
Digital Transaction Model in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises
(MSMEs) to Target Millenial Generation Consumers in
Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Lastri Anggi Fani
1
and Zakiyah Mawaddah
2
1
Economics and Business Maritime Faculty, Raja Ali Haji Maritime University,
Dompak Main Road, Tanjungpinang, Indonesia
2
Information Technology and Business Faculty, AKPRIND Technology and Science Institute,
Kalisahak Street,Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Digital Transaction, TAM, TPB, Millenials.
Abstract: The current millennial generation is the majority generation in Indonesia, this generation has characteristics
that are accustomed to using digital technology. This generation is undoubtedly responsible for driving the
growth of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). This study aims to understand the factors that
significantly influence the adoption of digital transactions in micro, small, and medium enterprises
(MSMEs) in the millennial consumer generation in Yogyakarta. This study combines the TAM (Technology
Acceptance Model), TPB (Theory of Planned Behaviour) and transaction costs which include the variables
of perceived ease of use, perceived risk, subjective norms, and transaction costs. In this research, CFA
(Confirmatory Factor Analysis) is utilized. The study utilizes a quantitative research design that utilizes
primary data obtained through questionnaire distribution. The questionnaires collected in this study were
100 respondents. The sampling method used was purposive sampling. The data was analyzed with SPSS 25
using multiple regression analysis techniques. Data testing in this study used the T test and F test. The
results of the T test by comparing the T-calculated value with the T-Table showed that the variables
perceived of use, transaction costs and subjective norms had an influence on the dependent variable, namely
adoption, while the variable perceived risk had no influence on the adoption variable. Then, using the F test,
the results showed that all independent variables had a simultaneous influence on the dependent variable.
The results show that reduced transaction costs, perceived ease of use, and the role of peer influence are
factors that significantly influence Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in adopting digital
transactions. Meanwhile, the perceived risk factors for using technology do not significantly affect MSMEs
in adopting digital transactions.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Indonesia, the current millennial generation is the
majority generation. Based on The National
Socioeconomic Survey (SUSENAS) in 2017, it is
known that the number of millennials is currently
around 33.75% of the total population in Indonesia
or around 88 million people. The millennial
generation is the generation born between 1980 and
2000 (Central Agency of Statistics, 2018).
The millennial generation is a generation that is
accustomed to using digital technology. This
generation drives innovation in the digital payment
industry. It is known that 98% of millennials use
smartphones and 97% of them actively use social
media (Mamanaova, 2019). The preference of 65%
of millennials is to use their phones to make
payments for certain products or services
(Mamanaova, 2019). The reason why millennials
use cellphones is that they believe it is more
comfortable, saves time, and provides more options
(Visa, 2016). The use of digital wallets allows a
business to expand market reach and attract the
attention of consumers and is one of the strategies in
an effort to face competition between similar
products and businesses (Erlina, 2021). The focus
for several industries, particularly the Small, Micro,
and Medium Enterprises industry, is on this.
58
Fani, L. and Mawaddah, Z.
Digital Transaction Model in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterpeises (MSMEs) to Target Millenial Generation Consumers in Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0012643500003798
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Maritime, Economics and Business International Conference (MEBIC 2023) - Sustainable Recovery: Green Economy Based Action, pages 58-63
ISBN: 978-989-758-704-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
Apart from that, the reason why many consumers
use digital transactions is also supported by
circumstances that require them to be more cashless.
According to Bagas (2021), which cites
Neurosensum, the pandemic in Indonesia has
resulted in an increase in the number of digital
wallet users over the past year. Neurosensum data
indicates that the growth of digital wallet users has
increased by 44 percent. The pandemic in Indonesia
has forced people to comply with the rules limiting
direct social contact and maintaining physical
distance from each other, so that the existence of
digital wallets can support people in implementing
these rules.
