
Public Opinion Contract Purchase Stream Care Account Display
Customer Dependency
R. Ramachandran
*
and G. Anitha
†
Department of Computer Applications, Karpagam Academy of Higher Education, Coimbatore, India
Keywords: Interdependency Security, Investment Security, Cloud-Insurance, Cyber Breach, and Stackelberg Game.
Abstract: Over a intervening years, the advancement of technologically advanced security approaches has led to a simple
decision none internet safeguard can totally minimise the hazards consumers confront. With this context,
online-insurance was originally created as a mechanism for consumers to mitigate the harm brought on by
computer viruses by shifting the technical hazards over to an operator. We investigate an online privacy
protection sector comprised of both consumers and county protection service companies in this research. To
safeguard their online customer service, cloud platform customers can acquire a cloud security package from
CSSVs. If the online business gets assaulted and forgotten, clients will obtain reimbursement against CSSVs.
The CSSV is given the motivation to improve the cloud-based safety measures in order to reduce the likelihood
of an actual assault. In particular, he designs and investigate the cloud-based privacy services sector using a
two phases Stackelberg game. During the higher level, CSSVs led behind their individual tactics, such as the
costs if the web protection package plus the degree of investments to enhance their given sky secure
solution.Customers elect on buying of the online safety programme at the entry level based on the pricing of
the internet safety programme plus the anticipated cyber-attack chance of the internet protection provider. We
prove computationally that the so-called Stackelberg equilibria happens but is distinctive. Whenever clients
are very dependant, for instance internet security software companies' earnings be higher.
1 INTRODUCTION
Database security was one of the most important areas
of need for database technology that arose. It improves
service providers' ability to guarantee that data is
maintained securely and safely. This allows
developers to upload sensitive data contained in the
database in an encrypted way. It also makes it
relatively easy for viewers to examine the material
from afar. The data is captured and stored in various
forms of information storage in the data centre, and it
is further protected by two distinct types of encrypted
formats at a prominent to medium level. These data
may be stored in the data centre for backup and
restoration purposes. The data centre is that part that
makes up the company model. Their capacity Our
recommended application is an encryption technique
that uses key creation and a random number generator
to safeguard data transfer to other apps. It also
employs a validation method to verify that no illicit
*
MCA Student
†
Associate Professor
access or alterations occur. The presented model
preserves our application's natural silhouette for
simple retrieval, manipulation, and
encrypting/decryption control parameters without
sacrificing security because each key will be produced
distinctly for each encryption in a random operation.
This proposal would assist us in managing production
and product data while ensuring data security from
source to destination. It may result in hybridised and
numerous database configurations, which are
increasingly recommended for the methods used for
converting raw data into business logical data.
It concentrates on the topic of liability transmission,
in which policyholders bear the expense of hazards.
The rate description is a crucial component of danger
transmission in insurance for cybercrimes. The study
in this field is primarily classified into two categories:
separate and interconnected protection. The issue of
linked together health has drawn an enormous amount
of interest from academic communities because the
Ramachandran, R. and Anitha, G.
Public Opinion Contract Purchase Stream Care Account Display Customer Dependency.
