
Blockchain Based Outsourced Storage Schema in Untrusted
Environment
N Pandi Venkatesh
*
and R Gunasundari
†
Department of MCA, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Coimbatore, India
Keywords: Unsupervised Label Refinement (ULR), Search-Based Face Annotation (SBFA), Content-Based Image
Retrieval (CBIR), Clustering-Based Approximation (CBA).
Abstract: Data outsourcing, a crucial service offered by the cloud service provider (CSP), can assist the data owner
(DO) in overcoming large data's storage constraints. Typically, DOs utilise third-party metadata management
(TPMM) to manage the data link and outsource data replication to many CSPs (multiple CSPs) to ensure data
availability. However, in the process of outsourcing, it is difficult for DO to ensure the reliability of TPMM,
and TPMM will do something bad to affect the reliability of information. Therefore, due to an over-reliance
on TPMMs that are only semi-trusted for managing replication metadata, DO invariably experiences data
security concerns. In this study, we concentrate on the issue of displaying multiple CSP credentials in an
untrusted environment, i.e., how to store and examine the duplicated data's metadata in a multi-trust CSP
environment. In response to this problem, we created a reliable outsourcing service platform using the new
blockchain technology as a tool. In addition, we have considered all new features such as blockchain
decentralized architecture, redundant storage, aggregation and non-tamper to ensure that data cannot be
negatively altered. First, we developed a blockchain-based outsourcing service to store recycled data in an
unreliable environment, We develop a new concept of Validation Node (VP) to manage the data by a copy of
the blockchain, and each local saves the entire blockchain to prevent metadata damage. We offer a
collaborative method suggested by VPs to store and analyse the replicated metadata. We finished the analysis
and thoroughly tested all the CSP situations. Our strategy was the most effective, according test findings.
1 INTRODUCTION
Unique The key outsourced data services' success is
that CSP can provide dispersed techniques to provide
"horizonless" storehouse capacity for data proprietors
(DO), allowing them to get around the difficulties of
storing large amounts of data while also lowering
their physical and financial costs. Still, since DO
cannot guarantee the CSP's reliability when using the
outsourced data services, The reliability of handling
the data through a single CSP may be questioned.
Unique If the services are unexpectedly stopped or
suspended by an unreliable CSP, DO will specifically
run into several challenging problems as data
movement, data error, and sequestration exposure A
distinct To increase the reliability of outsourced data
services, it would appear to be simple as maintain
these data independently. Unique Additionally, DO
can obtainEven yet, this naive outcome is constrained
*
PG Scholar
†
Professor & Head
and unreliable for the reasons listed below. Unique In
order to guarantee the density of all., DO must first
maintain distinct dispatches with each CSP. Unique
As an alternative, DO must control each replication's
metadata to prevent unauthorised access to the
outsourced data's physical address. Reproduced In the
end, DO is unable to determine whether replication
metadata created by several CSPs has been
maliciously altered or falsified. Compare Unique
Blockchain, the technology that underpins
cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, is seen
as a disruptive creative area of computing knowledge.
Unique Decentralisation, redundant storage,
collaborative conservation, and tamper resistance are
some of the characteristics of blockchain. It is
comparable to a distributed database that is managed
by a number of peers that don't completely trust one
another. Blockchain's capacity to save and exchange
in data without the requirement.
Venkatesh, N. and Gunasundari, R.
