
An Efficient Secured AODV Routing Protocol to Mitigate Flooding
and Black Hole Attack in VANETs for Improved Infotainment
Services
Shaik Shafi, M. Anusha and Chandan
Electronics and Communication Engineering, B V Raju Institute of Technology, Narsapur, Medak, Telangana, India
Keywords: AODV, Black Hole, VANET.
Abstract: The latest developments in wireless communication encourages the researchers to focus more in the expansion
of Vehicular Ad hoc Networks (VANETs), offers the required infotainment facilities. Nevertheless, because
of decentralized architecture, design of secure transmission is still a challenging problem in VANETs. Due
to security issues, there may be loss of communication between high speed vehicles. Thus, it is obligatory to
find and prevent such security issues. Thus, in this paper, Secure AODV Routing Protocol (S-AODV) to
mitigate Flooding and Black Hole Attacks in VANET is proposed. In this, primarily, the cooperative
intermediate vehicles are chosen based on Congestion and Residual Energy values at each vehicle to avoid
unnecessary transmission (Flooding) of huge number of routing packets to non-existent destinations. Thus
reduces routing overhead and routing cost. Secondly, the optimal secure path to the destination is identified
through trust estimation among the selected relay vehicles in the network. Here, the trust value is estimated
using distinct metrics like Hop Count and Network Lifetime. Then, the vehicles with utmost trust value are
preferred to reduce packet drop rate (Black Hole attack). Thus improves packet delivery ration and throughput
of the network. The performance of the proposed S-AODV is carried out using NS (Network Simulator)-2
and compared over existing routing schemes under attack. Simulation results showed that the proposed S-
AODV outperforms over existing AODV based routing schemes for different network parameters like, delay,
energy factor, reliability and packet delivery ratio. Therefore, the infotainment services like emergency and
multimedia message transmission is improved in VANE.
1 INTRODUCTION
VANET is an infrastructure less self-configuring ad-
hoc network, consists of mobile nodes and connects
wirelessly (Yo and Kim, 2011). Thus, maintaining the
reliability in VANETs is a challenging task as the
vehicles would reduce the network lifetime and leads
to link failures due frequent topology changes. In
addition to frequent link failures, security in VANETs
is another major issue to be addressed due to its
wireless channel vulnerability to many security
threats (Singh and Nand, 2016). Towards this, there
exists attacks in the network layer for two main
reasons: One is not transmitting the data packets and
the second is to change parameters of the control
messages. A simple attack that blocks sending the
data packets. Due to this, any malicious intruder may
act as routing agent and interrupt the entire network
operation. Thus, identifying this kind of malicious
nodes is very challenging within the network over any
other attacker from outside. Towards this researchers
have proposed several secure routing approaches
along with futuristic research challenges in high
speed mobile networks.
VANET routing schemes are categorized into
three types, namely reactive routing, proactive
routing and hybrid routing (Murthy and Manoj,
2004). Among these, authors have proposed that the
reactive routing scheme known as Ad-hoc On-
demand Distance Vector (AODV), an efficient
protocol for high density VANET (Shafi and D V
Ratnam, 2018).
However, in the process of selecting relay
vehicles, the AODV protocol may be susceptible to
some routing attacks, this is due to the presence of
single or multiple untrusted nodes in the network.
Thus, Black Hole attack, a kind of Denial of Service
(DoS) attack occurs frequently when attacker acquire
and re-program the mobile vehicles to block packets
Shafi, S., Anusha, M. and Chandan, .
An Efficient Secured AODV Routing Protocol to Mitigate Flooding and Black Hole Attack in VANETs for Improved Infotainment Services.
DOI: 10.5220/0012517000003739
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of Things: Accelerating Innovation in Industry and Consumer Electronics (AI4IoT 2023), pages 447-453
ISBN: 978-989-758-661-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
447

instead of sending to destination. Therefore, the
information does not reach the destination which
generates longer delay in delivering packets and
completely reduces the network throughput. In
addition, unnecessary transmission of routing packets
takes place during selection of relay vehicles towards
destination. The unnecessary transmission leads to
flooding attacks in the network (Shafi et.al, 2023).
