
A Study on Determining the Employee Performance in Servant
Leadership Style in the Banking Sector
Durga Bhavani
Mohan Babu University, India
Keywords: Employee Performance, Servant Leadership, Banking Sector.
Abstract: Servant leadership is a well-established idea; the word was first used in 1970 by Robert K. Greenleaf in his
article "The Servant as Leader," which was published in Harvard Business Review. "The servant leader is
first and foremost a servant," Greenleaf said. Greenleaf felt that institutions, rather than merely people, could
be servant leaders as well as servants. Servant leadership culture is becoming more popular among top-ranking
corporations throughout the globe, as they recognize the pragmatic effect it has on both leaders and followers.
The rise of servant leaders has flipped the power hierarchy in the banking sector on its head. Serving their
followers, the servant leader has evolved into a leader who is accountable for guiding the firm. The impact of
servant leadership and its impact on organizational effectiveness, there has been little research into the
relationship between servant leadership and employee performance. There has also been little research into
how to determine employee performance through moderating. Employee performance is influenced by factors
such as the workplace environment, leadership, career development programs, and incentive systems, as well
as training skills and new talents to meet the current and future needs of the firm. Employee engagement, as
well as employee performance, is a significant component in determining employee performance. It is
possible to evaluate employee performance in terms of the organization's current and future needs and
requirements.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human resources may be considered to be the
resourcefulness of several sorts of individuals as well
as other people who are accessible to the company.
These most precious people in the organization with
multi-faceted talent and skills are directed in a proper
way to achieve the goals of the organization. These
most precious people in the organization with multi-
faceted talent and skills are directed in a proper way
to achieve the goals of the organization. The success
and growth of any business organization largely
depends on the key person who holds the steering
wheel of the form organization in a right direction.
There emerges the form ‘Leadership ‘in Banks is vast
sector in which the entire economy is depended
country’s growth is in the hands of banking sector this
growth is having a direct link with the employees in
the organization the relationship between leader and
follower is that of nation of Servant this analysis is
studied in the present study. Servant leadership is the
kind of leadership that most closely resembles
participatory leadership. While history frequently
lists few instances of management theories other than
autocratic, or authoritarian, leadership until the 1950s
or 1960s, servant leadership is really a centuries-old
method that dates back to the ancient Greeks. As early
as 500 BC, the Chinese philosopher Lao-Tzu spoke
about servant leadership in the classic work "Tao Te
Ching."
The servant leadership style is one that is aspired
to. Serve as a servant leader by demonstrating the
following five characteristics: love; empowerment;
trust; humility; and vision. Any organization's ability
to monitor employee performance has become a
standard practice. Servant leadership is one
component that might have an impact on an
employee's overall success. Employees are the most
valuable assets that any firm may have. Why?
Because the employee had a significant and active
part in the organization's progress toward success;
otherwise, the organization's progress would have
been impossible to achieve.
Bhavani, D.
A Study on Determining the Employee Performance in Servant Leadership Style in the Banking Sector.
DOI: 10.5220/0012533300003792
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR 2023), pages 971-976
ISBN: 978-989-758-687-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
971

2 SERVANT LEADERSHIP
IMPACT ON EMPLOYEE
PERFORMANCE
Servant leadership is relatively a new concept. The
servant leadership is aspired to lead. There are five
dimensions in servant leadership such as love,
empowerment, trust, humility and vision. Employee
performance becomes a measurement for any
organization. One factor that can influence the
employee performance is servant leadership.
Employees are the major assets of the every
organization. Why because the employee was play a
major and active role of the organization towards
success otherwise it should not possible to get success
of the organization. Employee performance is a key
factor that contributes directly to the performance of
the company. Companies today, with increased
competition in the business arena, are keen to boost
employee performance in order to enhance their
profitability, market reach and brand
recognition. Employee performance is associated
with working environment, leadership, career
development programmer, and reward system,
training skills, new skills of present & future
requirements of the organizations. As well as
employee engagement is major factor of determine
employee performance. Employee performance can
be measured by present and future need and
requirements of the organization.
