
Design and Construction of a Wave Power Plant in the Coastal
Region of North Jakarta
Didit Sumardiyanto, Sri Endah Susilowati and Kukuh Seno Septyantoro
Faculty of Engineering and Informatics, Universitas 17 Agustus 1945, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Waves, Power Plant, Green Energy.
Abstract: The world is experiencing an energy crisis due to depletion of oil reserves sourced from fossil energy, and
global problems such as international conflict, increasing demand due to changes in lifestyle. The solution is
to switch to renewable energy sources, where Indonesia, with its long coastline, more than 108,000 km, has
great potential as an energy source, especially wave-powered electrical energy. Even though Indonesia's
coastal energy potential is large, its use is still limited because the technology and investment required is quite
large. Further efforts in research and development are needed to optimize utilization. One promising source
of renewable energy is wave energy, where a hydraulic float device has been designed to convert wave
movement into electrical energy through a gear and generator mechanism. This research proves the success
of this device, producing electrical power variations from 10.92 to 35.52 watts.
1 INTRODUCTION
The global issue of energy supply shortages, caused
by various factors such as oil depletion, international
conflicts, and growth in energy demand due to
changes in lifestyle, drives the importance of
switching to renewable energy sources. This effort
not only addresses the current energy crisis, but also
prepares for the future by optimizing available natural
resources. Various types of renewable energy such as
wind, solar and geothermal energy have great
potential without major negative impacts, but
technological development and research are needed
for sustainable energy generation systems.
Indonesia has great potential in coastal energy
through a coastline of 95,181 km and a water area of
58 million square km (71% of the total area), but
development requires large efforts and costs. North
Jakarta, in DKI Jakarta, offers the potential for energy
utilization beach with a coastline of around 60 km and
an area of around 5,000 hectares, needs further
research (Lilly Aprilya Pregiwati, 2019).
Ocean waves have great potential as a source of
renewable energy. Even though Ocean Waves Power
Plants ”Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Ombak” (PLTO)
Produces lower power than Solar Power Plants/
“Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Surya” (PLTS), the
author's effort is to utilize this innovative potential to
meet electricity needs in the coastal communities of
North Jakarta in the future.
The float type PLTO is suitable for the coast of
North Jakarta because of its accessibility and
avoiding corrosive problems. The hydraulic system
converts the float's movement into electrical energy
through the push of waves. In this final project, the
author will develop this method with the latest
models, aiming to increase electrical efficiency
through various tool models.
The process for converting wave energy from
ocean waves shows variations in peak height, but
statistically significant ocean wave heights can still be
identified at certain locations. Utilization of ocean
current energy has environmental advantages and
high kinetic energy. Due to the greater density of
seawater, it produces compact ocean current turbines.
Utilization of ocean current energy has weaknesses
related to sinusoidal wave patterns due to complex
tidal fluctuations. At full moon tide, strong currents
flow, while at neap tide, the speed decreases. Another
challenge is the high cost of device installation and
maintenance. The working principle involves
collecting ocean wave energy to drive a generator
turbine.
Sumardiyanto, D., Susilowati, S. and Septyantoro, K.
Design and Construction of a Wave Power Plant in the Coastal Region of North Jakarta.
DOI: 10.5220/0012584500003821
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023), pages 445-448
ISBN: 978-989-758-691-0; ISSN: 2828-853X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
445

Anaconda Bulge Wave System
The movement of sea waves is used to fill flexible
tubes measuring 6-15 meters with a length of 150
meters. As the wave rises, water enters through the
valve, the fan with the change of wave, the tube
continues to fill and the pressure increases at the back
due to the swelling effect. A rear hydraulic system,
connected to an electric motor, operates this process
according to the height and speed of the wave and the
dimensions of the tube. Similar to the peristaltic
movement of human digestion.
Oyster Hydraulic Piston System
The hydraulic system is connected to the piston,
converting ocean wave energy into piston movement.
This movement is used to lift water into the high
pressure channel. Water is channeled through the
channel to a hydroelectric generator, producing
electrical energy. One of the main technologies today
is a device called "oyster" by the company
Aquamarine Power Ltd. Worldwide, the potential use
of hydraulic pistons is estimated to reach around 60
gigawatts (GW).