Blockchain Based Outsourced Storage Schema in Untrusted Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0012611600003739
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of Things: Accelerating Innovation in Industry and Consumer Electronics (AI4IoT 2023), pages 221-226
ISBN: 978-989-758-661-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
221
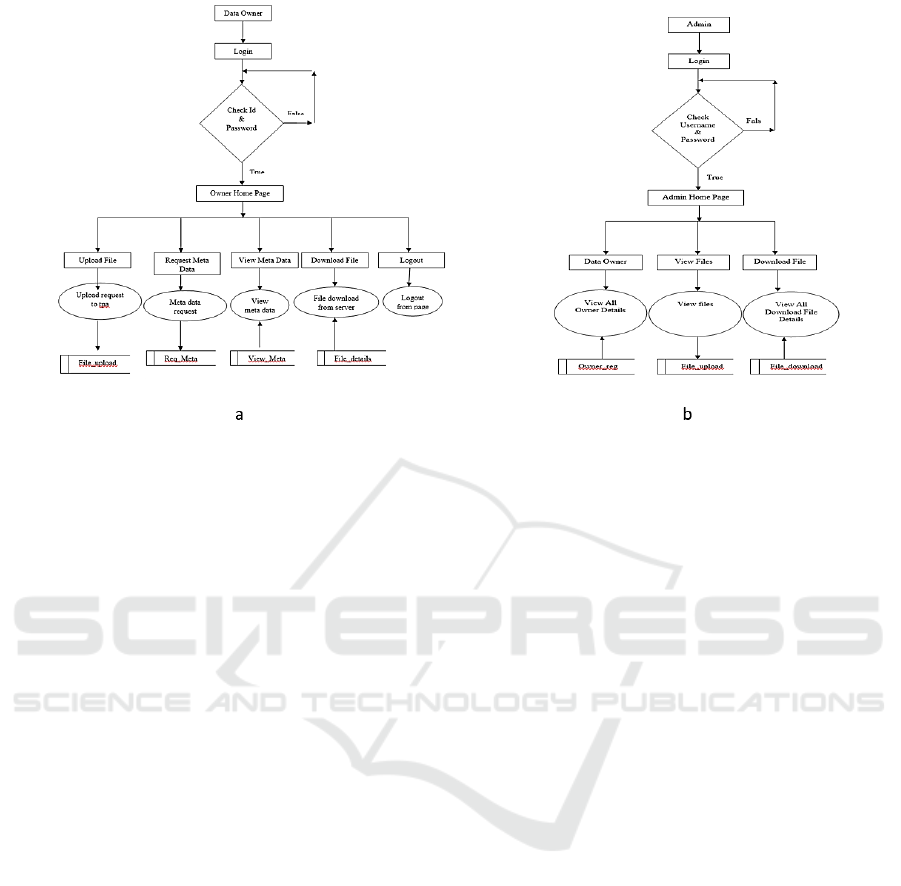
Figure 1: (a) Working diagram of Data owner login (b) Admin login.
2 REVIEW OF LITERATURE
A. Overview of outsourced storage and security
concerns One of the primary security concerns
associated with outsourced storage is data
confidentiality. This can occur due to the failure to
implement proper access controls or as a result of
malicious attacks, such as hacking or phishing. To
mitigate this risk, Techniques like encryption can be
used to keep data private.
Another security concern associated with
outsourced storage is data integrity. This can occur
due to technical errors, as well as malicious attacks.
To ensure data integrity, techniques such as
checksums and digital signatures can be used to
detect unauthorized modifications to data.
Additionally, backups and redundancy can be used to
prevent data loss due to technical failures or disasters.
Finally, availability of data is also a security
concern in outsourced storage. If the third-party
server hosting the data becomes unavailable or
experiences downtime, it can result in the
unavailability of data to authorized users.
In summary, outsourced storage provides many
benefits in terms of cost and accessibility, but it also
introduces several security concerns that need to be
addressed. Techniques such as encryption, access
control, data integrity checks, redundancy, and
disaster recovery can be used to mitigate.
B. Performance Evaluation of Block-Based
Outsourced Storage Solutions:
Latency: This measures the time it takes to retrieve a
block of data from the storage system.
Throughput: This calculates the volume of data
that can be moved to and from the storage system in
a specific amount of time. For applications like big
data analytics that need to process a lot of data
quickly, high throughput is ideal.
IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second)
measures how many input/output operations the
storage system is capable of handling in a second. For
applications like databases that need quick data
access, high IOPS are preferred.
Data transfer speed:This is used to measure the
speed of data transfer to and from the storage system.
High data transfer speeds are desirable for
applications that require fast data transfer, such as
multimedia streaming.
