
A Comprehensive Study of the Effects of User Competence and
Internal Control on the Quality of Accounting Information Systems
Mustamin, Nurul Intawaty, Halim, Fiona Suryawan and Rapina Rapina
Maranatha Christian University, Department of Accounting, Bandung, Indonesia
Keywords: User Competence, Internal Control, Quality of Information System.
Abstract: Information systems have become an important part of business and have been integrated into daily business
activities such as accounting, finance, operations management, marketing, human resource management or
other key business functions, a poor quality information system will have a negative impact on a company or
organization. The goal of this study was to assess the impact of user competence on the quality of information
systems in Indonesian banks, as well as the impact of internal control on the quality of information systems
in Indonesian banks. The sample in this study was selected by random sampling technique which is part of
probability sampling and Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) is used as the data
analysis technique. This study's finding has two major conclusions, first is that User competence has a
significant and positive effect the quality of the banking Information system in Indonesia, and the second
finding is internal control positively and significantly affects the quality of the banking Information system
in Indonesia.
1 INTRODUCTION
The business world is currently developing very
dynamically and with increasingly fierce
competition, companies are required to be able to
maintain their existence by maintaining their
competitive advantage to achieve goals and win the
competition. One way companies can increase their
competitiveness is to focus on information system
technology as a means of enhancing effectiveness and
efficiency. Accounting, finance, operations
management, marketing, human resource
management, and other major business processes
have all been incorporated into information systems,
which have become an integral component of
business (Mardia et.al, 2021). Information System is
a system that can be applied and has an important role
in a company.
The accounting information system differs from
other information systems in that it is exclusively
connected to the accounting function in processing
data about the operations of firm organizations that
have economic worth (Suprihatin et al, 2022).
Accounting information systems are required to
convert accounting data from diverse sources into
accounting information required by various users to
assist in company decision-making. The
characteristics of a quality information system
include flexibility, simplicity of use, system
transparency, and integrity.
The quality of information systems in Indonesia is
still lacking. The example of Bukalapak's financial
statements being recorded incorrectly (Safitri, 2022)
can prove this. Fairuza Ahmad Iqbal, Bukalapak's
Head of Media and communications, stated that there
was a recording error that resulted in the procurement
of IDR 14.3 billion being written down to IDR 14.3
trillion. In this case, it is known that the users
involved in the information system affect the quality
of the information system. Therefore, users must have
the knowledge, expertise, and ability to use the
information system. User capability is one of the
factors that influence the successful implementation
of information systems to produce quality
information (Nisa et al, 2020). The ability of
information system users to operate information
systems is needed so that the system can operate
optimally, this can be seen from how system users run
existing information systems (Robbins Judge, 2013).
Previous research on a manufacturing business in
Bandung city has shown that user capability has a
favorable and substantial impact on the quality of
information systems. The more the capacity of the
Mustamin, ., Intawaty, N., Halim, ., Suryawan, F. and Rapina, .
A Comprehensive Study of the Effects of User Competence and Internal Control on the Quality of Accounting Information Systems.
DOI: 10.5220/0012643600003798
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Maritime, Economics and Business International Conference (MEBIC 2023) - Sustainable Recovery: Green Economy Based Action, pages 115-122
ISBN: 978-989-758-704-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
115

user, the higher the quality of the present information
system (Nisa et al, 2020).
As an open system, the information system cannot
be guaranteed to be free of faults or fraud. Internal
control is a method for a system to defend itself
against harmful acts (Basri, 2020). Quoted from
Hasanuddin (2020), the case of breaking into a
customer's account at one of the international private
banks in Indonesia amounting to Rp. 22 billion which
was committed by a bank branch head is one of the
cases which shows that internal control is needed to
guarantee the quality of a product information
system. Previous research explained that internal
control has a significant influence on the quality of
information systems, which means that the better the
implementation of internal control, the better the
quality of information systems, and the worse internal
control, the lower the quality of information systems
(Astria et.al, 2017).
