
Analysis of the Implementation of SMKK (Construction Safety
Management System) Based on the Regulation of the Minister of
PUPR No.10/2021 on the Construction Project of Coastal Safety
Development
Novelin Adriana Fransisca Tumatar and Bangun Marpaung
Civil Engineering Department, Universitas 17 Agustus 1945 Jakarta, Sunter, Jakarta Utara, Indonesia
Keywords: Safety, Management System, Permen Ppr No.10/2021.
Abstract: The regulation governing the construction safety management system in Indonesia is the Regulation of the
Minister of Public Works and Public Housing (Permen PUPR No. 10 Tahun 2021). The need for awareness
of work safety and safety management systems is an obligation for all stakeholders in construction projects.
This research aims to analyze the implementation of a construction safety management system in one of the
coastal safety construction projects. For the following, this research aims to provide recommendations for
applicable regulations based on a review of related literature. The method used in this research uses a
quantitative approach with data analysis using descriptive analysis. Data collection was carried out using
questionnaire distribution techniques and observation techniques. Observation and questionnaires forms refer
to applicable regulations (Permen PUPR No. 10 Tahun 2021). The responses received and recorded which
were included in the data analysis were 13 respondents, of which 13 respondents came from almost all
divisions in the project. The number of articles included in this study is 25 articles. The results of the
observation analysis 93% and questionnaires 96%. These results confirm that the implementation of the Work
Safety Management System in the Coastal Protection Development Project has been implemented well or at
a satisfactory classification level and is in accordance with applicable regulations. Based on the literature
review, 4 things need to be considered in amending the observation form based Permen PUPR No. 10 of 2021,
such as (1) imposition of sanctions; (2) provision of rewards; (3) workers have the right to express objections
if the construction safety policy is doubted by workers; (4) training workers regarding the importance of
implementing construction safety management system. The limitation of this study is that it only refers to a
construction project which is a water sector construction project. To expand research and increase the level
of percentage that is more mature, it is necessary to increase the sample of types of construction projects in
the fields of building construction, highways, and other types of construction.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cases of accidents due to work in the construction
sector are one of the highest cases of work accidents
throughout the world (ILO, International Labor
Organization). OSHA (Occupational Safety and
Health Administration) also states that the
construction industry has the highest risk of death
compared to other industrial sectors. For the
following, the number of work accidents in Indonesia
based on the Social Security Administrator for
Employment (BPJS Ketenagakerjaan) has increased
continuously from the annual report year on year until
2021 reaching more than 200 thousand cases, where
half of the number of work accident cases occurred in
the construction industry.
Sustainable infrastructure development
increases construction activity in Indonesia. But in
fact, various problems are still found in the
construction area, especially in the implementation of
the Occupational Safety and Health Management
System (SMK3). Implementation of an Occupational
Safety and Health Management System (SMK3) is
very necessary in controlling the risk of work
accidents. However, there are huge of personnel do
not realize and implement this management system
that caused increase in the risk or potential risk of
work accidents in the construction industry.
Tumatar, N. and Marpaung, B.
Analysis of the Implementation of SMKK (Construction Safety Management System) Based on the Regulation of the Minister of PUPR No.10/2021 on the Construction Project of Coastal
Safety Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0012584400003821
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023), pages 437-444
ISBN: 978-989-758-691-0; ISSN: 2828-853X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
437
Therefore, legislation was created as an effort to
control the risk of work accidents, especially in the
construction sector by ratifying the Regulations for
Implementing the Construction Safety Management
System (SMKK) which are currently in force, one of
which is by the Government. Regulation. Regulation
of the Minister of Public Works and Public Housing
Number 10 of 2021 (Permen PUPR No.10 Tahun
2021) concerning Guidelines for Construction Safety
Management Systems.
In this research, the aim is to measure the
implementation of the work safety management
system (SMKK) by taking one of the case studies of
coastal safety construction projects. Apart from that,
another objective of this research will be to examine
the applicable laws and regulations to provide
recommendation points based on a review of related
literature.
1.1 Construction Safety Management
System (SMKK)
In the Construction Safety Management System
(SMKK) Regulations contained in PUPR Ministerial
Regulation number 10 of 2021, it is part of the
Construction Work implementation management
system to ensure the realization of Construction
Safety (PUPR Ministerial Regulation Number 10 of
2021, 2021).
The development of the construction industry in
Indonesia is increasingly rapid, but the increase in
construction work is not in line with improvements in
the management of construction activities to
minimize the risk of work accidents in construction.
