
The Function of Social Media in the Lives of Today's Young Adults
Brahmmanand Sharma, Navita Nathani and Praveen Aronkar
Prestige Institute of Management and Research, Gwalior
Keywords: Social Media, Social Network Sites, NPI, Narcissism, Millennials.
Abstract: In today's digital world, social media, and particularly social network sites, have become a divisive
intersection where the majority of the population projects their preconceived notions without any deliberate
intent to understand the entire context of a situation. This has the effect of creating a polarising environment.
While one half of the story can be explained by all good things such as expanding geographies, breaking
cages, patron engagement, and social uprising in areas where there are hindrances by the society but on a
broader level has placed social media tool as on a higher stratum, the other half of the story can be visualised
on an individual level where influencers, viewers, news promoters, followers, and members of virtual
communities where social media has an ascendancy for leveraging the amplification The exponential growth
in the use of social networking sites (SNS) among millennials over the past few years raises the question of
whether or not millennials become more narcissistic as a result of their use of social media, which would have
implications for both their personal and professional lives. Measures of the NPI-16 and the NPI-40 can provide
a researcher with aspects of the theory that are mutually exclusive, but they cannot prove an interrelationship
with an external stimulus that moulds, influences, and participates in the personality development of an
individual over the course of some period of time. The psychographic profile of the respondents was mapped
with their intake of social media and their narcissistic behaviour through the use of a descriptive study that
was cross-sectional in nature. This study investigates the fundamental characteristics of narcissism, including
Authority, Exhibitionism, Exploitativeness, Superiority, and Entitlement, as well as the interrelationships
between these characteristics.
1 INTRODUCTION
Those who suffer from narcissism are always looking
for ways to validate their exaggerated sense of self-
importance. The story of Narcissus, a lovely young
man who falls in love with his own image, is where
the word "self-love," also known as "narcissism,"
originated. Narcissus is said to have been a narcissist.
Narcissists, who are characterised by an unwarranted
need for admiration, are among the most prolific users
of social media. This is because social media may
assist narcissists in achieving their goals of being
admired by a large number of people, without the
need for establishing any sort of intimate connection
with those people. Narcissists have a delusion that
they are exceptional and unique; as a result, they are
always looking for new ways to attract attention to
themselves, and they fantasise about achieving
celebrity. They attempt to distinguish themselves
from others in order to attract attention. Those who
have a high level of narcissism are more inclined to
be more domineering in making decisions that are
both visible and task-related in order to demonstrate
their authority and superiority. They also have a
propensity to embrace big behaviours that attract
attention, such as making large acquisitions.
Narcissism is almost always connected to the
characteristics of an individual's personality.
Narcissism is defined as "a chronic pattern of
ostentation (in fantasy or action), craving for
admiration, and lack of empathy" in the fourth edition
of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental
Disorders (DSM IV) (American Medicine
Association, 1994: 661). The Diagnostic Statistical
Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM IV) describes
narcissism as “A pervasive pattern of ostentation (in
fantasy or behavior), need for admiration, and lack of
empathy” (American Medicine Association, 1994:
661). This definition includes nine specific traits -
inflated sense of self-importance, fantasies of
unlimited success or power, perception of special
status, entitlement, exploitation, envy, lack of
empathy, arrogance, and excessive need for
692
Sharma, B., Nathani, N. and Aronkar, P.
The Function of Social Media in the Lives of Today’s Young Adults.
DOI: 10.5220/0012501400003792
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR 2023), pages 692-698
ISBN: 978-989-758-687-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

admiration - which, when exhibited in combination as
a persons’ dominant behavior, comprise the
narcissistic personality (APA, 1994). Narcissism is
exhibited by individuals as an ego-defense to
maintain fragile self-esteem (Kets de Vries & Miller,
1985a), and is characterized by exhibitionism,
entitlement and exploitation (Judge et. al., 2009). In
the extreme, these behaviors are pathological.