2.1 The Differences Between
Traditional and Servant
Leadership
The differences between these leadership styles
originate from those priorities we covered in our
previous example figure 1.
Figure.1. Traditional and Servant Leadership.
Like traditional leaders, servant leaders will create a
vision and values for the organization. They will set
goals and objectives for team members to achieve.
Servant leaders, however, share power with team
members to enable them to achieve the vision, live the
values, and hit the goals.
Unlike traditional leaders, servant leaders use
their power to:
● Empower more and micromanage less;
● Coach more and direct less;
● Involve more and exclude less;
● Ask questions more and assume less; and
● Listen more and talk less.
A traditional organizational structure would
typically look like the traditional leadership pyramid
illustrated below. If you asked a servant leader to
draw their org structure, however, it would look quite
different, the reverse of a traditional structure.
2.2 Banking Structure in India
The Indian banking system is divided into two
categories: "non-scheduled banks" and "scheduled
banks." Not included in the second schedule of the
Banking Regulation Act, 1965, non-scheduled banks
are those that do not meet the requirements set out in
that schedule and so do not fall under the jurisdiction
of the Act's second schedule. As defined by the
Second Schedule of Banking Regulation Act, 1965,
schedule banks are those that meet the following
criteria: a bank must (1) have paid up capital and
reserves of not less than Rs. 5 lakh and (2) satisfy the
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) that its affairs are not
conducted in a manner detrimental to the interest of
its depositors.
2.2.1 The following Are Some of the Most
Significant Steps in the Development of
Modern Banking in India
1) Agency Houses: When English merchants first
arrived in India, they had difficulties in acquiring
operating money because of the linguistic barrier.
Therefore, they founded Agency Houses, which
integrated trade with banking services to serve their
customers. In 1770, the Bank of Hindustan, which
was created by a single agency house, became India's
first bank.
2) Presidency Banks: The East India Company, the
ruling power in India, took the initiative in creating
Presidency Banks by providing 20% of its share
capital in order to fulfil its own need for finances.