DOI: 10.5220/0012613200003739
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of Things: Accelerating Innovation in Industry and Consumer Electronics (AI4IoT 2023), pages 265-270
ISBN: 978-989-758-661-3
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
265
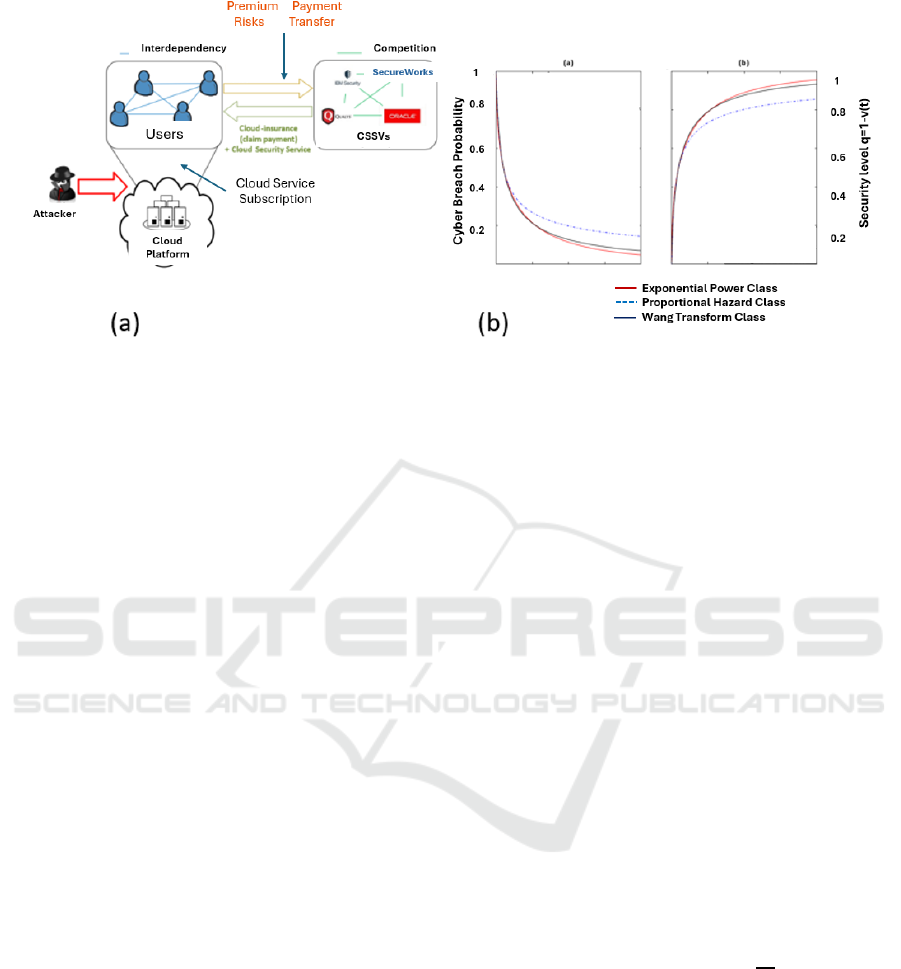
Figure 1: (a) System model linked works (b) Authentication investment for zsss.
dangers encountered by each user are also contingent
on the situations faced by everybody else in an
independent connection.
Interconnected consumers may be via direct or
indirect means assaulted by hostile neighbours. They
assess the boost in privacy that those who buy cyber-
insurance after taking into account the system's force,
its interconnectedness.
Customers could think about acquiring protection
for the possibility that worked for assaults in addition
to implementing safety features such as proxy
servers, surveillance for network intrusions software,
and traffic ingress analysis. As a result, by assuring
the system's stability, customers may easily govern
the consequences via cyber-insurance. To the greatest
of our ability, no research has investigated secure
expenditures, price, and user interdependence, all of
which serve key roles in the safety service
marketplace.
2 STRUCTURE EXPLANATION
In this paper, we look at ways to handle the price plus
safety precaution issues associated with the dynamic
online safety industry. CSSVs fight to offer their
interchangeable safety policies in the competitive
field beneath examination. The deal includes online
security services as well as cloud insurance. The
online security provider serves to defend the
fundamental internet services that customers
appreciate, and its reinsurance company pays out
claims if the internet defence company is unable to
stop an assault against occurring.
2.1 Openings
Here we find the effectiveness of all the data that
could be shared along with the security which
addresses the weakness of every function that is used
for the business sector and also for communicating.
The Wang Renovate Session of this purpose of
finding the probability at cyber breach is
Therefore the function distribution could be dented by
Φ for the normal value ossr the distribution of
probability in the cyber breach and the value might be
greater than 1 for the value of Z and it need to be
greater than 0 for the value α.
2.2 Structure Archetypal
In case of doing the presentation, we may need to
study a huge amount of information regarding the
cloud authentication at the service market. In that
sense one need to compete with the sell for the
authentication of the cloud through getting the
authentication plan of one cloud.
and
,
In the above formula, one may need to use some of
the quadratic function in the linear sector that is in the
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
266

form of ss, aixi-bixi2 this is used for capturing the
decremental value of the total users. A rationale for
all the above is because the linear feature merely
provides for a feasible evaluation plus a decent lower-
order estimate of negative payoffs, but it also
provides insight into the nature of cautious costumers.
Specifically, dA
The two formulas are used for maximizing the profits
by their own. And their profit tends to be as,
correspondingly. The total amount of investments
that is used in the current situation is
which is
used to gain the authentication of cloud service. Yet
Another time, CSSVs hold the fragment along which
their investments for each users demands.
of
for the user i by using this we need
to gain the authentication of the cloud service which
is mandatory to be breached
2.3 Stackelberg Inclined Preparation
Here they have provided the techniques that could be
used for CSSVs that might not able to in-cooperate
with the game in which the user gains the interest
hence we could able to use some of the strategies.