The narcissists have the traits like : Authority, that
shows the person’s leadership skills and thirst for
power, and to dominate. Superiority, that is person’s
feelings of superiority over others around them.
Exhibitionism, people who forever yearn to be
admired and be the center of attention, eagerness to
ensure they are center of attraction. Exploitativeness,
how willing a person is to abuse others in order to
meet their own needs and goals. Entitlements,
unreasonable expectations of especially, favorable
treatment or automatic compliance with one’s
expectations, are the common characteristics of
narcissists. Some people misunderstand narcissism
with self-esteem, Professor Twenge points out that
narcissism is distinct from the concept of self-esteem.
“Someone high in self-esteem values individual
achievement, but they also value their relationships
and caring for others,’ she says. ‘Narcissists are
missing that piece about valuing, and caring for their
relationships, so they tend to lack empathy, they have
poor relationship skills. That's one of the biggest
differences, that the communal and caring traits tend
to be high in most people with self-esteem but not
among those who are high in narcissism.”
Panek, Nardis & Konrath (2013) defined Narcissism
as “ ones affinity to believe one’s self to be superior
over others, to relentlessly pursue adoration from
others, and to participate in egotistical thinking and
behavior:, and further added that “Narcissism is
recognized in the employment of private
communication as a way for self-enhancement and
self-publicity, and thus due to the obsession with
one’s self, it inhibits them from establishing lasting
intimate relationships”. Alloway, Runac, Qureshi,
and Kemp, (2014) added that this self obsession can
damage an individual’s ability to shape healthy,
mutually valuable relationships in their personal as
well as professional lives.
Twenge (2009) and Campbell (2011), found in their
study with more than 15000 respondents, found that
the people born in recent generations, like generation
x or y or z, scored high in narcissism measures than
those in previous generations. They also observed
that “increasing narcissism correlated with
materialism and a greater desire of money, fame and
image”. Another researcher found that the millennials
score higher on such traits as extraversion, self-
esteem, self-liking, high expectations, and
assertiveness, and these traits are too often related to
narcissism and entitlement.
Rapid growth in media and technologies that allows
society today to engage in social media using more
SNS’s, has brought an increase in the amount of
narcissism in Millennials. According to a news report
published in the economic times by IMRB , Internet
users in India pegged at 566 million in 2018 and
expected to exceed 627 million by 2019, primarily
due to the unprecedented growth seen in the rural
areas. The report stated that out of the total user base
nearly 293 million active users resided in the urban
India, while the rest were active users in rural India
and 97% of the total users used mobile phone as one
of the devices to access internet, with the internet
usage being more gender balanced than ever before,
due to increased internet accessibility at affordable
data costs and more than two-thirds of the active users
accessing internet for entertainment and
communication. The growing dependence on
technology, especially the Smartphone, has allowed
users to access any type of social networking sites in
no time and with just a few swipes of a finger. A
profile on at least one social networking website has
been established by more than three quarters of
today's Millennials. People typically spend about one
hour of their eight-hour workdays on various social
media websites. This may seem like a significant
portion of the workday, but for Millennials, who
spend an average of 1.8 hours a day on social media
sites, this proportion is even more significant. An
overwhelming majority of people who fall into the
high income and upper middle income brackets are
active on at least one social media platform. Yet, their
major purpose in using the various forms of social
media is rather different from one another in a
significant way. People use social media to keep up
with their favourite brands, chat with friends, gather
or share information, follow celebrities, and do a
variety of other things. Some of these activities
include sharing photos and videos, chatting, and
sharing photos and videos. Other activities include
following chats, following celebrities, and gathering
information.
The term "social media" refers to a group of
computer-based technologies that enable users to
communicate with one another, share information and
ideas, and create online communities. The concept of
social media is predicated on the usage of the internet
and the provision of users with simple means of
electronic communication for the exchange of
personal information and other content, such as
The Function of Social Media in the Lives of Today’s Young Adults
693

movies and photographs. People connect to social
media through laptops, personal computers, or
smartphones using web-based applications or
internet-based software systems, and their primary
purpose for doing so is to send and receive electronic
messages. Some examples of social media sites are
Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and Linkedin, in
addition to blogs and other websites that feature
content that is based on user engagement and user-
generated content.
