
Comparing Novel Recurrent Neural Networks with Artificial Neural
Networks for Predicting Mental Depression from Online Video
Gaming
P. Sampath Lakshmi and S. Kalaiarasi
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Saveetha School of Engineering, Saveetha Institute of Medical and
Technical Sciences, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, 602105, India
Keywords: Artificial Neural Network, Disability, Mental Depression, Online Gaming Novel Recurrent Neural Network,
Internet.
Abstract: The aim of this research was to enhance the accuracy in predicting mental depression in online gamers using
the Novel Recurrent Neural Network, juxtaposed against the Artificial Neural Network algorithms. Data,
sourced from various online platforms and supplemented with recent research findings, was scrutinised with
a 95% confidence interval for mean and standard deviation, iterating the process 20 times. The Novel
Recurrent Neural Network proved more accurate with a 94% precision rate, as opposed to the Artificial Neural
Network's 91%. An Independent Sample T-test further corroborated the significant disparity in predictive
abilities between the two, highlighted by a p-value of 0.00 (p<0.05). In conclusion, within the set constraints,
the Novel Recurrent Neural Network offers a superior predictive capability for mental depression in online
gamers.
1 INTRODUCTION
The auditor's primary consideration is determining
the high level of authenticity of mental depression in
online gaming (Gackenbach and Brown 2017;
Mamun et al. 2022). The analysis of mental
depression caused by online gaming involves
conducting experiments on various examples and
with different individuals (Fazeli et al. 2020). This
study utilises MATLAB source code and multiple
samples for each participant. Predictions can be made
for bipolar disorder, persistent depressive disorder,
and major depressive disorder, among other forms of
depression (Maruta, Nazarchuk, and Denysenko
2015; Irie et al. 2022). Whilst the precise origin of
depression remains elusive, it results from a
combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Depression is typically addressed through a blend of
treatments, medications, and lifestyle adjustments.
This research draws upon 1700 articles related to
the identification of mental depression or disability,
including 350 from IEEE Xplore, 100 from
Researchgate, 900 from Google Scholar, 200 from
Hindawi, and 150 from Elsevier (Mun and Lee 2021;
AS, Vickram et al. 2013). It's vital to seek help if
experiencing depressive symptoms. Depression is a
treatable condition, and with proper care, most
individuals can alleviate their symptoms and lead
fulfilling lives (Jung, Yi, and JeongDongJin 2018). If
you suspect you might be suffering from depression,
it's essential to consult a medical professional or
mental health specialist to secure an accurate
diagnosis and treatment plan (Bonnaire and Baptista
2019). If either you or someone you know is
grappling with depression, seeking assistance from a
trusted source or mental health expert is imperative
(Dias, Barbosa, and Vianna 2018; G.R et al 2014).
Table 1: Accuracy values for novel recurrent neural
network and artificial neural network.
S NO
Novel Recurrent Neural
Network
Artificial Neural
Network
1
92.02
88.94
2
92.74
89.17
3
93.39
89.77
4
93.94
90.07
5
94.87
90.46
6
95.54
91.38
7
95.85
91.92
8
96.28
92.62
9
96.93
92.85
10
97.27
93.30
128
Lakshmi, P. and Kalaiarasi, S.
Comparing Novel Recurrent Neural Networks with Artificial Neural Networks for Predicting Mental Depression from Online Video Gaming.
DOI: 10.5220/0012598700003739
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of Things: Accelerating Innovation in Industry and Consumer Electronics (AI4IoT 2023), pages 128-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-661-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

The survey identified a gap in research. Although
many methods for detecting mental depression or
disability exist, most have limited success rates. The
aim of this study is to enhance the accuracy of mental
depression detection by employing both Novel
Recurrent Neural Networks and Artificial Neural
Networks algorithms.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
NOVEL RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS
A Novel Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) operates
on the principle of retaining memory from previous
stages. Imagine trying to predict the next word in a
sequence without knowing the preceding context; it
would be quite tricky. Accurate predictions hinge on
this context. Traditional neural networks often
operate under the assumption that inputs and outputs
are entirely separate entities. However, in many real-
world scenarios, this isn't the case.