Pelamis System Attenuator
Oyster Hydraulic Piston System. The hydraulic
system is connected to the piston, converting ocean
wave energy into piston movement. This movement
is used to lift air into the high pressure channel. Air is
fed through these channels to a hydroelectric
generator, producing electrical energy. One of the
main technologies today is a device called "oyster" by
the company Aquamarine Power Ltd. Worldwide, the
potential use of hydraulic pistons is estimated at
around 60 gigawatts (GW).
Pelamis Attenuator System
Attenuators are formed by wave elements floating in
parallel, generating energy through the movement of
their interactions. This moves hydraulic components in
the tube, driving an electric generator like on the
Pelamis. The pelamis moves vertically and laterally,
consists of at least three segments, 500 meters long,
tube diameter 3 meters. Studies show that Pelamis is
180 meters long, 4 meters in diameter, at a depth of 50
meters, producing 750 Kw of electrical energy. The
movement of the waves flexes the Pelamis Structure,
utilized through a hydraulic take-off system that can
lengthen/contract, producing electricity that is
channeled through underground cables.
Oscillating Water Column
A Wave Power Plant (PLTO) with a Wave-Wind
(OWC) design produces energy from fluctuations in
air pressure in a container due to wave movement.
These fluctuations drive the wind turbine through
compressed air after passing through the control
valve. This turbine is connected to a generator and
converts movement into electrical energy.
Archimedes Wave Swing System
AWS uses Archimedes' concept to divide objects in
water into 3 categories: floating, floating, and
sinking. The movement of wave height variations is
converted into vertical movement. Inside the tube,
there is a stator and rotor. The stator is attached to the
seabed, while the rotor connected to the tube moves
up and down with the rhythm of the waves. Although
it is being tested in Europe and the United States,
AWS production costs tend to be higher than other
PLTO systems, limiting its widespread use.
Wave Dragon
Wave Dragon operates by collecting sea waves in
open water and channeling them into a pool. In the
pool, there is a water turbine with a low fall height.
The flow of water from the pool drives a water
turbine, converting the movement of water into
energy. In 2009, the first trial of Wave Dragon was
carried out in Nissum Bredning, Denmark,
successfully installing Wave Dragon with a capacity
of 7 MW (A. Hasnan, et al., 2010).
1.1 Freewheel
It is a sprocket that has a locked direction of rotation,
meaning that in a certain direction the shaft and the
driver move simultaneously, but if the direction of the
drive is opposite, the shaft continues to rotate in the
original direction so that it rotates freely.
Figure 1: Freewheel.
The main advantage of freewheels is that they are
more economical than freehubs (W. Dian, 2011).