Thus, in this paper, Secure AODV Routing
Protocol (S-AODV) is presented. Here, the concept
of trust estimation is added to the existing AODV
protocol to detect attacks in Vehicular ad-hoc
networks. In comparison with traditional AODV, the
proposed S-AODV includes multi-layer structure to
extract the various routing parameters from different
layers. Therefore, proposed S-AODV scheme
exhibits more effective in addressing the intrusion
detection issue.
The remaining portion of the paper comprises of
several sections. Section 2 illustrates the existing
works. Section 3 demonstrates the proposed S-
AODV protocol. Then, the performance study of the
S-AODV is examined in section 4. Section 5
concludes the paper.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In this section, the existing routing protocols to
defend flooding and black hole attacks in ad-hoc
network are explained. Towards this, authors have
proposed a novel routing protocol. A new field named
as suspicious value is added to the relay nodes routing
table. Then, based on threshold value the malicious
nodes are identified (Su, M. Y. (2011). A trust based
malicious node detection scheme in highly dynamic
networks is presented by defending both the Black-
hole and grey-hole attacks. The trusted nodes ensures
the security in the network (Sargunavathi and Martin
Leo Manickam, 2019).
Authors have proposed an efficient AODV
routing scheme to advance the security in the network
by detecting packet drop ratio at each relay node to
increase the efficacy of the network (Li, J. S., and
Lee, C. T. (2006)).
On the other side, another on demand based
routing protocol was designed to address power
consumption and overhead issues in the network
(Daoud and Rafla, 2019). A new intrusion detection
scheme was developed to interchange data between
the nodes in high mobility networks. Further,
multiclass SVM techniques were included to
minimize the overhead in the network (Arthur, 2018).
On the other side, authors have presented a new
version of AODV to defend various attacks in highly
dynamic ad-hoc network using statistical approach
(Rmayti, Begriche, Khatoun and Gaiti, D 2015).
Similarly, cryptographic based source and destination
nodes detection algorithm is presented to improve the
security in VANETs (Kumar, A., Varadarajan, V.,
Kumar, A., Dadheech, P., Choudhary, S. S., Kumar,
V. A & Veluvolu, K. C., 2021). An efficient
algorithm is presented to defend Black hole attacks in
VANETs based on dynamic threshold value (Malik,
A., Khan, M. Z., Faisal, M., Khan, F., & Seo, J. T,
2022).
Nonetheless, the prevailing on demand intruder
detection approaches designed using one or two
routing the parameters like radio hop count and
direction. To this end, A Secure AODV Routing
Protocol (S-AODV) is proposed. The detained
working of the protocol is exemplified in the next
section.
3 PROPOSED WORK
In this section, secured routing protocol by making
use of traditional AODV to defend both flooding and
black hole attacks in VANETs is explained. In this,
primarily, the cooperative intermediate vehicles
(CRVs) are chosen based on Congestion and Residual
Energy values at each vehicle to avoid unnecessary
transmission (Flooding) of control packets to non-
existent destinations. Thus reduces routing overhead
and routing cost.
Secondly, the optimal secure path to the
destination is identified through trust estimation
among the selected relay vehicles in the network.
Here, the trust value is estimated using distinct
metrics like Hop Count and Network Lifetime. Then,
the vehicles with utmost trust value are preferred to
reduce packet drop rate (Black Hole attack). Thus
improves packet delivery ration and throughput of the
network.
3.1 Selection of CRVs
In the proposed S-AODV, the individual node in the
network hold the 1 hop information of 1-hop
neighbors using HELLO packets, same as traditional
AODV. In addition, in the proposed S-AODV each
node maintain congestion and residual energy
information in the routing table. All the three
parameters like, Hop-count (H), Congestion (C) and
Residual Energy (RE) are obtained using the
following equations given below.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
448
H = Node Count - 1
(1)
C = αt
(2)
RE = Initial Energy – Final Energy
(3)
From equation (2), the congestion at a vehicle is
obtained by measuring the total number of packets
striking at a rate of ‘α’ over a period t. From equation
(3), residual energy is the energy at a node before and
after simulation. Thus, source vehicle choses the 1
hop neighbouring vehicle with less congestion and
higher residual energy values as relay forwarder.