To address this, RNNs were introduced. Central
to the RNN's design is the Hidden Layer, which plays
a pivotal role in overcoming this challenge. The
hidden state, intrinsic to the Novel RNN, stands out
as its most defining characteristic, pivotal for
retaining sequential information.
Procedure
Step 1: Load a dataset comprising a collection of job
adverts.
Step 2: Carry out pre-processing on the dataset to
cleanse and ready the data for analysis.
Step 3: Extract a set of features from the pre-
processed dataset.
Step 4: Choose a classification algorithm and use it to
categorise the job adverts based on the extracted
features.
Step 5: Determine the accuracy of the classification
algorithm by assessing its performance on ten
randomly selected samples from the dataset.
2.1 Artificial Neural Networks
Artificial neural networks have garnered interest as a
potential diagnostic and therapeutic tool for
predicting mental illnesses, including depression.
Given their capacity to manage and analyse vast
amounts of data, such as patient details and various
clinical data, Artificial Neural Networks are aptly
suited for this purpose. One application of Artificial
Neural Networks in the realm of mental health is
predicting a patient's likelihood of developing
depression. For instance, a study utilising Artificial
Neural Networks to assess data from a large patient
cohort, as published by the Journal of Affective
Disorders, found that the algorithm was remarkably
precise in predicting the onset of depression or
disability.
2.1.1 Procedure
Step 1: Define the input and output datasets for the
neural network.
Step 2: Pre-process the data.
Step 3: Initialise the weights and bias for the artificial
neural network.
Step 4: Iterate over the training data.
Step 5: Test the Artificial Neural Network on the
dataset to assess its performance.
Step 6: Generate accuracy values for ten samples.
Table 2: Group statistics displaying the mean and standard
deviation were 94% and 1.79858, 91% and 1.58348
respectively.
GROUP NAME
N
Mean
Standard
Deviation
Standard Error
Mean
Accuracy
Novel Recurrent
Neural Networks
10
94.88.
1.79
.56
Artificial Neural
Networks
10
91.04
1.58
.50
2.1.2 Statistical Analysis
The study examined independent variables associated
with online gaming disorders. The dependent
variables in this context are accuracy, game hours,
and platform. Among the independent variables are
the search for excitement and basic psychological
needs. The results of the novel recurrent neural
network were compared with those of the artificial
neural network using the t-test (Mun and Lee 2021).
3 RESULTS
Table 1 provides a comparison of accuracy between
an artificial neural network and a novel recurrent
neural network classifier. Table 2 displays the mean
and standard deviation for the accuracy of the
Artificial Neural Networks and Novel Recurrent
Neural Networks algorithms, which stood at 94%
with a deviation of 1.79858, and 91% with a deviation
of 1.58348, respectively. The Artificial Neural
Networks demonstrated a smaller standard error of
.50074 in comparison to the Novel Recurrent Neural
Networks. The independent sample t-tests indicate a
significant difference in accuracy between the two
Comparing Novel Recurrent Neural Networks with Artificial Neural Networks for Predicting Mental Depression from Online Video Gaming
129
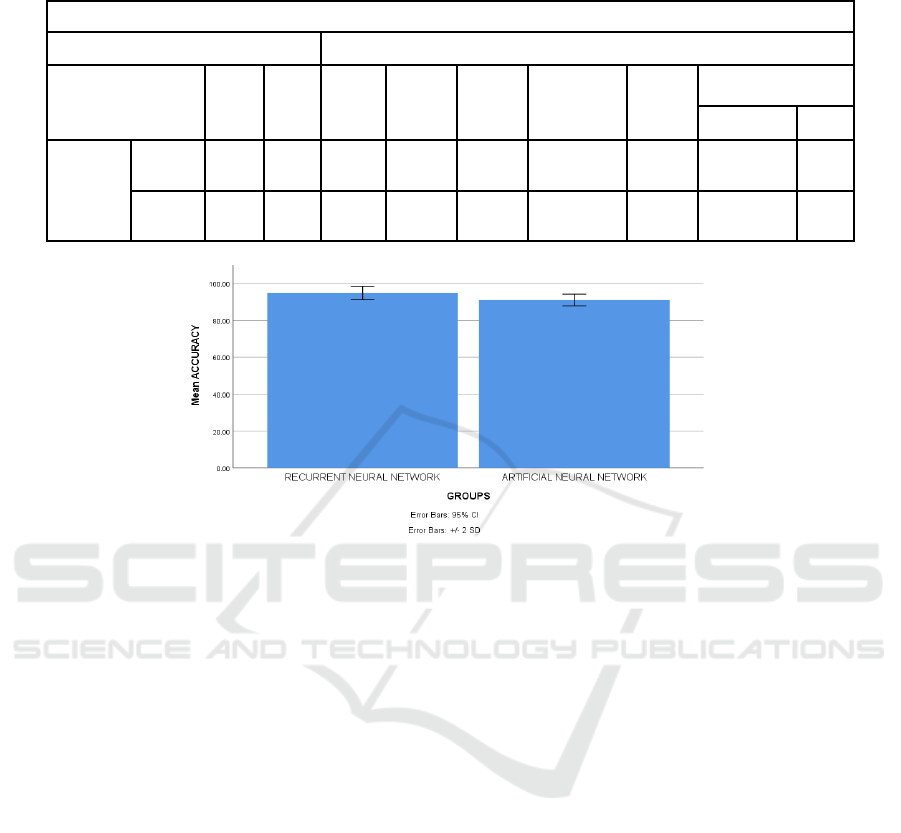
Table 3: The independent sample test revealed a substantial variation in accuracy among the suggested two stages and the
standard single stage. Since P=0.000 and p<0.05, there is a substantial variation between the two methods.