Scalability: This measures the ability of the
storage system to scale up or down to accommodate
changing workloads. High scalability is desirable for
applications that require flexible storage solutions.
Availability: This measures the percentage of
time that the storage system is available for use. High
availability is desirable for applications that require
continuous data access, such as mission-critical
applications.
To evaluate the performance of block-based
outsourced storage solutions, organizations can
conduct benchmark tests using standardized
performance testing tools and methodologies. These
tests can help identify bottlenecks and performance
issues, as well as provide insights into the optimal
configuration and tuning of the storage system.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
222

C. Block-Based Storage and Its Advantages
Block-based storage is a type of data storage system
where data is divided into small, fixed-sized blocks,
each with a unique identifier. These blocks can then
be stored, retrieved, and managed independently of
each other. Block-based storage offers several
advantages over other storage models, including:
Improved data management: With block-based
storage, data can be managed at a granular level,
allowing for more efficient allocation and utilization
of storage resources. This means that blocks of data
can be moved, replicated, or deleted without affecting
the rest of the data.
Faster data access: Block-based storage allows for
faster data access because data can be retrieved at the
block level, rather than at the file or object level. This
means that only the specific blocks needed to access
the data are retrieved, reducing latency and improving
performance.
Better data reliability: Block-based storage
provides better data reliability because blocks can be
replicated across multiple servers or disks, ensuring
that data is always available even if one server or disk
fails. Additionally, block-based storage allows for
data checksums and other integrity checks to be
performed at the block level, ensuring that data is not
corrupted or tampered with.
Greater scalability: Block-based storage is highly
scalable because blocks can be added or removed as
needed, without affecting the rest of the data. This
makes it easier to add capacity to the storage system
as data needs grow.
D. Access Control Mechanisms for Block-Based
Outsourced Storage
To implement access control mechanisms in block-
based outsourced storage, organizations should
define access policies and procedures that are aligned
with their security requirements and industry
standards. To make sure that only those with the
proper authority may access the storage system, they
need also establish robust authentication and
authorisation systems. Furthermore, regular auditing
and monitoring of user activity and access can aid in
identifying and preventing unauthorised access to
data.
E. Security Challenges in Block-Based Outsourced
Storage
Data confideData stored in block-based outsourced
storage can be vulnerable to unauthorized access or
disclosure. To address this challenge, organizations
can implement access control mechanisms such as
encryption, authentication, and authorization to
restrict access to sensitive data.
Data integrity: Data stored in block-based
outsourced storage can be vulnerable to unauthorized
modification, deletion, or corruption.
Data availability: Block-based outsourced storage
solutions can experience downtime or service
disruptions due to hardware failures, network
outages, or malicious attacks. To address this
challenge, organizations can implement backup and
disaster recovery solutions to ensure data availability
in the event of a service disruption.
The protection of sensitive data. To address this
challenge, organizations can implement security
controls and processes that comply with industry
standards such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR.
Vendor management: Organizations must
carefully select and manage their block-based
outsourced storage providers to ensure that they meet
the organization's security requirements. This
includes conducting due diligence on the provider's
security controls, policies, and procedures, and
regularly monitoring their compliance with
contractual obligations.
Organisations should put in place a thorough
security architecture with technical, administrative,
and physical controls to reduce these security risks.
To keep this framework useful in addressing new
threats and vulnerabilities, it should be periodically
examined and updated. Organisations should also
regularly teach their staff members on security
awareness so that they are aware of their roles and
responsibilities in securing sensitive data.
F. Literature Survey
(1) A paper has been proposed by Y. Zhu, Zhang, Jin,
Zhou, and . Yan. 1820–1831 in IEEE, 2019. Similar
to force chain operations, digital means transfers,
philanthropy, etc. advocated in several operations to
build trust among different parties. Decentralised
databases typically employ blockchain platforms.