Social media is generally considered as ‘Facebook’
or ‘Instagram’; social media exists online in several
forms. Obar et al. described social media as having
several key facets . Firstly, social media services are
(presently) Web 2.0 Internet-based applications. At
the core of the social media is the content created by
the users themselves. According to the report
published by Statista Research Department in June
2019, India accounted for close to 300 million
Facebook users in 2018, and with the entry of
WhatsApp, its reach extended to all the classes, with
18-25 year-olds used in the most daily. It was found
that the current generation is well aware about their
social statuses or reputes and they are actively
engaging in updating the content and the looks of
their profiles. Researchers reported that the “teens
expressed Facebook is an extension of their social
communication and an essential part of their social
life.” Duggan & Smith,( 2013) found that the youth ,
especially the teens measured their social standing
based on the number of “likes” on their posts and
pictures and did not shy from updating, deleting and
manipulating their posts and “selfies”. The act of
taking selfies and posting on their social media
accounts have become so popular that these days
majority of the smart phone have very high quality
front cameras for taking selfies. A google search in
December 2019 reported 209 best selfie camera apps
for smart phone, such is the craze of selfies.
Millennials tend to use many social networking sites
such as Twitter, instagram, snapchat, tik-tok, as a way
to escape the drama and pressure they feel on
Facebook. Smith & Zickuhr, (2012) in their study
found significant correlation in the increasing
narcissism and social media consumption in the youth
. According to (Przybylski and Weinstein, 2013,
Roberts and David, 2016), conclusive results have
found lower levels of perceived relationship quality,
partner trust, and perceived empathy in the presence
of mobile phones. In addition to this, media reports
have also commented on the intended and unintended
disconnection among people that occurs when people
using social media on smartphones (Barford, 2013,
Kelly, 2015, Mount, 2015) Narcissists crave the
attention and approval of others and seek out external
sources of admiration and attention to help maintain
their self-esteem (Campbell et al., 2002; Morf &
Rhodewalt, 2001).
Social networking sites, such as Facebook and
Twitter, are an easy route through which people
engage in the attention-seeking, self-important
behaviors, which is in same line as of narcissists. It is
important for narcissists to share their experiences
online because they believe all of their friends and
followers online are genuinely interested in knowing
what they are up to or what they are doing (Carpenter,
2012).
The Research has shown that those who use these
types of social networking sites tend to create their
online profiles in such a way that it portrays how they
want to be seen (Gabriel, 2014). In doing this, the
person tends to exaggerate certain character traits,
and present a persona that they believe is appealing to
the general public (Alloway, Runac, Qureshi &
Kemp, 2014). Because of the fact that every user has
full control over the information that is displayed on
their profile, various social media sites, such as
Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, make it easy for
users to present an unrealistic version of themselves.
Previous research indicates that narcissism may be
positively related to posting different types of self-
promoting content on social networking platforms
(Alloway, Runac, Qureshi & Kemp, 2014).
2 OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY
The research study aim to determine the use of social-
media platform in the millennial generation and
understanding, if social media is making this
generation more narcissistic. Different authors have
proposed different time periods of Millennial
generation, but in this research the people who were
born between 1980’s to 2000’s are taken as research
target group. The research study provides the answers
to important issues like, "Why do millennials use
social media, and how is it making them more
narcissistic, and how does it therefore influence both
their personal and professional life?" Use of various
social media platforms has been conceptually
unpacked and discussed at length in a variety of
scholarly publications. In addition to the qualitative
research studies that can be found in the literature,
this study also provides the readers with some
quantitative results. For the purpose of the study, a
questionnaire will be given to around 300 Indians
who are between the ages of 18 and 38. The study
uses basic traits of narcissism like (Authority,
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
694

Exhibitionism, Exploitativeness, Superiority,
Entitlement), already established by various other
researchers and questionnaire based on these traits
and relation between certain behaviour on social
media help us to answer some questions of this
research. In this research social media platforms
referred to are Facebook, Instagram, snapchat , twitter
and WhatsApp due to their popularity among the
people of the generation in question. The following
hypotheses were empirically examined.
