
Efficiency of the Tanjung Modang Nagari Tanjung Bonai Weaving
Production Process Using the Data Envelopment Analysis Method
Fresi Ariesti, Rizal, Nil Firdaus, Khairulis Shobirin and Chitra Indah Sari
Universitas Islam Negeri Mahmud Yunus Batusangkar, Indonesia
Keywords: Data, Envelopment, Analysis.
Abstract: The main problem of this research is that the Lintau Weaving Village industry has never conducted an
inspection of its production work unit. This research is quantitative. The data collection technique used is
observation. The study's findings indicate that DMU 2, 4, and 5 pertain to the VRS model calculations in both
2018 and 2021. In the input variable that is not optimal, namely the total cost of raw materials so that
improvements can be made by minimizing the use of raw material costs and planning raw material
requirements by analyzing sales records of weaving which have not been done before. The output variable
that is not optimal is the number of products. Improvements can be made by increasing resources, expanding
marketing, and promoting through various social media platforms.
1 INTRODUCTION
Efficiency is a word that describes the success of a
person or organization in the work being done,
according to how many resources are used to achieve
the results of these activities. Efficiency refers to the
ratio of input to output. (Liana, 2019) Regarding
system theory, efficiency is the ratio of input and
output. The output of input processed by a certain
process will be based on certain sizes and parameters.
Production efficiency in an industry such as the
weaving industry is measured by the output in terms
of the number of woven products and consumers. The
achievement of goals requires competence to do a job
in accordance with the planned objectives (Asmarani,
2019).
One way to increase income in the Lintau
Weaving Village, Jorong Tanjung Modang, Nagari
Tanjung Bonai, Lintau Buo Utara District, Tanah
Datar Regency, is to use production inputs as
efficiently as possible in order to maximize the profits
obtained by the workforce in the Lintau Weaving
Village. The efficient utilization of production inputs
can result in an increase in weaving production. So
far, Lintau Weaving Village has never conducted
inspections of production work units and also the
amount of production produced is only based on the
number of existing workers so it is not yet known
whether production output is efficient or not.
Therefore, it is necessary to measure efficiency to
determine efficiency in the production process.
The DEA method was used to conduct a study in
light of these problems. DEA was introduced to the
public by Charnes, Cooper, and Rhodes. The DEA
method is a method that can be used to measure the
efficiency of a company with the advantage of
accommodating many inputs and outputs in various
dimensions, so that a more accurate efficiency
measurement is obtained as a first step in increasing
productivity. Data Envelopment Analysis is a
productivity multi-factor analysis model to measure
the efficiency of a homogeneous Decision Making
Unit (DMU) group, so the DEA method can be used
because it can accommodate many inputs and outputs
in many dimensions and a more accurate efficiency
measurement will be obtained as a first step in
increase the productivity of a company. Therefore we
need measurements that involve multiple inputs. For
example, the number of workers, the hours worked,
and the total cost of raw materials. The efficiency of
the production process in each company is affected by
the number of customers and products involved in
multi-output.
10
Ariesti, F., Rizal, ., Firdaus, N., Shobirin, K. and Sari, C.
Efficiency of the Tanjung Modang Nagari Tanjung Bonai Weaving Production Process Using the Data Envelopment Analysis Method.
DOI: 10.5220/0012643400003798
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Maritime, Economics and Business International Conference (MEBIC 2023) - Sustainable Recovery: Green Economy Based Action, pages 10-16
ISBN: 978-989-758-704-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Efficiency
Efficiency is the best ratio between input and output
or in other words the optimal results to be achieved
by using existing or limited resources (Munthe,
2019). The higher the ratio of output to input, the
higher the level of efficiency achieved. Efficiency can
also be understood as the achievement of maximum
output through the utilization of specific resources. If
the resulting output is greater than the resources used,
the higher the efficiency achieved. Therefore, this
efficiency is related to the value chain, which refers
to the linkages between activities carried out in
creating goods and services.