That is denoted by N which also indicates the total
number of users.
And
also we have provided many
strategies and techniques for the users with the non-
cooperative frontrunner.
h
This defines the domail of the security and price.
and
are defined side by side of the p in a
similar way.
2.4 Stackelberg Symmetry
Investigation
In order to increase the finest result aimed at the
stoner- position inclined game, hence here we might
go through receiving the segment of the rapid growth
Let
,
,
,
,
, and
Let
, this provides us the better
results.
Interation 1. The change and gain defines of the game
Therefore, the effectiveness of the purpose plan
for operator is
and
. Moreover, we also have
and
Consequently, the dissimilarity is most widely used
for the satisfaction of the user during the game.
Hence, we need to use the slant dominance inside the
matrix
3 RECITAL ESTIMATION
Mathematical Consequences: The display the finest
comeback and the required estimation of results
correspondingly. AS the initial and foremost step we
need to validate the profits of the game. While
changing the total number of users might get the
increased count of investments that could enhance the
security level.
Public Opinion Contract Purchase Stream Care Account Display Customer Dependency
267
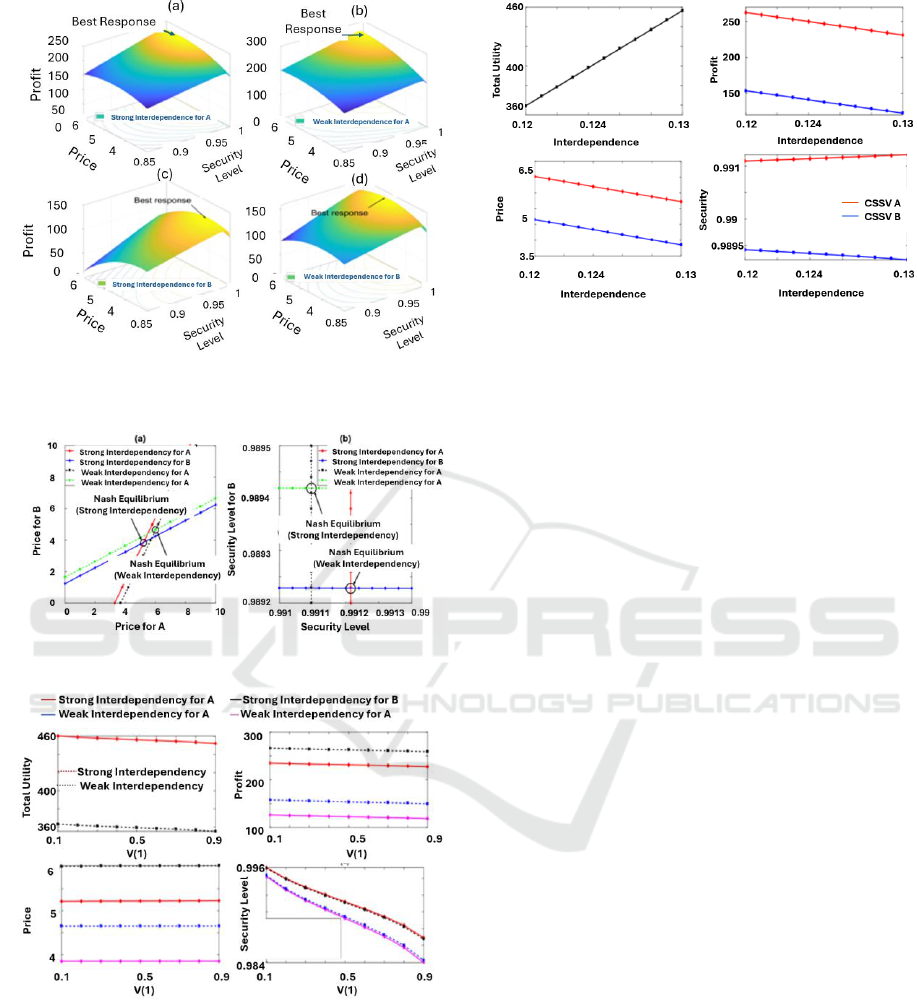
Figure 2: robust interdependency and scrawny
interdependency.
Figure 3: Price level and security level.
Figure 4: Utility, price, profit and security.
