Optimizing Dynamic Multi-Agent Performance in E-Learning
Environment
D. K. Aarthi and E. J. Thomson Fredrik
Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, India
Keywords: Web Usage Analysis, Web Content Analysis, Web Customization, Lingo, E-Learning Platform, HITS.
Abstract: The instructor-centric paradigm has been displaced as the most cutting-edge method of learning with the
introduction of web-based learning and content management systems. For e-learning systems, web mining is
extremely essential. The user can alter the learning setting in a personalized E-Learning system according to
their preferences. A link that receives the most hits will be displayed first in a general search procedure. To
construct a customizable system, user logs must be used to store each user's historical information. The
proposed approach provides a novel viewpoint by combining web usage mining, the HIT algorithm, and web
content mining. It combines user logs and web page hit statistics and contains data that has been clustered
using the Lingo clustering method. We will discuss a method in this article that makes use of content mining
and web usage to personalized e-Learning services. The usefulness and advantages of web mining for e-
learning are examined in this essay.
1 INTRODUCTION
The World Wide Web has evolved into a powerful
and sophisticated medium for the exchange of data.
Different clients who are geologically located in
superior locations must efficiently access the
different data types. The online get-to-log record,
which is a massive store created by the travels of users
with online destinations, can be searched to discover
the client's navigational patterns. Web Usage Data
Mining is a term used to describe the analysis of Web
traffic trace records. The Internet data explosion has
established degrees of search engine popularity.
People are far from content with how the
implementation of Question noting frameworks has
appeared online to help users find more precise
answers to queries made in a previous period of
search engines. This new generation of frameworks
attempts to organize documents, in contrast to
traditional search engines that only use watchwords
to do so. This new generation of frameworks tries to
understand the client's query and suggests some
comparable queries that other people have frequently
raised and for which the framework has the correct
responses. The truth is that most of the time, suitable
responses have been organized or double-checked by
human editors.
This ensures that, if one of the suggested
questions is truly similar to the client's, the appropri-
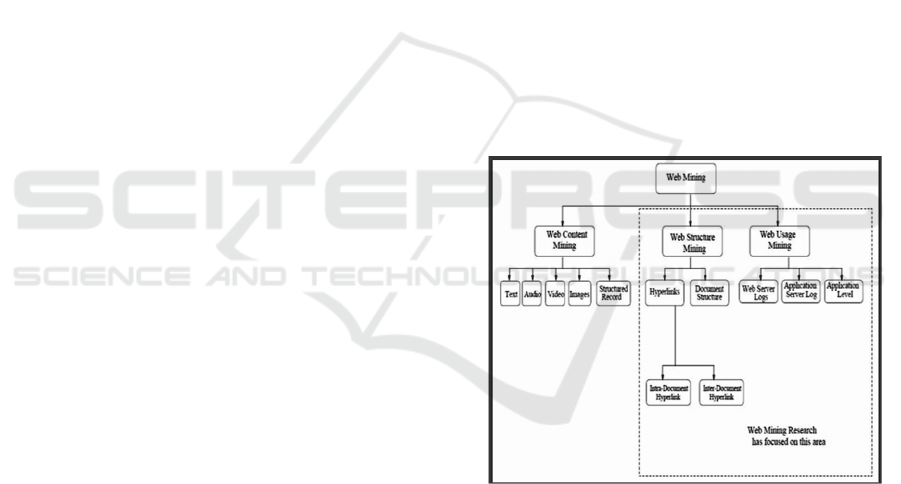
Figure 1: Structure of Web Scrapping (Mining)
web content
analysis.
ate answers provided by the framework will be
applicable. The underlying premise of such a
framework is that numerous people are frequently
preoccupied with comparable questions. Some web
search engines have developed strategies to suggest
alternative queries to users to solve the problems.
These techniques are used to give clients the option
to include optional related queries in their search
process, either to address their data requirements or to
rephrase their query strategy to find more relevant
search results. The techniques employed in these
Aarthi, D. and Fredrik, E.
Optimizing Dynamic Multi-Agent Performance in E-Learning Environment.
DOI: 10.5220/0012613000003739
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of Things: Accelerating Innovation in Industry and Consumer Electronics (AI4IoT 2023), pages 259-264
ISBN: 978-989-758-661-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
259
constrictive business frameworks are often secure,
but be careful that some of the suggested searches
provided by these search engines contain identical
phrases. This may indicate that those proposed
queries will likely be created by straightforward
query expansion techniques. For example, if a user
searches for Yahoo! search engine, the following
related searches are displayed: messenger, best yahoo
mail. Yet, as we can assume, there is a tonne of
additional queries that concern mail but likely don't
directly mention "yahoo" in their term vectors.