Therefore, the unnecessary transmission (flooding) of
routing packets can be minimized in the network for
route establishment, in turn reduces flooding attacks.
4 OPTIMAL PATH SELECTION
In the proposed S-AODV, the optimal or finest path
from the several available routes between source to
destination is identified using Trust Value obtained at
each CRV. It is mathematically given by equation (4).
Trust Value = H+NLT
(4)
It is recommended to have less hop-count and
high Network Life Time (NLT), The NLT at each
node is defined as the ratio of Residual Energy at a
node to that of the Energy Consumption Rate at the
same node for any instance of time T. Then, the
obtained Trust Values are stored in the routing tables
of each node in the path selected towards destination.
The routing table is updated on reception of Route
Request packet. The trust value lies in between 0 to 1.
The value 0 shows an untrustworthy vehicle and 1
depicts a trusted forwarder. Therefore, the CRVs with
≤0.5 will be discarded. The latest trust value of a
particular CRV is exchanged with all other vehicles
in the network.
Introduction to the Trust Value:
Importance of Trust estimation
Based on the existing schemes, the vehicles in the
network transmits data to each other without any
centralized administration. Therefore, all the vehicles
behaves as a route and shares network information.
Nonetheless, trusting all the vehicles without
estimating the behaviour may introduce wide variety
of vulnerabilities among fast moving vehicles. Here,
we exemplify the process of selecting suitable route
based on a trust evaluation. In the proposed S-AODV,
the desired route is estimated by incorporating a new
field known as ‘Trust Value’ to S-AODV RREQ
packet. Thus avoids packet transmission through
untrusted vehicles. The S-AODV RREQ packet
consists of the following new fields like:
1. Congestion
2. Residual Energy
3. Initial Energy
4. Final Energy
Algorithm 1: Selection of relay vehicle.
Step1: Initialize the network.
Step2: Procedure-Select the relay vehicle
Step3: Calculate congestion at each vehicle using (2)
Step4: Calculate RE at each vehicle using (3)
Step5: Repeat the step 3 & 4 at each vehicle
Step6: Compare the values of congestion and RE with
threshold values
Step7: Discard the vehicle which violates the
threshold.
Step8: Update the routing table at each vehicle
5 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
In this section, the proposed S-AODV protocol is
analysed using Network Simulator (NS)-2.34. The
simulation is conducted for 200 vehicles through over
1000m X 1000m area. The range of each node is set to
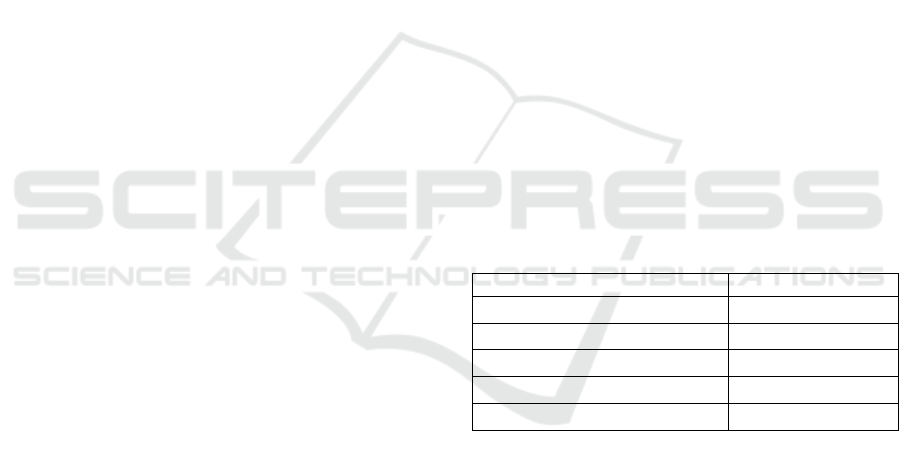
250m. Table 1 exemplifies the remaining parameters.