The high frequency of work accidents in the
construction sector that occurred later became the
beginning of a commitment to create zero accidents
which was then transformed into statutory policies
related to construction safety as a standard in the
implementation of construction work to realize
construction safety (Badaruddin et al., 2022).
1.2 Implementation of a Construction
Safety Management System
The implementation of the SMKK (Construction
Safety Management System) in Indonesia has been
implemented by the Indonesian Government on the
long run by time. The regulations regarding
Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) in Indonesia
have existed since the Dutch East Indies government.
After Indonesia's independence and the enactment of
the 1945 Constitution, several regulations including
regulations regarding work safety has impacted at that
time, Specifically the Veiligheids Reglement, were
revoked and replaced with Law no. 1 of 1970
concerning Work Safety (Wahyuno, 2021).
According to PUPR Ministerial Regulation No.10 of
2021, Construction Safety Management System
(SMKK) implementation require security, safety,
health, and sustainability standards.
1.3 Elements of Implementing a
Construction Safety Management
System
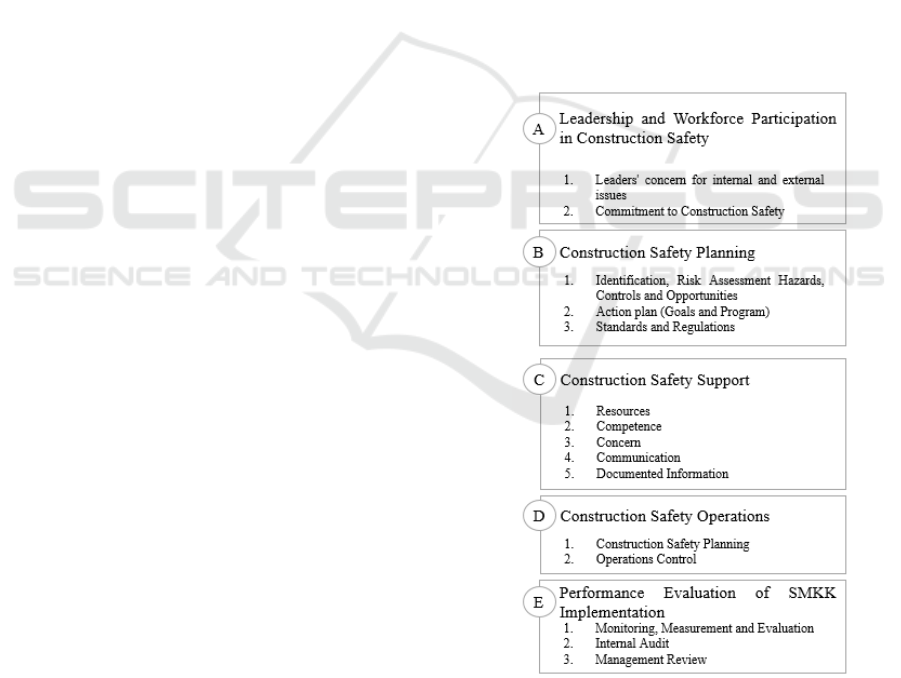
In implementing the Construction Safety
Management System (SMKK) according to Ministry
Publics Works and Housing regulation no. 10 / 2021,
it is necessary includes Construction Safety
Management System (SMKK) elements in the
construction safety plan document. There are 5 (five)
main elements in implementing Construction Safety
Management System (SMKK). Following the details
of the elements.
Figure 1: Elements and sub-elements in implementation
construction safety management (SMKK).
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
438

2 METHODS
This research was work on data collection in 2 months
period of time start from May 2023 to June 2023. The
research method used was a quantitative approach.
The philosophy of positivism that underlies the
quantitative approach method used to research
populations and certain statistical samples (Sugiyono,
2013). Other definition emphasize that quantitative
research is a systematic, planned and structured
research method (Siyoto & Sodik, 2015).
The data collection technique in this research
uses 3 (three) method based on the type of research
data observation and questionnaires for primary data
and literature review for secondary data. The
population in this research define by stakeholders in
the construction project X beach for safety
development project. The population is an
object/subject area with certain characteristics
(Sugiyono, 2013). While the sample is a portion of
the population with certain characteristics (Sugiyono,
2013). In this study the sample was selected using
purposive sampling/certain considerations and have
been determined by contractors, supervisors, and
workers that responsible on the X Beach Safety
Development Project.
Data collection by observation and
questionnaires uses the following assessment scale:
- Appropriate = 3, means "if the activity is fully
implemented"
- Minor = 2, means "if the activity is implemented
but not fully"
- Major = 1 means "if the activity is not
implemented"
The data analysis on this research is primary data
obtained through observation and distribution of
questionnaires. The data collection analyzed using
descriptive analysis to determine level of
implementation classification based on government
regulation of the Republic of Indonesia no.50 of 2012
concerning the implementation of occupational safety
and health management systems (PP Republic
Indonesia Number 50 of 2012, 2012).