Banks such as the Bank of Bengal, the Bombay
Savings & Loan Association, and the Bank of Madras
were formed in 1806; 1840; and 1943, respectively.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
972
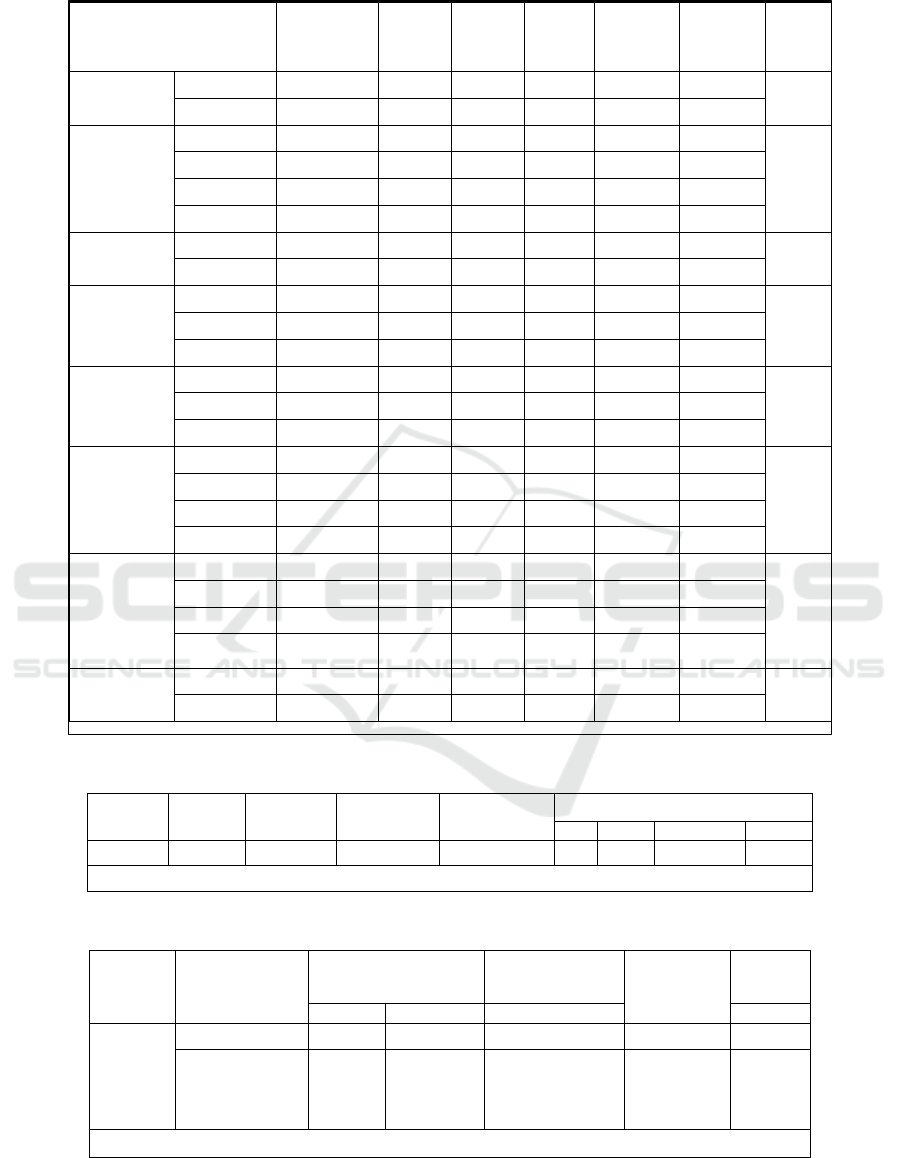
Table 1: Employee’s Response towards Servant Leadership.
Table 2: Regression Model Summaries for the Servant Leadership on Employee performance.
Table 3: Predictor effects and Beta Estimates.
Demographic Description
Total
sample
n=750
Most
Unlikely
Unlikely
Neutral
Likely
Very
much
likely
Chi Sq
Gender
Male
253(33.73)
0(0)
3(1.19)
23(9.09)
171(67.59)
56(22.13)
8.383, df4
>0.05
Female
497(66.27)
3(0.6)
21(4.23)
31(6.24)
338(68.01)
104(20.93)
Age
25 - 35 Yrs
548(73.07)
3(0.55)
13(2.37)
41(7.48)
381(69.53)
110(20.07)
37.280,
df12,
<0.05
35 - 45 Yrs
149(19.87)
0(0)
4(2.68)
6(4.03)
99(66.44)
40(26.85)
45 - 55 Yrs
32(4.27)
0(0)
3(9.38)
5(15.63)
21(65.63)
3(9.38)
> 55 Yrs
21(2.8)
0(0)
4(19.05)
2(9.52)
8(38.1)
7(33.33)
Marital
Status
Married
688(91.73)
2(0.29)
21(3.05)
48(6.98)
466(67.73)
151(21.95)
5.123,
df4,>0.05
Unmarried
62(8.27)
1(1.61)
3(4.84)
6(9.68)
43(69.35)
9(14.52)
Education
SSC/Diploma
101(13.47)
0(0)
4(3.96)
9(8.91)
67(66.34)
21(20.79)
3.096,
df8,>0.05
Degree
373(49.73)
2(0.54)
9(2.41)
28(7.51)
256(68.63)
78(20.91)
Postgraduate
276(36.8)
1(0.36)
11(3.99)
17(6.16)
186(67.39)
61(22.1)
Cadre
Junior Level
424(56.53)
2(0.47)
13(3.07)
34(8.02)
285(67.22)
90(21.23)
2.140,
df8,>0.05
Middle Level
259(34.53)
1(0.39)
9(3.47)
16(6.18)
175(67.57)
58(22.39)
senior Level
67(8.93)
0(0)
2(2.99)
4(5.97)
49(73.13)
12(17.91)
salary
15-30,000
167(22.27)
0(0)
11(6.59)
5(2.99)
116(69.46)
35(20.96)
23.761,
df12,
<0.05
30-40,000
115(15.33)
0(0)
1(0.87)
11(9.57)
77(66.96)
26(22.61)
40-50,000
365(48.67)
3(0.82)
12(3.29)
30(8.22)
237(64.93)
83(22.74)
above 50,000
103(13.73)
0(0)
0(0)
8(7.77)
79(76.7)
16(15.53)
Experience
0- 2 years
397(52.93)
1(0.25)
11(2.77)
34(8.56)
276(69.52)
75(18.89)
15.718,
df12,>0.0
2-5 years
206(27.47)
0(0)
9(4.37)
16(7.77)
129(62.62)
52(25.24)
5-10 years
145(19.33)
2(1.38)
4(2.76)
4(2.76)
103(71.03)
32(22.07)
above 10
years
2(0.27)
0(0)
0(0)
0(0)
1(50)
1(50)
Organization
SBI
375(50)
1(0.27)
10(2.67)
32(8.53)
252(67.2)
80(21.33)
2.901,
df4,>0.05
ICICI
375(50)
2(0.53)
14(3.73)
22(5.87)
257(68.53)
80(21.33)
Model
R
R Square
Adjusted R
Square
Std. Error of
the Estimate
ANOVA Results
df1
df2
F-Value
Sig.
