
Teaching Competency of Secondary School Teachers of Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh: A Comparative Study
Firdoos Ahmad Tantry and Tasleema Jan
Department of Education, University of Kashmir, Srinagar, India
Keywords: Teaching Competency, Stratified Sampling, Secondary School Teachers.
Abstract: The goal of the present research is to assess the teaching competency of secondary school teachers of Jammu
& Kashmir and Ladakh. This study is descriptive-survey in nature. 600 teachers were selected randomly from
different secondary schools in Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh by using a stratified random sampling technique.
Out of these 600 secondary school teachers, 300 from Jammu & Kashmir and 300 from Ladakh were selected.
The General teaching competency scale developed and standardised by B.K.Passi and Lalitha was used to
collect the data. Inferential statistics were used to examine the data. The data showed that 19.64% of Jammu
& Kashmir and 13.66% of Ladakhi secondary school teachers have high teaching competency. The data
further reveals that a good percentage of 64.33 secondary school teachers in Jammu & Kashmir and 61.66%
of Ladakhi secondary school teachers were found to have medium teaching competency. The data also shows
that 16% of secondary school teachers in Jammu & Kashmir and 24.66% of secondary school teachers in
Ladakh have a low level of teaching competency. The datafurther reveals that there is no significant difference
between Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakhi secondary school teacherson composite scores of Teaching
Competency.
1 INTRODUCTION
A competent teacher helps us overcome the
shortcomings of our educational system. Only an
effective teacher can ensure that students receive
high-quality learning. The provision of high-quality
learning is only achievable through the employment
of qualified educators. The accomplishments of
pupils are a testament to the excellent work of
teachers. "The educator can foster in children the
capability for investigation and enquiry, as well as the
ability to employ cutting-edge information and the
ability to exercise true integrity."(A. P. J. Abdul
Kalam, 2015).
There are two main interpretations of the term
"competence." The very first characteristic is the
capacity to finish the work. In the restricted definition
of the competency framework, the specific list of
responsibilities assigned to an instructor is separated
from the occupational activities of the educator.
However, according to the comprehensive view,
competency is expressed considering information,
capabilities, experiences, and dispositions that are
demonstrated in the setting of a specially picked set
of actual occupational duties, because of the
widespread use of technology, times change in each
sphere of life. As a result, the teaching and learning
processes have changed as well, and they must take
advantage of these advancements. According to the
United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural
Organization (2008), a professional educator must
know a lot about his or her subject and be able to use
technology in the classroom.
Teaching competency is defined by Haskew
(1956), Wilson (1973), and Biddle (1964) as the
ability of a teacher to operate in a way that result in
the intended outcomes of a method being used. As
defined by Rama (1979), teaching competency can be
defined as an instructor's ability to present her or
himself in the school through a succession of overt
teacher-led school activities. To put it another way,
this is a set of quantifiable acts taken by teachers
which promote the learning outcomes of pupils.
Consequently, for the sake of this research, "teaching
competency" where have been defined as "good
achievement of all quantifiable teacher tasks that
result in acceptable results for teacher trainees."
Many researchers, teachers, and organizations that
are now engaged in the development of standards for
Tantry, F. and Jan, T.
Teaching Competency of Secondary School Teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh: A Comparative Study.