2.2 Efficiency Measurement
The efficiency of a DMU is measured by its relative
efficiency against that of other DMUs in a sample
population. Here the condition applies that the DMUs
contain the same type of inputs and outputs (Munthe,
2019).
2.3 Production
In terminology, the word production means to make
an object and add value to it. The value of a product
increases when it provides new or more benefits than
previously. In general, production is the creation of
goods, which means the ability of a product or service
to meet certain human needs (Lubis, 2017).
2.4 Production Process
Process is a way, method, or technique for
implementing a certain thing. While production is an
activity designed to add or create benefits, it also
considers the form, timing, and location of production
factors that are beneficial to satisfying consumers.
This can be interpreted that the production process is
a step or stage of activity to make an input into an
output that has added value.
2.5 Data Envelopment Analysis Method
Thanassoulis (2001) stated that DEA is a method for
measuring the relative efficiency of homogeneous
operating units like schools, hospitals, industrial
centers, and so forth. The purpose of DEA is to
determine efficiency in production processes and find
improvement strategies for inefficient production
processes. The advantage of DEA is that it
accommodates many inputs and outputs in various
dimensions, so that a more accurate measurement of
efficiency can be obtained.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
This research is a quantitative study aimed at
analyzing Data Envelopment Analysis in measuring
efficiency. The object of this research is the input and
output data from the weaving village. While the
subject of this research is weaving or songket from
Lintau weaving village as a DMU.
The population used in this study is all woven
production in 2018-2021 in Lintau Weaving Village.
The sample of this research is the Decision Making
Unit (DMU), which consists of 5 DMUs including the
Dewi Weaving Unit, Era Weaving Unit, Riza
Weaving Unit, Siti Weaving Unit and Triya Weaving
Unit because the level of efficiency will be measured.
The instruments in this study were processed by
researchers using company data results. In this study,
LINDO 6.1 is utilized as the software. The data
collection technique that the researchers used was
observation, namely the method of collecting data by
taking data directly in the field and by direct
interviews with the weaving village. In this study,
primary and secondary data were used. Primary data
is data obtained from direct interviews with the
weaving village. Secondary data is data that has been
collected and processed by other parties and doesn't
need to be measured again.
Data Analysis Techniques is an attempt to create
a detailed description for further study. The data that
has been obtained is then calculated and analyzed on
the results obtained. The data needed for this research
are product data, labor data, production working
hours data, raw material cost data, and customer data.
The data obtained is data related to the weaving
production process. The data used is data for 2018-
2021. The variables that are employed are both input
and output variables in the process of production.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 What Is the Weaving Efficiency
Level?
Based on the calculations that have been done, in
2018, the results obtained were less than 1
(inefficient), specifically for the Era Weaving Unit,
Siti Weaving Unit, and Triya Weaving Unit. The
Efficiency of the Tanjung Modang Nagari Tanjung Bonai Weaving Production Process Using the Data Envelopment Analysis Method
11

efficiency value for the Era Weaving Unit is
0.8250000, Siti's Weaving Unit is 0.6875000, and
Triya's Weaving Unit is 0.8491666. The variable that
has the highest average weight is the number of
customers with a value of 0.0438332. The customer
variable is the most influential variable among all
other variables. This means that the number of
customers is relatively important in the Lintau
weaving village. Next is the variable amount of raw
material costs, which has an average weight of
0.0000444. Next is the variable amount of working
hours, which has an average weight of 0.000081.
Whereas the variable number of products has an
average weight value of 0 and the variable number of
workers has an average weight of 0. This means that
relatively the labor and product variables do not affect
the value of efficiency in Lintau Weaving Village.
Based on the calculations that have been carried
out, in 2019 the results obtained were less than 1
(inefficient), namely the Siti Weaving Unit with an
efficiency value of 0.9444444The variable that has
the highest average weight is the number of
customers with a value of 0.0533336. The customer
variable is the most influencing variable compared to
other variables. The importance of customers is
relative in Kampung Tenun Lintau. Next is the
variable amount of raw material costs, which has an
average weight value of 0.0002516. Next is the
variable amount of working hours, which has an
average weight value of 0.000044. Meanwhile, the
average weight value of the variable number of
products is 0 and the average weight value of the
variable number of workers is also 0. This means that
relatively the labor and product variables do not affect
the value of efficiency in Lintau Weaving Village.