Table 1: Network Simulation Parameters.
Parameter
Value
Node densities
0-200
Max Speed
0-100 Kmph
Simulation Time
900sec
MAC Protocol
802.11p
Packet size
512 (bytes)
The performance evaluation of S-AODV over
existing schemes is obtained by considering the
performance metrics like Reliability, Energy Factor,
End to End delay and packet Delivery Ration under
two different scenarios such as, different vehicle
densities and change in vehicle velocities.
Figure 1, shows the variation of reliability over
different vehicle densities in the network for the
proposed S-AODV and existing protocols. The
reliability of S-AODV is superior due to selection of
CRVs through congestion metric and optimal path
selection using trust estimation. Finally, the reliability
in S-AODV is 82%, 83% higher over existing
mechanisms. Figure 2, explains the variation in
energy factor for number of vehicles and is high in
proposed S--AODV over En-AODV and AODV.
An Efficient Secured AODV Routing Protocol to Mitigate Flooding and Black Hole Attack in VANETs for Improved Infotainment Services
449
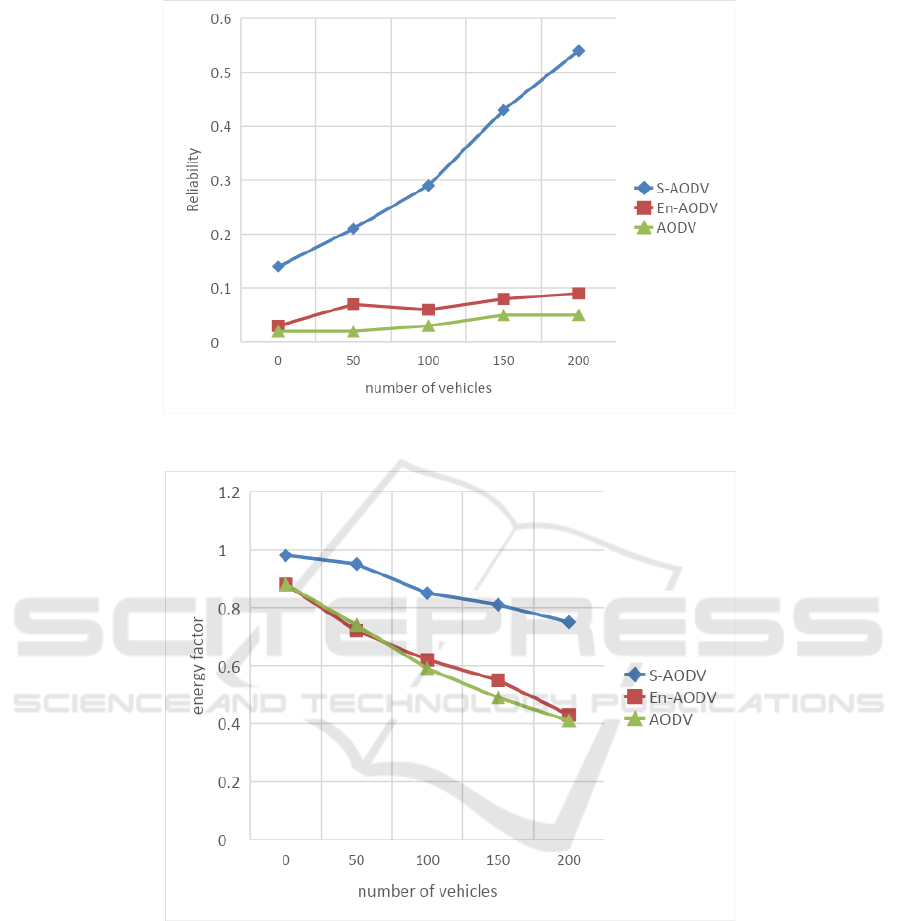
Figure 1: Variation in reliability for number of vehicles.