DOI: 10.5220/0012503400003792
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR 2023), pages 773-778
ISBN: 978-989-758-687-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
773
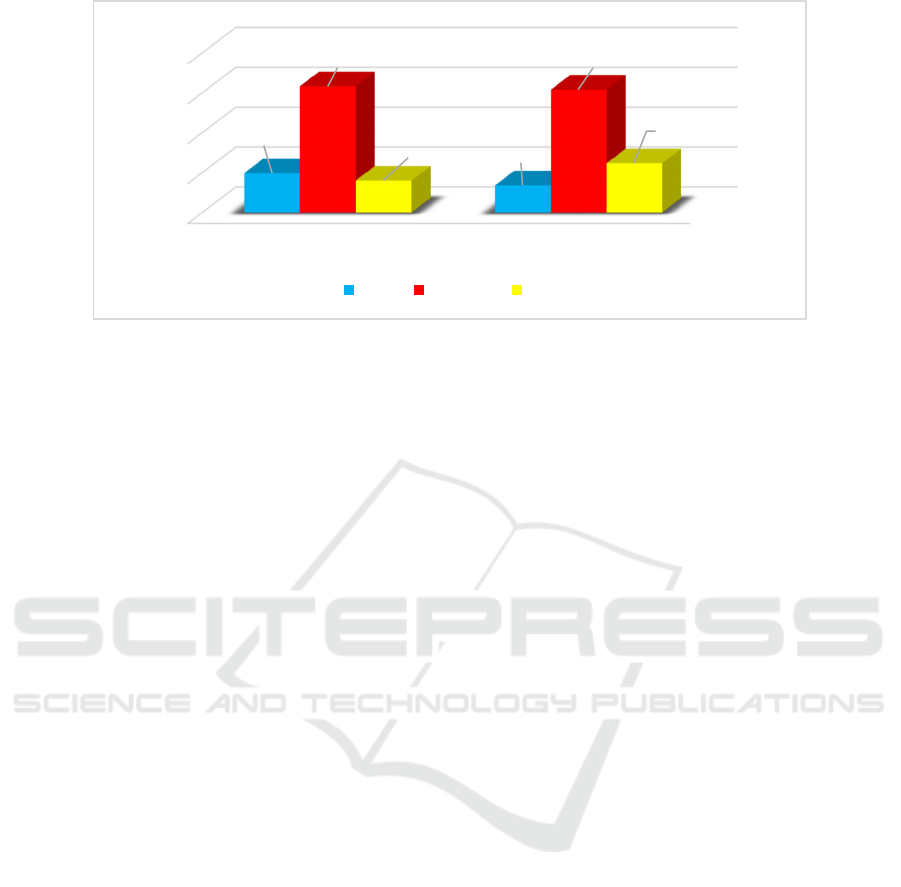
Figure 1: Showing the percentage distribution of Teaching competency of secondary school teachers of Jammu and Kashmir
and Ladakh.
the content and professional development of teachers
have attempted to explain the effectiveness of
teachers considering the aspect of "competency" that
is atplay. Because educational procedures are based
on relationships between people, this idea is
important in all fields of work, but especially in
research in education.
Competencies refer to the broad variety of
abilities and information that a teacher is supposed to
possess in addition to enhancing the benefits of
learning. It is necessary for teachers to have
competence in a broad range of abilities for them to
be effectively prepared for the tasks ahead of them.
These skills will help them solve important problems
that need to be solved in order to have a good
educational environment (Jackson, 1990).
2 DIMENSIONS OF TEACHING
COMPETENCY
There are various aspects of teaching competency,
but five of them are particularly important: These are
now the following:
2.1 Planning
This refers to the pre-instruction stage. It includes
choosing the goals, subject matter, and organization
of the subject matter, as well as audio and video
equipment that will be used.
2.2 Presentation
In this section, we will talk about how to introduce a
lesson, what questions you should ask, and how to
make sure your students are paying attention. We will
also talk about how fast you should present and how
you should reinforce what you are saying with both
verbal and non-verbal methods.
2.3 Closing
This pertains to the right way to end a lesson as well
as giving the students assigned tasks that are suitable
for them and pertinent to what they learned. All the
important parts of a teaching moment have been
grouped together. This includes current information
and understanding that were learned before, and what
will be learned in the long run.
2.4 Managerial
This relates to how the students come and go, how the
classroom is run, and so on. A teacher was able to see
that some of the students did not show up for class.
2.5 Evaluation
In the teaching-learning process, evaluation is one of
the most important things to keep an eye on. The main
goal of assessment is to help the kids and make them
more convenient if they are taught and learn about
skills and discrepancies in their learning are found.
Thus, the assessment process has played a big role in
the high attrition rates in schools. It can be seen that
these aspects, as well as components, have a big
impact on how well teachers can explain (Sarmah,
2016).