Independent Sample Test
Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances
T-test for Equality of Means
F
Sig.
T
Df
Sig. (2-
tailed)
Mean Difference
Std. Error
Differences
95% Confidence Interval
of the Difference
Lower
Upper
Accuracy
Equal
Variances
assumed
.13
722
5.06
18
0.0
3.83
.75
2.24
5.4
Equal
Variances
not assumed
5.06
17.71
0.0
3.83
.75
2.24
5.4
Figure 1: Mean accuracy comparison of novel recurrent neural network (94%) and artificial neural network (91%) on online
gaming mental disorder identification. X-axis represents novel recurrent neural network and artificial neural network; Y-axis
represents mean accuracy ± 2 SD.
techniques. Table 3 underscores that the independent
sample test showcased a notable difference in
accuracy between the proposed two-stage approach
and the conventional single stage. Given that P=
0.000 (p<0.05), there exists a significant difference
between the two techniques.
Figure 1 depicts the mean accuracy results derived
from the artificial neural network method and the
proposed input relative to the selected input. The title
of the graph reads: "Diagnosing mental illnesses in
online gamers: A comparison of the mean accuracy
of artificial neural networks versus innovative
recurrent neural networks". The proposed technique
achieved a mean accuracy of 94%, surpassing the
91% accuracy of the artificial neural network. The X-
axis signifies accuracy while the Y-axis illustrates
mean accuracy ± 2SD.
4 DISCUSSION
From the tests, it's evident that the Novel Recurrent
Neural Networks algorithm outperformed the
Artificial Neural Networks. Accuracy was measured
using the SPSS tool for both the Novel Recurrent
Neural Networks and the Artificial Neural Networks.
The results for mental depression or disability in the
dataset indicated that the Novel Recurrent Neural
Network achieved an accuracy of 94%, which is
better than the 91% achieved by the Artificial Neural
Networks.
The focus of this study is the exploration of the
correlation between young adults' use of social media
and their mental well-being. Recent studies have
identified a connection between increased social
media engagement and declining mental health. This
link is particularly alarming given that young adults,
the most frequent users of social media, face an
unusually high risk of mental health challenges. This
dissertation delves into both individual and societal
theories that could elucidate the still enigmatic
relationship between social media engagement and
mental health. It examines the impact of social media
on personal relationships, inappropriate behaviour,
sleep disruption due to exposure to blue light, the
influence of social media on children, and the
repercussions of sedentary behaviour on mental well-
being.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
130

Online gaming is associated with an elevated risk
of mental disorders, including depression. Both
Novel Recurrent Neural Networks and Artificial
Neural Networks are recent subjects of research as
promising tools for predicting and addressing the
adverse effects of online gaming on mental health
(Paulus et al. 2018). One potential application of
Artificial Neural Networks and Novel Recurrent
Neural Networks in this realm is to predict a gamer's
probability of developing depression based on their
gaming patterns and other factors (Biolcati, Pupi, and
Mancini 2021). The Novel Recurrent Neural
Networks, a subtype of Artificial Neural Networks, is
adept at analysing a player's in-game behaviour over
time since it excels in handling sequential data
(Hussain and Griffiths 2009).