Hypothesis 1: Narcissism is positively related to the
number of persons followed by the respondents on the
instagram.
Hypothesis 2: Narcissism is positively related to the
time spent on social media.
Hypothesis 3: Narcissism is positively related to the
frequency of updates on social media.
Hypothesis 4: Narcissism is positively related to the
age of the respondents.
2.1 Methods
The study involved a survey of 200 Indians between
the age of 18 years to 38 years and data was collected
on their psychographic profile, Narcissistic
Personality Inventory, NPI 16 was used to determine
the degree of narcissism in the respondents; they were
also asked about their perception and behavior on
social media and understand how it impacts their
social media consumption.
2.1.1 Measures Narcissism
The respondents were asked to complete the
Narcissistic Personality Inventor (NPI 16), which had
16 paired statements with each pair with one
narcissistic and the other non-narcissistic response.
The NPI-16 developed by Ames, Rose, & Anderson,
(2006) is a 16-item short-form of the original 40- item
NPI (Raskin & Hall, 1979). Ames et al.(2006), in
their research described the new NPI-16 as having
“notable face, internal, discriminant, and predictive
validity and that it can serve as an alternative and
shorter measure of narcissism”. Narcissistic scores
were obtained by adding up all the narcissistic
responses, higher scores indicating more narcissistic
personality. The Cronbach alpha was .758.
3 SOCIAL MEDIA USAGE
Social Media usage was assessed using six statements
like how many friends do you have on Facebook, how
many followers on Instagram and how many do you
follow on instagram, the number of hours spent on
social media daily and the frequency of updating
posts and selfies.Social Media Behavior:The
perception of the respondent’s rationale for using
social media behavior was assessed by eight items.
The Cronbach alpha of the scale was .796.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Of the 200 respondents surveyed, only 147 responses
were used for the analysis. Majority (n=88, 60%) of
the respondents were born between the year 1990-
2000, 20% were of the birth year cohort of 1980-
1990, followed by 9% in 1970-1980 cohort and 11%
in the 1960-1970 cohort. Sixty percent of the
respondents were male and the rest 40% were female,
and there was no correlation between the age and
gender of the respondents.
Test of Hypotheses
The sample used for the study was small and the
cross-cultural diversity was not taken into
consideration. The perception of the survey
respondents of their self reported reasons for using
social media was assessed using an eight item scale
with the Cronbach alpha .796. The results of the
correlation analysis indicated a significantly positive
relationship between narcissism and the perception of
the respondents that the social standing and
popularity of an individual was based on the likes s/he
gets on their social media; a positive relationship
between narcissism and the reason of posting selfies
and posts on social media as the expectation for the
likes; positive relationship between narcissism and
the feeling of depression if the individual doesn’t get
as much likes on social media updates as expected;
and also a significantly positive relationship between
narcissism and the use of social media or being
appreciated more by online peers.
The results from the study found that, Narcissism
had a significant, positive relationship with the
number of persons followed on the instagram and the
number of people the respondents followed on the
instagram, hence hypothesis 1: Narcissism is
positively related to the number of persons followed
by the respondents on the instagram, was supported.
However there was no correlation between narcissism
and the number of friends on Facebook. The reason
could be that with the new social media apps like the
instagram, twitter and snapchat etc, the respondents
were less active on the Facebook. Also statistical
The Function of Social Media in the Lives of Today’s Young Adults
695

analysis of the survey responses indicated that there
was a significant correlation between the average
number of hours spent on social media, hence
supporting hypothesis 2. The frequency of posting
selfie or status on social media and the NPI
narcissistic scores of the respondents were also found
to be positively correlated, thereby supporting
hypothesis 3. However there was no relationship
between the frequency of checking the social media
with the narcissistic score, which reinforces our
premise that individuals who are high on narcissism
are concerned more with their own posts on social
media rather than posts about others.