Based on the phenomena discussed, the
information system requires a solution since a low-
quality information system could negatively affect a
firm or organization. The quality of accounting
information on local government in West Java was
the topic of prior studies.The findings of this study
reveal that employee competence has a substantial
influence on the quality of accounting information;
nevertheless, internal control has no significant effect
since risk assessment did not go smoothly. However,
study findings differ in that the internal control
system influences the quality of the information
system; if the internal control system improves, the
quality of the information system improves (Tresyani,
2019). As a result, the purpose of this research is to
establish the impact of internal control and user
capabilities on the quality of financial information
systems, particularly in the banking industry.
This study will contribute to the literature on the
influence of information system quality because it
will examine the variables that affect the quality of
financial information systems from internal control
variables and the capabilities of information system
users. The goal of this study was to assess the impact
of user competence on the quality of information
systems in Indonesian banks, as well as the impact of
internal control on the quality of information systems
in Indonesian banks. This research is different from
previous studies because it has not examined all
variables simultaneously in relation to the quality of
the information system in banks.
2 THEORETICAL REVIEW
2.1 Internal Controls
Internal control is a procedure that helps an
organization or corporation achieve operational
efficiency and effectiveness, financial reporting
dependability, asset security, and compliance with
laws, rules, and other requirements (Nugroho et al,
2019). This is also backed by the viewpoint that
internal control is a collection of norms of conduct
produced and accepted by the majority of the
organization's/company's members as a manual for
managing the organization or resolving both internal
and external problems (Syahputra, 2022). Internal
control, then, can be defined as a set of procedures
that are intended to help a business achieve
operational effectiveness and efficiency, financial
reporting accuracy, asset security, and compliance
with laws, rules, and other regulations. Internal
control requires companies to achieve efficiency and
effectiveness. In this study, researchers used an
understanding of efficiency, which said that
efficiency is the amount of output that can be
produced using certain inputs by minimizing wasted
effort or costs (Hafidz, 2022). Companies must
consider efficiency when developing their internal
controls. Effectiveness is a condition that indicates
the success of an organization in achieving a certain
goal by using existing resources with a predetermined
size (Bormasa, 2022).
2.2 User Competence
User competence, according to Wijayanti (2023), is
the ability of each individual, which includes aspects
of knowledge, skills, and individual abilities, to
achieve the expected results. User competence is a
unique/special characteristic that is formed from the
knowledge, expertise, skills, and motivation of an
individual that has a relationship with the successful
performance of the individual which can be seen from
the way of their thinking and behavior (Marjulin,
2019). The same thing was said by Mejia et al (2010)
by defining competence as a characteristic that has
been attached to a person and has a relationship with
the successful performance of a person.
Based on the above understanding, the
competence of users of an information system is a
characteristic of someone who can be seen from the
knowledge, expertise, skills, and motivation of
someone who has a close relationship with the
success of their performance. Therefore the
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
116

dimensions that will be used in this study are the
dimensions of knowledge and expertise.
Knowledge, according to Simbolon (2022), is
information that someone owns. Employee
knowledge also impacts the success or failure of task
implementation; employees with sufficient
knowledge will boost the company's efficiency;
employees with insufficient knowledge will be
difficult to deal with. The quality of the information
system itself is determined by the knowledge of the
personnel who administer it.
In addition to knowledge, users must also have
skills in operating or running programs used in an
information system to determine the quality
produced. The benefits of carrying out a sequence of
activities that are derived from studies and job
experience are referred to as skills (Chaeruddin et al,
2020).
2.3 Quality of Information Systems
This A quality information system is very important
in accounting because it will provide accounting
information from a company that will be used by
internal and external parties of the company.
Suprihatin (2022) states that information systems are
created with the primary purpose of translating
accounting data from numerous sources into
accounting information required by diverse users in
order to reduce risk while making decisions. This is
corroborated by Susanto's (2017) viewpoint.
According to the definition, an accounting
information system is an integration of both physical
and non-physical subsystems/components that are
interconnected and function in harmony to manage
transaction data related to financial issues into quality
financial information.
Based on this understanding, it can be interpreted
that the information system is a process for
processing accounting data into harmoniously
integrated information for managing transaction data
related to financial issues into quality financial
information.
According to Soelistya (2021) integrity is an
activity of uniting smaller components into a system
that functions as one. Integration is needed between
each division within a company to ensure proper
system operation.