Another possible application of Artificial Neural
Networks and Novel Recurrent Neural Networks in
the domain of online gaming and mental health is to
identify early indicators of potential problems
(Hussain and Griffiths 2009; Mancini, Imperato, and
Sibilla 2019; Jung, Yi, and JeongDongJin 2018). In
summary, Artificial Neural Networks and Novel
Recurrent Neural Networks possess the unique
capability to serve as potent tools for predicting and
mitigating the negative effects of online gaming on
mental health. However, further research is vital to
fully understand their potential and limitations in this
context (Jung, Yi, and JeongDongJin 2018).
Moreover, due to lockdowns and the subsequent
disruptions to work and education, individuals might
have excess leisure time, or they might find
themselves more easily distracted by online gaming
while working from home. Additionally, diverse
connections were observed between gamers'
motivations for playing and their choice of game
genres in relation to their psychological well-being.
Notably, those motivated by distraction and action
game enthusiasts displayed the most pronounced
effects. Further studies are essential to ascertain
whether these threats to mental health are caused by
or a consequence of video gaming.
5 CONCLUSION
The study at hand sought to utilise cutting-edge
machine learning methods to forecast mental
depression among online video game players. The
findings revealed that the Novel Recurrent Neural
Network algorithm notched an accuracy of 94%,
while its counterpart, the Artificial Neural Network
algorithm, achieved a slightly lower rate of 91%. In
juxtaposing the two, the Novel Recurrent Neural
Network algorithm exhibited superior performance in
the accuracy domain over the Artificial Neural
Network algorithm, with a mean accuracy difference
of 3.83500 between them. Delving deeper into the
research paper, it was accentuated that the Novel
Recurrent Neural Network algorithm, in the context
of predicting mental depression amongst online
gamers, surpasses the Artificial Neural Network
algorithm. Such results underscore the significance of
progressive machine learning methods, with special
emphasis on the Novel Recurrent Neural Network
algorithm, as promising tools for pinpointing and
addressing mental health challenges tied to online
gaming.
REFERENCES
AS, Vickram, Raja Das, Srinivas MS, Kamini A. Rao, and
Sridharan TB. "Prediction of Zn concentration in
human seminal plasma of Normospermia samples by
Artificial Neural Networks (ANN)." Journal of assisted
reproduction and genetics 30 (2013): 453-459.
Biolcati, Roberta, Virginia Pupi, and Giacomo Mancini.
2021. “Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing
Game (MMORPG) Player Profiles: Exploring Player’s
Motives Predicting Internet Addiction Disorder.”
International Journal of High Risk Behaviors and
Addiction. https://doi.org/10.5812/ijhrba.107530.
Blasi, Maria Di, Maria Di Blasi, Alessandro Giardina,
Cecilia Giordano, Gianluca Lo Coco, Crispino Tosto,
Joel Billieux, and Adriano Schimmenti. 2019.
“Problematic Video Game Use as an Emotional Coping
Strategy: Evidence from a Sample of MMORPG
Gamers.” Journal of Behavioral Addictions.
https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.8.2019.02.
Bonnaire, Céline, and Darlèn Baptista. 2019. “Internet
Gaming Disorder in Male and Female Young Adults:
The Role of Alexithymia, Depression, Anxiety and
Gaming Type.” Psychiatry Research 272 (February):
521–30.
Dias, Lucas Pfeiffer Salomão, Jorge Luis Victória Barbosa,
and Henrique Damasceno Vianna. 2018. “Gamification
and Serious Games in Depression Care: A Systematic
Mapping Study.” Telematics and Informatics.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tele.2017.11.002.
Fazeli, Sara, Isa Mohammadi Zeidi, Chung-Ying Lin,
Peyman Namdar, Mark D. Griffiths, Daniel Kwasi
Ahorsu, and Amir H. Pakpour. 2020. “Depression,
Anxiety, and Stress Mediate the Associations between
Internet Gaming Disorder, Insomnia, and Quality of
Life during the COVID-19 Outbreak.” Addictive
Behaviors Reports 12 (December): 100307.
