
Systematic Review: The Effect of ARI Recurrence on Unhealthy
Lifestyles
Mega Haryani and Ida Paulina
Master of Pharmacy, Faculty Pharmacy, University 17 August 1945 Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: ISPA, Unhealthy, Lifestyle.
Abstracts: ARI is a very serious infectious disease that occurs when the body's immune system weakens, for example
due to illness or stress. Viruses are the most common cause of ARI. The most common types of infection
are Rhinovirus (RhV), Respiratory Syncytial Virus (PSV), Influenza (IFN), Parainfluenza Virus (PIV),
Covid (CoV), Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV), Heterovirus (EV), Adenovirus (AdV) and Bocavirus
(HBoV). Antibiotics are substances or ingredients used to prevent and treat infections caused by bacteria. In
the United States there are 50 million unnecessary antibiotic prescriptions out of 150 million prescriptions
each year, the use of antibiotics continues to increase, which causes, among other things, inappropriate use
of drugs will cause many problems in terms of effectiveness, side effects, interactions, economics and drug
abuse, thus providing many negative impacts including quality and management of drug services, drug
resistance, side effects on patients, allergies for alergicpatients and psychosocial. This study aims to
determine the relationship between the use of antibiotics and the recurrence rate of ARI. The research
method used was a systematic review by searching for published articles related to the intensity of
recurrence in ARI patients who received antibiotics. Literature searches were conducted in July-August
2023 using electronic database searches, namely ProQuest and google scholar. The next international
journal search was conducted by the researchers through ProQuest with the keywords "relationship between
the use of antibiotics and recurrence in ARI patients" and the search year was limited from 2010 to 2017.
The results of the systematic review of 2 published journals showed that statistically there are factors that
influence ARI recurrence, namely cigarette smoke is very influential in ARI recurrence, and food intake
patterns can also affect nutritional status, and frequent interaction with people who have symptoms can
increase the risk of recurrent relapse.
1 INTRODUCTION
In developed countries, ARI is often caused by
viruses, whereas in developing countries it is caused
by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae and
Haemoplus influenzae, and is responsible for 10-
25% of deaths in developing countries. The
incidence of ARIs is also influenced by several
factors, including poor nutrition, indoor air
pollution, measles vaccination and lack of exclusive
breastfeeding. ARIs are generally mild in nature and
are usually caused by infections and
microorganisms. ARI is a disease caused by various
microorganisms and can cause contamination.
Deaths from the disease are 2-6 times higher in
developing countries. Contamination is one of the
variable causes of death in children under five
(Ministry of Health, 2018).
ARI is a very serious infectious disease caused
by a weakening of the body's immune system, for
example due to illness or stress. In the early stages,
symptoms include nasal pain, dryness and irritation,
followed by persistent wheezing, nasal congestion
with runny nose, fever and migraines. The outer
layer of the nasal mucous membrane appears red and
enlarged. As the disease progresses, mucus thickens
and nasal congestion increases. If there are no
problems, the symptoms disappear after 3-5 days.
Acute respiratory infections are a major cause of
death in agricultural countries. In general, ARI is a
disease of the upper or lower respiratory tract that is
usually contagious and can cause a variety of
illnesses, ranging from mild or asymptomatic
contamination, to asymptomatic or mild disease, to
persistent, severe and fatal disease, depending on
natural factors.
Haryani, M. and Paulina, I.
Systematic Review: The Effect of ARI Recurrence on Unhealthy Lifestyles.
DOI: 10.5220/0012642100003821
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 4th International Seminar and Call for Paper (ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023), pages 205-209
ISBN: 978-989-758-691-0; ISSN: 2828-853X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
205

The availability of different antibiotics requires
better knowledge to choose the right antibiotic to
treat ARI. Health education about ARI is an effort or
activity to help individuals, groups or communities,
especially parents, to improve their knowledge and
skills in caring for infants with ARI so that optimal
quality of health is achieved. ARI is one of the
infectious diseases that is a national priority.
Similarly, ARI is often characterised as a severe
respiratory illness caused by an intolerable specialist
sent from one person to another. Onset is usually
rapid, within a few hours to a few days. Symptoms
include fever, sore throat, coryza (runny nose),
shortness of breath, wheezing or difficulty breathing.
Unwanted natural conditions also build up diseases
that experts breed and work with the course of
disease transmission. One of the factors causing ARI
is also the actual climate conditions and the support
of the home climate. Supporting the home climate
by keeping the house tidy, controlling the air trade in
the house, keeping the home climate tidy and
seeking sunlight into the house during the day,
keeping the air guard in the house clean to prevent
microbes and including trying not to pack as it is
seen as a risk of expanding the incidence of ARI.