2 RELATED WORK
A Progressive Molecule Multitude Enhancer
and Its Versatile Variation by S. Janson
and M. Middendorf
This research presents a different leveled version of
the molecular swarm enhancement (PSO)
metaheuristic. The particles are arranged in a
dynamic chain of importance in the new technique
known as H-PSO, which is used to describe an area
structure. The nature of the particles' currently best-
understood arrangement determines whether they go
up or down the chain of command. This increases the
impact of powerful particles on the swarm as they
advance in the progressive system. In this form of the
H-PSO, the progressive system is perfectly adjusted
as the computation is being done. Another approach
is to assign different behavior to the individual
particles depending on where they fall in the
significance chain. We test H-PSO and its variants on
a commonly used combination of streamlining
capabilities and are compared to PSO's use of several
standard neighborhood layouts.
B Finding and following Several Intuitive
Optima by a Substantial Swarm Model
using Speciation by D. Parrott and X. Li
To deal with the challenges of continuous
improvement and to track many optimums in a
dynamic environment, this work offers an improved
molecular swarm analyzer that applies the species
idea to identify its local best qualities. According to
their similarity, the swarm populace is divided into
species subpopulations in the proposed species-based
molecular swarm streamlining (SPSO). Every species
is worked around an expert particle known as the
species seed. For each of these unique species
bunches
independently, species seeds are chosen
from the complete population at each cycle stage. At
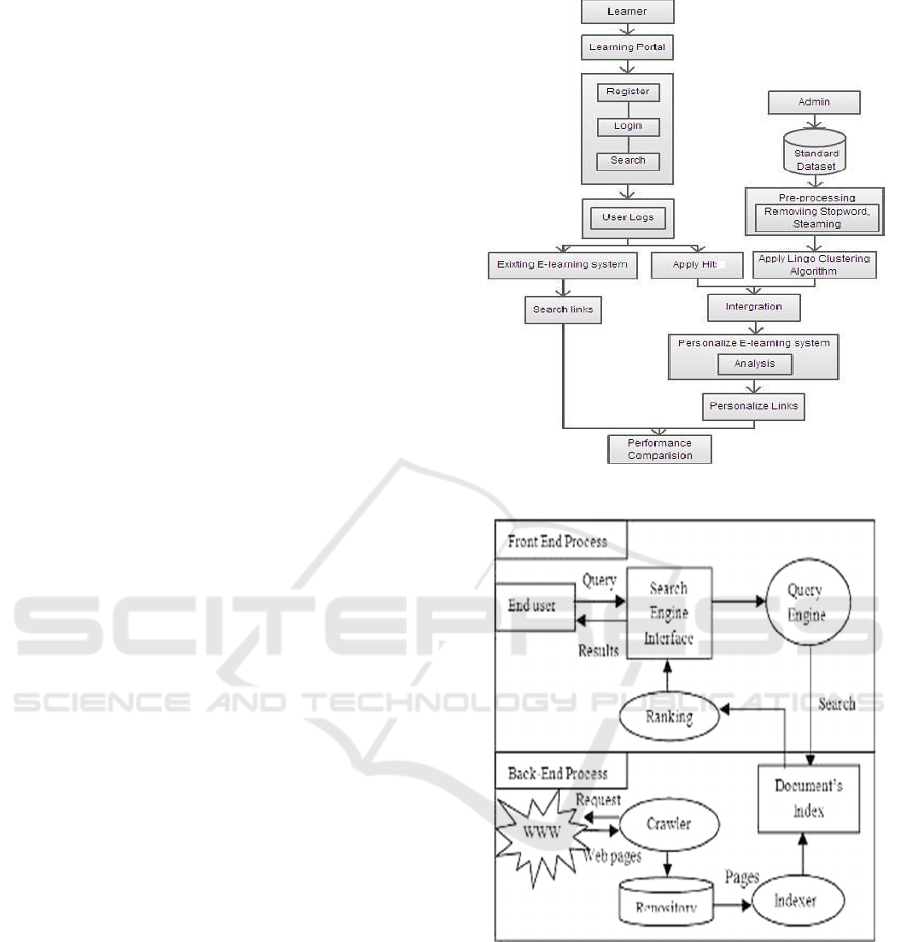
Figure 2: The architecture of the proposed approach.