Figure 5: Total druggies’ serviceability, (b) turnover, (c)
value and(d) refuge.
The explanation behind this is that, even if their
are safeguarded by cyber insurance, consumers may
become less secure as the chance of an intrusion
increases. Furthermore, the CSSVs' profitability are
hurt by the reduction in the safety and quality of cloud
security services. As the overall quality of cloud
security services decreases, the possibility of
collecting lawsuits increases. Even if the cloud
security plan costs remain constant, the earnings
potential for the two CSSVs decreases as v (1)
increases. The consequence of client dependency is
demonstrated. The marketplace had 80 individuals,
and g got boosted. If interconnectedness grows,
customers' total utilities rise, while CSSV cost and
earnings fall, as demonstrated in (a), (b), and (c). As
interdependence grows to preserve rivalry, the CSSV-
A's level of security climbs marginally.
Figure 6 compares the shared marketplace's
results against the outcomes for the intended rival
market. Popular to the collective bazaar, they work
together to maximise their entire total profit, or the
sum from their respective incomes. The monthly fee
of an on-demand safety programme continues to be at
the maximum level, at pu, in the group market, per
Fig. 6(c). The expense of an online privacy insurance
continues to be at the maximum level, or pu, in the
collective consumers. The total revenue from the
collective market with high interdependence is
precisely equivalent to the profit in the cooperation
market with low interdependence.
It therefore is the consequence of changes
affecting the cloud storage service's level of
protection as well as pricing changes. the initial
expense of an online safety precaution.
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
268
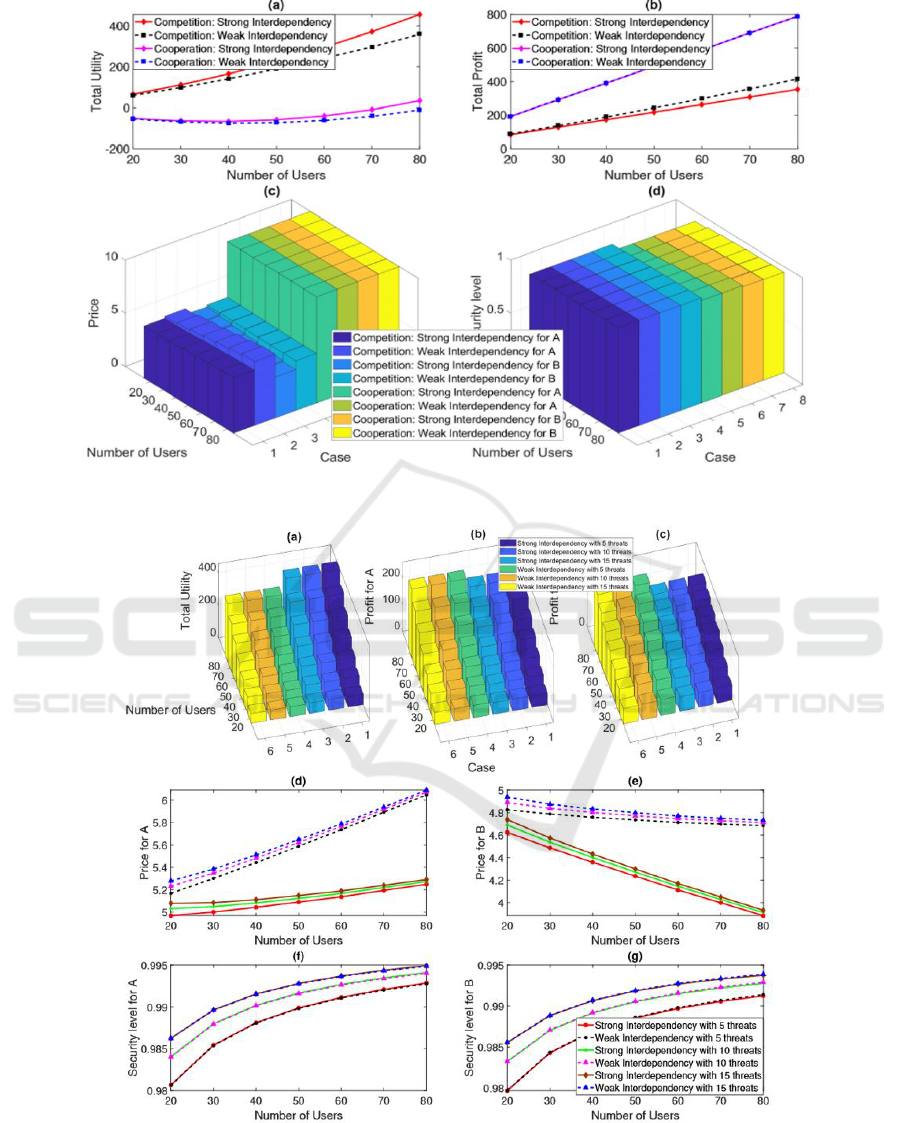
Figure 6: (a) Whole value operators’ (b) turnover gained, (c) worth level and (d) safety level.