Figure 2: Variation in energy factor for number of vehicles.
This is due to selection of CRVs through congestion
metric and optimal path selection using trust
estimation. Therefore, S-AODV has 55%, 56%
higher energy factor over existing schemes.
Figure 3, explains the disparity in delay for
number of vehicles and is less in S-AODV over En-
AODV and AODV. Delay parameter is decreased in
S-AODV by 33% over En-AODV.
Figure 4, explains the enhanced packet delivery
ratio in S-AODV over En-AODV, AODV. This is
due to selection of CRVs through congestion metric
and optimal path selection using trust estimation. It is
further observed that the PDR in S-AODV is
enhanced to 30%, 33% with respect to existing
schemes.
Figure 5, shows the improvement in energy factor
for change in velocity. It can be observed the energy
factor is more in S-AODV over En-AODV and
AODV. This is due to selection of relays through
congestion metric and optimal path selection using
trust estimation.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
450
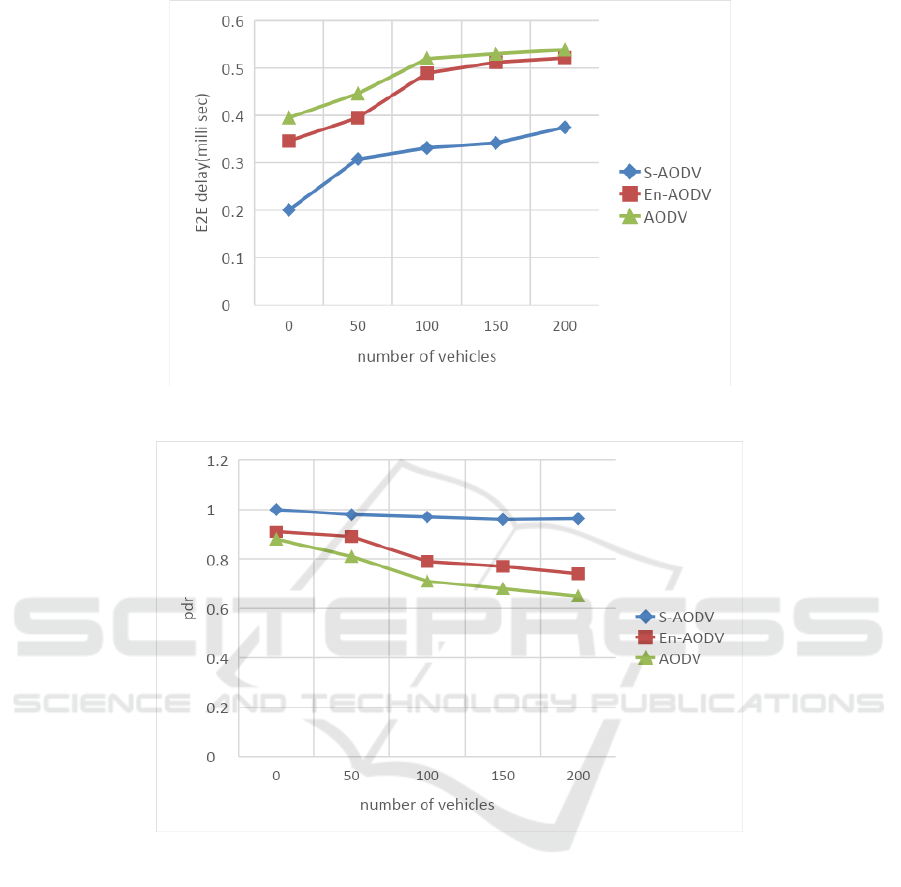
Figure 3: Variation in delay for number of vehicles.
Figure 4: Variation in PDR for number of vehicles.