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises
(MSMEs) contribute 60.5 percent to the Gross
Domestic Product (GDP), 96.9 percent employment,
and 16.6 percent exports (Ministry of Cooperatives
and SMEs of the Republic of Indonesia, 2023).
Currently, the number of MSMEs in Indonesia is
around 60 million (Ministry of Cooperatives and
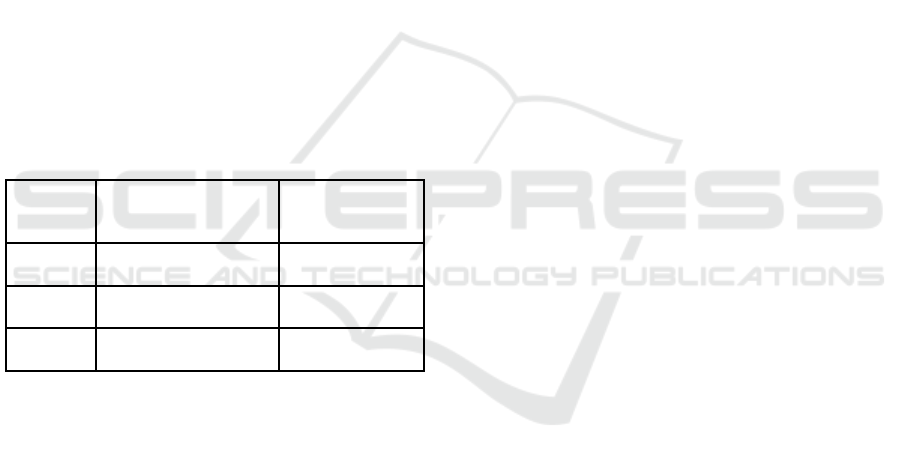
SMEs of the Republic of Indonesia, 2023). Table 1
below were criteria’s for MSMEs according to Law
of the Republic of Indonesia Number 8 of 2003.
Table 1: MSMEs Criteria by Capital and Sales.
Business
Scale
Capital (IDR) Sales (IDR)
Micro up to 50 billion up to 300 billion
Small up to 500 billion up to 2.5 million
Mediu
m
u
p
to 2.5 million u
p
to 50 million
In Yogyakarta, the number of Micro, Small and
Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) was 344,293 units
(Bappeda.jogjaprov.go.id., 2023). Based on the type
of business, there are 326.114 units of Micro, 16.069
units of Small and 2,110 units of Medium
Enterprises (Bappeda.jogjaprov.go.id., 2023). Based
on location, Bantul Regency has 87.429 units,
Gunungkidul has 54.306 units, Kulon Progo has
36.298 units, Sleman has 114.609 units, and
Yogyakarta City has 32.917 units (Bappeda.
jogjaprov.go.id., 2023).
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and
Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) are two factors
that can influence MSMEs to adopt digital
transactions. TAM is a model based on perceptions
of digital transaction adoption (Davis et al., 1989).
TAM aims to track how users react to digital
transactions, whether they accept or reject them.
TAM is a model that focuses on two main factors
that influence technology adoption: perceived
usefulness and perceived ease of use.
Perceived usefulness is the user's belief that a
technology will improve their performance, while
perceived ease of use is the user's belief that a
technology is easy to learn and use. TAM has been
validated as an effective model for predicting the
adoption of digital transactions by MSMEs in
several studies.
TPB explains individual behaviour based on
attitudes, social norms and the ease or difficulty of
doing it (Ajzen, 2001). Human behaviour
(individual) is formed from the presence of certain
motivations. The TPB is a more comprehensive
model that includes three factors that influence
human behavior: attitudes, social norms, and
perceived behavioral control. Attitudes are the user's
positive or negative feelings about a technology,
social norms are the perceived pressure from others
to use or not use the technology, and perceived
behavioural control is the user's belief that they have
the ability to use the technology. TPB has been
shown to be a reliable model for predicting MSMEs'
adoption of digital transactions in a number of
studies.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Technology Acceptance Model
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) was a
theory adapted from Theory of Reasoned Action
(TRA) and developed by Davis et al. (1989). TAM
is the most widely applied technology acceptance
methodology for business units (Wu, 2009). TAM
has two specific factors, namely Perceived
Usefulness (PU) and Perceived Ease of Use (PEU)
(Davis et al., 1989).