Even Nevertheless, blockchain platforms are much
less user-friendly than conventional databases., they
lack the capacity to efficiently and effectively
simulate complicated operations. SEBDB is the first
platform that takes into account both usability and
scalability, as opposed to being workshop, sale is
recorded. where each sale is represented by a tuple
with a number, We encourage accessible operation
development by employing SQL language as the
common rather than law-position APIs, in normal
operations to fit the that platform. while our system
does not rely on RDBMS, it regards it as a critical
component because to its lengthy track record of
performance. We measured the quality of the main
database. build a mini-benchmark. The results of
extensive experiments show how effective and
efficient our method is.
(2) A paper has been proposed by K. Christidis and
M. Devetsikiotis 2016. We also enter and discuss
comibination of a blockchain 1) makes it possible to
Blockchain Based Outsourced Storage Schema in Untrusted Environment
223

share services and funds, creating a good service, and
2) enables us to create several laborious workflows in
empirical way. We also highlight a few concerns that
need to be taken into account prior to the deployment
to blockchain environment, ranging from
sequestration to the expected value of the digital
assets transacted on the network. We note outcomes
and workarounds where appropriate. We conclude
that the blockchain-IoT combo is crucial and can
result in considerable benefits. Our analysis leads us
to the conclusion that the blockchain-IoT combo is
substantial and has the potential to produce large
transformations across various fields, opening the
door for new business models and creative,
distributed operations.[ We then transition into the
Internet of Things (IoT) space and explain how a
blockchain-IoT combination 1) makes it easier for
people to share services and resources, which creates
a market for services between bias, and 2) enables us
to automate several laborious workflows in a
cryptographically empirical way. Additionally, we
highlight a number of concerns that should be taken
into account prior to the deployment of a blockchain
network in an IoT environment, ranging from
transactional sequestration to the anticipated digitize.
(3) A paper has been proposed by Zhang,. Cai, G.
Chen, W. Fu, B. C. Ooi, and P. Ruan, 2018.
Existing data storage technologies provide a wide
variety of functions to support a wide variety of
applications. New classes of applications, such as
blockchain and collaborative analytics, have however
emerged. These application. As a result of
incorporating the aforementioned needs into the
storage, they offer new options for storage systems to
effectively support such applications. We introduce
created for blockchain and fo apps, in this article. Core
application attributes are incorporated into the storage
by ForkBase. ForkBase saves development effort
while also delivering good performance. The store
maintains provides two fork variations that allow for
various fork workflows. Due to a cutting-edge index
class that provides quick searches and accurate content
duplication detection. ForkBase is quick and space-
efficient.and a collaborative analytics application—are
used to show off ForkBase's functionality. We carry
out thorough experimental comparisons with the
relevant. The findings demonstrate that outperforms
the competition while drastically reducing
development time.
(4) A paper has been proposed by, 2017. J. Mao, Y.
Zhang, P. Li, T. Li, Q. Wu, and J. Liu.
According to the storage of the cloud, in that
architecture,Unauthorised access to the data is now
significantly more likely. Making ensuring the data
being outsourced is accurate is one of the biggest
issues with cloud storage. In particular, we must
guard against unauthorised access to these data and
detect and restore user data following unforeseen
modifications. In this research, we present strategy
for dynamic maintenance and integrity protection of
cloud data that is publicly verifiable. In order to allow
users to compute.
(5) A paper has been proposed by G. Zyskind, O.
Nathan
In the model it controls vast quantities of private
information is being allow into increase questions in
the cases of spying and jeopardising privacy of the
users. Bit coin has demonstrated that reliable,
auditable computing is achievable in the financial
sector by utilising a decentralised network of peers
and a public ledger. The decentralised personal data
management system we propose This article ensures
that individuals own and control their data. We
implemented a mechanism that turns a block chain
into an independent access-control manager without
requiring third-party trust. Transactions in our
system, unlike Bit currency, are used to transport
instructions such as storing, searching, and
transferring data. rather than being strictly financial.
We conclude by talking about potential block chain
extensions in the future that might help society solve
its problems with trusted computing in a
comprehensive way.