Figure 3: The mechanism for the browser's search interface.
each stage of the evolution, species are adaptively
framed in accordance with the information gleaned
from the multimodal wellness scene. Species can
continue to evolve towards different optimum states
over increasing emphasis, paying little attention to
whether they are close or global. Our studies using a
powerful SPSO (DSPSO) to track numerous altering
optimal circumstances in a dynamic environment and
the SPSO to locate many ideal conditions in a static
area have demonstrated the SPSO's outstanding
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
260

capability to handle multimodal improvement tasks in
the two scenarios.
C Developing a Customized E-Learning
Framework in Light of Hereditary
Calculation and Case-Study Thinking
Approach by M.- J. Huang, H.- S. Huang,
and M.- Y. Chen
Students can access instructional resources on a
special platform provided by the World Wide Web.
When instructional content is delivered in
hypermedia form in a framework for learning that is
based on the Web, learning transforms into an
activity-driven process. It encourages pupils to look
into independent navigational routes within the
region while studying from numerous resources
throughout the globe. To facilitate Online education
through the Internet and offer flexible teaching
techniques, A number of analysts have been
concentrating on creating e-learning frameworks with
movable learning elements. While providing
customized educational program sequencing
administrations, the majority of customized
frameworks do take student preferences, premiums,
and reading habits into account. Nevertheless, these
frameworks typically fail to consider whether student
ability and the degree of difficulty of the suggested
training materials are compatible. In this manner, our
suggested approach is based on the evolution method
using adaptable electronic testing (CAT). At that
moment, a perfect learning method is created for each
learner using case-based reasoning (CBR) and
hereditary calculation (GA). Three fundamental
promises are made in this essay: (3) The proposed
methodology can develop the right course materials
for students, taking into account individual student
needs, to help them learn more effectively, as
demonstrated by the observational study. This is
accomplished by (1) laying out the case-based
reasoning needed to construct an integrated analysis
or evaluation investigation, (2) outlining the
hereditary-based educational programs sequencing
approach, and (3) outlining the case-based thinking to
build up a customized educational module
sequencing.
D H. Izakian, A. Abraham, and V. Snael's
paper, "Fuzzy Clustering Utilizing Hybrid
Fuzzy c-means and Fuzzy Particle Swarm
Optimization"
An important problem called fluffy bunching is the
focus of dynamic study in a few real applications. The
most effective, straightforward, and straightforward
to use fluffy grouping method is the fluffy c-implies
(FCM) computation. Nonetheless, FCM is easily
caught in surrounding optima and is sensitive to the
statement. Many advancement challenges are
resolved using molecular swarm optimization (PSO),
a stochastic global streamlining method. This paper
proposes a fluffy grouping method based on fluffy
PSO (FPSO) and FCM, utilizing the advantages of the
two computations. Trial findings show that our
suggested method is effective and capable of
revealing outcomes that are inspiring.
E Adaptive Molecule Multitude Enhancement
by Z.- H. Zhan, J. Zhang, Y. Li, and H. S.-
H. Chung
A flexible molecule swarm improvement (APSO) is
presented that emphasizes preferred search efficacy
over conventional molecule swarm streamlining
(PSO). Most importantly, It is capable of doing a
faster mixing rate global search across the whole
search universe. There are two main breakthroughs in
the APSO. To determine one of the other four defined
transformational states, a consistent developing state
estimation approach is first applied. Inquiry, abuse,
combination, and jumping out of all ages, by
assessing population circulation and molecular well-
being. To increase the efficiency and speed of the
assembly process, It makes it possible to code the run
control of algorithmic parameters like quickening
coefficients and idleness weight. When the
developmental condition is at that point, an elitist
learning system is implemented state of delegated
combination. The approach will look for the molecule
that can exit a potential neighboring optimum the
fastest overall. The APSO's performance was
extensively evaluated against 12 benchmark single-
functional and multifunctional capabilities. We'll
think about the effects of elitist learning and
parameter tweaking. The results show that APSO
significantly improves the implementation of the PSO
perspective in terms of blending speed, global
optimality, arrangement precision, and calculation
consistency. Only two new elements are introduced
to the PSO viewpoint by APSO; no further plans or
multifaceted use characteristics are offered.
F
Multicluster, Rejection, and against
Combination in Dynamic Conditions by T.
Blackwell and J. Branke
Some real problems are dynamic, necessitating a
streamlined computation that can consistently monitor
Optimizing Dynamic Multi-Agent Performance in E-Learning Environment
261

Figure 4: Console of the implemented system.
an evolving ideal over time. So, we examine novel
iterations of molecular swarm advancement (PSO)
that are specially designed to perform excellently in
challenging circumstances. The key idea is to organize
the particle population into a group of interacting
clusters. These swarms are connected locally by a
parameter for avoiding conflict and globally by a
different administrator who forbids intermingling.