PU, namely someone who believes that
adopting technology can provide benefits, increase
performance and productivity, and efficiency (Davis
et al., 1989). PEU, someone believes that using
digital transactions is something that is easy to do
and does not require much effort to do (Davis et al.,
1989). PU and PEU are factors that influence
attitudes towards use (Attitude Toward Using/ATU),
namely a person's attitude towards technology
acceptance, namely the adoption of digital transact-
tions. This attitude will lead to Behavioural Intention
to Use (BI), namely a person's desire to adopt digital
transactions and finally Actual system use.
Digital Transaction Model in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterpeises (MSMEs) to Target Millenial Generation Consumers in Yogyakarta,
Indonesia
59
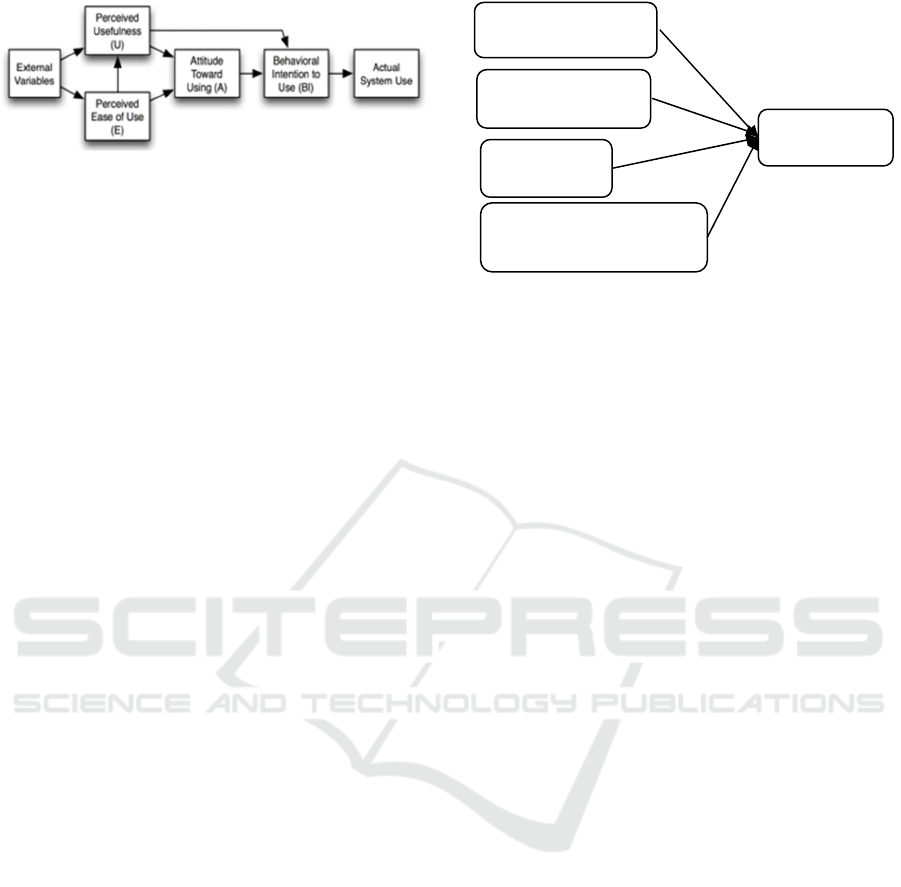
Figure 1: Theory Acceptance Model.