Viruses are the most common cause of ARI. The
types of infections that commonly cause ARI are
Rhinovirus (RhV), Respiratory Syncytial Virus
(PSV), Influenza (IFN), Parainfluenza Virus (PIV),
Covid (CoV), Human Metapneumovirus (hMPV),
Heterovirus (EV), Adenovirus (AdV) and Boca
Virus (HBoV) infection (Organisation, 2007).
About a third of antibiotic prescriptions for
children with URI may be inappropriate. A Finnish
study monitored antibiotic prescribing for children
with upper urinary tract infections over seven years.
During this time, the number of paediatric visits for
which antibiotics were prescribed increased. This
happens when the procedure for using antibiotics is
not appropriate. Inappropriate use of antibiotics can
lead to bacterial resistance to antibiotics, which
allows bacteria to adapt to their environment.
Several factors can increase the incidence of
recurrent ARI in young children, one of which is
parental smoking habits, as cigarette smoke is very
influential in the recurrence of ARI. Feeding
patterns can also affect nutritional status, and
frequent interaction with people who have
symptoms can increase the risk of relapse (Chand et
al, 2023).
2 RESEARCH METHODS
The research method used was a systematic review
by searching for published articles related to the
intensity of relapse in ARI patients who received
antibiotics. Literature searches were conducted in
July-August 2023 using electronic database
searches, namely ProQuest and google scholar. The
next international journal search was conducted by
the researchers through ProQuest with the keyword
"relationship between the use of antibiotics and the
recurrence of ARI patients" and the search year was
limited from 2010 to 2017. The national journal
search was conducted through Google Scholar with
the keywords "Relationship between the recurrence
rate of ARI patients and the use of antibiotics" and
the search year was limited from 2010 to 2017. The
journals and articles obtained were then filtered by
title and abstract. The articles selected by the
researcher were based on the desired criteria, namely
the relationship between recurrence and antibiotic
use. Journals that were not relevant to the research
topic were excluded. The selected journals were
evaluated according to the inclusion and exclusion
criteria of the study, and based on the sorting of
these criteria, journals suitable for the systematic
review were obtained. The inclusion criteria used in
the systematic review are journals published from
2010 to 2017, the use of antibiotics, patients with a
primary diagnosis of ARI, the intensity of relapse in
patients, socio-demographics of patients. Literature
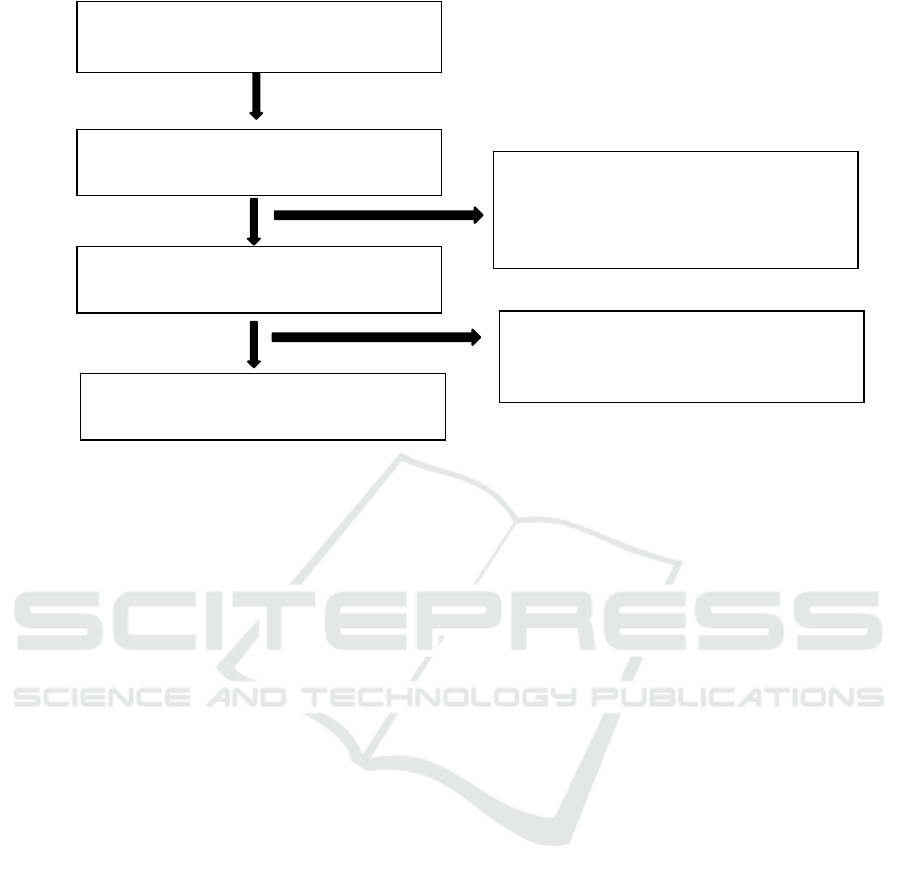
search results, obtained 72 articles in ProQuest and
google scholar data. By selecting the title and
abstract of the article, 43 articles were obtained.