Based on the calculations that have been done, in
2020 the results obtained are less than 1 (inefficient),
namely the Siti Weaving Unit with an efficiency
value of 0.8875740. While the Triya Weaving Unit
has an efficiency value of 0.9230769. The variable
with the highest average weight is the number of
customers, with a value of 0.0809882. The customer
variable is the most influencing variable compared to
other variables. The number of customers in
Kampung Tenun Lintau is a significant factor. Next,
namely the variable number of workers who have an
average weight with a value of 0.0150474, the
variable total cost of raw materials with an average
weight of 0.0002744, then the variable number of
hours worked with an average weight of 0.000022.
The number of products is variable and their average
weight is 0. This means that the product variable does
not affect the efficiency value in Lintau Weaving
Village.
Based on the calculations that have been done, in
2021 the results obtained are less than 1 (inefficient),
namely the Era Weaving Unit with an efficiency
value of 0.975, Siti Weaving Unit with an efficiency
value of 0.9 while the Triya Weaving Unit with an
efficiency value of 0.9. The variable with the highest
average weight is the number of customers, with a
value of 0.063. The customer variable is the most
influencing variable compared to other variables. The
number of customers in Kampung Tenun Lintau is a
significant factor. Next is the variable number of
workers who has an average weight with a value of
0.04, then the variable amount of raw material costs
with an average weight of 0.0001016. The variable
number of products and hours worked has an average
weight value of 0. This means that relatively the
product variable does not affect the value of
efficiency in Lintau Weaving Village.
The CRS Dual model, which was carried out
using LINDO 6.1, produces Technical Efficiency
(TE) and Slack variables. The dual CRS (constant
return to scale) model is a continuation of the primal
CRS, but in dual CRS, there is no linear relationship
between output and input variables.
The results of CRS Dual in 2018, namely DMU 1
and DMU 3 have a TE value of 1 because the value
of z = 1 and are considered efficient, while DMU 2
TE is 1.3872992751 , DMU 4 TE is 1.6647591302 ,
DMU 5 TE is 1.3868984969. for DMU 2 there is
Slack at Y1 of 0.000133 , X3 of 0.000041. DMU 4
has Slack at Y1 of 0.000133, X3 of 0.000041 and
DMU 5 has Slack at Y1 of 0.000137, X3 of 0.000063.
The Era Weaving Unit has a CRS Dual efficiency
value of 0.7208250, this means that the Era Weaving
Unit is not optimal based on technical and scale
aspects simultaneously. From the CRS Dual
calculation, the slack output value for the number of
So1 products is 0.000133, and the slack input value
for the total Si3 raw material cost is 0.000041. The
Siti Weaving Unit has a CRS Dual efficiency value of
0.6006875, which means that it is not optimal based
on technical and scale aspects simultaneously. From
the CRS Dual calculation, the slack output value for
So1 is 0.000133 and the slack input value for Si3 is
0.000041. The Triya Weaving Unit has a CRS Dual
efficiency value of 0.7210333, which means that it is
not optimal based on technical and scale aspects
simultaneously. The CRS Dual calculation shows that
So1 has a slack output value of 0.000137 and Si3 has
a slack input value of 0.000063. Meanwhile, the Dewi
Weaving Unit and Riza Weaving Unit have a dual
CRS value that is already efficient and optimal,
namely 1 from a technical and concurrent scale
perspective. A DMU that has slack functions to make
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
12

improvements, by adding or subtracting the value of
each variable in the DMU to achieve an optimal
objective function based on the results of CRS Dual.