The hypothesis 4: Narcissism is positively related
to the age of the respondents, was tested using
ANOVA. The comparison between the mean scores
of the respondents on their narcissism NPI scores and
the age revealed that there is a significant difference
across the respondents regarding their narcissism.
Table 1: Correlations between Narcissism NPI and Social Media Usage.
Correlations
N
PI SCORE
Number of
Friends on
Facebook
Number of
followers on
Instagram
People you
follow on
instagram -
Numbe
r
Hours spent on
social media -
average
Frequency of
posting selfie
or status on
social media
Number of Friends on
Faceboo
k
.161 1
Number of followers on
Instagra
m
.226
**
.528
**
1
People you follow on
insta
g
ram - Numbe
r
.254
**
.522
**
.759
**
1
Hours spent on social media -
avera
g
e
.179
*
.266
**
.483
**
.482
**
1
Frequency of posting selfie or
status on social media
.180
*
.109 .130 .115 .155 1
frequency of checking online
p
rofile
.152 .139 .213
**
.231
**
.271
**
.301
**
**. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed).
*. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed).
Table 2: ANOVA of Narcissism and age of respondents of various age cohorts.
ANOVA
NPI SCORE
Sum of Squares df Mean Square F Sig.
Between Groups 218.078 3 72.693 4.106 .000
Within Groups 2514.202 142 17.706
Total 2732.281 145
Further analysis using the means plot indicates that
the cohort of respondents born between the years
1990-2000, also called as the millennial generation
has the highest scores on narcissism.The regression
analysis indicated that age along with the social
media usage behavior was able to explain 12.9%
variance in the narcissism of the respondents. The F
ratio is 10.631, p< .05, which shows the strength of
the model.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
696
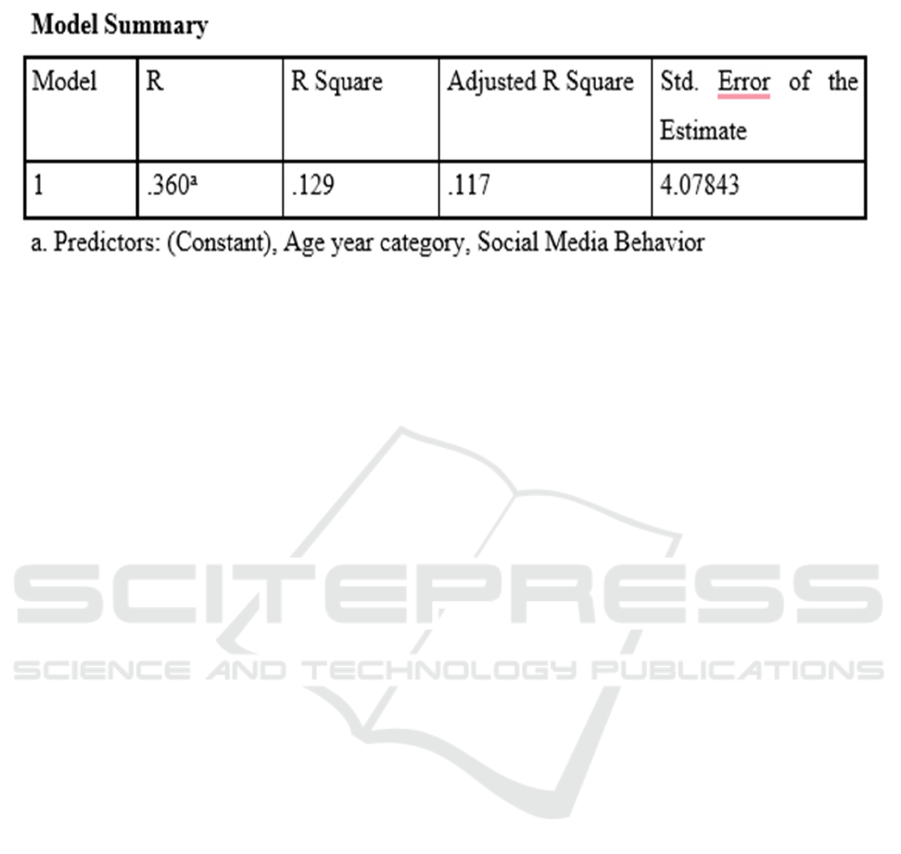
Table 3: Regression Summary of the Dependent and Independent variable.