From this evaluation, 19 articles were excluded. The
remaining 10 articles had full manuscripts. From the
ten articles obtained, 4 articles were suitable for
systematic review.
Research design. The systematic review
identified four articles that used a cross-sectional
study design.
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
206
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of the analysis of several articles
conducted in a systematic review, the factors that
influence the recurrence rate of patients who use
antibiotic therapy in ARI patients were obtained.
Factors that influence the recurrence of ARI are
cigarette smoke is very influential in the recurrence
of ARI and food intake patterns can also affect
nutritional status, and frequent interaction with
people who have symptoms may increase the risk of
recurrent relapse. Based on the results of a
systematic review of two articles, antibiotics are one
of the most commonly used treatments in healthcare
settings. However, it is important that antibiotics are
used rationally to provide optimal benefit according
to the patient's clinical needs, including the right
dose. Therefore, the rationality of antibiotic
administration is crucial (Ramlah et al., 20-21).
Research using respondent characteristics, namely
age, sex, diagnosis, antibiotic administration,
number of visits. Research (Tomatala et al., 2019)
suggests that respondent characteristics after chi-
squared test obtained significant results with the
recurrence rate of ARI patients, namely p value less
than 0.05. Patients who are male are 51-54.84%
more than patients who are female, and the age of
patients is more at the age of over 41 years (Reza et
al., 2020).
Research (Riswanto et al., 2018) shows that the
perception of one form of irrational prescribing is
the use of drugs when the indication of the disease is
needed, as in this study the use of antibiotics in
patients with ARI instead of pneumonia. The more
compliant respondents are in carrying out the steps
to establish the diagnosis of ARI. Factors
influencing the use of antibiotics include factors
related to prescribing, drug manufacturing and
patients. Prescribing factors can be influenced by
things such as the level of knowledge about the use
of antibiotics, where a low level of knowledge about
the use of antibiotics can lead to misdiagnosis and
difficulty in distinguishing between bacterial and
viral infections. The availability of diagnostic
facilities and supporting investigations, patient
demand, drug promotion, level and frequency of
supervision in this case seen from the level of
supervision whether strict or not strict and the
frequency of supervision. Supervision by superiors
may increase the rationality of antibiotic use or,
conversely, may lead to under- or over-prescription
of antibiotics due to concerns about prescribing. The
high prevalence of ARIs and their impact leads to
high consumption of over-the-counter medicines
(such as anti-influenza, cough medicines,
multivitamins) and antibiotics. The high incidence of
ARI, including pneumonia, in children under five is
due to the high frequency of recurrent ARI in
children under five. The use of antibiotics for acute
respiratory infections, especially in patients under
five years of age, who are the most affected by ARI,
requires special attention.
The results obtained the use of antibiotics against
ARI infants as much as 53.95%, infants experienced
Systematic
Review
Issued, N=8
The research method does not
match the research criteria.
Full Manuscript
Assessment
Excluded, N = 19
Title does not fit the study criteria,
not related to haemodialysis patients
Selection based on title and abstract
N=43
Database Search
N=72
Systematic Review: The Effect of ARI Recurrence on Unhealthy Lifestyles
207

a recurrence of 46.34% and Chi Square test obtained
a p value of 0.004 (p = <0.05). In this study, the use
of antibiotics in ARI is often irrational. Data from
the Ministry of Health in 2011 showed that 60% of
patients with ARI used antibiotics inappropriately,
i.e. too high or inappropriate dosage, inappropriate
duration of use, prescription of drugs not according
to diagnosis and self-medication with drugs that
should be obtained by prescription. Taking
antibiotics too often means killing all the good
bacteria that are beneficial to the body. When the
population of benign germs that are beneficial to the
body is wiped out, the balance of the body's
microorganisms can be disturbed, so that fungi that
were previously afraid of germs in our bodies have
the opportunity to attack more easily, causing
recurrences or new diseases (Tomatala et al., 2019).