Figure 7: (a) Total value operators’ (b) profit gained CSSVs A & B.
Public Opinion Contract Purchase Stream Care Account Display Customer Dependency
269

4 CONCLUSION
Therefore, in this research paper, we analysed the
authentication at the cloud by including the price and
safety issues. The subject matter is being studied
specifically within the context of an a two-stage
Stackelberg tournament. At the highest level, CSSVs
offer consumers privacy plans that include cloud
insurance and cloud security services. CSSVs are in
charge of making strategic decisions, such as cost and
safety investments. On the higher the platform, the
battle had been modelled as a CSSV-level
noncooperative subgame. The suggested Stackelberg
its stability was successfully demonstrated to be
present and to be singular. We gave detailed statistical
results for the suggested game. For an element of our
long-term efforts, we will include indemnification in
the internet cybersecurity industry.
REFERENCES
G. Xu, H. Li, S. Liu, M. Wen and R. Lu, “Efficient and
privacypreserving truth discovery in mobile crowd
sensing systems,” IEEE Transactions on Vehicular
Technology, vol. 68, no. 4, pp. 3854– 3865, 2019.
CALYPTIX, “Top 5 risks of cloud computing,”
https://www.caly ptix.com/research-2/top-5-risks-of-
cloud-computing/.
I. security, “Cloud security,” https://www.ibm.com/
security/s aas.
O. C. Security, “Cloud security: A reason to move to
cloud,” https: //www.oracle.com/security/index.html.
A. Piva, F. Bartolini and M. Barni, “Ieee internet
computing: Issue addendum - managing copyright:
Watermark and cryptography algorithms,” IEEE
Distributed Systems Online, vol. 3, no. 5, 2002.
R. Anderson and T. Moore, “Information security
economics–and beyond,” in Annual International
Cryptology Conference. Springer, August 2007, USA,
pp. 68–91.
M. Lelarge and J. Bolot, “Economic incentives to increase
security in the internet: The case for insurance,” in
INFOCOM. IEEE, April 2009, Brazil, pp. 1494–1502.
McAfee, “Net losses: Estimating the global cost of
cybercrime,” Tech. Rep., Center for Strategic and
International Studies, Economic Impact of Cybercrime
II, Jun, 2014.
I. T. R. Center and CyberScout, “Identity theft resource
center data breach reports,”
http://www.idtheftcenter.org/2016databre aches.html.
R. Pal, L. Golubchik, K. Psounis and P. Hui, “On a way to
improve cyber-insurer profits when a security vendor
becomes the cyberinsurer,” in IFIP Networking
Conference. IEEE, May 2013, USA, pp. 1–9.
P. Naghizadeh and M. Liu, “Opting out of incentive
mechanisms: A study of security as a non-excludable
public good,” IEEE Transactions on Information
Forensics and Security, vol. 11, no. 12, pp. 2790–2803,
2016.
X. Lu, D. Niyato, H. Jiang, P. Wang and H. V. Poor, “Cyber
insurance for heterogeneous wireless networks,” arXiv
preprint arXiv:1709.07198, 2017.
TechTarget, “cloud insurance,” http://searchcloudstorage.
techtar get.com/definition/cloud-insurance.
R. Pal, L. Golubchik, K. Psounis and P. Hui, “Security
pricing as enabler of cyber-insurance a first look at
differentiated pricing markets,” IEEE Transactions on
Dependable and Secure Computing, March 2017.
AIG, “Cyberedge,” https://www.aig.com/business/
insurance/c yber-insurance.
J. Chase, D. Niyato, P. Wang, S. Chaisiri and R. Ko, “A
scalable approach to joint cyber insurance and security-
as-a-service provisioning in cloud
AI4IoT 2023 - First International Conference on Artificial Intelligence for Internet of things (AI4IOT): Accelerating Innovation in Industry
and Consumer Electronics
270