The primary goal of teachers is to ensure that
pupils learn successfully and quickly. In order to
accomplish this, a teacher must perform several tasks,
including properly planning lessons, delivering
0
20
40
60
80
J & K Ladakh
19.66 %
13.66 %
64.33%
61.66%
16.00 %
24.66 %
High Medium Low
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
774

effective teaching, and assessing students' progress
using acceptable methods and procedures. This
means the teacher must engage in a variety of tasks
both within and outside the classroom setting. The
effectiveness (or ineffectiveness) of teaching is very
closely linked to the abilities of the people who teach
(Soundari, 2018).
3 SOME RELATED STUDIES
Ratheeswari (2020) concludethat the medium of
instruction, gender, teaching subject, type of
institution, area of school, and teaching experience of
high school teachers shows an average level of
teaching competency, and no significant difference
was found among sub samples like area of school,
gender, medium of instruction, kind of school,
teaching experience, and teaching subject of high
school teachers in terms of teaching competency.
Bhullar (2019) found that private and government
secondary school teachers differ significantly on self-
efficacy and teaching competency. Sahay
(2019)concluded that male and female secondary
school teachers not differ significantly on teaching
competence but differ significantly on multiple
intelligence, private and public secondary school
teachers not differ significantly on multiple
intelligence, but private and public secondary school
teachers differ significantly on teaching competency
and self-esteem, also significant positive relationship
was found between multiple-intelligence and teacher
competency, multiple intelligence and self-esteem,
and teacher competency and self-esteem of secondary
school teachers.Mishra (2017) found that significant
differenceamong teachers on teaching competencies
based on teaching experience and gender, but no
significant difference was found between teachers
teaching science and non-science courses. Kaur
(2017). showed that rural and urban high school
teachers differ significantly on teacher efficacy and
teaching competency. Das &Nalinilatha
(2017)concluded that teachers with a high level of
socio-economic status had higher levels of teaching
competency than teachers with a moderate level of
socio-economic status. The data also revealed that
teachers working in private schools that did not
receive any outside assistance had higher levels of
teaching competency than those teachers working in
public schools. It was also shown that male and
female secondary school teachers not differ
significantly on teaching competency.
4 RATIONAL AND OBJECTIVES
OF THE STUDY
The most important aspect of the educational process
is teaching. Teaching competence relates to the
cognitive expertise of teachers that must have an
impact on children's achievement in order to be
effective. The words "competency-based teaching" as
well as "learning" can also be used to refer to this type
of teaching. An approach in teaching and learning
which tries to prepare pupils for specialized class
competencies is referred to here as the "teaching
capabilities paradigm" in relation to teaching
abilities. It entails the application of instructional
approaches like the process of communication,
research, microteaching, simulations, and so on.
Kumari and Srivastava (2005) say that a great teacher
shows that he or she can teach well, know a lot of
information, and be able to interact with his or her
students through his or her actions (Jakson, 1990).