5 CONCLUSION
The concurrent rise in the narcissism and the social
media usage and behavior implies that social media
has led to an increased narcissism in the social media
users, as it gives them an opportunity to promote and
self brand themselves by curating their own public-
image to gain approval and attention in the public
space. Narcissism and Narcissistic personality
disorder may be responsible for people’s obsession
with social media and an impediment in
organizational productiveness. However caution
should be taken as the results of the study cannot
generalizied , not all social media users are
narcissists.
REFERENCES
Alloway, T., Runac, R., Qureshi, M., & Kemp, G. (2014).
Is Facebook linked to selfishness? Investigating the
relationships among social media use, empathy, and
narcissism. Social Networking, 3(03), 150.
Al‐Saggaf, Y., & MacCulloch, R. (2018, December 13–16).
Phubbing: How Frequent? Who is Phubbed? In Which
Situation? And Using Which Apps? Proceedings of the
Thirty Ninth International Conference on Information
Systems (ICIS), San Francisco, 1–9. AISNET.
American Psychiatric Association. (1996). APA (1994).
Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders,
4.
Ames, D. R., Rose, P., & Anderson, C. P. (2006). The NPI-
16 as a short measure of narcissism. Journal of Research
in Personality, 40, 440-450.
Bachmann, A., Becker, A., Buerckner, D., Hilker, M.,
Kock, F., Lehmann, M., … Funk, B. (2011). Online
peer‐to‐peer lending‐a literature review.Journal of
Internet Banking and Commerce, 16(2), 1.
Blair, C. A., Helland, K., and Walton, W. (2017). Leaders
behaving badly: the relationship between narcissism
and unethical leadership behavior. Leadersh. Organ.
Dev. J. 38, 333–346. doi: 10.1108/LODJ-09-2015-0209
Blair, C. A., Hoffman, B. J., and Helland, K. (2008).
Narcissism and manager effectiveness: An empirical
examination of the dark side. Hum. Perform. 21, 254–
276. doi: 10.1080/08959280802137705
Campbell, W. K., Hoffman, B. J., Campbell, S. M., and
Marchisio, G. (2011). Narcissism in organizational
contexts. Hum. Resour. Manag. Rev. 21, 268–284.
Campbell, W. K., Rudich, E., & Sedikides, C. (2002).
Narcissism, self-esteem, and the positivity of selfviews:
Two portraits of self-love. Personality & Social
Psychology Bulletin, 28, 358–368.
Campbell, W.K., Hoffman, B.J., Campbell, S.M. and
Marchisio, G. (2010), “Narcissism in organizational
contexts”, Human Resource Management Review, Vol.
21 No. 4, pp. 268-284.
Carpenter, C. J. (2012). Narcissism on Facebook: Self-
promotional and antisocial behaviour. Personality and
Individual Differences, 52, 482–486.
Duggan, M., & Smith, A. (2013). Cell internet use 2013.
Washington, DC: PewResearchCenter.
Duggan, M., & Smith, A. (2013, December 30). Social
media update 2013. Retrieved November 20, 2019,
from Pew Research Internet Project website:
http://www.pewinternet.org/2013/12/30/ social-media-
update-2013/
Emmons, R. A. (1987). Narcissism: Theory and
measurement. Journal of Personality and Social
Psychology, 52(1), 11-17.