2.2 Theory of Planned Behaviour
Theory of Planned Behavior is a theory that
developed from TRA. TPB explains about human
behaviour (Ajzan & Madden, 1989). The existence
of a certain behavioural intention (intention to do
something) is the basis of human behavior. Factors
that influence behavioural intention, namely attitude,
subjective and perceived behavioural control.
Subjective norms are social norms or
surrounding norms that are felt by humans to do or
not to do behaviour (Ajzen, 1991). In this case,
social factors become the cause of the formation of
certain behaviours. For example, one of MSMEs
adopts digital transactions due to the influence of
other MSMEs who use digital technology in their
transactions, which attracts consumer interest.
Behavioural intention/BI means that the person
concerned has the intention to take action, in this
case, namely to accept technology. The stronger a
person's intention, the more likely the person is
expected to try the behaviour, the more likely the
behaviour will be carried out (Ajzen and Madden,
1986: Ajzen, 1991). For example, in this study, the
intention of MSMEs to adopt high-digital
transactions eventually led to their adoption.
Perceived behavioural control, namely the ease or
difficulty that someone feels in doing something.
TPB is then refined by adding trust and
perceived risk (Mazzocchi et al., 2005). Perceived
risk is the potential for loss when users use digital
transactions in their transactions (Mazzocchi et al.,
2005).
3 HYPOTHESES AND
FRAMEWORK
Figure 2 displays the theoretical model linking the
Technology Acceptance Model (perceived ease of
use) (Davis, 1989), Theory of Planned Behaviour
(subjective norms, perceived risk (Ajzen, 1991),
transaction cost (Dodgson et al., 2015), and adoption
of digital transactions.
Figure 2: Research Framework.
Users prefer applications or technology that are
easy to use because there is no need to spend
excessive effort. Excessive effort can drain the
resource. According to theory Davis (1989), an
application or technology perceived to be easier to
use than another is more likely to be used. In this
study, the respondents are MSMEs, they focused on
profit and minimazed costs. Learning a new
application or technology definitely costs a lot of
money, so people will choose to use something that
is easier to use. We hypothesise as follows:
H1: Perceived ease of use positively influences the
adoption of digital transactions.
No user likes risk, especially if the risk has a
negative impact on the company and consumers.
Choosing an application or technology must be more
careful. Users will choose and use applications or
technology that have minimal risk. We hypothesise
as follows:
H2: Perceived risk positively influences the
adoption of digital transactions.
According to (Ajzen, 1991), the role of social
pressure or peer influence in the adoption of
technology has had mixed results. Conley and Udry
(2010) found that peer exposure had a positive
impact on technology adoption. The study above
shows that companies can be influenced by the
actions of others to adopt technology. Companies
will not want to be left behind in adopting
technology that can bring in many profits and
consumers. We hypothesise as follows:
H3: Subjective norms positively influence the
adoption of digital transactions.
The primary objective of companies, particularly
MSMEs, in adopting digital transactions is to
decrease transaction costs. Digital transactions also
provide many benefits, according to Dodgson et al.
Perceived Ease
of Use
Perceived Risk
Subjective
N
orms
Transaction Cost
Adoption
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
60
(2015) that digital transactions have the potential to
offer opportunities for revenue growth, reduce the
costs of handling cash, and startup costs to provide
new opportunities for economic and social
entrepreneurship. We hypothesise as follows:
H4: Transaction costs positively influence the
adoption of digital transactions.
There are many considerations when companies
adopt digital transactions. The more benefits a
company receives, the more likely it is to adopt
digital transactions. Ease of using technology, low
risk, low transaction costs can be obtained by users
by adopting digital transactions, we hypothesise as
follows:
H5: Perceived ease of use, perceived risk,
subjective norms, and transaction costs
simultaneously positively influence the adoption of
digital transactions.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Method and Data Collection Result
Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) is a research
technique that tests if the proposal structure model
can explain the data collected. CFA is based on the
assumption that the data collected can be represented
by several laten factors, which cannot be observed
directly. CFA is multivariate analysis method used
to test or confirm a hypothesis model (hair et al.,
2019)
. The data we use in this research is primary,
namely by distributing questionnaires to
respondents. After distributing the questionnaire to
the respondents, the total number of questionnaires
filled out was 100. Thus, the quantity of
questionnaires that can be processed is 100. These
questionnaires were analysed using Multiple
Regression Analysis (MRA) with SPSS 25.