3 BACKGROUND STUDY
Economic viability, technical, and social viability are
the first three.
1)Economic viability: An organisation makes
wise system investments. As a result, they ought to be
worthy of the money invested in the system. Always
consider the financial advantage, which must be
greater than or equal to the system cost but not more
than that.
The system's overall cost of investment is
examined.
Considering how to cut costs by taking into
account the price of the hardware and software.Every
organisation wants to cut costs, but at the same time,
service quality must be preserved. The system is
created in accordance with the concern's cost
estimation. The proposed solution in this project will
undoubtedly save costs, speed up production, and
reduce manual labour.
2)Technic viability: Technical viability refers to
the evaluation of the software and how it is included
into the research of our project. This has a number of
technical issues that need to be noted.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
224

• Is equipment technically capable of storing the
data necessary for the new system?
After this project is finished, can this system be
expanded? Exists a technique that guarantees
security, reliability while accessing data, and
accuracy? Will the system respond to the requester's
repeated requests in a suitable manner?The
technological problems are brought up when
researching our system's viability. Consequently, the
technical evaluation assesses the Oracle serves as the
system's back end and JSP serves as its front end.
Additionally, they offer enough memory to store and
handle the data. It is the least expensive and most
effective method because the company will install
every process in the system.
The whole request submitted by the user is
accepted by this system technique, and the response
is delivered promptly and without error. It examines
the resources that are available and how they may be
used to create a workable system. It is a crucial step
in the analysis and definition process to evaluate the
technological feasibility in parallel.Oracle can easily
handle the vast amount of information that has to be
stored and retrieved. Due to the fact that the Oracle
can be used with any system and that its functionality
is constant. So, it's successful.
3)Social viability: Only once they are transformed
into an information system and tailored to the needs
of the organization's operations will the proposed
project be useful. For the procedure, the following
concerns are taken into account:
•Does this system offer the user and management
enough support?
What approach ought to be used in this project
•Were the users involved in the initiatives'
planning and development?
•Will the proposed system result in any harm,
negative outcomes, a loss of control, or a reduction in
the system's accessibility.
Minor problems can occasionally turn into severe
ones in the process. It serves as a gauge for how well
users can interact with the system. When making
decisions, these things should be taken into account.
The system is extremely user-friendly and well
supported with reference to the project. In order to
prevent injury or data loss, the techniques are
described effectively and with the appropriate
criteria. It has a GUI interface since using a GUI is
more user-friendly.
4 METHODOLOGY
Problem Definition
The requirement for a secure and effective technique
to store data in an outsourced environment when the
storage provider may not be entirely trusted is the
issue being addressed by the "Block-Based
Outsourced Storage " project. The goal is to develop
a schema that allows data to be stored in a distributed
manner, while ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and
availability of the data.The schema involves breaking
the data into blocks and storing them on different
storage servers, with each block being replicated
multiple times for redundancy. To ensure security,
each block is using a key,it is encrypted and access
control policies are implemented to restrict
unauthorized access to the data.
Objective
Input design is the process of converting a description
of the input that is recognisable to stoners into a
computer-baseThis design is important for deterring
crimes during data entry and outlining the right step
to take to get correct information from the motorised
system. It is performed by creating data entry
defences that are able to manage massive amounts of
data that are weed-friendly. Making data entering
simpler and crime-free is the goal of input design. The
veracity of the entered data will be verified. Defences
allow for the entry of data. So that the stoner won't be
caught in a moment of sludge, necessary alerts are
delivered as neededAs a result, creating an input
layout that is easy to grasp is the aim of input design.
Modules
Admin Module
In this admin module, admin can view all data owners
who are upload the file into the server. Admin can
view all file details which are stored in server and
finally they can view download files.
Data Owner Module
In this module, data owner can upload the file in the
server. they can request file meta data to the meta data
admin. if the meta data admin can accept the owner
request they send the meta data details and they also
download the files from the server.
Server Module
In this module, server admin can view data owner file
upload request and then they store the file into proper
place in the server.
