedom = 712, p 0.001), and the
χ2/df ratio was 0.664 which was below 2.0, a sign of
a good fit. The Goodness of Fit Index
Table 1:
Reliability Analysis
Table 1: Reliability Analysis.
S.
No.
Variable
Name
Cronbach’s
Alpha
No. of
Items
1. Emotional
Stability
.847 12
2. Psychological
well being
.828 15
(AGFI) was .974. The Comparative Fit Index (CFI)
was 1.000, and the Tucker-Lewis coefficient (TLI)
was 1.018, both exceeding 0.9. The Root Mean Square
Error of Approximation (RMSEA) was 0.000, which
is lower than 0.05, indicating a very good fit. Thus, the
values from the table analysis demonstrate that Model
6 is a good fit.
Emotional Stability and Psychological Well Being of Investors: Role of Stock Market Swings
559

Table 2: CFA Table for Emotional stability
Figure:1.
e.2) Confirmation of Factors of Psychological
Well Being: The 14-item test was created to assess
psychological well-being. Exploratory Factor
Analysis was used to investigate the elements
influencing psychological well-being, yielding four
factors. Further CFA was used to confirmed these
factors, Statistical testing resulted in 8 models out
of which 8
th
model was found to have good fit.
Final Model of Psychological Wellbeing. The
results of the eighth order confirmatory test, which
consists of multiple components, is illustrated in the
figure and table below. The χ2/df ratio was 1.123
which is lower than 2.0, implying a strong fit. The
χ2 statistic was 11.230 with 712 degrees of freedom
and a p value of 0.001. The Goodness of Fit Index
(GFI) was 0.986 and the Adjusted Goodness of Fit
Index (AGFI) was 0.951, while the Tucker-Lewis
coefficient (TLI) was 0.991 and the Comparative Fit
Index (CFI) was 0.997. All of these values exceed 0.9,
which is considered an acceptable result. The Root
Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) was
0.025, less than 0.05, indicating a good fit. Therefore,
we may conclude that the eighth model has a
satisfactory fit.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
560
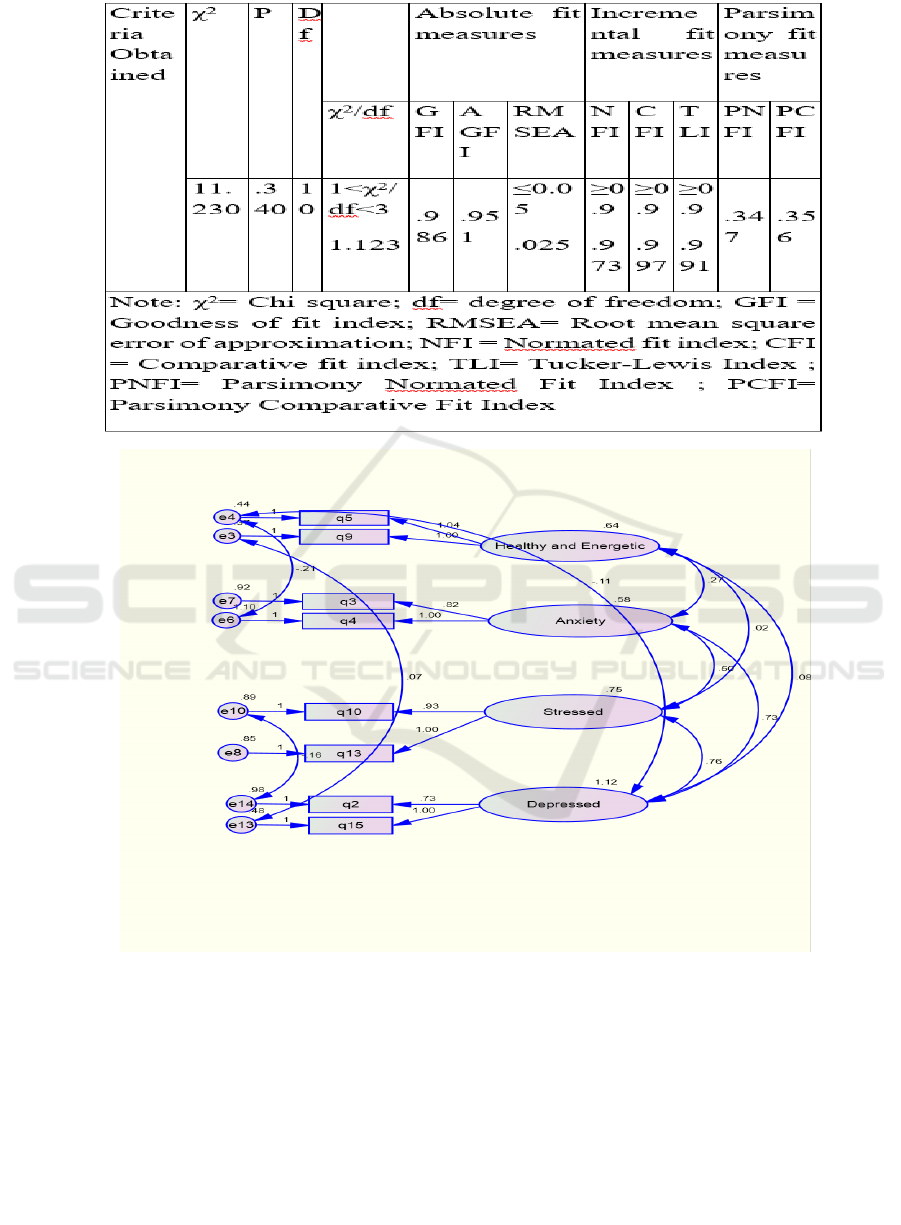
Table 3: CFA table for Psychological-Wellbeing.