1
.398
a
.159
.157
.77780
1
547
103.186
0.000
a. Predictors: (Constant), Employee Performance
Model
Variable
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
t-Value
Sig.
B
Std. Error
Beta
1
(Constant)
3.070
.267
11.478
.000
Servant Leadership
Style
.452
.045
.398
10.158
.000
a. Dependent Variable: Employee Performance
A Study on Determining the Employee Performance in Servant Leadership Style in the Banking Sector
973

3) Joint Stock Banks: In 1884, the concept of limited
liability was introduced into banking, allowing banks
to be founded as joint stock companies. In due time,
this aided in the formation of financial institutions.
4) Imperial Bank of India: In order to compete with
international banks, the three Presidency Banks were
merged in 1921, resulting in the establishment of a
formidable Imperial Bank of India with a network of
branches across the country.
5) The establishment of the Reserve Bank of India:
Despite the fact that the banking industry was
booming, there were a slew of bank failures owing to
a lack of oversight and the inability to provide timely
help. As a result, the general public developed a
negative attitude toward financial institutions.
6) Nationalization of the RBI and the Banking
Regulation Act: In 1949, these two significant
milestones were taken forward. The Reserve Bank of
India (RBI) was granted extensive regulatory and
control powers immediately after independence, and
by putting those authorities to good use, the RBI was
successful in establishing confidence in Indian
banking.
7) Banks were nationalized in 1969 and 1980,
respectively. A further substantial stride forward was
made in 1969 with the nationalization of 14 large
Indian commercial banks. The next year, six
additional banks were nationalized. The
nationalization of banks resulted in a significant shift
in the policies, attitudes, processes, functions, and
geographic reach of financial institutions.
3 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
Afsar, Lee, Luu et al., Tuan, (2020) was focused
and analyzed on servant leaders whose primary
objective is to ensure that all people under their
stewardship have the best possible opportunity to
grow, thrive, prosper, and reach their full potential, as
well as the efficient and effective approaches used by
servant leaders to accomplish their origination goals.
Arain and colleagues, Frémeaux and Pavageau,
Giambatista and colleagues (2020)
According to
defined, Servant leaders are expected to think
carefully on and examine their own value systems in
order to discover areas where they may develop as
leaders in order to guide their followers along a
successful path while working in the proper manner.
In addition, He described the essential characteristics
of leadership demonstrated by the Prophet, including
courage, integrity, practical wisdom, moral authority,
humility, leading by example, sharing and enduring
hardship, doing things at the right time in the right
way, innovation, and trustworthiness, among other
characteristics.
Smith, Montagno, &Kuzmenko (2004) The authors
say that "servant leadership emphasizes a leader's
care for the well-being of his or her followers, which
is shown via attentive, non-judgmental listening and
a readiness to learn from others. Servant leadership is
distinguished by its ability to foster a "spiritual
generative culture," while transformational
leadership results in an "empowered dynamic
culture."