Table 1: Classification of SMKK Implementation Levels.
No
Percentage (%)
Classification
1
0 – 59 %
Kurang
2
60 – 84 %
Baik
3
85 – 100 %
Memuaskan
The secondary data collection was collected by
journal articles related to the research topic and full
reviewing with purposes adding aspects need to pay
attention and will be aspects recommendation for
amandement of the Ministry Public works and
Housing No.10 2021.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Data Characteristics
3.1.1 Respondent Characteristics
The collections data using distributing the
questionnaire collected 13 respondents consist of
supervisors, consultants, contractors, skilled workers.
The following table summarize the characteristics of
the respondents’ samples on this research.
Table 2: Respondent Characteristics.
No Age
Last
Education
Position
Work
Experience
Respondent
Group
R1
>35
Tahun
S2/S3
PPK
Pengawas
5-10 Tahun Pengawas
R2
>35
Tahun
D3/D4/S1
Leader
Konsultan
>10 Tahun
Konsultan
Supervisi
R3
>35
Tahun
S2/S3
Tenaga Ahli
Struktur
5-10 Tahun
Konsultan
Supervisi
R4
>35
Tahun
Lainnya Welder <5 Tahun Pekerja
R5
>35
Tahun
SMA/SMK Logistik <5 Tahun Pekerja
R6
>35
Tahun
SMA/SMK
Intalasi
Listrik
<5 Tahun Pekerja
R7
>35
Tahun
SMA/SMK Mekanik 5-10 Tahun Pekerja
R8
>35
Tahun
SMA/SMK
Driver
Lapangan
<5 Tahun Pekerja
R9
20-35
Tahun
D3/D4/S1
Manajer
Operasi
5-10 Tahun
Karyawan
Kontraktor
R10
20-35
Tahun
D3/D4/S1 Drafter 5-10 Tahun
Karyawan
Kontraktor
R11
20-35
Tahun
SMA/SMK Drafter 5-10 Tahun
Karyawan
Kontraktor
R12
20-35
Tahun
D3/D4/S1 Adm. Teknik
<5 Tahun
Karyawan
Kontraktor
R13
20-35
Tahun
SMA/SMK Adm. Teknik
5-10 Tahun
Karyawan
Kontraktor
*Note: R define Respondent
3.1.2 Literature Collected for Reviewing
The results of the literature study obtained by
reviewing journals related to the application of
occupational safety and health in construction
projects with the aim of classifying and grouping each
construction safety management system (SMKK)
element found in these journals to review elements
that are not yet listed in PUPR Ministerial Regulation
no.10 of 2021, The results of these findings will be
recommended as amendments The Ministry Public
Works and Housing no.10, 2021. 25 journals were
collected on this research for reviewing to catch out
aspects for the regulation amendments.
Analysis of the Implementation of SMKK (Construction Safety Management System) Based on the Regulation of the Minister of PUPR
No.10/2021 on the Construction Project of Coastal Safety Development
439
Table 3: Literature review article.
No. Judul Penulis
1
Analisis Penggunaan Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada Proyek
Pembangunan RSUD
Sunan Kalijaga Demak
Hari Setijo. P, dkk
(2018)
2
Kendala Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3)
Pada Kontraktor di Bali
G.A.P Candra
Dharmayanti, dkk
(2018)
3
Implementasi Kebijakan
SMK3 di Perusahaan
Kontraktor di Yogyakarta
R.A.