Fernando, J. (1998). The etiology of narcissistic personality
disorder. Psychoanalytical Study of the Child, 53, 141-
158.
Gabriel, M. T., Critelli, J. W., & Ee, J. S. (1994).
Narcissistic illusions in self-evaluations of intelligence
and attractiveness. Journal of Personality, 62, 143–155.
Judge, K. S., Menne, H. L., & Whitlatch, C. J. (2009). Stress
process model for individuals with dementia. The
Gerontologist, 50(3), 294-302.
Judge, T.A., LePine, J.A. and Rich, B.L. (2006), “Loving
yourself abundantly: relationship of the narcissistic
personality to self- and other perceptions of workplace,
deviance, leadership, and task and contextual
The Function of Social Media in the Lives of Today’s Young Adults
697

performance”, Journal of Applied Psychology, Vol. 91,
pp. 762-76.
Kets de Vries„ M. F. R., and Miller, D. (1985). Narcissism
and leadership: an object relations perspective. Hum.
Relat. 38, 583–601. doi: 10.1177/ 1872678503800600
Morf, C. C., & Rhodewalt, F. (2001). Unraveling the
paradoxes of narcissism: A dynamic self-regulatory
processing model. Psychological Inquiry, 12, 177–196.
Mount, M., Ilies, R., & Johnson, E. (2006). Relationship of
personality traits and counterproductive work
behaviors: The mediating the effects of job satisfaction.
Personnel Psychology, 59, 591–622.
Obar, J. A., & Wildman, S. S. (2015). Social media
definition and the governance challenge-an
introduction to the special issue. Obar, JA and
Wildman, S.(2015). Social media definition and the
governance challenge: An introduction to the special
issue. Telecommunications policy, 39(9), 745-750.
Ones, D. S., Dilchert, S., Viswesvaran, C., & Judge, T. A.
(2007). In support of personality assessment in
organizational settings. Personnel Psychology, 60,
995–1027.
Ott, Adrian (November 2010) How Social Media Has
Changed the Workplace (Study), Fast Company.
Panek, E., Nardis, Y., & Konrath, S. (2013). Mirror or
megaphone? How relationships between narcissism and
social networking site use differ on Facebook and
Twitter. Computers in Human Behavior, 29(5), 2004–
2012.
Przybylski, A. K., & Weinstein, N. (2013). Can you connect
with me now? How the presence of mobile
communication technology influences face-to-face
conversation quality. Journal of Social and Personal
Relationships, 30(3), 237-246.
Raskin, R., & Terry, H. (1988). A principal-components
analysis of the Narcissistic Personality Inventory and
further evidence of its construct validity. Journal of
Personality and Social Psychology,
Roberts, J. A., & David, M. E. (2016). My life has become
a major distraction from my cell phone: Partner phubbing
and relationship satisfaction among romantic partners.
Computers in human behavior, 54, 134-141.
Statista (2019), “Statista web site”Social media usage in
India - Statistics & Facts , published by Statista Research
Department (2019), retrieved from
https://www.statista.com/topics/5113/social-media-usage-
in-india/,(accessed 14 December 2019).
Twenge, J. M., & Foster, J. D. (2010). Birth cohort
increases in narcissistic personality traits among
American college students, 1982–2009. Social
Psychological and Personality Science, 1(1), 99-106.
Twenge, J. M., and Foster, J. D. (2010). Birth cohort
increases in narcissistic personality traits among
American college students, 1982-2009. Soc. Psychol.
Pers. Sci. 1, 99–106. doi: 10.1177/1948550609355719
Zickuhr, K., & Smith, A. (2012). Digital differences. 2012.
URL: http://www. pewinternet.
org/Reports/2012/Digital-differences. aspx [accessed
2019-09-13
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
698