Wuryani et al. (2021) The author provided a critical
evaluation of evaluating employee performance using
a decision-supported system, with one of the factors
addressed being motivation as a predictor of
employee success. Conclusion: According to the
authors, situational leadership-supported decision
support systems do not considerably enhance
employee performance and only marginally improve
employee performance.
Atatsi et al. (2019) conducted a thorough
examination of the literature on employee
performance in various nations, with a special
emphasis on Africa, which has a distinct cultural
background. It demonstrates the existence of a
favorable correlation between employee behaviours
and performance, as well as variety across
interdisciplinary domains with cultural and
contextual value.
Sharma et al. (2016)
The employee's performance in
the workplace the interventions resulted in significant
changes in banking sectors, and they were effectively
used to drive financial inclusion by reaching out to
people and connecting them with banking systems
through the use of e-commerce technologies, which
have been shown to significantly improve employee
performance in the banking system.
4 OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
1. To study and understand the factors effecting
Servant leadership.
2. To adjudicate the impact of Employee
Empowerment on Employee Performance.
3. To analyses the mediating role of Employee
Empowerment on Employee Performance
over Servant Leadership Style.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
974

Formulation of Hypotheses
1. H1
0
: Servant Leadership will not have impact on
Employee Empowerment.
2. H2
0
: Servant leadership will not have impact on
Employee Performance.
Statistical Analysis
H1
0
: Servant Leadership will not have impact on
Employee Empowerment.
Table No: 1 Employee’s Response towards
Servant Leadership
H2
0
: Servant Leadership will not have
significant effect on Employee Performance.
The hypothesis of relationship between servant
leadership and employee performance were tested
using simple linear regression. The regression results
shown in revealed that the predictor variables
contribute significantly and had moderate impact on
the employee performance (R
2
= 0.398). The
corresponding ANOVA value (F =103.186, p=0.000)
for the regression models had indicated the validation
with employee performance.
The coefficient summary shown in Table revealed
that beta values of servant leadership style (β=0.452,
t=10.158, p=0.000) was significant with employee
performance. The results were implicit that predictor
variable was related with dependent variable. Hence,
null hypothesis was disproved and alternate
hypothesis was accepted as their p-values were less
than 0.05. Here the following simple linear
regression model
Employee Performance (Y) = 3.070+ 0.452
(Servant Leadership style) X
The significant effect of servant leadership style on
employee performance is measured through
significance of regression coefficient of servant
leadership style, when mean servant leadership style
is regressed upon mean employee performance. This
regression coefficient is found to be 0.852 and its
standard error is found to be 0.037 respectively. T
statistic corresponding this regression coefficient
(0.852/0.037) was found to be significant at 5% alpha
(p <0.05). This regression coefficient is termed as “c”
and its standard error is termed as SE(c). “C” is also
termed as “TOTAL EFFECT”
5 FINDINGS OF THIS STUDY
1. The present study has established that policies,
procedures, practices, conditions, HRD climate
and organizational performance are the most
influential factors in understanding the
perceptions of banks
2. This study enables both HR employees and
researchers to understand the tendency of high
potential influencing factors of servant
leadership models. This knowledge can be used
to identify how to inculcate the emotional
healing practices among their work force.
3. This study has underscores the importance of
servant leadership models which is decisive in
determining employee performance.
4. The regression results revealed that the predictor
variables contribute significantly and had
moderate impact on the employee performance
(R
2
= 0.398). The corresponding ANOVA value
(F = 103.186, p=0.000) for the regression
models had indicated the validation with
employee performance.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The purpose of this research was to add to the
expanding body of literature on analyzing the
function of servant leadership style in measuring
employee performance, which is now under
investigation. This hypothesis has been tested in the
field, and it has been shown that a moderating
element in the link between servant leadership and
employee performance. Great leadership has a
favorable impact on the culture of a company; servant
leadership takes this advantage to the next level by
instilling in managers the belief that success is a
shared and selfless experience. This sounds
wonderful on paper, but seeing it in action typically
leaves the most lasting impact, and doing so involves
dedication and hard effort on the part of the
individual. And since servant leaders are already
preoccupied with the improvement and development
of others, they are excellent role models for teaching
others how to do the same. Employees require a
workplace in which they feel safe not only in order to
develop professionally, but also in order to put their
faith in the services that their managers provide.