Machfudiyanto dan
D.P. Utomo (2019)
4
Peninjauan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan
dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) Pada Proyek
Pekerjaan Pondasi Condotel Multifungsi Aston
Padang
Embun Sari Ayu
(2019)
5
Analisis Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja Pada
Pembangunan Gedung dan Perumahan
Steven & Mega
Waty (2020)
6
Usulan Perbaikan Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada Perusahaan Konstruksi Jalan
Fauzan Ariswa,
dkk (2020)
7
Analisis Penerapan Kesehatan Dan
Keselamatan Kerja (K3) di Perusahaan Jasa
Konstruksi Kota Payakumbuh
Ade Dwi Putra,
dkk (2021)
8
Analisis Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja (K3)
Jurisman Amin &
Kirami Bararah
(2021)
9
Analisa Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Kesehatan dan Keselamatan Kerja (SMK3)
Pada PTPN VI di Kecamatan Pangkalan Koto
Baru Sumatera Barat
Mahdika P. N &
Rina H (2022)
10
Analisis Penerapan Keselamatan dan Kesehatan
Kerja (K3) Terhadap Kinerja Pekerja
Konstruksi
Moh. Midchol
Afan, dkk (2022)
11
Kajian Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja pada Perusahaan Konstruksi
Jalan di Indonesia
Fajar Susilowati,
dkk (2022)
12
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) pada Masa Pandemi
Covid
-19 di Proyek Konstruksi Maritime
Tower
Anisah, dkk (2022)
13
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada Proyek
Konstruksi Gedung Kejaksaan Tinggi
Kalimantan Timur
Habir, dkk (2022)
14
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan
Konstruksi Dalam Pandemi Covid
-19 Pada
Proyek Pembangunan Struktur Atas Jembatan
Progo Tempuran
-Salaman
Kasih
Puspitasari,
dkk (2022)
15
Analisis Penerapan Sistem Manajemen K3 dan
Kelengkapan Fasilitas K3 Pasa Proyek
Konstruksi Gedung di Surabaya
A. F. Priyono &
Feri Harianto
(2019)
16
Analisis Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja
Pada Proyek
Konstruksi Gedung Betingkat Tinggi
Ida Yuliana (2020)
17
Analisis Tingkat Risiko dan Penerapan SMK3
pada Proyek Pembangunan Rumah Sakit
Umum Daerah Mangusada Badung
I Ketut Sutapa, dkk
(2020)
18
Evaluasi Pelaksanaan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3)
pada Proyek Pembangunan Gedung Bertingkat
di Tanah Lunak
Henry Wardhana,
dkk (2021)
19
Evaluasi Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja Pada Proyek
Konstruksi di Kota Banda Aceh
Aldina Fatimah
dkk (2021)
20
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) Di Fakultas Teknik
Nurokhman, dkk
(2021)
21
Evaluasi Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3)
Pada Proyek Konstruksi di
Provinsi Gorontalo
Maulin
Wadipalapa, dkk
(2022)
22
Analisis Faktor
-Faktor Penghambat Kontraktor
dalam Penerapan Sistem Manajemen K3 pada
Proyek Konstruksi Gedung di Palangka Raya
C.M.Br Sinulingga,
dkk (2023)
23
Analisis Penerapan Sistem
Management
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3)
pada Proyek Konstruksi Gedung
Amari & Machmud
Efendi (2023)
24
Evaluasi Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3)
pada Perusahaan Konstruksi
Ira Riswana dan
Susilawati,
(2023)
25
Pengaruh Penerapan SMK3 Pada Proyek
Konstruksi Terhadap Kualitas Pekerjaan (Studi
Kasus: Proyek Rehabilitas Gedung Kantor
Kejaksaan Kota Madiun)
O. P. W. Prabowo
& Moh. Abduh,
(2023)
*List of number literature source from indonesian researchers
3.2 Data Analysis
3.2.1 Data Analysis of Observation Results
The data is processed by calculating points based on
an assessment scale which determines the percentage
per sub-element and construction safety management
system (SMKK) element using equation (1).
P = ∑p/(p x n) x 100% (1)
with:
P = percentage
p = points
∑p = total points
n = amount of data
Based on the results of observation data
processing, the percentage of observation data can be
presented on Table 4.
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
440

Table 4: Percentage of Implementation of SMKK
Observation Results.
No.
Criteria
Element/Criteria Percentage
A
Leadership and Workforce
Participation in Construction Safety
98%
B
Construction Safety Planning
95%
C
Construction Safety Support
94%
D
Construction Safety Operations
92%
E
Performance Evaluation of SMKK
Implementation
89%
Average Percentage
93%
The results of the analysis of criterion A
(Leadership and Worker Participation In
Construction Safety) with percentage of 98%,
criterion B (Construction Safety Planning) with
percentage of 95%, criterion C (Construction Safety
Support) with percentage of 94%, criterion D
(Construction Safety Operations) with percentage of
92% and criterion E (Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation) with percentage of 89%.
For those result, identify that criteria E is the smallest
percentage. The value is caused by the construction
safety evaluation has not been carried out because the
project is on early-stage project working.
The processed observation data analyzed based on
the construction safety management system (SMKK)
implementation classification level table which refers
to Government Regulation no.50/2012. The average
percentage of all elements of construction safety
management system (SMKK) implementation in the
observation results was 93%. Based on the
classification level table for construction safety
management system (SMKK) implementation, it was
found that the level of construction safety
management system (SMKK) implementation in the
Coastal Safety Development Project included the
"Satisfactory" classification.