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
446
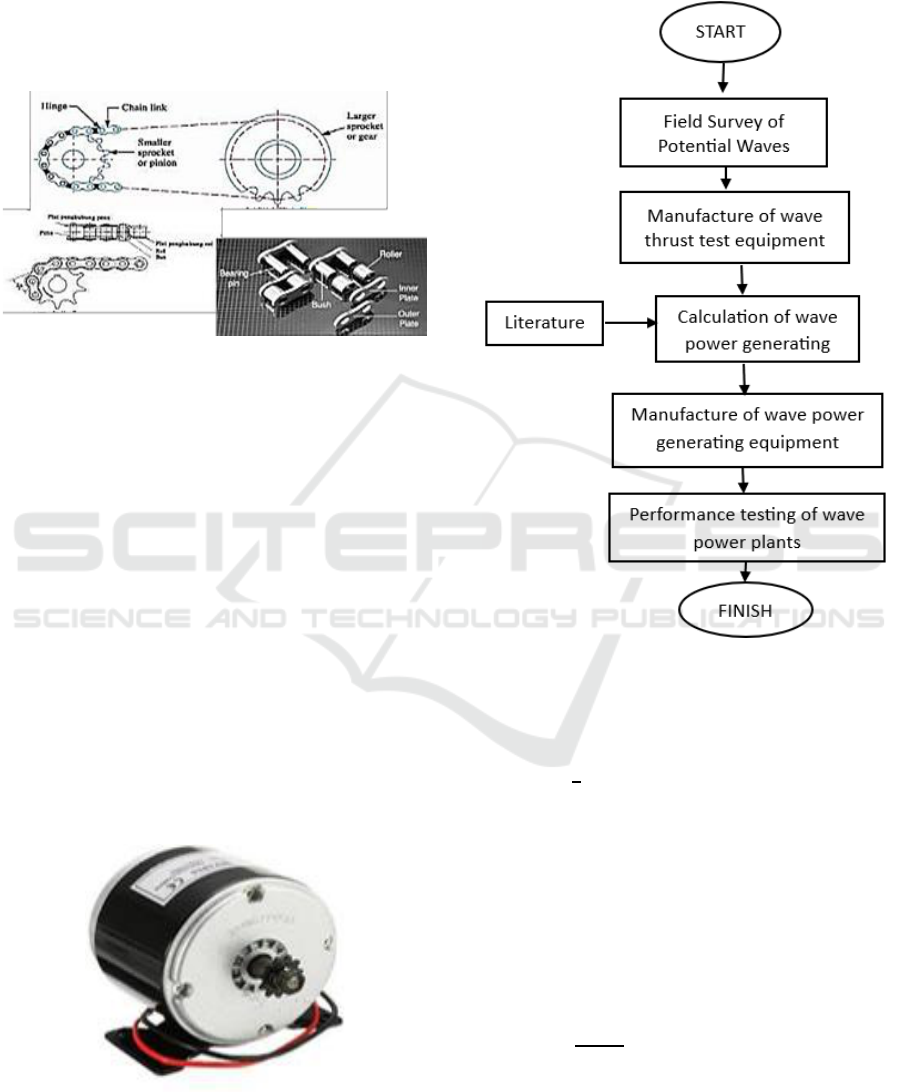
1.2 Chain Transmission
Transmission has an important role in transferring
power from one drive axle to the driven axle. Apart
from being able to transmit relatively large amounts
of power, chain transmissions also have a high service
life.
Figure 2: Chain transmission.
Chain transmission allows the flow of strong Pull
force. When transferring energy from the rotating
shaft, the chain interacts with the sprocket gears.
Although suitable for long distance travel, this system
is more efficient in transmitting power without losing
power due to friction compared to belt and pulley
systems. However, it is not ideal for high speeds and
can produce significant vibration (K. Sularso & Suga,
1991).
1.3 Generator
A generator is a dynamic machine device that
converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The function of the generator is based on the principle
of electromagnetic induction, where the rotating
movement of the coil in a magnetic field results in the
generation of electrical energy (M. H. Johanda,
2017).
Figure 3: Generator.
2 DESIGN AND BUILD
METHODOLOGY
Figure 4: Design process flow.
Basic Theory of Calculation
Pressure: (p)
F = p x A
Explanation:
F: Force (N)
A: Area (cm
2
)
Torsion (T, N.m)
Power (N, kW)
Power in electric unit
Watt = 0.85 x Ampere x Volt
Design and Construction of a Wave Power Plant in the Coastal Region of North Jakarta
447

Figure 5: Shop drawing.
3 TEST RESULT
From the test results, it was recorded that the lowest
power that could be produced was 10.92 watts at
13.00, while the highest peak power occurred at 16.00
with 35.52 watts. The average power produced was
25.35 watts. At the initial design calculation stage, the
average power anticipated to be generated by the
device was approximately 42 watts. However, there
are several factors that influence the difference
between power calculations at the design stage and
equipment testing results. Some of these factors
include float characteristics, swing arm design, drive
gear properties, pillow block bearing performance,
axle performance, gear and chain efficiency, as well
as the influence of natural elements such as wind
speed, wave movement and solar radiation.
REFERENCE
Lilly Aprilya Pregiwati, “Laut Masa Depan Bangsa Mari
Jaga Bersama,” Kementrian Kelautan dan Perikanan,
2019.
A. Hasnan, Pengenalan Potensi Arus Laut Sebagai Energi
Terbarukan Dan Berkelanjutan Di Indonesia”, 2010.
W. Dian, “Universitas Kristen Petra Surabaya,” Dimens.
Inter., vol. 8, no. 1, pp. 44–51, 2011, [Online].
Available: publication.petra.ac.id/ index.php/sastra-
tionghoa/article/view/121
K. Sularso & Suga, “Dasar-Dasar Perencanaan Dan
Pemilihan Elemen Mesin,” Jakarta: Pradnya
Paramita, 1991.
M. H. Johanda, “Pengaruh Pembebanan Terhadap
Temperatur Stator Generator Sinkron pada PLTU
Pelabuhan Ratu,” Universitas Sumatera Utara, 2017.
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
448