The results of CRS Dual in 2019, namely DMU 1,
DMU 2, DMU 3 and DMU 5 have a TE value of 1
because the z=1 value is considered efficient, while
DMU 4 TE is 1.1624054819, for DMU 4 there is
Slack at Y1 of 0.000136, X1 of 0.023767. The Siti
Weaving Unit has a CRS Dual efficiency value of
0.8602850, this means that the Siti Weaving Unit is
not optimal based on technical and scale aspects
simultaneously. The CRS Dual calculation results in
a slack output value of 0.000136 for the number of
So1 products, compared to a slack input value of
0.023767 for Si1. Meanwhile, the Dewi Weaving
Unit, Era Weaving Unit, Riza Weaving Unit and
Triya Weaving Unit have a dual CRS value which is
efficient and optimal, namely 1 from a technical point
of view and concurrent scale. A DMU that has slack
functions to make improvements, by adding or
subtracting the value of each variable in the DMU to
achieve an optimal objective function based on the
results of CRS Dual.
The results of CRS Dual in 2020, namely DMU 1,
DMU 2, and DMU 3 have a TE value of 1 because
the z=1 value is considered efficient, while DMU 4
TE is 1.2322274298, for DMU 4 there is Slack at Y1
of 0.000158, X1 of 0.038067 . DMU 5 TE is
1.0833333604, for DMU 5 there is Slack at Y1 of
0.000155, X1 of 0.025541 and X3 of 0.000044. The
Siti Weaving Unit is not the optimal choice due to its
CRS Dual efficiency value of 0.8115385, which takes
into account both technical and scale aspects
simultaneously. The CRS Dual calculation yields a
slack output value of 0.000158 for So1 products, and
an input SI1 value of 0.038067. The Triya Weaving
Unit has a CRS Dual efficiency value of 0.9230769,
which means that it is not optimal based on technical
and scale aspects simultaneously. From the CRS Dual
calculation, the slack output value for the number of
So1 products is 0.000155, while the slack input Si1 is
0.025541, and Si3 is 0.000044. Meanwhile, the Dewi
Weaving Unit, Era Weaving Unit, and Riza Weaving
Unit have a dual CRS value which is efficient and
optimal, namely 1 from a technical and concurrent
scale perspective. A DMU that has slack functions to
make improvements, by adding or subtracting the
value of each variable in the DMU to achieve an
optimal objective function based on the results of
CRS Dual.
The results of CRS Dual in 2021 are that DMU 1
and DMU 3 have a TE value of 1 because the value
of z=1 is considered efficient, while DMU 2 TE is
1.2091423251, for DMU 2 there is Slack at Y1 of
0.000124, X3 of 0.000041. DMU 4 TE is
1.3666803335, for DMU 4 there is Slack at Y1 of
0.000126, X1 of 0.025700. DMU 5 TE is
1.204456489, for DMU 5 there is Slack at Y1 of
0.000130, X1 of 0.036650. The Era Weaving Unit has
a Dual CRS efficiency value of 0.8270325. This
means that the Era Weaving Unit is not optimal based
on technical and scale aspects simultaneously. From
the CRS Dual calculation, the slack output value for
the number of So1 products is 0.000124 and the slack
input Si3 is 0.000041. The Siti Weaving Unit has a
CRS Dual efficiency value of 0.7317, which means
that the Siti Weaving Unit is not optimal based on
technical and scale aspects simultaneously. The CRS
Dual calculation shows that the slack output value for
So1 products is 0.000126, compared to the slack input
SI1 being 0.025700. The Triya Weaving Unit has a
CRS Dual efficiency value of 0.83025, which means
that the Triya Weaving Unit is not optimal based on
technical and scale aspects simultaneously. From the
CRS Dual calculation, the slack output value for the
number of So1 products is 0.000130 and the slack
input Si1 is 0.036650. Meanwhile, the Dewi Weaving
Unit and Riza Weaving Unit have a dual CRS value
which is already efficient and optimal, namely 1 from
a technical and concurrent scale perspective. A DMU
that has slack functions to make improvements, by
adding or subtracting the value of each variable in the
DMU to achieve an optimal objective function based
on the results of CRS Dual.