Four dimensions can be used to assess the quality
of information from an information system.
information that is correct, relevant, timely, and full
(Susanto, 2017). This is becoming a dimension for
researchers when examining the quality of
information systems.
3 RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
3.1 The Influence of User Capability on
the Quality of Information Systems
In several previous studies, such as Nisa and Citra
(2020), it has been proven that user ability has an
influence on the quality of information systems.
Similar research conducted by Endraria (2016) also
concluded that user competence influences the
quality of the information system. Similarly, Ruhul
Fitros (2022) in his research found that information
system quality is significantly influenced by user
competence. The quality of existing information
systems can be affected by implementation errors
caused by employees' lack of knowledge and skills in
the process of applying information systems. Based
on theoretical studies and supported by previous
research, The first hypothesis in this study is:
H1 = User capability has a significant effect on
the quality of information systems.
3.2 The Influence of Internal Controls
on the Quality of Information
Systems
Internal control is critical in an information system;
the greater the internal control, the higher the quality
of an organization's information system (Mulyanti,
2017). Suswandera, Nurhayati, and Halimatusadiah
(2018) found that internal control has a significant
positive impact on improving the quality of
information systems. The research conducted by Nisa
and Citra (2020) found that internal control findings
had an impact on the quality of the information
system. Internal control is a factor that can affect the
quality of information systems; internal control is
required to be utilized as a reference or the application
of restrictions by the firm to reduce the risks that can
develop while using information systems to achieve
company goals. Similar findings were presented by
Kuniawan et al in their research in 2017, stating that
Internal control has an impact on the quality of
information systems, and it is important to have
internal control in order to produce high-quality
information systems.
Based on theoretical studies and supported by
previous research, The second hypothesis in this
study is as below:
H2 = Internal control has a significant effect on the
quality of information systems.
A Comprehensive Study of the Effects of User Competence and Internal Control on the Quality of Accounting Information Systems
117
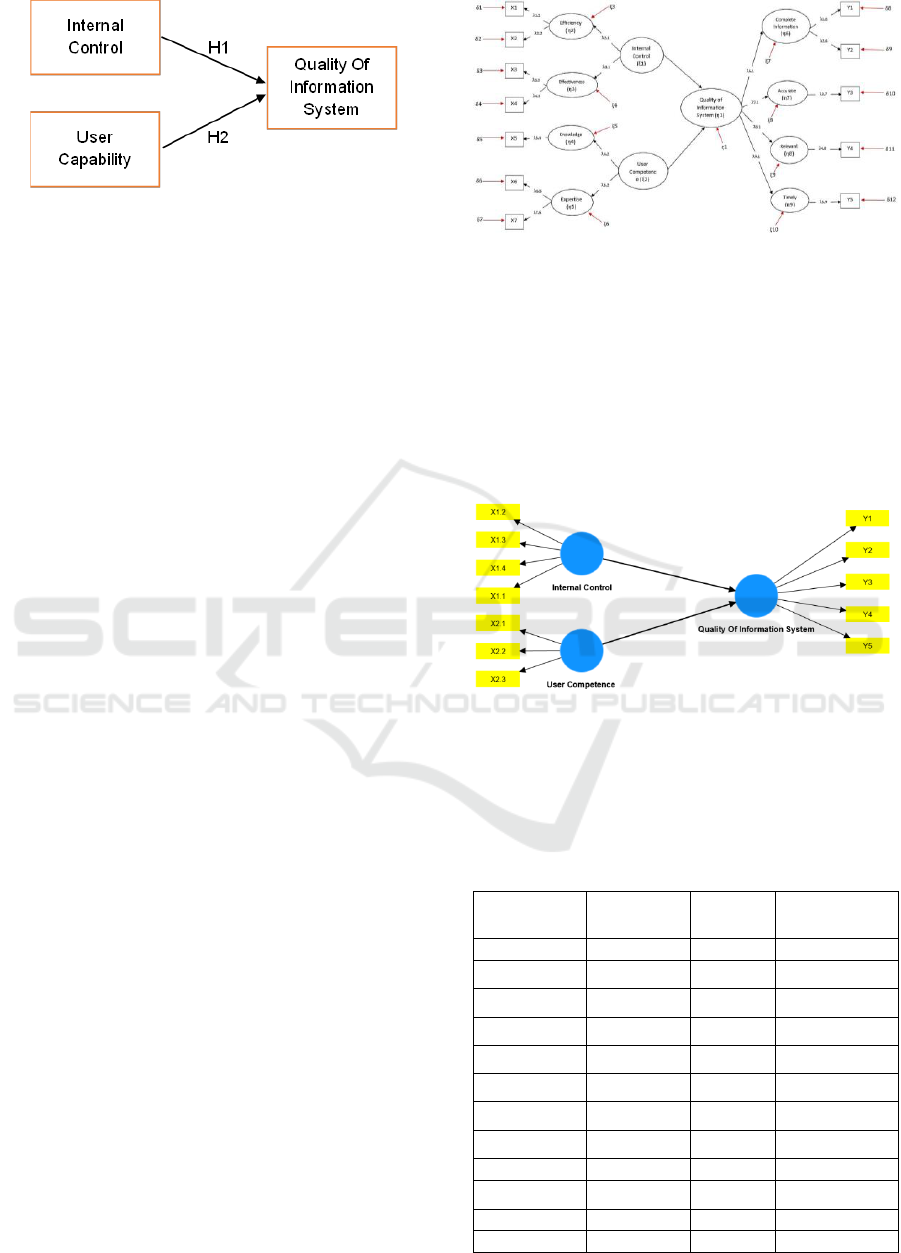
Figure 1: Research Model and Framework
4 RESEARCH METHODS
The quantitative research method was applied in this
investigation. The quantitative research method is a