4.2 Demographic Characteristics of
Respondents
After collecting the data, it is processed to observe
the demographic characteristics of the respondents,
which are presented in Table 2 as follows.
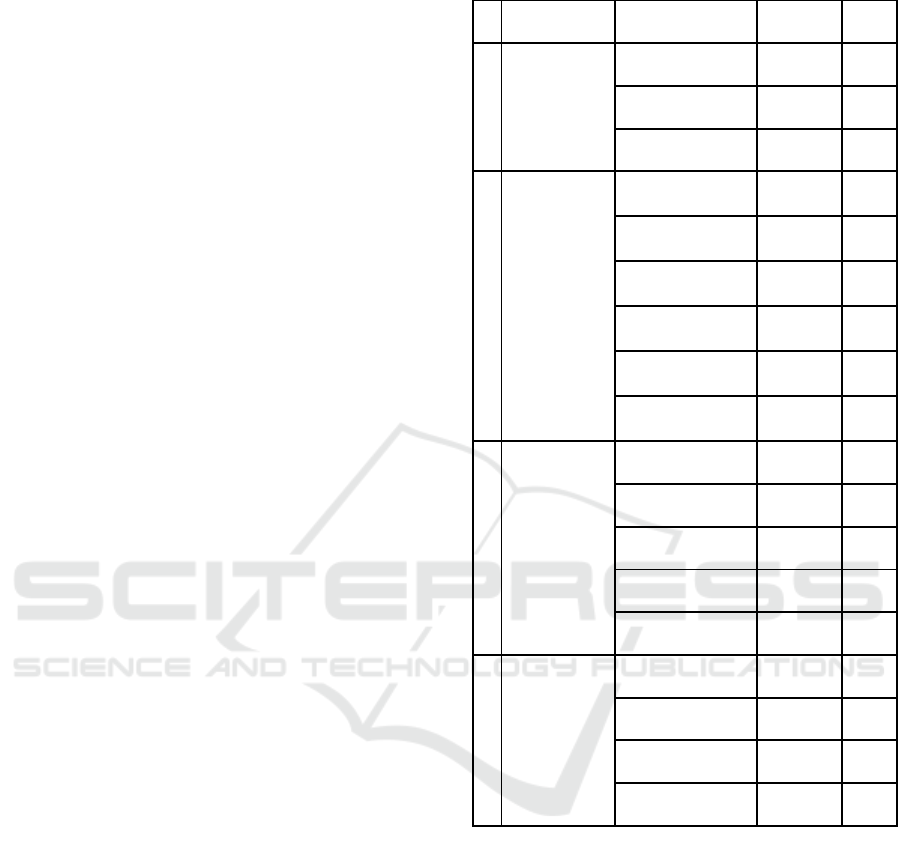
Table 2: Characteristics of respondents.
No Characteristics Category
Quantit
y
(%)
1. Gender Man 72 72%
Woman 28 28%
Total 100 100%
2.
Aged <25 years old
16 16%
25-30 years old
8 8%
31-35 years old
49 49%
36-40 years old
10 10%
>40 years old
17 17%
Total
100 100%
3.
Duration of
MSMEs
Establishme
nt
1-3 years 21 21%
4-7 years 52 52%
8-10 years 11 11%
>10
y
ears 16 16%
Total 100 100%
4.
Type of
MSMEs
Micro business 17 17%
Small Business 56 56%
Medium Business 27 27%
Total 100 100%
Based on Table 2, it can be seen that the total
number of respondents was 100 respondents with the
majority being male with total 72 respondents (72%)
and the majority of the MSMEs have been
established for 4-7 years, comprising 52 respondents
(52%). The most types of MSMEs are small
business totalling 56 (56%).