Gackenbach, Jayne, and Johnathan Bown. 2017.
Boundaries of Self and Reality Online: Implications of
Digitally Constructed Realities. Academic Press.
G. Ramkumar and M. Manikandan, "Uncompressed digital
video watermarking using stationary wavelet
Comparing Novel Recurrent Neural Networks with Artificial Neural Networks for Predicting Mental Depression from Online Video Gaming
131

transform," 2014 IEEE International Conference on
Advanced Communications, Control and Computing
Technologies, Ramanathapuram, India, 2014, pp. 1252-
1258, doi: 10.1109/ICACCCT.2014.7019299.
Hussain, Zaheer, and Mark D. Griffiths. 2009. “Excessive
Use of Massively Multi-Player Online Role-Playing
Games: A Pilot Study.” International Journal of Mental
Health and Addiction. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-
009-9202-8.
Irie, Tomonari, Hiroki Shinkawa, Masanori Tanaka, and
Kengo Yokomitsu. 2022. “Online-Gaming and Mental
Health: Loot Boxes and in-Game Purchases Are
Related to Problematic Online Gaming and Depression
in Adolescents.” Current Psychology.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03157-0.
Jung, Kyeo-Woon, Inhyae Yi, and JeongDongJin. 2018.
“Effect of Gaming Motivation on Internet Gaming
Addiction in Massively Multiplayer Online Role
Playing Game (MMORPG) Users: Mediating Effects of
In-Game Behavior.” Korean Journal of Health
Psychology.
https://doi.org/10.17315/kjhp.2018.23.2.013.
Kishore Kumar, M. Aeri, A. Grover, J. Agarwal, P. Kumar,
and T. Raghu, “Secured supply chain management
system for fisheries through IoT,” Meas. Sensors, vol.
25, no. August 2022, p. 100632, 2023, doi:
10.1016/j.measen.2022.100632.
Mamun, Mohammed A., Irfan Ullah, Norina Usman, and
Mark D. Griffiths. 2022. “PUBG-Related Suicides
during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Three Cases from
Pakistan.” Perspectives in Psychiatric Care 58 (2): 877–
79.
Mancini, Tiziana, Chiara Imperato, and Federica Sibilla.
2019. “Does Avatar’s Character and Emotional Bond
Expose to Gaming Addiction? Two Studies on Virtual
Self-Discrepancy, Avatar Identification and Gaming
Addiction in Massively Multiplayer Online Role-
Playing Game Players.” Computers in Human
Behavior. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.11.007.
Maruta, N., O. Nazarchuk, and M. Denysenko. 2015. “The
Typology of Depressions with Comorbid Other Mental
Disorders.” European Psychiatry.
https://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-9338(15)32018-6.
Mun, Il Bong, and Seyoung Lee. 2021. “The Influence of
Parents’ Depression on Children’s Online Gaming
Addiction: Testing the Mediating Effects of Intrusive
Parenting and Social Motivation on Children’s Online
Gaming Behavior.” Current Psychology.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-01854-w.
Paulus, Frank W., Susanne Ohmann, Alexander von
Gontard, and Christian Popow. 2018. “Internet Gaming
Disorder in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic
Review.” Developmental Medicine and Child
Neurology 60 (7): 645–59.
V. P. Parandhaman, "An Automated Efficient and Robust
Scheme in Payment Protocol Using the Internet of
Things," 2023 Eighth International Conference on
Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics
(ICONSTEM), Chennai, India, 2023, pp. 1-5, doi:
10.1109/ICONSTEM56934.2023.10142797.
Yuan, Kai, Ping Cheng, Tao Dong, Yanzhi Bi, Lihong
Xing, Dahua Yu, Limei Zhao, et al. 2013. “Cortical
Thickness Abnormalities in Late Adolescence with
Online Gaming Addiction.” PloS One 8 (1): e53055.
Yuan, Kai, Chen Wang Jin, Ping Cheng, Xuejuan Yang,
Tao Dong, Yanzhi Bi, Lihong Xing, et al. 2013.
“Amplitude of Low Frequency Fluctuation
Abnormalities in Adolescents with Online Gaming
Addiction.” PloS One 8 (11): e78708.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
132