3.2.2 Data Analysis of Questionnaire Results
Analyzing of questionnaire data is based on the
results of distributing questionnaires that have been
carried out referring to Ministry Public Works and
Housing Regulation no.10/2021. Processing
questionnaire data in this research is calculates based
on the questionnaire results assessment scale and
determine the percentage on sub-element and
construction safety management system (SMKK)
element using equation (2).
P = ∑p/(p x n) x 100% (2)
with:
P = percentage
p = points
∑p = total points
n = amount of data
Based on the results of questionnaire data processing,
the percentage of questionnaire data presented on
Table 5.
Table 5: Percentage of Implementation of SMKK
Questionnaire Results.
No.
Criteria
Element/Criteria Percentage
A
Leadership and Workforce
Participation in Construction Safety
100%
B
Construction Safety Planning
97%
C
Construction Safety Support
94%
D
Construction Safety Operations
97%
E
Performance Evaluation of SMKK
Implementation
91%
Average Percentage
96%
Analysis of questionnaire distribution data
identify that criteria A (Leadership and Worker
Participation in Construction Safety) with percentage
of 100%, criteria B (Construction Safety Planning)
with percentage of 97%, criteria C (Construction
Safety Support) with percentage of 94%, criteria D
(Operations Construction Safety) with percentage of
97% and criteria E (Construction Safety Performance
Evaluation) with percentage of 91%. Criteria E which
is the smallest percentage of all acquisitions for each
element. This occurs because a construction safety
evaluation has not been carried out because the work
is only at an early stage.
Based on the table of classification levels for
SMKK implementation which refers to Government
Regulation no.50/2012, the classification level for
SMKK implementation is based on the results of
distributing questionnaires with an average
percentage of 96%, including the "Satisfactory"
classification.
3.2.3 Analysis of Literature Study Data
Based on a literature review that amount of journal
articles included for this study, which aims to review
elements/criteria/aspects that not mentioned in
Ministry Public Works and Housing Regulation
no.10/2021 as a guideline for implementing SMKK.
The total amount of 25 articles were obtained as
material for findings that will be recommended as
amendments Ministry Public Works and Housing
Regulation no.10/2021.
Analysis of the Implementation of SMKK (Construction Safety Management System) Based on the Regulation of the Minister of PUPR
No.10/2021 on the Construction Project of Coastal Safety Development
441
Table 6: Literature Study Data Analysis.
Year
Writer
Element/Criteria
A
B
C
D
E
2018
Abied et al.
*
2018
Dharmayanti et al.
*
*
*
2019
Priyono & Harianto
*
*
*
*
*
2019
Machfudiyanto & Utomo
*
*
*
*
*
2019
Embun Sari Ayu
*
*
*
2020
Steven & Waty
*
*
*
*
*
2020
Ida Yuliana
*
*
*
*
2020
Sutapa et al.
*
*
*
*
*
2020
Ariswa et al.
*
*
2021
Ade Dwi Putra et al.
*
*
*
*
2021
Amin & Bararah
*
*
*
*
2021
Wardhana et al.
*
*
*
*
2021
Fatimah & Zein
*
*
*
*
2021
Nurwildani
*
*
*
*
*
2022
Nanda & Hardianti
*
*
*
2022
M. Afan et al.
*
*
2022
M. Wadipalapa et al.
*
*
*
*
*
2022
Susilowati et al.
*
*
*
*
2022
Anisah et al.
*
*
*
*
*
2022
Habir & Mardianti
*
*
*
*
*
2022
Puspitasari et al.
*
2023
Sinulingga & Dewantoro
*
*
*
2023
Amari & Effendy
*
*
2023
Riswana & Susilawati
*
*
*
2023
Prabowo & Abduh
*
*
Total
17
16
21
18
17
Based on the results of the literature review
identify that the journals reviewed mostly discussed
element C (Work Safety Support). Additionally,
elements obtain as recommendations for amendments
to Ministry Public Works and Housing Regulation
no.10/2021 presented on Table 7.
Table 7: Additional Elements of Literature Study Results.
No
Title
Writer
Element Criteria
1
Kendala Penerapan
Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada
Kontraktor di Bali
G.A.P Candra
Dharmayanti,
dkk (2018)
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Provide sanctions
for workers who do not
comply with construction
safety implementation
2
Implementasi
Kebijakan SMK3
di Perusahaan
Kontraktor di
Yogyakarta
R.A.
Machfudiyanto
dan D.P.