At this stage, the VRS model is calculated to
determine if the DMU efficiency is purely technical
efficiency or influenced by other factors outside the
DMU. This VRS model is a refinement of the CRS
DUAL model by providing a convexity constrain = 1.
In 2018, in the VRS calculation, there was only 1
inefficient DMU, namely DMU 2 Era, where the Era
Weaving Unit had a slack output value of So1 of
0.000107 and slack input of Si3 of 0.000041.
In 2019, in the VRS calculation, there were only
2 inefficient DMUs, namely DMU 2 Era and DMU 3
Riza, where the Era Weaving Unit had a slack output
value of So1 of 0.000118 and slack input Si1 of
0.023767. Meanwhile, the Riza Weaving Unit has a
slack output value of 0.000118 at So1 and 0.000228
at Si2.
In 2020, in the calculation of VRS, all DMUs are
efficient.
In 2021, in the VRS calculation, there are only 3
inefficient DMUs, namely DMU 2 Era, DMU 4 Siti,
and DMU 5 Triya where the Era Weaving Unit has a
slack output value of So1 of 0.000115 and slack input
Si3 of 0.000041, Siti's Weaving Unit has a slack value
the output at So1 is 0.000117 and the slack input at
Efficiency of the Tanjung Modang Nagari Tanjung Bonai Weaving Production Process Using the Data Envelopment Analysis Method
13
Si3 is 0.000057. While the Triya Weaving Unit has a
slack output value at So1 of 0.000120 and a slack
input at Si3 of 0.000081.
TE values are produced by the calculations of
CRS and VRS models that can be used to calculate
scale efficiency (SE) values. The TE value is obtained
by dividing the optimum efficiency value (1) with the
efficiency value of each DMU for both CRS and VRS
calculations. To get the SE value for each DMU, the
TECRSDUAL value is divided by TEVRS.
4.2 How are DMUs Targeted for
Improvement?
DMUs that have efficient results can become a
reference for improvement for DMUs that have
inefficient results by forming a peer group. Formation
of peer groups by using hierarchial cluster analysis
using SPSS software by looking at the closest squared
euclideant distance between DMUs. The smaller the
squared euclideant distance between the 2 DMUs, the
more similar the DMUs are. The following is the