4.3 Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis testing carried out in this study was
testing Multiple Regression Analysis (MRA) using
the SPSS 25 application. The multiple regression
analysis test consisted of two tests, the T-test and F-
test.
Digital Transaction Model in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterpeises (MSMEs) to Target Millenial Generation Consumers in Yogyakarta,
Indonesia
61
4.3.1 T- Test
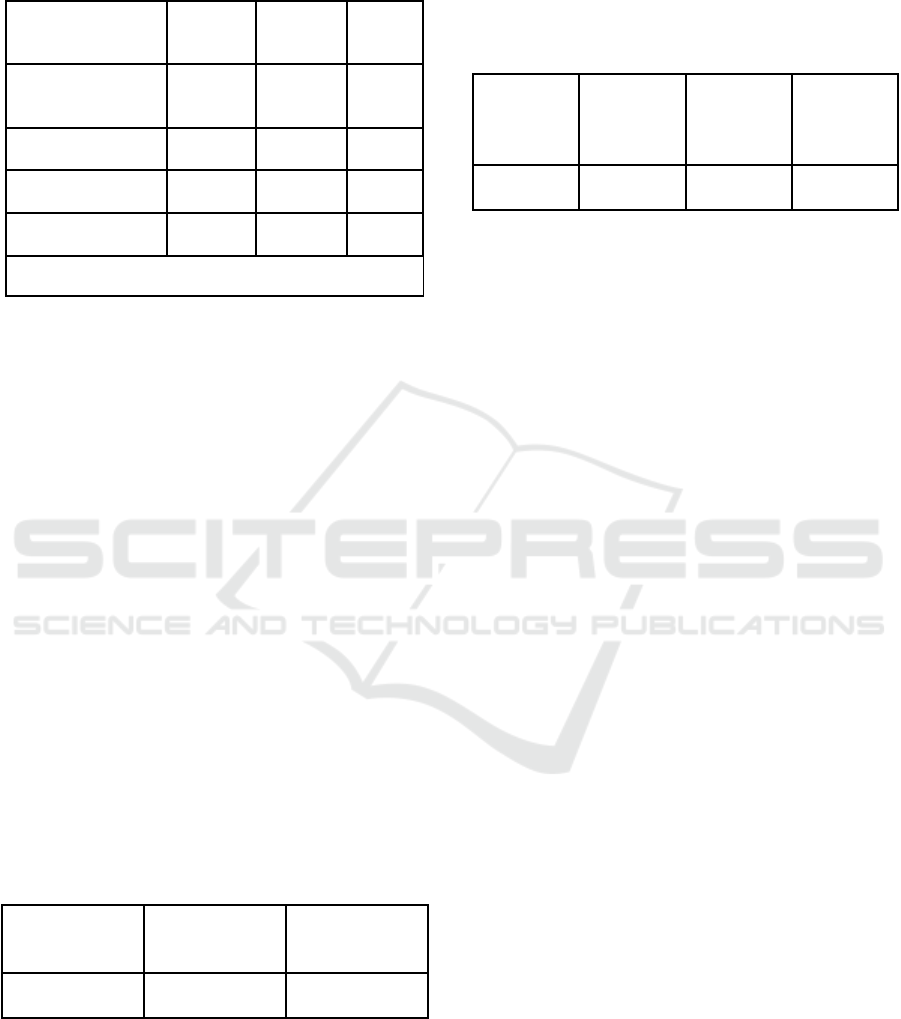
Table 3: Table of T-Test Result.
Variable T-Table Calculated
T-value
Sig.