The use of antibiotics that are not in accordance with
therapeutic studies will increase negative effects,
such as bacterial immunity to some antibiotics,
increased incidence of drug side effects, high health
care costs. On the basis of all this, the use of
antibiotics needs to be regulated so that it can be
used appropriately with a structural approach. If
antibiotics are widely used in hospitals and other
health services in inaccurate doses and for long
periods, resistance will develop (Riswanto et al.,
2018).
If antibiotics are administered at too low a dose,
bacterial resistance to the drug will develop, leading
to increased healthcare costs. Factors that affect the
maximum effect of drugs include determining the
correct dose, route and duration of administration.
The pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic
properties of the drug will affect the amount of dose
and the method and frequency of administration,
while the duration of drug administration is based on
the nature of the disease, such as acute, chronic or
recurrent. The main cause of antibiotic resistance is
the widespread and irrational use of antibiotics.
Approximately 80% of antibiotic consumption is for
human use and at least 40% is based on
inappropriate indications such as viral infections.
Factors that can lead to failure of antibiotic therapy
include the emergence of resistant organisms or
organisms that infect changes that can cause disease
recurrence (MOH RI, 2013). Standard prescribing is
rational drug prescribing, i.e. prescribing drugs
according to the standards used. Standard drug
prescribing means prescribing drugs that are correct,
clear and in accordance with patients' needs, taking
into account the type of drug, dosage, duration of
administration and affordability for the community.
Inappropriate drug prescribing leads to inappropriate
treatment, which can have consequences such as the
emergence of antimicrobial resistance, the
occurrence of adverse effects, excessive financial
expenditure and relapse due to the use of drugs that
exceed the limit.
Antibiotics are a class of drugs used to treat and
prevent infections, so antibiotics are used when there
is an infection or for prophylactic purposes (to
prevent infection). Antibiotics are drugs that are
widely used to treat infections caused by bacteria.
Various studies have shown that about 40-62% of
antibiotics are used inappropriately, including for
conditions that do not require antibiotics. The use of
antibiotics that is not in accordance with therapeutic
studies will increase negative effects, such as
bacterial immunity to some antibiotics, increased
incidence of drug side effects, and high health care
costs. On the basis of all this, the use of antibiotics
needs to be regulated so that it can be used
appropriately with a structural approach. If
antibiotics are widely used in hospitals or other
health services in inaccurate doses and for long
periods, they will become resistant (WHO, 2021). In
the study (Azzahra et al., 2023) The data collection
process used secondary data, then the data were
processed using univariate analysis and bivariate
analysis, this analysis was used to determine the
hypothesis by determining the relationship between
variables with the antibiotic.
Chi-square analysis test. Based on the bivariate
analysis of the relationship between antibiotic use
and ARI recurrence, it shows that out of 106
samples given antibiotics, 80 (49.7%) experienced a
recurrence and those who did not relapse were 26
(16.1%). While the group of samples that were not
given antibiotics there were 53 samples consisting of
49 (30.4%) who relapsed and 6 (3.8%) who did not
relapse. From the results of the statistical analysis to
see the relationship between antibiotic use and ARI
recurrence, a value of p=0.040 was obtained,
indicating a significant relationship between
antibiotic use and ARI recurrence. The high
prevalence of ARI in the study area has an impact on
increasing the use of antibiotics and over-the-
counter medicines and increasing the risk of ARI
recurrence, especially in children under five. These
effects significantly increase the incidence of ARI in
the area. The results of Kausar's research (Kausar,
2020) showed that out of 137 populations, 70
patients diagnosed with ARI and using antibiotics,
with an age category ≤5 years, 38 (54.28%) of them
were infants. This shows that there are still many
young children diagnosed with ARI who are given
antibiotics. In addition, the study also showed that
ISCP UTA ’45 JAKARTA 2023 - THE INTERNATIONAL SEMINAR AND CALL FOR PAPER (ISCP) UTA ’45 JAKARTA
208

young children aged 1-5 years are at high risk of
relapse because their immune system is not fully
developed and their age of growth and development
increases their exposure to the outside world.
Therefore, it is important to consider these risk
factors when treating ARI in young children, as the
disease may have a worse clinical impact in infants
and children compared to adults (Yoon et al., 2017).
4 CONCLUSION
Based on research from systematic reviews that
cigarette smoke is very influential in the recurrence
of ARI, and food intake patterns may also affect
nutritional status, and frequent interaction with
people who have symptoms may increase the risk of
recurrence. The use of antibiotics that are not in
accordance with therapeutic studies will increase
negative effects, such as bacterial immunity to some
antibiotics, and giving antibiotics that are under-
dosed will cause bacterial resistance to these drugs,
which will cause health to deteriorate and the
intensity of relapse to increase. There is a
relationship between the use of antibiotics and the
relapse rate of ARI, where the higher the use of
antibiotics in patients with non-pneumonia ARI, the
more likely they are to relapse.