The primary goal of teachers is to ensure that pupils
learn successfully and quickly. In order to accomplish
this, a teacher must perform several tasks, including
properly planning lessons, delivering effective
teaching, and assessing students' progress using
acceptable methods and procedures. This means the
teacher must engage in a variety of tasks both within
and outside the classroom setting. The effectiveness
(or ineffectiveness) of teaching is very closely linked
to the abilities of the people who teach (Soundari,
2018). A comprehensive understanding of the
material is required for teaching competencies. The
techniques, a comprehension of student psychology,
and the process of learning are the primary
components that make up a teacher's competency. It
is claimed that the ability to adapt theory to practical
settings is one of the most important aspects of
teaching proficiency. The ever-increasing complexity
of our educational system has resulted in the
emergence of new dimensions, and as a direct
consequence, the function of the educator has
undergone significant expansion and taken on a new
significance. The cutthroat rivalry that exists in every
aspect of modern life necessitates highly qualified
educators who can equip pupils with the tools
necessary to meet the ever-evolving demands of a
globalized world. Competency in teaching is a
function of a few different variables, including
gender, teaching subject, teaching experience, kind of
school, location of school, whether the school is run
by the government or privately, qualification, and so
on. The influence of these factors on the teaching
competence of secondary school teachers has been
analyzed using the tool GTCS's five teaching skills to
Teaching Competency of Secondary School Teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh: A Comparative Study
775
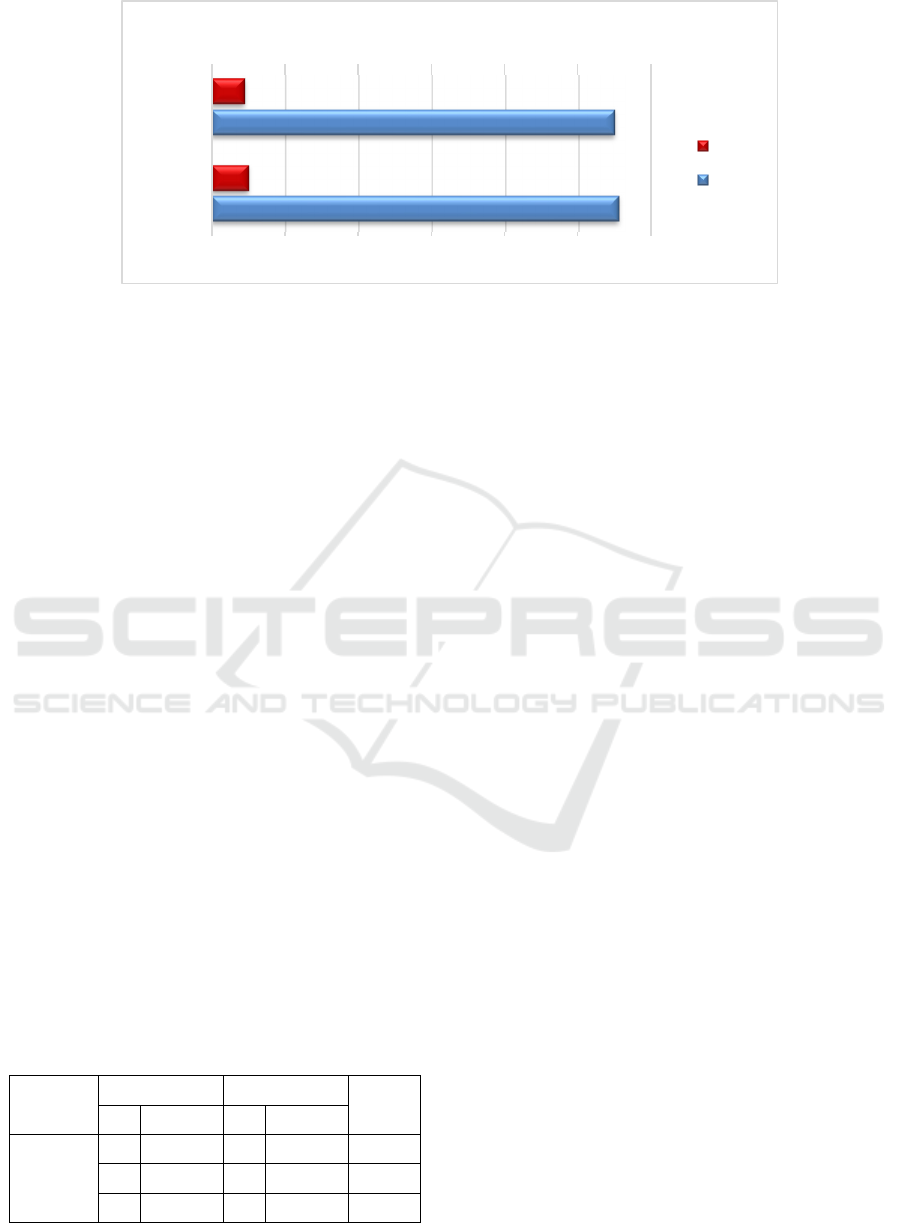
Figure 2: Showing the mean comparison among secondary school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh on
composite scores of Teaching Competency.
make this determination planning, presentation,
closing, evaluation, and managerial skills (Shivani,
2019). Hence, the current study aims to assess the
teaching competency of secondary school teachers of
Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh based upon the
fallowing objectives:
1. To studythe teachingcompetency of
secondary school teachers of Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh.