result of forming a peer group using SPSS software.
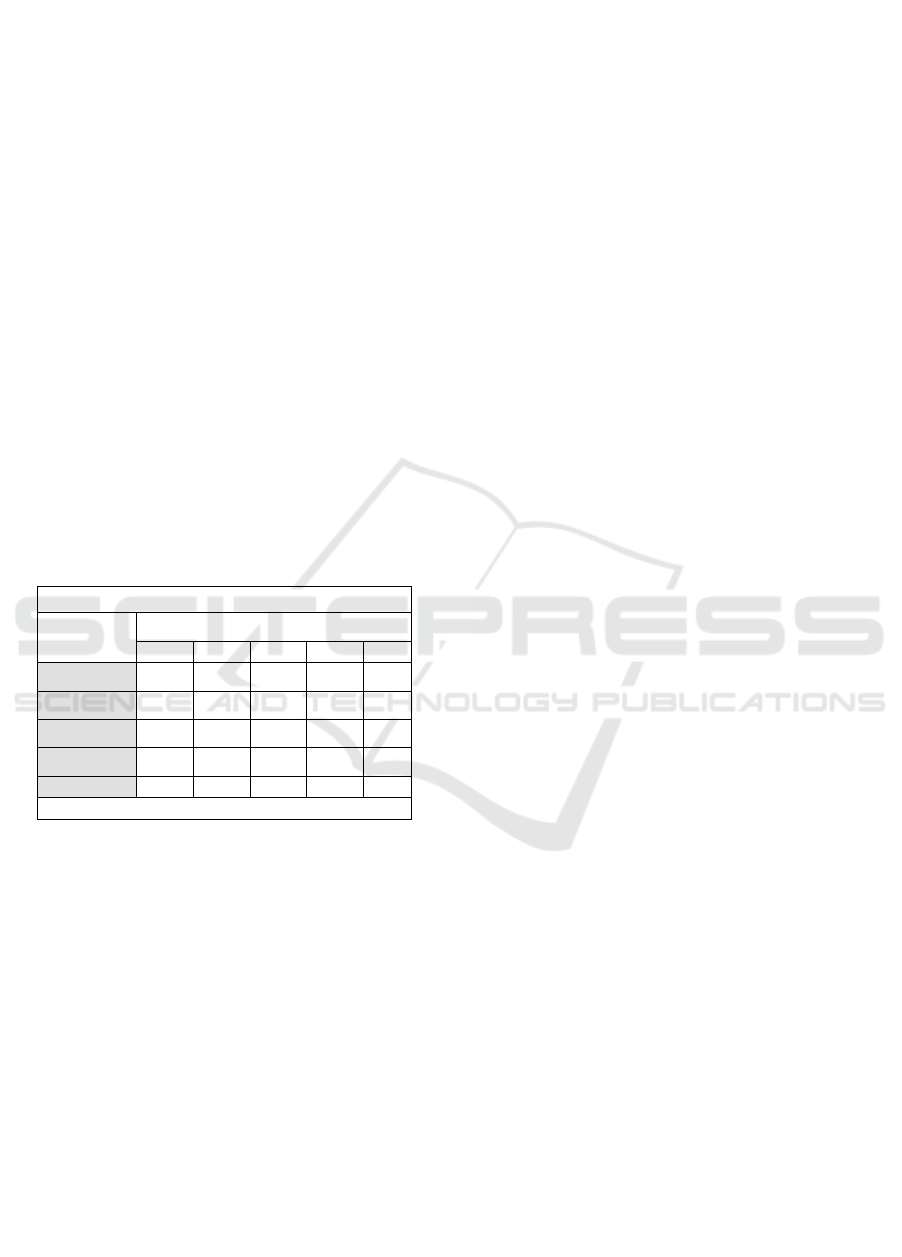
Tabel 1: Hasil Peer Group 2018.
Proximity Matrix
Case
Squared Euclidean Distance
1
2
3
4
5
1
,000
,228
,000
,884
,299
2
,228
,000
,228
,251
,026
3
,000
,228
,000
,884
,299
4
,884
,251
,884
,000
,154
5
,299
,026
,299
,154
,000
This is a dissimilarity matrix
The table shows that DMU 1 has the smallest
proximity value to DMU 2 of 228. In DMU 2 it has
the closest distance to DMU 3 of 228. Meanwhile,
DMU 4 has the smallest proximity value to DMU 5
of 154. At DMU 5 has the smallest closeness value
with DMU 2 of 026.
DMUs that have an inefficient score can be
considered efficient DMUs, as improvements can be
made to one or more DMUs with the help of a peer
group. Peer groups can be done using SPSS software
using the Hierarchial Cluster Analysis method,
namely by looking at the closest squared Euclidean
distance between DMUs. Where closeness is done to
provide a reference for an inefficient DMU to an
efficient DMU.
The results of the SPSS software discuss the value
of Squared Euclidean Distance, where the smallest
value is between the Triya Weaving Unit and the Era
Weaving Unit, which is .026, while the largest value
is between the Dewi Weaving Unit, Riza Weaving
Unit and Siti Weaving Unit, which is .884.
In 2018, the dual DMU CRS model, which has an
inefficient value, is the Era Weaving Unit, Siti
Weaving Unit, and Triya Weaving Unit. The DMU
VRS model is only inefficient for the Era Weaving
Unit. Therefore the Era Weaving Unit becomes an
inefficient DMU based on the 2 models CRS dual and
VRS. At DMU Era, the variable that experienced
target improvement was y1 from a value of 21600 to
21618.000133 with an improvement of 0.083% and
the x3 variable from a value of 5000 to 3604.124959
with an improvement of 27.91%. Meanwhile, based
on DMU Era's VRS calculations, there were 2
variables that experienced target improvements,
namely the number of products from 21600 to
21618.000107 with an improvement of 0.083% and
the raw material cost variable from 5000 to
4540.749959 with an improvement of 9.1%.