Servants are leaders who put the needs of others first.
This is an external mentality that encourages all
workers to face outwards in order to serve one
another, which helps the whole business. Typically,
the "others" are the personnel under their supervision,
but servant leadership should extend beyond direct
subordinates or individuals inside the business to
include the whole community in which they operate.
Customers, stockholders, clients, and the larger local
and global community might all be included in this
category.
A Study on Determining the Employee Performance in Servant Leadership Style in the Banking Sector
975

REFERENCES
Adamson, L. (2009) ‗Servant Leadership in a Community
College: A Multivariate Analysis of Employees‘
Perceptions‘, Dissertations Abstracts International,
AAT 3342496.
Adjibolosoo, Senyo B.-S.K. (1995) The Human Factor in
Leadership Effectiveness (Mustang, OK: Tate
Publishing).
Alimo-Metcalfe, B. and Alban-Metcalfe, J. (2005)
‗Leadership: Time for a New Direction?‘, Leadership,
1: 51–71.
Alio, R. (2006) ‗Factors Influencing Leadership in
Nursing: The Experience of Nurse Directors in the
NHS‘, Presentation at the 2008 Nursing Research
Conference, Liverpool, UK.
Alston, J.A. (2005) ‗Tempered Radicals and Servant
Leaders: Black Females Persevering in the Super in
tendency‘, Educational Administration Quarterly, 41:
675–88.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1996) Creativity: Flow and the
Psychology of Discovery and Invention (New York:
HarperCollins).
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (2003) Good Business. Leadership,
Flow, and the Making of Meaning (New York: Penguin
Putnam Inc).
Daft, R.L. (2007) The Leadership Experience (Boston, MA:
South-Western College). Daft, R.L. (2002) The
Leadership Experience (Mason, OH: SouthWestern
College). Daft, R.L. (1999) ‗Contextual Implications
for Transformational and Servant Leadership‘,
Management Decision, 43: 10.
De Pater, I.E., Van Vianen, A.E., Bechtoldt, M.N., and
Klehe, U.C. (2009). Employees‘ challenging job
experiences and supervisors. Personnel Psychology,
62(2), 297–325.
DeVaro, J. (2006). Strategic promotion tournaments and
worker performance. Management Journal, 27, 721–40.
DeVoe, S.E., and Iyengar, S.S. (2004). Managers‘ theories
of subordinates: A cross-cultural examination of
manager perceptions of motivation and appraisal of
performance. Organizational Behavior and Human
Decision Processes, 93(1), 47–61.
Engstrom, T. (1976) The Making of a Christian Leader:
How to Develop Management and Human Relations
Skills (Grand Rapids MI: Zondervan).
Erez, A., Misangyi, V. F., Johnson, D. E., LePine, M. A.
and Halverson, K. C. 2008. ‗Stirring the Hearts of
Followers: Charismatic Leadership as the Transferal of
Affect‘, Journal of Applied Psychology, 93: 602–15
Lawler, E.E., Benson, G.S., and McDermott, M.
(2012).Performance management and reward systems.
World at Work Journal, 21, 19–28.
. Lazarus, R.S. (1991). Emotion and Adaptation. New York:
Oxford University Press.
Li, S. L., He, W., Yam, K. C. & Long, L. R. (2015).When
and why empowering leadership increases followers‘
taking charge: A multilevel examination in China. Asia
Pacific Journal of Management 32, 645-670.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (1990). A theory of goal
setting & task performance. Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Maynard, M. T., Mathieu, J., Marsh, W. M. & Ruddy, T.
M. (2007). A multilevel investigation of the influences
of employees‘ resistance to empowerment. Human
Performance 20, 147-171.
Nature and Role of Historical Precedents‘, Leadership
Quarterly, 19: 426–38. Cater, J.J. (2006) ‗Stepping Out
of the Shadow: The Leadership Qualities of
Successors in Family Business‘, Dissertation Abstracts
International, 67(08), 3055, UMI no. 3229207.
PAMIR 2023 - The First Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
976