2. To compare the teaching competency of
secondary school teachers of Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh (factor wise and on
composite scores).
5 HYPOTHESES
The following hypothesis were formulated for this
research:
H
1
. Secondary school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir
and Ladakh differ significantly on Teaching
Competency (factor wise).
H
2.
Secondary school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir
and Ladakh differ significantly on Teaching
competency (composite scores).
Table 1. Showing the percentage distribution of Teaching
competency of secondary school teachers of J&K and
Ladakh.
Construct
J&K Ladakh
Category
N Percentage N Percentage
Teaching
competency
59 19.66 41 13.66 High
193 64.33 185 61.66 Medium
48 16.00 74 24.66 Low
6 METHODOLOGICAL
FRAMEWORK
The present research study was conducted by using
descriptive method of research. The study was
conducted to assess the teaching competency of
secondary school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and
Ladakh. In this study, the secondary school teachers
of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh consists the sample
for the present investigation. The sample of 600
secondary school teachers was selected randomly
from different secondary schools of Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh by using stratified random
sampling technique.
The General Teaching Competency Scale
developed by Passi and Lalitha was used by the
researcher to collect the data. The data was collected
through the personal visit of these schools with the
help of above- mentioned scale. The data was put into
a table as per the manual of the scale. The investigator
used percentage statistics, mean, S.D. and t-test to
analysis the data and draw the inferences.
The above table 1 shows the level of teaching
competency of secondary school teachers 0f Jammu
&Kashmir and Ladakh. The statistical data reveals
that 19.66% of Jammu &Kashmir and 13.66% of
Ladakhi secondary school teachers have high
teaching competency. The data further reveals that a
good percentage of 64.33 secondary school teachers
in Jammu &Kashmir and 61.66% Ladakhi secondary
school teachers were found to have medium teaching
competency. The data also shows that 16% of
secondary school teachers in Jammu &Kashmir and
24.66% of secondary school teachers in Ladakh have
low level of teaching competency. The above table 2
shows the mean compression among secondary
school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh on
111.02
109.89
10.09
9.02
0 20406080100120
J & K
Ladakh
Composite Scores of T.C. Between J & K and Ladakh
S.D.
Mean
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
776
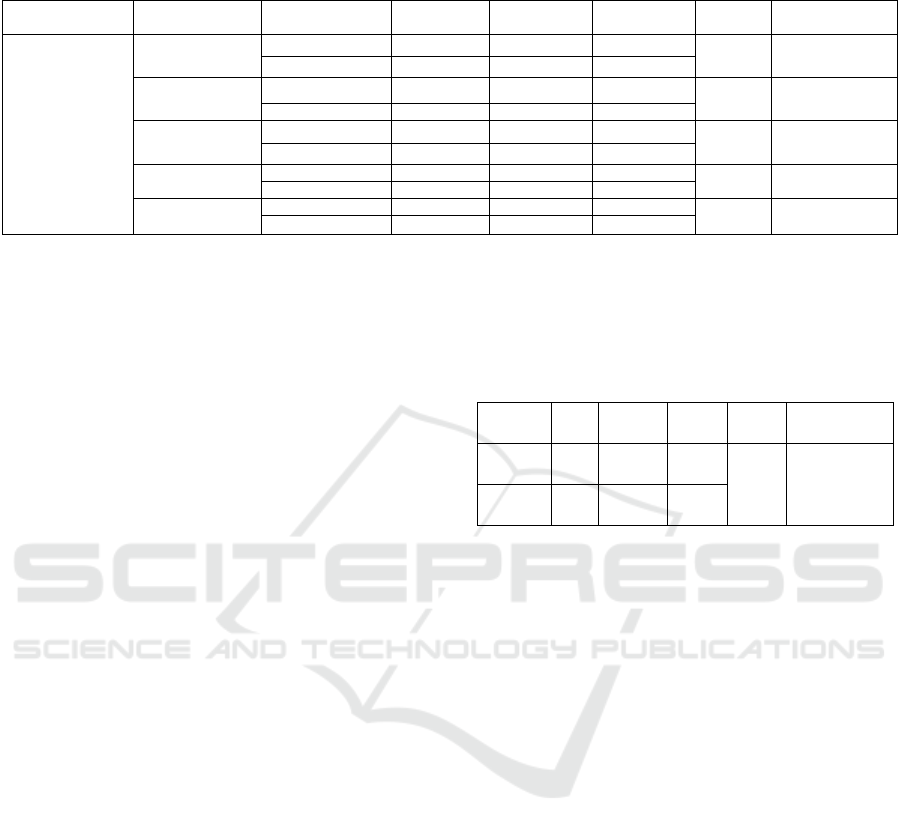
Table 2. Showing the mean comparison among secondary school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh on factor wise
of Teaching Competency.