Similarly, figure 6 illustrates that the variation in
reliability for change in velocity and it is observed
enhanced reliability in S-AODV. Further, it is
observed that the reliability in case of S-AODV is
improved to 50% and 53% over existing schemes.
Figure 7 explains the variation in delay metric for
change in vehicle velocity under three protocols.
The delay parameter is less in case of S-AODV.
Similarly, figure 8 shows the variation in PDR for S-
AODV over En-AODV and AODV. Nonetheless, S-
AODV shows enhanced PDR. Overall, the PDR is
enhanced to 11%, 10% in S-AODV over existing
algorithm.
An Efficient Secured AODV Routing Protocol to Mitigate Flooding and Black Hole Attack in VANETs for Improved Infotainment Services
451
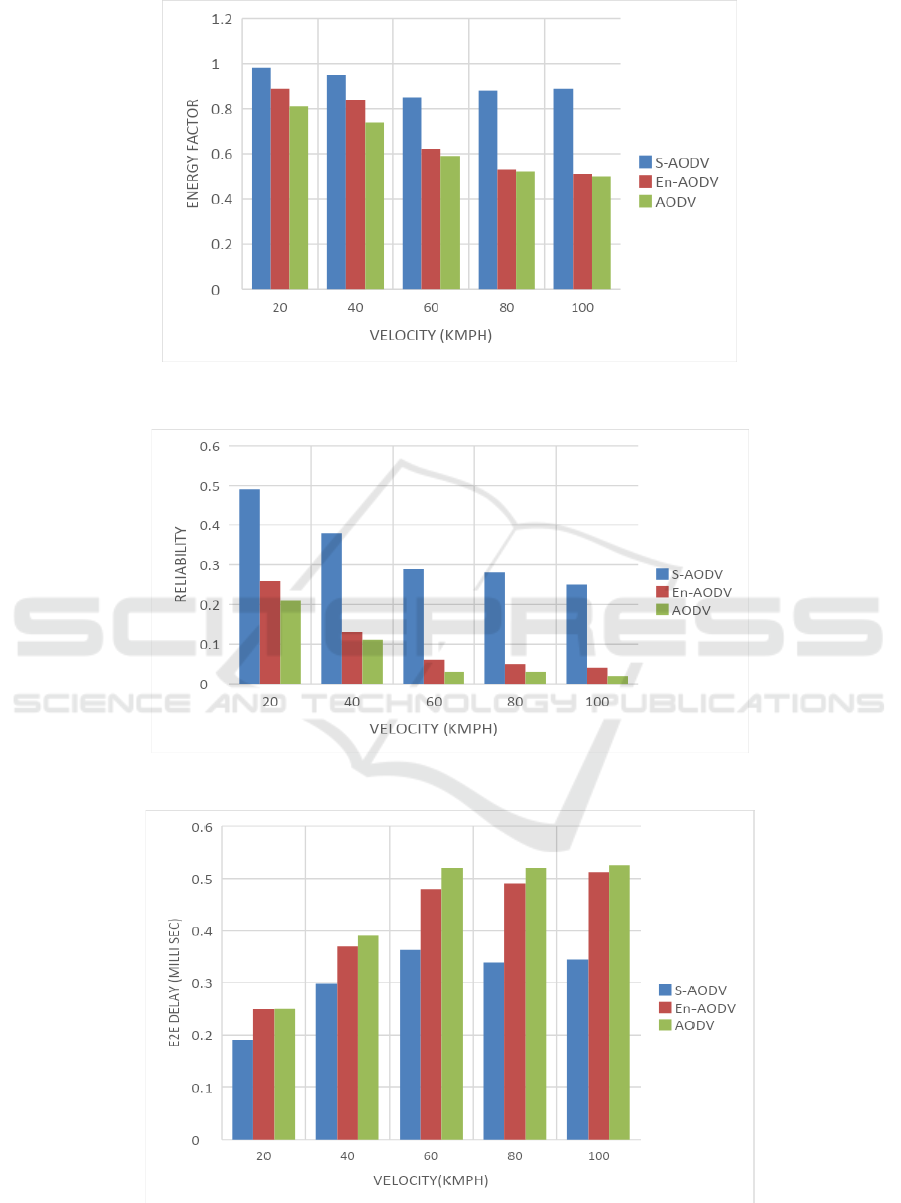
Figure 5: Variation in energy factor for change in velocity.