Meta Data Admin Module
Blockchain Based Outsourced Storage Schema in Untrusted Environment
225

In this module, admin can view meta deta details and
view the user file request. If they accept send the meta
data information to the data owner.
Block Chain Module
In this module, data owner can view the file storage
information. This is happened by means of using
block chain. Because block chain is used for
transparency and security. This meta data information
is transparent only for data owner.
5 RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS
The block-based outsourced storage schema is a
common approach used in cloud computing
environments to store large amounts of data in an
efficient and secure manner. In this schema, the data
is divided into blocks and stored on multiple servers
located in different geographic locations to ensure
redundancy and fault tolerance.
However, in an untrusted environment, where the
cloud service provider cannot be fully trusted. One
way to achieve this is by using encryption techniques
to secure the data before it is stored on the cloud
servers.
In addition, data can be further protected by using
a data backup and recovery mechanism that ensures
the data can be restored recovery procedures can be
put in place to restore data in case of any issues.
Overall, the block-based outsourced storage
schema can be a reliable and secure approach to store
data in an untrusted cloud environment, provided the
necessary security measures are taken to protect the
data.
6 CONCLUSIONS
A new trustworthy schema for controlling outsourced
replication metadata saved by many CSPs in
unreliable situations We create a novel architecture
comprised of a group of VPsbased on the
extraordinary properties of blockchain Then, we
present a cooperative algorithm for saving and
validating replication metadata. VPs build a metadata
block during the store phase using the provided
signatures and accompanying metadata, then they
write that block onto local data. On the verify step,
VPs gave back local data by using signing use to
extract relevant data. The results offers great
scalability while also effectively storing and verifying
the metadata.
REFERENCES
S. A.Weil, S. A. Brandt, E. L. Miller, D. D. Long, and C.
Maltzahn, “Ceph: A scalable, high-performance
distributed file system,” in Proceedings of the 7th
symposium on Operating systems design and
implementation. USENIX Association, 2006, pp. 307–
320.
J. Mao, Y. Zhang, P. Li, T. Li, Q. Wu, and J. Liu, “A
position-aware merkle tree for dynamic cloud data
integrity verification,” Soft Computing, vol. 21, no. 8,
pp. 2151–2164, 2017.
Buterin, “A next-generation smart contract and
decentralized application platform,” 2014.
J. H. Park and J. H. Park, “Blockchain security in cloud
computing: Use cases, challenges, and solutions,”
Symmetry, vol. 9, no. 8, p. 164, 2017.
Dorri, S. S. Kanhere, and R. Jurdak, “Blockchain in internet
of things: Challenges and solutions,” 2015.
H. T. Vo, A. Kundu, and M. Mohania, “Research directions
in blockchain data management and analytics,” 2018.
K. Christidis and M. Devetsikiotis, “Blockchains and smart
contracts for the internet of things,” IEEE Access, vol.
4, pp. 2292–2303, 2016.
Lee and J. H. Lee, “Blockchain-based secure firmware
update for embedded devices in an internet of things
environment,” Journal of Supercomputing, vol. 73, no.
3, pp. 1–16, 2017.
M. Ali, J. Nelson, R. Shea, and M. J. Freedman,
“Blockstack: A global naming and storage system
secured by blockchains,” 2016.
T. T. A. Dinh, R. Liu, M. Zhang, G. Chen, B. C. Ooi, and
J. Wang, “Untangling blockchain: A data processing
view of blockchain systems,” arXiv preprint
arXiv:1708.05665, 2017.
S. Cohen and A. Zohar, “Database perspectives on
blockchains,” arXiv preprint arXiv:1803.06015, 2018.
Y. Yong and W. Feiyue, “The development status and
prospects of blockchain technology,” Acta Automatica
Sinica, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 481– 494, 2016.
J. Wang, X. Chen, J. Li, J. Zhao, and J. Shen, “Towards
achieving flexible and verifiable search for outsourced
database in cloud computing,” Future Generation
Computer Systems, vol. 67, pp. 266–275, 2017
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
226