Also,
each
swarm
maintains
a
respectable
level
of
variation through the use of stimulating or quantum
particles. In this study, which also sets criteria for
choosing the included parameters, the multiswarm
computations are assessed on a range of examples of
the multimodal lively moving pinnacles benchmark.
Further comparisons between the results with other
PSO and developmental calculations are made the
new multiswarm streamlining agent fundamentally
outperforms earlier approaches, closer to the
authoring.
3 WEB MINING PERTINENT TO
E-LEARNING
Web Mining Methodologies
Web mining is a significant subfield in data mining.
Finding important information or trends in web data
is known as web mining. As indicated in the figure, it
may be divided into the three following figure.
1. Web Content analysis
2. Web Structure analysis
3. Web Usage analysis
The practice of extracting significant information
from the text of online sites is known as web content
mining. The web page's content comprises text,
photos, audio, and video, as well as strategies like
grouping or associating websites based on the
relevant branches. It also makes data mining easier.
Web structure mining analyses the web, and one of its
applications is to locate better publications, as well as
websites pertinent to a specific subject or area, or to
find web communities. It is also used to determine the
structure of web pages from web pages by detecting
the current scenario.
Web Structure Analysis
The objective of web structure mining is online
analysis, and one of its applications is to find better
papers. Also, it helps in locating important websites
for a particular subject or branch as well as online
forums.
Moreover, it is employed to make the schema of
web pages apparent.
Web Usage Analysis
Data mining techniques known as "web use mining"
are used to uncover intriguing usage patterns from
web data to better understand and accommodate the
needs of web-based applications. Usage information
keeps track of both the identities of internet users and
the habits of their web browsing. The most important
research initiatives in the area of Web use mining and
customization are also covered. Yet the effectiveness
of this strategy for customization is not as great.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
262

Web Mining-Based E-Learning System
There are three components to the e-learning system.
User, learning platform, and collection of teaching
resources. A storage server for storing various kinds
of educational resources is called an education
resource library. This web-based system's user is the
learner. The learning platform that provides users
with a web-based learning environment is the web
server.
To create a standard dataset with learning objects,
the administration is in charge. Stop words and stems
are removed from this dataset after preprocessing.
First, a new user registers with the learning portal. As
soon as a user comes into the system using their
unique username and password and performs a
subject-specific search, their search logs are kept on
the server. After that, the hit method is used to give
those logs more weight. In the suggested method, the
lingo clustering algorithm is used to mine content
using preprocessed data. Preprocessed data are then
used to create clusters. User logs, the hits method, and
clustering findings are used to generate the final
results.
4 THE HYPERTEXT-INDUCED
TOPIC SEARCH ALGORITHM
The HIT Search algorithm is a method for locating
documents that are pertinent to a given keyword
topic. When you type a question or term into the
Google search engine, which was developed by
Krishna Bharat while he was working at the Compaq
Systems Research Center, The Hypertext Induced
Topic Search algorithm aids in locating pertinent
keywords whose outcomes are more educated
regarding the search term or question.
The method uses a systematic index of expert
documents. These are pages that are focused on a
single subject and contain links to numerous
unrelated sites on that subject. If authors from non-
affiliated organizations create a page, that website is
considered non-affiliated. The relevancy of the
description text for hyperlinks on expert pages
referring to a particular result page is taken into
consideration when ranking the results.
The system's performance is assessed in various
contexts and in contrast to the earlier approach, which
is only based on the use of mining. Based on a user's
browsing history, the program may be used to provide
customized recommendations. We have covered a
wide range of study topics for a customized E-
learning system in this essay. This work proposes a
unique web mining approach that is based on a
synthesis of web usage analysis and web content
analysis (HITS algorithm), displaying superior
performance improvement than the prior method
based on the current limitations.
5 FUTURE SCOPE
In the future, a personalized curriculum will be
established using the learner's time distribution
pattern, and a feedback system will be constructed
using the learner's social trend. We will also deliver
varied training based on the different levels of
learners. Research can be conducted to create
integration strategies for techniques that can precisely
predict students' success in courses and ways that
assist in choosing a subject or set of courses based on
student's interests.
REFERENCES
A. Rosen, e-Learning 2.0: Proven Practices and Emerging
Technologies to Achieve Real Results. New York, NY,
USA: American Management Association, 2009.
E. Pontes, A. Silva, A. Guel_, and S. Kofuji,
Methodologies, Tools and New Developments for E-
Learning. Rijeka, Croatia: InTech, Feb. 2012.