Variable Factors Groups N Mean S.D. t-value Level of
si
g
nificance
Teaching
Competency
Planning
J & K 300 21.32 4.31
2.18
Significant at 0.05
level.
Ladakh 300 20.60 4.08
Presentation
J & K 300 61.08 8.94
1.91
Not significant
Ladakh 300 59.80 7.88
Closing
J & K 300 9.21 1.89
1.78
Not significant
Ladakh 300 8.96 1.74
Evaluation
J &
K
300 10.20 2.31
2.14
Significant at 0.05
level.
Ladakh 300 9.90 1.94
Managerial
J &
K
300 10.10 1.21
2.22
Significant at 0.05
level.
Ladakh 300 9.90 1.26
factors wise of teaching competency. The data revels
that there is a significant mean difference between
Jammu& Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that
both the groups differ significantly on Planning
factor of teaching at 0.05 level of significance.
Though the mean difference favours the secondary
school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir, which means
that theses teachers have better planning of teaching
as compared to secondaryschool teachers of Ladakh.
On the Presentation factor of teaching competency,
the statistical data shows that there is no significant
mean difference between Jammu & Kashmir and
Ladakh, which confirms that both the groups have
almost similar presentation skills of teaching. Though
the mean difference favours the Jammu & Kashmir
secondary school teachers, but the difference failed to
arrive at any level of confidence. On the Closing
factor the statistical data shows that there is no
significant mean difference between Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that, both the
groups have closing skills of teaching. Though the
mean difference favours the Jammu & Kashmir
secondary school teachers, but the difference failed to
arrive at any level of confidence. On the Evaluation
factor the statistical data shows that there is a
significant mean difference between Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that both the
groups differ significantly on evaluation skills of
teaching at 0.05 level of significance. Though the
mean difference favours the Jammu & Kashmir
secondary school teachers, which means that these
teachers are better on evaluation skills of teaching as
compared to the secondary school teachers of Ladakh.
On the Managerial factor the data reveals that there
is a significant mean difference between Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that both the
groups differ significantly on management related
activities of teaching at 0.05 level of significance.
Though the mean difference favours the secondary
school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir, which means
that these teachers have better management related
activities of teaching as compared to secondary school
teachers of Ladakh.
Table 3. Showing the mean comparison among secondary
school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh on
composite scores of Teaching Competency.
Group N Mean S.D.
t-
value
Level of
significance
J&K 300 111.02 10.09
1.88 Not significant
Ladakh 300 109.89 9.02
The above table 3 shows the mean difference between
secondary school teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and
Ladakh on composite scores of teaching competency.
The statistical data reveals that there is no insignificant
mean difference between Jammu & Kashmir and
Ladakhi secondary school teachers, which implies that
both the groups are equally similar on composite
scores of teaching competency.