Figure:2.
7 CONCLUSION
The primary objective of this research was to
explore and confirm the determinants of “Emotional
Stability” and “Psychological Wellbeing” of
individuals. Initially reliability was checked using
the Cronbach alpha value, further Exploratory
Factor Analysis was applied wherein, three
components emerged for emotional stability namely
overconfidence, optimism, and self-image, and four
factors emerged for psychological wellbeing which are
healthy and energetic, anxiety, stressed, and depressed.
Further CFA was used on both variables to corroborate
the components that emerged from EFA. Confirmatory
factor analysis revealed six models for emotional
stability. Models 1–5 did not meet the specifications,
Emotional Stability and Psychological Well Being of Investors: Role of Stock Market Swings
561

but the last model did. For psychological wellbeing
8 CFA models were constructed with 1 to 7 models
failing to meet requirements and the 8th model
proving to be a good fit. As per 2012 WHO research
report states that a person's capacity to make daily
judgements and choices depends largely on their
mental health. The capacity to control one's
thoughts, feelings, behavior, and relationships with
others is ultimately what determines one's mental
health and well-being.
Investors should analyze market and economic
indicators before making any decisions because
they have an impact on how well shares perform on
the market. Instead of focusing on just one
environmental factor, investors should evaluate all
of them. To reduce risks and increase returns,
investors should also diversify their holdings by
building a portfolio of investments. This research
may help other researchers gain a deeper
understanding of the variables that affect
psychological health and emotional stability.
Behavioral finance may explain complex
difficulties that traditional finance theory and
classic economic theory are unable to explain by
integrating finance theory and practice
REFERENCES
Cotti, & Simon. (2016). The Impact of Stock Market
Fluctuations on the Mental and Physical Wellbeing of
Children, Department of Economics Working Paper
Series. 1-35.
Alam, N., Arshad, S., & Rizvi, S. A. R. (2016). Do
Islamic stock indices perform better than
conventional counterparts? An empirical
investigation of sectoral efficiency. Review of
Financial Economics, 31, 108-114.
Aren, S., & Hamamci, H. N. (2020). Relationship
between risk aversion, risky investment intention,
investment choices: Impact of personality traits and
emotion. Kybernetes.
Nurfadilah, D., & Samidi, S. (2017). Factors that
influence stock market volatility: A case study from
Malaysia. International Journal of Business Studies,
1(1), 15-21.
Demir, C. (2019). Macroeconomic determinants of stock
market fluctuations: The case of BIST-100.
Economies, 7(1), 8.
El-Gayar, A., Metawa, S., & El-Hayes, I. (2021). The
Impact of Investor Sentiment and Herding Behavior
on Stock Market Liquidity "An Empirical Study on
the Egyptian Stock Exchange".
Nagy. (2017). Behavioural Economics and effect of
psychology on the stock marketwong, lee, Ho, Li, Ip,
& Chow. (2017). Stock Market Fluctuations and Self
Harm among Children and Adolescent in Hong Kong.
Nurfadilah, D., & Samidi, S. (2017). Factors that influence
stock market volatility: A case study from Malaysia.
International Journal of Business Studies, 1(1), 15-21.
Vincent, & Bamiro. (2013). Fluctuations in Stock Market
Prices: What went wrong, its Implications to Nigerian
Economy. American Journal of Theoretical and Applied
Business , 3(3), 43-53.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
562