C.-T. Yang and H.-C. Ho, ``shareable e-learning platform
using data grid technology,'' in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. e-
Technol., e-Commerce e-Service, Mar./Apr. 2005, pp.
592_595.
C.-M. Chen, H.-M. Lee, and Y.-H. Chen, ``Personalized e-
learning system using item response theory,'' Comput.
Educ., vol. 44, no. 3, pp. 237_255, Apr. 2005.
M.-J. Huang, H.-S. Huang, and M.-Y. Chen, ``Constructing
a personalized e-learning system based on genetic
algorithm and case-based reasoning approach,'' Expert
Syst. Appl., vol. 33, no. 3, pp. 551_564, Oct. 2007.
C.-P. Chu, Y.-C. Chang, and C.-C. Tsai, ``PC2PSO:
Personalized e-course composition based on particle
swarm optimization,'' Appl. Intell., vol. 34, no. 1, pp.
141_154, Feb. 2011.
C.-M. Chen, Y.-L. Hsieh, and S.-H. Hsu, ``Mining learner
profile utilizing association rule for Web-based
learning diagnosis,'' Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 33, no. 1,
pp. 6_22, Jul. 2007.
C. Romero and S. Ventura, ``Educational data mining: A
survey from 1995 to 2005,'' Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 33,
pp. 135_146, Jul. 2007.
J. M. M. Vazquez, J. A. O. Ramirez, L. Gonzalez-Abril, and
F. V. Morente, ``Designing adaptive learning itineraries
using features modeling and swarm intelligence,''
Neural Comput. Appl., vol. 20, no. 5, pp. 623_639, Jul.
2011.
L. de Marcos, J.-J. Martínez, and J.-A. Gutierrez, ``Swarm
intelligence in e-learning: Swarm intelligence in e-
Optimizing Dynamic Multi-Agent Performance in E-Learning Environment
263

learning: A learning object sequencing agent based on
competencies,'' in Proc. 10th Annu. Conf. Genetic Evol.
Comput., Atlanta, GA, USA, Jul. 2008, pp. 17_24.
P. Brusilovsky and C. Peylo, ``Adaptive and intelligent
technologies for Web-based education,'' Int. J. Artif.
Intell. Educ., vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 159_172, Apr. 2003.
R. Stathacopoulou, M. Grigoriadou, M. Samarakou, and D.
Mitropoulos, ``Monitoring students' actions and using
teachers' expertise in implementing and evaluating the
neural network-based fuzzy diagnostic model,'' Expert
Syst. Appl., vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 955_975, May 2007.
Y.-M. Huang, J.-N. Chen, T.-C. Huang, Y.-L. Jeng, and Y.-
H. Kuo, ``Standardized course generation process using
dynamic fuzzy Petri nets,'' Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 34,
no. 1, pp. 72_86, Jan. 2008.
[14] A. Carlisle and G. Dozier, ``An off-the-shelf PSO,'' in
Proc. Part. Swarm Optim. Workshop, Apr. 2001, pp.
1_6.
Y.-M. Chen, T.-Y. Chen, H.-C. Chu, and K.-C. Su,
``Ontology-based adaptive dynamic e-learning map
planning method for conceptual knowledge learning,''
Int. J. Web-Based Learn. Teach. Technol., vol. 11, no.
1, pp. 1_20, Jan. 2016.
K. Almohammadi, H. Hagras, D. Alghazzawi, and G.
Aldabbagh, ``A survey of artificial intelligence
techniques employed for adaptive. Educational systems
within e-learning platforms,'' J. Artif. Intell. Soft
Comput. Res., vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 47_64, Dec. 2016.
T. Gopalakrishnan and P. Sengottuvelan, ``A hybrid PSO
with Naïve Bayes classi_er for disengagement
detection in online learning,'' Program, vol. 50, no. 2,
pp. 215_224, Apr. 2016.
S. Janson and M. Middendorf, ``A hierarchical particle
swarm optimizer and its adaptive variant,'' IEEE Trans.
Syst., Man, Cybern. B, Cybern., vol. 35, no. 6, pp.
1272_1282, Dec. 2005.
T. Blackwell and J. Branke, ``Multiswarms, exclusion, and
anti convergence in dynamic environments,'' IEEE
Trans. Evol. Comput., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 459_472, Aug.
2006.
D. Parrott and X. Li, ``Locating and tracking multiple
dynamic optima by a particle swarm model using
speciation,'' IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput., vol. 10, no. 4,
pp. 440_458, Aug. 2006.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
264