Sensitivity analysis is conducted to observe
changes in efficiency that occur after targeted
improvements are made. The optimization reference
is obtained from the dual price value, as the given
limiting function will bind the target function.
The results of calculations from the dual CRS and
VRS models will be subjected to sensitivity analysis
to find out which model will be used as a reference in
increasing efficiency based on target improvements.
In 2018 based on CRS Dual calculations, the Era
Weaving Unit has 2 variables that are not optimal,
namely the output variable y1 (number of products)
and the input variable x3 (raw material costs). Based
on the results of calculations using LINDO software,
the variable y1 has a dual price value of -0.000100,
while the variable x3 has a dual price value of
0.000141. This means that the variable y1 will
increase the efficiency of the Era Weaving Unit by
0.0018000133 so that it will change the efficiency
value at DMU 2 Era by 0.7226250132. The variable
x3 will increase the efficiency of the Era Weaving
Unit by 0.1968183808, thereby changing the
efficiency value of the Era Weaving Unit by
0.9176433807.
Based on the calculations on the VRS model, the
Era Weaving Unit has 2 variables that are not optimal,
namely the output variable y1 (number of products)
and the input variable x3 (raw material costs).
Calculations from the LINDO software produce a
dual price value for variable y1 (output) of -0.000100,
while for variable x3 it is 0.000141. This means that
the variable y1 will increase the efficiency of the
DMU by 0.0018000107, which will also increase the
efficiency of the Era Weaving Unit by 0.9063499893.
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
14

The variable x3 will increase the efficiency of the Era
Weaving Unit by 0.0647542558, which will change
the efficiency value of DMU 2 by 0.9693042344.
Based on the results of the sensitivity analysis, it can
be seen that the repair value has not reached its
optimal value. The two results indicate that the
improvement will be attributed to the VRS model due
to its higher efficiency value than the CRS dual
efficiency value.
4.3 The Right Strategy in Increasing
Efficiency?
Based on the results of the calculations that the
researcher has performed, the solutions that will be
provided only refer to DMUs that have non-optimal
or inefficient efficiency values. In 2018, the CRS
Dual model has 3 inefficient DMUs, namely the Era,
Siti and Triya Weaving Units. Whereas in the DMU
VRS model, only the Era Weaving Unit has non-
optimal values. The improvements made are 2
solutions, namely by using the CRS Dual or VRS
model. Referring to the results of the sensitivity
analysis, it was found that VRS's improvement is
better than CRS Dual, so the solution to be given
should be based on the VRS model. In the calculation
of the VRS model, there is an Era Weaving Unit
DMU which has a non-optimal value. The Era
Weaving Unit's efficiency values are influenced by
two variables: y1 (number of products) and x3 (raw
material costs). The improvement solution required is
for variables y1 (number of products) and x3 (raw
material costs). The increase in target improvements
from DMU 2 or Era Weaving Units also takes into
account the results of peer groups as shown in table
4.27 which shows that Era Weaving Units can
perform benchmarking referring to DMUs with the
lowest and closest value, namely DMU 1 or Dewi
Weaving Unit and DMU 3 or Unit Riza Weaving. In
the Era Weaving Unit there are 18 products while in
the Dewi Weaving Unit there are 25, therefore DMU
Era can refer to DMU Dewi or DMU Riza by
increasing sales results in order to increase the value
of variable y1 (number of products). Increasing sales
can be done by promoting or cooperating with other
companies. The raw material costs of the Era
Weaving Unit will be raised by 9.1% in relation to the
Dewi Weaving Unit. The Dewi Weaving Unit's raw
materials cost is the lowest among all DMUs.