Perceived ease of
use
8.620 1.985
0.00
Perceive
d
risk -0,135 1.985 0.893
Transaction cost 3.888 1.985 0.00
Subjective norms 7.295 1.985 0.00
Dependent variable: Adoption
The sig value for testing X1 (perceived of use) to Y
(adoption) is 0.00 <0.05 and the t-count value is
8.620 > t table 1.985, so it can be concluded that H1
is accepted which means there is an influence
between X1 (perceived of use) on Y (adoption).
Other than that sig value. for testing X2
(perceived risk) to Y (adoption) is 0.893 > 0.05 and
the t-count is -0.135 <t table 1.985. So, it can be
concluded that hypothesis H2 is rejected, which
means that there is no effect of perceived risk on
adoption Y.
The Sig. value for testing X3 (transaction cost)
on Y (adoption) is 0.00 <0.05 and the t-count value
is 3.888 > t table 1.985, so it can be concluded that
H3 is accepted which means there is an influence
between X3 (transaction cost) on Y (adoption).
The Sig. value for testing X4 (subjective norm)
on Y (adoption) is 0.00 <0.05 and the t-count value
is 7.295 > t table 1.985, so it can be concluded that
H4 is accepted which means there is an influence
between X4 (subjective cost) on Y (adoption).
4.3.2 F-Test
Table 4: Table of F-Test Result.
T- Table Calculated
T-Value
Sig.
2.47
222.941 .000
Based on the output above it is known that the
significance value for the influence of X1, X2, X3
and X4 simultaneously on Y is 0.000 <0.50 and the
calculated F value is 222.941 > F table 2.47, so it
can be concluded that H5 is accepted which means
there is an influence of X1, X2, X3 and X4
simultaneously against Y.
4.3.3 Coefficient of Determination
Table 5: Table of Coef. Determination.
R-Value R Square Adjusted R
Square
Std. Error
of the
Estimate
0.951 0.904 0.900 0.235
Based on the output above, it is known that the R
Square value is 0.904, this means that the
simultaneous influence of X1, X2, X3 and X4 on the
Y variable is 90.4% and the other 9.6% is influenced
by other variables not examined in this study.
4.4 Result
This research aims to test hypotheses and analyze
the influence of digital transaction models on micro,
small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) to target
millennial generation consumers in Yogyakarta,
Indonesia. The analysis of hypothesis 1 shows that
perceived ease of use is a factor in adoption. This is
because individual users find it easy to use and do
not need to spend a lot of time learning it, according
to Davis, Bagozzi and Warshaw (1989) who state
that PEOU (Perceived Ease of Use) positively
influences the intention to use information
technology.
In research conducted by Anjali and Ranjani
(2020), it was stated that perceived ease of use
influences the intention to adopt digital transactions
among Indian micro businesses. This is because
micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs)
usually have limited resources and do not have many
staff, resulting in limited services provided by the
workforce to customers, in this case the use of
technology is highly recommended because it can
increase effectiveness and efficiency.
The results of hypothesis 2 prove that perceived
risk does not influence adoption. This means that
consumers, namely the millennial generation,
assume that the risks associated with implementing
digital transactions in their activities of buying
something at micro, small and medium enterprises
(MSMeS) can still be borne, apart from that,
consumers who decide to use digital transactions
feel increasingly accustomed to adoption. People
should become familiar with technology that
involves digital transactions to make them
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
62

comfortable using it and ensure that the risks are not
excessive. This is also in line with previous research
such as research conducted by Kim and Malhotra
(2005) which found that perceived risk did not have
a significant influence on the use of information
technology.
Hypothesis 3's findings demonstrate the
influence of transaction costs on adoption.
Transaction costs are costs incurred to carry out
transactions both commercial and non-commercial.
These costs can be direct costs, such as commission
fees, administration, and shipping costs, or indirect
costs, such as time and labor costs. So transaction
costs have a significant influence on adoption
because low transaction costs can encourage
technology adoption, while high transaction costs
can be an obstacle to technology adoption.