Utomo (2019)
A. Leadership and
Worker Participation in
Construction Safety
A.2.8 Workers can object
to work if the construction
safety policy is doubted
by the worker except in
special cases that can be
accounted for by the
person in charge of the
SMKK management
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Give sanctions to
the project team if work
safety violations occur
3
Peninjauan Sistem
Manajemen
Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada
Proyek Pekerjaan
Pondasi Condotel
Multifungsi
Aston
Padang
Embun Sari
Ayu (2019)
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Provide sanctions
for workers who do not
implement work safety
4
Analisis Penerapan
Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja
(K3) Terhadap
Kinerja Pekerja
Konstruksi
Moh. Midchol
Afan, dkk
(2022)
C. Construction Safety
Support
C.3.3 Educate workers
about the importance of
implementing SMKK
5
Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen
Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada
Proyek Konstruksi
Gedung Kejaksaan
Tinggi Kalimantan
Timur
Habir, dkk
(2022)
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Provide sanctions
for violations of
construction safety
implementation
E.5 Awards
E.5.1 Give
awards/rewards to
workers who always
comply with construction
safety practices
6
Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen
Keselamatan
Konstruksi Dalam
Pandemi Covid
-19
Pada Proyek
Pembangunan
Struktur Atas
Jembatan Progo
Tempuran
-
Salaman
Kasih
Puspitasari,
dkk
(2022)
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Give sanctions if
you violate the provisions
for implementing work
safety
7
Evaluasi
Pelaksanaan
Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) pada
Proyek
Pembangunan
Gedung Bertingkat
di Tanah Lunak
Henry
Wardhana, dkk
(2021)
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Give warnings and
binding sanctions if you
violate the provisions for
implementing work safety
to provide a deterrent
effect
8
Analisis Faktor
-
Faktor Penghambat
Kontraktor dalam
Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen K3
pada Proyek
Konstruksi Gedung
di Palangka Raya
C.M.Br
Sinulingga,
dkk (2023)
E. Construction Safety
Performance Evaluation
E.4 Compliance Sanctions
E.4.1 Provide sanctions
for violations of
construction safety
implementation
E.5 Awards
E.5.1 Give
awards/rewards to
workers who always
comply with construction
safety practices
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
442

Identification from table of additional elements,
implementation the construction safety management
system (SMKK) necessary to impose compliance
sanctions to workers that deterrent effect for workers
avoid implementation the construction safety
management system (SMKK). Provides reward and
award for workers that implement well the
construction safety management system (SMKK).
Apart from that, aspects related to workers have the
right to express objections if construction safety
policies are doubted by workers as well as aspects
related to training workers regarding the importance
of implementing construction safety management
system (SMKK). All these aspects can be considered
to be included in the Ministry Public Works and
Housing Regulation which as policy for construction
safety management system (SMKK) as an effort to
increase the implementation of construction safety
management system (SMKK).
4 CONCLUSIONS
The result of this study conclude has been carried out
to several points.
1. The observation results showed that the
overall classification level of SMKK
implementation was 93% and could be classified
as satisfactory, meaning that the implementation
of SMKK in the Coastal Safety Development
Project was satisfactory and in accordance with all
existing standards and regulations.
2. The results of the questionnaire analysis
identify that the overall classification level for
construction safety management system (SMKK)
implementation was 96% and could be classified
as satisfactory. On the other definition that the
implementation of construction safety
management system (SMKK) in the Coastal
Safety Development Project was satisfactory.
3. The results of a literature study analysis the
total of 25 articles regarding the implementation of
occupational safety and health management
systems in Indonesia. Obtained aspects of the
construction safety management system (SMKK)
implementation elements that recommendation
aspects for amendments to Ministry Public Works
and Housing Regulation number 10, 2021, such as:
- Impose compliance sanctions on workers to
provide a deterrent effect for workers who do not
properly implement the SMKK program.
- Provide rewards for workers who implement the
SMKK program well.
- Workers have the right to objections if the
construction safety policy is doubted by workers.
- Workers coaching on the importance of SMKK
implementation.
4. For the future research can involve more
stakeholders regarding the implementation of
construction safety management system (SMKK)
and SMK3, starting from service users, service
providers, governments, universities, and to obtain
research results and assessments related to more
optimal implementation of SMKK or SMK3.
REFERENCES
Abied, W., Febrita, S., Pudjihardjo, H. S., & Tutuko, B.
(2018). Analisis Penggunaan Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3)
Pada Proyek Pembangunan Rsud Sunan Kalijaga Demak
(Studi Kasus Pada Pembangunan RSUD Sunan Kalijaga
di Demak). Teknika, 13(2), 33–40.
Adiratna, Y., Astono, S., Fertias, M., Subhan, Sugistria, C.
A., Prayitno, H., Khair, R. I., Brando, A., & Putri, B. A.