Therefore, by referring to the Dewi Weaving Unit, the
cost of raw materials in the Era Weaving Unit can
make improvements by minimizing the use of raw
material costs and planning raw material
requirements by analyzing records of weaving sales
which have not previously been carried out by the Era
Weaving Unit.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the results of the study it can be concluded as
follows:
1. The results of measuring the efficiency of the
weaving production process in Tanjung Modang
using Data Envelopment Analysis in 2018 show
that the Era Weaving Unit is a DMU that has an
inefficient value with an efficiency value of
0.9081500. In 2019 it shows that the Siti Weaving
Unit is a DMU that has an inefficient value with a
value of 0.8602850. In 2020 it shows that the Siti
Weaving Unit and the Triya Weaving Unit have
an inefficient value. In 2021 it shows that the Era
Weaving Unit, Siti Weaving Unit and Triya
Weaving Unit are DMUs that have an inefficient
value with values of 0.9250975, 0.8895 and 0.999.
2. The 2018 improvement target for the Era
Weaving Unit is because the value obtained is <1
with the variables that are the target for
improvement, namely Y1 (number of products)
and X3 (raw material costs). In 2019, after
improvements were made to the VRS model, the
Siti Weaving Unit, which was previously
inefficient, became efficient. In 2020, after
improvements were made with the VRS DMU
model, which was previously inefficient, it will
become efficient. The target for improvement in
2021 for the Era Weaving Unit and Siti Weaving
Unit is because the values obtained are <1 with the
variables that are the target of improvement,
namely Y1 (number of products) and X3 (raw
material costs). The Triya Weaving Unit is the
optimal DMU after target improvement on y1 and
x3.
3. Based on the results of data processing and
analysis carried out in 2018 and 2021. The Era
Weaving Unit, Siti Weaving Unit and Triya
Weaving Unit refer to the calculation of the VRS
model. In the input variable that does not yet have
an optimal value, namely the variable amount of
raw material costs so that the three DMUs can
make improvements by minimizing use of raw
material costs and planning raw material
requirements by analyzing records of weaving
sales that had not previously been carried out. The
output variable that is not optimal is the number
of products so that improvements can be made by
increasing resources, expanding marketing and
promoting from various social media platforms.
Efficiency of the Tanjung Modang Nagari Tanjung Bonai Weaving Production Process Using the Data Envelopment Analysis Method
15

REFERENCES
Asmarani, D. (2019). Analisis faktor-faktor yang
mempengaruhi efisiensi Bank Umum Syariah (BUS) di
Indonesia periode 2015-2019. 101.
Kusuma, D. (2020). Benchmarking Kinerja Rantai Pasok
Ikm Kulit di Sleman Menggunakan Metode Data
Envelopment Analysis (DEA) [universitas islam
indonesia yogyakarta].
Liana, W. (2019). Usaha Meningkatkan Efisiensi Sumber
Daya Manusia Pada Kinerja Karyawan PT Indosat Tbk
Palembang. Jurnal Ilmiah Ekonomi Global Masa
Kini,10(2),124.https://doi.org/10.36982/jiegmk.v10i2.851
Munthe, winda julianti. (2019). Implementasi Metode Data
Envelopment Analysis (Dea) Pada Pengukuran
Efisiensi Kinerja Program Studi Di Lingkungan
Implementasi Metode Data Envelopment Analysis (
Dea) Pada Pengukuran Efisiensi Kinerja. Skripsi.
Pratiwi, I. (2018). Benchmarking Kinerja Procurement
Kantor Kecamatan Dengan Pendekatan Data
Envelopment Analysis (Dea). 99.
Saragih, J. (2014). Pengukuran Kinerja Supplier Pada
Rantai Suplai Menggunakan Metode Fuzzy - Data
Envelopment Analysis (Dea) Di Pt Pusaka Prima
Mandiri (Ppm) Medan. 1–196.
Zaenal Arifin. (2018). Penggunaan Software Lindo Dalam
Matakuliah Program Linear. THEOREMS, Vol. 3 No.,9.
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
16