The results of hypothesis 4 also prove that there
is an influence between subjective norms on
adoption. Subjective norms are a person's perception
of what others expect of them when adopting a
technology. Subjective norms have an influence on
technology adoption because they can increase the
intention to use a technology. Research conducted
by Herniyati, et.al. (2022) found that subjective
norms have a positive influence on the intention to
use the figma application. The research results show
that the higher the subjective norm, the higher the
intention to use the figma application.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research that has been
done, it can be concluded that perceived ease of use
has a positive effect on the adoption of digital
transactions (hypothesis 1) and the perceived risk
variable does not affect the adoption of digital
transactions. Besides that, transaction costs have an
influence on the adoption of digital transactions
(hypothesis 3) and subjective costs also have an
influence on the adoption of digital transactions
(hypothesis 4) then from the research it is also
known that simultaneously there is an influence
between variables X1, X2, X3 X4 on Y (Adoption).
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior.
Organizational Behavior and Human Decision
Processes, 50(2), 179-211. https://doi.org/10.1016/074
9-5978(91)90020-T.
Anjali and Ranjani. (2020). Adoption of Digital
Transaction Model by Micro Enterprises to Target
Millenials in India: An Exploratory Study. Social
Business. Vol. 10, No. 4, pp. 411-434 https://
doi.org/10.1362/204440820X15813359568318.
Bagas, F. (2021). Research: Digital wallet consumers in
Indonesia increase, what do they use most?
https://nextren.grid.id/read/012582036/riset-konsumen
-dompet-digital-di-indonesia-naik-most-dipakai-apa?
page=all.
Conley, T., & Udry, C. (2010). Learning about a New
Technology: Pineapple in Ghana. American Economic
Review, 100(1), 35-69. https://doi.org/10.1257/
aer.100.1.35.
Davis, F.D. et al. (1989), “User acceptance of computer
technology: A comparison of two theoretical models”,
Management Science, 35(8), 982-1003.
Dodgson, M., Gann, D., Wladawsky-Berger, I., Sultan, N.,
& George, G. (2015). Managing digital money.
Academy of Management Journal, 58(2), 325-333.
https://doi.org/10.5465/ amj.2015.4002.
Erlina, E. (2021). Analysis of Marketing Strategy in
Increasing Consumer Attractiveness. Digital
Repository. Retrieved from http://repository.iain
purwokerto.ac.id/eprint/10364.
Hair, J. F. Jr., Black, W.C., Babin, B.J., dan Anderson,
R.E., (2019). Multivariate Data Analysis, Eight
Edition, New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall.
Kim, S. S., Malhotra, N. K., & Narasimhan, S. (2005).
Research Note—Two Competing Perspectives on
Automatic Use: A Theoretical and Empirical
Comparison. Information Systems Research, 16(4),
418–432. doi:10.1287/isre.1050.0070.
Mamonaova, Y. (2019, January 10). How Millennials Are
Reshaping The Digital Payments Landscape [Blog
site]. Ikajo. Retrieved from https://ikajo.com/blog/
millennials-digital-payments-trends.
Mazzocchi, M., Lobb, A.E., & Traill, B.W. (2005). Causal
Model Estimation Results. TRUSTProject Deliverable
No. 9. Florence, Italy: Florence University Press.
VISA (2016, July). Understanding the millennial mind-set
and what it means for payments in the GCC. VISA
Performance Solutions. Retrieved 8.10.2019 from
https://usa.visa.com/dam/VCOM/global/partner-with-
us/documents/millennial-digital-payment-trends-in-gc
c.pdf.
Wu, J. H., & Wang, S.C. (2005). What drives mobile
commerce? An empirical evaluation of the revised
technology acceptance model. Information &
management, 42(5), 719-729. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.im.2004.07.00.
Digital Transaction Model in Micro, Small, and Medium Enterpeises (MSMEs) to Target Millenial Generation Consumers in Yogyakarta,
Indonesia
63