Figure 6: Variation in reliability for change in vehicle velocity.
Figure 7: Variation in delay for change in vehicle velocity.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
452
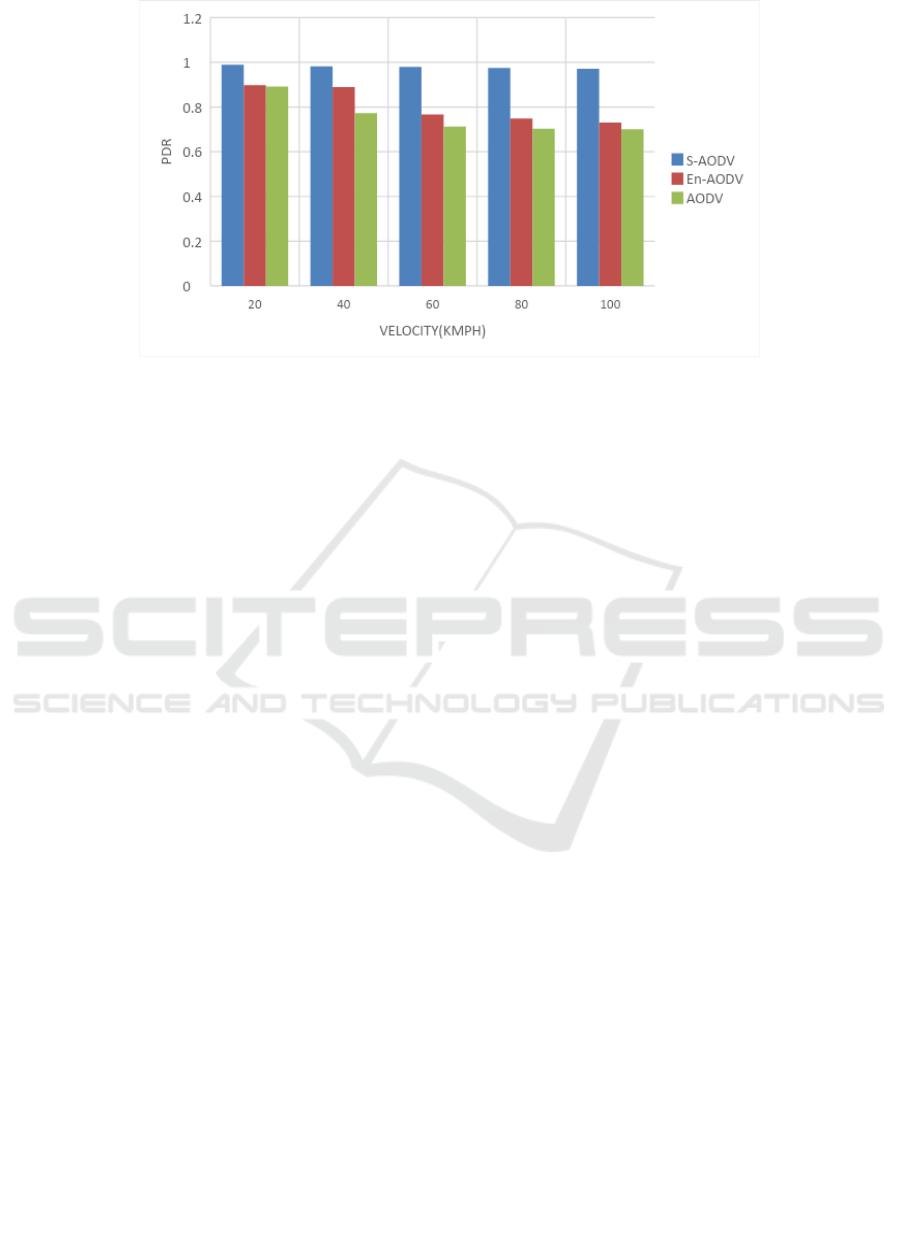
Figure 8: Variation in PDR for change in vehicle velocity.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work, An Efficient Secure AODV protocol (S-
AODV) is presented to overcome various attacks in
VANET. S-AODV reduces routing overhead and
routing cost through the selection of CRVs. Further,
the optimal secure path to the destination is identified
through trust estimation among the selected relay
vehicles in the network. Here, the trust value is
estimated using distinct metrics like Hop Count and
Network Lifetime. Further, The S-AODV has been
examined using NS-2.34 and results showed that the
S-AODV is superior over existing schemes.