(2022). Profil Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja
Nasional Indonesia Tahun 2022 (1st ed.). Kementerian
Ketenagakerjaan Republik Indonesia.
Afan, M. M., Riwibowo, N. R., Wijaya, O. D., & Rohman,
M. (2022). Analisis Penerapan Keselamatan Dan
Kesehatan Kerja (K3) Terhadap Kinerja Pekerja Proyek
Konstruksi. Device, 12(2), 144–153.
Amari, A., & Effendy, M. (2023). Analisis Penerapan
Sistem Management Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan
Kerja (SMK3) Pada Proyek Konstruksi Gedung.
Seminar Keinsinyuran Program Studi Program Profesi
Insinyur, 3(1).
Amin, J., & Bararah, K. (2021). Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja. Tameh:
Journal of Civil Engineering, 10(1), 20–27.
Anisah, A., Ramadhan, M. A., & Sofiyanti, A. (2022).
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan Dan
Kesehatan Kerja (Smk3) Pada Masa Pandemi Covid-19
Di Proyek Konstruksi Maritime Tower. Jurnal
Rekayasa Sipil, 18(2), 102–116.
Ariswa, F., Andriani, M., & Irawan, H. (2020). Usulan
Perbaikan Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan
Dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) Pada Perusahaan
Konstruksi Jalan (Studi Kasus: PT Karya Shakila
Group). JISI: Jurnal Integrasi Sistem Industri, 7(2), 91–
100.
Ayu, E. S. (2018). Peninjauan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) Pada
Proyek Pekerjaan Pondasi Condotel Multifungsi Aston
Padang. JURNAL REKAYASA, 8(2), 179–186.
Badaruddin, S., Sulistiawati, R., Hamzah, Z., Bustan, B., &
Zakaria, A. (2022). Studi Faktor-Faktor Dominan
Penerapan Rencana Keselamatan Konstruksi terhadap
Keselamatan Konstruksi pada Proyek Gedung di
Analysis of the Implementation of SMKK (Construction Safety Management System) Based on the Regulation of the Minister of PUPR
No.10/2021 on the Construction Project of Coastal Safety Development
443

Makassar. In Journal of Applied Civil and
Environmental Engineering (Vol. 2, Issue 1).
Dharmayanti, G. A. P. C., & Pramana, G. N. P. S. (2018).
Kendala Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan
dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) pada Kontraktor di Bali.
Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 15(1), 12–18.
Fatimah, A., & Zein, K. C. S. (2021). Evaluasi Penerapan
Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja
pada Proyek Kontruksi di Kota Banda Aceh. Seminar
Nasional Ketekniksipilan, Infrastruktur Dan Industri
Jasa Konstruksi (KIIJK), 1(1), 79–84.
Habir, H., & Mardianti, N. (2022). Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada Proyek Konstruksi Gedung Kejaksaan
Tinggi Kalimantan Timur. DEDIKASI: Jurnal Ilmiah
Sosial, Hukum, Budaya, 23(1), 24–40.
ILO. (n.d.). World Statistic The enormous burden of poor
working conditions. ILO (International Labour
Organization). Retrieved April 13, 2023, from
https://www.ilo.org/moscow/areas-of-work/
occupational-safety-and-health/WCMS_249278/lang--
en/index.htm
Peraturan Menteri Pekerjaan Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat
Nomor 10 Tahun 2021 Tentang Pedoman Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan Konstruksi, Pub. L. No. 10,
Jaringan Dokumentasi dan Informasi Hukum
Kementerian PUPR (2021). https://jdih.pu.go.id/detail-
dokumen/2884/1#div_cari_detail
Machfudiyanto, R. A., & Utomo, D. P. (2019).
Implementasi Kebijakan SMK3 Di Perusahaan
Kontraktor Di Yogyakarta. CivETech, 1(2), 47–56.
Nanda, M. P., & Hardianti, R. (2022). Analisa Penerapan
Sistem Manajemen Kesehatan Dan Keselamatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada PTPN VI di Kecamatan Pangkalan Koto
Baru Sumatera Barat. Jurnal Rekayasa Infrastruktur,
8(2), 29–34.
Nurwildani, F. (2021). Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamataan dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) Di
Fakultas Teknik. Engineering: Jurnal Bidang Teknik,
12(1), 53–64.