REFERENCES
Azzahra, L., Do Toka, W., Husen, A. H., & Yati, S.
(2023). Relationship between Antibiotic Use and
Recurrence of Acute Respiratory Infection in Toddlers
in Primary Care in Ternate City. Sari Pediatrics,
24(6), 377. https://doi.org/10.14238/sp24.6.2023.377-
81
Chand, K., Butt, M. I., & Tahir, H. M. (2023). Parental
Attitudes, Knowledge, and Practices Regarding the
Usage of Antibiotics for Upper Respiratory Tract
Infections in Children During the COVID-19
Pandemic. Cureus, 15(6), 17-24.
https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.39932
Indonesian Ministry of Health. (2013). Guidelines for
clinical management of ispa. Indonesian Ministry of
Health.
Kausar, F. Al. (2020). Evaluation of Antibiotic Use in
Patients with Acute Respiratory Infection (ARI) at the
Outpatient Installation of the H. Damanhuri Barabai
Regional General Hospital in 2019. Thesis, 1-14.
http://eprints.ums.ac.id/69073/1/Naskah Upper ARI
Publications.pdf
Indonesian Ministry of Health. (2018). Indonesia Health
Profile 2018. In M. K. drg. Rudy Kurniawan, M. S.
Yudianto, SKM, M. Boga Hardhana, S.Si, & M. K.
Tanti Siswanti, SKM (Eds.), Health Statistics.
https://www.kemkes.go.id/downloads/resources/downl
oad/pusdatin/profil-kesehatan- indonesia/profil-health-
indonesia-2018.pdf
Organisation, W. H. (2007). Infection prevention and
control of epidemic- and pandemic- prone acute
respiratory diseases in health care. Infection
Prevention and Control of Epidemic- and Pandemic-
Prone Acute Respiratory Diseases in Health Care,
14(4), 4906-4911.
https://doi.org/10.37506/ijfmt.v14i4.12406
Ramlah, S. T., Nur, D., & Hanifa, C. (2021). Rationality
of Antibiotic Use in Outpatients at Loa Janan Health
Centre in 2020. Borneo Student Research, 3(1), 2021.
Reza, V., Snapp, P., In, E., Di, I. M. A., Socialisation,
A., Cadger, O. F., To, M., Cadger, S., Programpadang,
R., Hukum, F., Hatta, U. B. U. B., Civil, F. T., Hatta,
U. B. U. B., Danilo Gomes de Arruda, Bustamam, N.,
Suryani, S., Nasution, M. S., Prayitno, B., Rois, I., ...
Rezekiana, L. (2020). Incidence of Respiratory Tract
Infections by Gender and Age at Upt Puskesmas
Dolok Merawan. Binus Business Law, 7(2), 33-48.
Riswanto, S. R., Basuki, D. R., & Romdhoni, M. F.
(2018). The Relationship between Antibiotic Use and
the Recurrence Rate of Infectious Diseases at the
Cilembang Health Centre, Tasikmalaya City Period 1
January -31 December 2016. Saintika Medika,
13(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.22219/sm.v13i1.5219
Tomatala, S., Kinasih, A., Kurniasari, M. D., De, F.,
Health, P., Nursing, P. S., Medicine, F., Kristen, U., &
Wacana, S. (2019). The Relationship Between
Physical Activity and Ispa Recurrence in Bringin
District. Respati Yogyakarta Nursing Journal, 6(1),
537-541.
WHO, (World Health Organisation). (2021). The Who
Essential Medicines List Improving antibiotic
Awareness.
WorldHealthOrganisationPublications/Draft, 424.
https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-
source/essential-medicines/eml-antibiotic-book-
draft.pdf?sfvrsn=cb6cb7c2_4&download=true
Yoon, Y. K., Park, C. S., Kim, J. W., Hwang, K., Lee, S.
Y., Kim, T. H., Park, D. Y., Kim, H.J., Kim, D. Y.,
Lee, H. J., Shin, H. Y., You, Y. K., Park, D. A., &
Kim, S. W. (2017). Guidelines for the antibiotic use in
adults with acute upper respiratory tract infections.
Infection and Chemotherapy, 49(4), 326-352.
https://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2017.49.4.32
Systematic Review: The Effect of ARI Recurrence on Unhealthy Lifestyles
209