7 CONCLUSION
On the basis of the statistical data, the following
conclusion have been drawn from the present
investigation:
In this study, table 1 shows the result that 19.66% of
Jammu &Kashmir and 13.66% of Ladakhi secondary
school teachers have high teaching competency. The
data further reveals that a good percentage of 64.33
secondary school teachers in Jammu &Kashmir and
61.66% Ladakhi secondary school teachers were
found to have medium teaching competency. The data
also shows that 16% of secondary school teachers in
Jammu &Kashmir and 24.66% of secondary school
teachers in Ladakh have low level of teaching
competency.
The table 2 factor 1shows the results that there is a
significant difference between Jammu & Kashmir and
Teaching Competency of Secondary School Teachers of Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh: A Comparative Study
777

Ladakh, which confirms that both the groups differ
significantly on planning of teaching at 0.05 level of
significance. On the second factor of teaching
competency the result showed that there is no
significant mean difference between Jammu &
Kashmir, which confirms that both the groups have
almost same presentation skills of teaching. On the
third factor of teaching competency the result showed
that there is no significant mean difference between
Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that
both the groups havebatter closing skills of teaching.
On the fourth factor the result showed that there is a
significant mean difference between Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that both the
groups differ significantly on Evaluation skills of
teaching at 0.05 level of significance. On the fifth
factor the result showed that there is a significant mean
difference between Jammu & Kashmir and Ladakh,
which confirms that both the groups differ
significantly on management related skills of teaching
at 0.05 level of significance
The table 3 showed the result that there is no
significant mean difference between Jammu &
Kashmir and Ladakh, which confirms that both the
groups are equally similar on composite scores of
teaching competency.
7.1 Educational Implications
1. This study provides practical facts to plan,
construct, and improve teaching practices
through practice teaching and internship.
2. The results will help teachers comprehend
the dynamic nature of teaching and how to
be flexible in the classroom.
3. This research will help to identify
competency-based course outcomes and
learner-specific outcomes.
4. The study is helpful to train the teachers
according to the new parading of teacher
education for developing learner centric
competencies.
5. It will aid in the inculcation of the desired
competences in teachers, enabling them to
become competent educators, and give
administrators and faculty of school
education with instructions for enhancing
the teaching effectiveness.
REFERENCES
Kalam, B. R. D. A. A. (2015). Health for all The Mission
of the People’s resident. Indian Journal of Community
& Family Medicine, 1(02).
Jackson, J. (1990). En route to adulthood: A high school
transition program for adolescents with disabilities.
Occupational Therapy in Health Care, 6(4), 33-51.
Sarmah, N. (2016). Teaching competency and teachers’
attitude towards teaching a study on the test qualified
teachers in Sonitpur District of Assam, (Ph.D. thesis,
University of
Gaughati).http://hdl.handle.net/10603/179259.
Soundari, M. (2018) Teaching competency of postgraduate
teachers in relation to organizational climate and
attitude towards teaching,(Ph.D. thesis, Tamil Nadu
Teacher Education university, Chennai 600-097).
http://hdl.handle.net/10603/346837.
Ratheeswari, K. (2020). ICT: A boon to teacher education.
journal of natural remedies, 21(3), 157-159.
Bhullar, K. (2019). Teaching competency of secondary
school teachers in relation to their self-efficacy. IOSR J
Humanities and Soc Sci, 24, 58-62.
Sahay, M. (2019). Relationship between multiple
intelligence, self-esteem, and teacher competency
among secondary school teachers. People:
International Journal of Social Sciences, 5(1), 460-475.
Mishra, S. (2017). Teaching Competencies among
Secondary School Teachers of Sikkim. Pedagogy of
Learning, 3(1), 17-26.
Kaur. P. (2017).
Study 0 f teacher Efficacy o f S e c o n d a r y S c hool
Teachers in Relation to Their Teaching Competency,
International educational & Research Journal, 3 (4).
Das, S., andNalinilatha, M. (2017). A Study on Teaching
Competency of Secondary School Teachers.
International Journal of Research-
GRANTHAALAYAH, 5(6), 508-513.
Shivani, N., R., (2019). Teaching Competency of
Secondary School Teachers in relation to selected
variables, Journal of research in education1(7), 2347-
56762
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
778