OSHA. (n.d.). Design for Construction Safety. OSHA
Aliance Program’s Construction Roundtable and the
Direstorate Cooperative and State Programs. Retrieved
March 30, 2023, from https://www.osha.gov/sites/
default/files/training-library_DfCSInstructorGuide.pdf
Peraturan Pemerintah Republik Indonesia Nomor 50 Tahun
2012 tentang Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan dan Kesehatan Kerja, Pub. L. No. 50,
Jaringan Dokumentasi dan Informasi Hukum Badan
Pemeriksa Keuangan Republik Indonesia (2012).
https://peraturan.bpk.go.id/Home/Details/5263/pp-no-
50-tahun-2012
Prabowo, O. P. W., & Abduh, M. (2023). Pengaruh
Penerapan SMK3 Pada Proyek Konstruksi Terhadap
Kualitas Pekerjaan (Studi Kasus: Proyek Rehabilitasi
Gedung Kantor Kejaksaan Kota Madiun. Seminar
Keinsinyuran Program Studi Program Profesi Insinyur,
3(1).
Priyono, A. F., & Harianto, F. (2020). Analisis penerapan
Sistem Manajemen K3 dan kelengkapan fasilitas K3
pada proyek konstruksi gedung di Surabaya. Rekayasa:
Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 4(2), 11–16.
Puspitasari, K., Susilowati, F., & Jannah, R. M. (2022).
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan Konstruksi
Dalam Pandemi Covid-19 Pada Proyek Pembangunan
Struktur Atas Jembatan Progo Tempuran-Salaman.
Reviews in Civil Engineering, 6(1), 22–31.
Putra, A. D., Syamsuir, E., & Wahyuni, F. I. (2021).
Analisis penerapan kesehatan dan keselamatan kerja
(K3) di perusahaan jasa konstruksi kota payakumbuh.
Rang Teknik Journal, 4(1), 76–82.
Riswana, I., & Susilawati, S. (2023). Evaluasi Penerapan
Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja
(SMK3) Pada Perusahaan Konstruksi. ZAHRA:
Journal of Health and Medical Research, 3(1), 177–183.
Sinulingga, C. M. B., & Dewantoro, D. (2023). Analisis
Faktor-Faktor Penghambat Kontraktor dalam
Penerapan Sistem Manajemen K3 pada Proyek
Konstruksi Gedung di Palangka Raya. Jurnal Serambi
Engineering, 8(1).
Siyoto, S., & Sodik, M. A. (2015). Dasar Metodologi
Penelitian (1st ed.). Literasi Media Publishing.
Steven, S., & Waty, M. (2020). Analisis Penerapan Sistem
Manajemen Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja Pada
Pembangunan Gedung Dan Perumahan. JMTS: Jurnal
Mitra Teknik Sipil, 547–554.
Sugiyono. (2013). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R&D (19th ed.). Alfabeta.
Susilowati, F., Prawenti, H., & Puspitasari, E. (2022).
Kajian Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan Kesehatan
Kerja pada Perusahaan Konstruksi Jalan di Indonesia.
Jurnal Teknik Sipil, 29(2), 189–198.
Sutapa, I. K., Suasira, I. W., Hermawati, P., & Dharma, I.
P. A. S. (2022). Analisis Tingkat Risiko Dan Penerapan
Smk3 Pada Proyek Pembangunan Rumah Sakit Umum
Daerah Mangusada Badung. Jurnal Ilmiah Poli
Rekayasa, 17(1), 25–31.
Wadipalapa, M., Tuloli, M. Y., & Sumaga, A. U. (2022).
Evaluasi Penenerapan Sistem Manajamen Keselamatan
Dan Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) Pada Proyek Konstruksi
Di Provinsi Gorontalo. Jurnal Penelitian Jalan Dan
Jembatan, 2(1).
Wahyuno, E. (2021). Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan Konstruksi Pada Proyek Klasifikasi Kecil
Pasca Diterbitkannya Peraturan Menteri Pekerjaan
Umum dan Perumahan Rakyat Nomor
21/PRT/M/2019. Prosiding CEEDRIMS 2021 Inovasi
Teknologi Dan Material Terbarukan Menuju
Infrastruktur Yang Aman Terhadap Bencana Dan
Ramah Lingkungan, 395–401.
Wardhana, H., Isramaulana, A., & Safitri, R. (2021). Evaluasi
Pelaksanaan Sistem Manajemen Keselamatan dan
Kesehatan Kerja (SMK3) pada Proyek Pembangunan
Gedung Bertingkat di Tanah Lunak. Prosiding Seminar
Nasional Lingkungan Lahan Basah, 6(1).
Yuliana, I. (2021). Analisis Penerapan Sistem Manajemen
Keselamatan Dan Kesehatan Kerja Pada Proyek
Konstruksi Gedung Bertingkat Tinggi. Bearing: Jurnal
Penelitian Dan Kajian Teknik Sipil, 7(1), 16–19.
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
444