REFERENCES
Shafi, S., & Venkata Ratnam, D. (2022). An Efficient Cross
Layer Design of Stability Based Clustering Scheme
Using Ant Colony Optimization in VANETs. Wireless
Personal Communications, 126(4), 3001-3019.
Singh, R. K., & Nand, P. (2016, April). Literature review of
routing attacks in MANET. In 2016 International
Conference on Computing, Communication and
Automation (ICCCA) (pp. 525-530). IEEE.
Murthy, C. S. R., & Manoj, B. S. (2004). Ad hoc wireless
networks: Architectures and protocols, portable
documents. Pearson education.
AL-Dhief, F. T., Sabri, N., Salim, M. S., Fouad, S., &
Aljunid, S. A. (2018). MANET routing protocols
evaluation: AODV, DSR and DSDV perspective.
In MATEC web of conferences (Vol. 150, p. 06024).
EDP Sciences.
Shafi, S., Mounika, S., & Velliangiri, S. (2023). Machine
Learning and Trust Based AODV Routing Protocol to
Mitigate Flooding and Blackhole Attacks in
MANET. Procedia Computer Science, 218, 2309-
2318.
Su, M. Y. (2011). Prevention of selective black hole attacks
on mobile ad hoc networks through intrusion detection
systems. Computer Communications, 34(1), 107-117.
Sargunavathi, S., & Martin Leo Manickam, J. (2019).
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Enhanced trust based
encroachment discovery system for Mobile Ad-hoc
networks. Cluster Computing, 22 (Suppl 2), 4837-
4847.
Li, J. S., & Lee, C. T. (2006). Improve routing trust with
promiscuous listening routing security algorithm in
mobile ad hoc networks. Computer
communications, 29(8), 1121-1132.
Daoud, L., & Rafla, N. (2019, August). Analysis of black
hole router attack in network-on-chip. In 2019 IEEE
62nd International Midwest Symposium on Circuits
and Systems (MWSCAS) (pp. 69-72). IEEE.
Arthur, M. P. (2018, September). An SVM-based
multiclass IDS for multicast routing attacks in mobile
ad hoc networks. In 2018 International Conference on
Advances in computing, communications and
Informatics (ICACCI) (pp. 363-368).
Rmayti, M., Begriche, Y., Khatoun, R., Khoukhi, L., &
Gaiti, D. (2015, August). Flooding attacks detection in
MANETs. In 2015 International Conference on Cyber
Security of Smart Cities, Industrial Control System and
Communications (SSIC) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
Kumar, A., Varadarajan, V., Kumar, A., Dadheech, P.,
Choudhary, S. S., Kumar, V. A. & Veluvolu, K. C.
(2021). Black hole attack detection in vehicular ad-hoc
network using secure AODV routing
algorithm. Microprocessors and Microsystems, 80,
103352.
Malik, A., Khan, M. Z., Faisal, M., Khan, F., & Seo, J. T.
(2022). An efficient dynamic solution for the detection
and prevention of black hole attack in
vanets. Sensors, 22(5), 1897.
An Efficient Secured AODV Routing Protocol to Mitigate Flooding and Black Hole Attack in VANETs for Improved Infotainment Services
453