type of research in which the specifications are
methodical, planned, and explicitly structured from
the beginning of the research design to the end. This
is consistent with Sugiyono (2019), who stated that
positive philosophy-based research procedures are
used to evaluate certain populations or samples, data
collection involves research tools, and data analysis
is quantitative or statistical with the goal of testing
predetermined hypotheses. This study used a
structured questionnaire as a data collecting tool.
Indicator measurement uses a Likert scale.
The population of 107 banking industries is the
unit of analysis in this study, which is public banking
registered with the Financial Services Authority
(OJK) in 2022. The sample for this study was chosen
through a random sampling technique, which is a type
of probability sampling. Random sampling is a
method of gathering samples from a population at
random, without consideration for the strata within
that population (Sugiyono, 2019).
The data analysis technique employed is the
Partial Least Square-Structural Equation Modeling
(PLS-SEM), which tests the hypothesis using the
route analysis test on primary data gathered from
surveys and questionnaire distribution. SEM is a
statistical modeling technique that can be used for
cross-sectional, linear, and general statistical
modeling, and it encompasses factor analysis, route
analysis, and regression. SEM is a multivariate
analysis approach used to create and test statistical
models, most of which are causal models (Usman et
al, 2020). Partial least squares (PLS) is an alternative
approach to analysis based on variation to Structural
Equation Modeling (SEM) (Usman et al, 2020).
PLTS has the advantage of not requiring assumptions
and can be estimated with a small sample size.
Figure 2: Path Diagram for Combination of Measurement
and Structural Models.
5 RESEARCH RESULTS
There are 2 independent variables which are denoted
by X1 (Internal Control), X2 (User Competence), and
Y (Quality of Information system), by using
SMartPLS the research model is obtained as follows
Figure 3: Research Model, via Smart PLS.
The tests to be carried out are Convergent Validity
and Discriminant Validity tests.
5.1 Convergent Validity
Table 1: Outer Loading.
Variable
Outer
Loading
Standard
Value
Information
X1.1 <- X1
0.744
0.700
High/Valid
X1.2 <- X1
0.831
0.700
High/Valid
X1.3 <- X1
0.789
0.700
High/Valid
X1.4 <- X1
0.821
0.700
High/Valid
X2.1 <- X2
0.742
0.700
High/Valid
X2.2 <- X2
0.846
0.700
High/Valid
X2.3 <- X2
0.753
0.700
High/Valid
Y1 <- Y
0.811
0.700
High/Valid
Y2 <- Y
0.863
0.700
High/Valid
Y3 <- Y
0.861
0.700
High/Valid
Y4 <- Y
0.751
0.700
High/Valid
Y5 <- Y
0.776
0.700
High/Valid
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
118
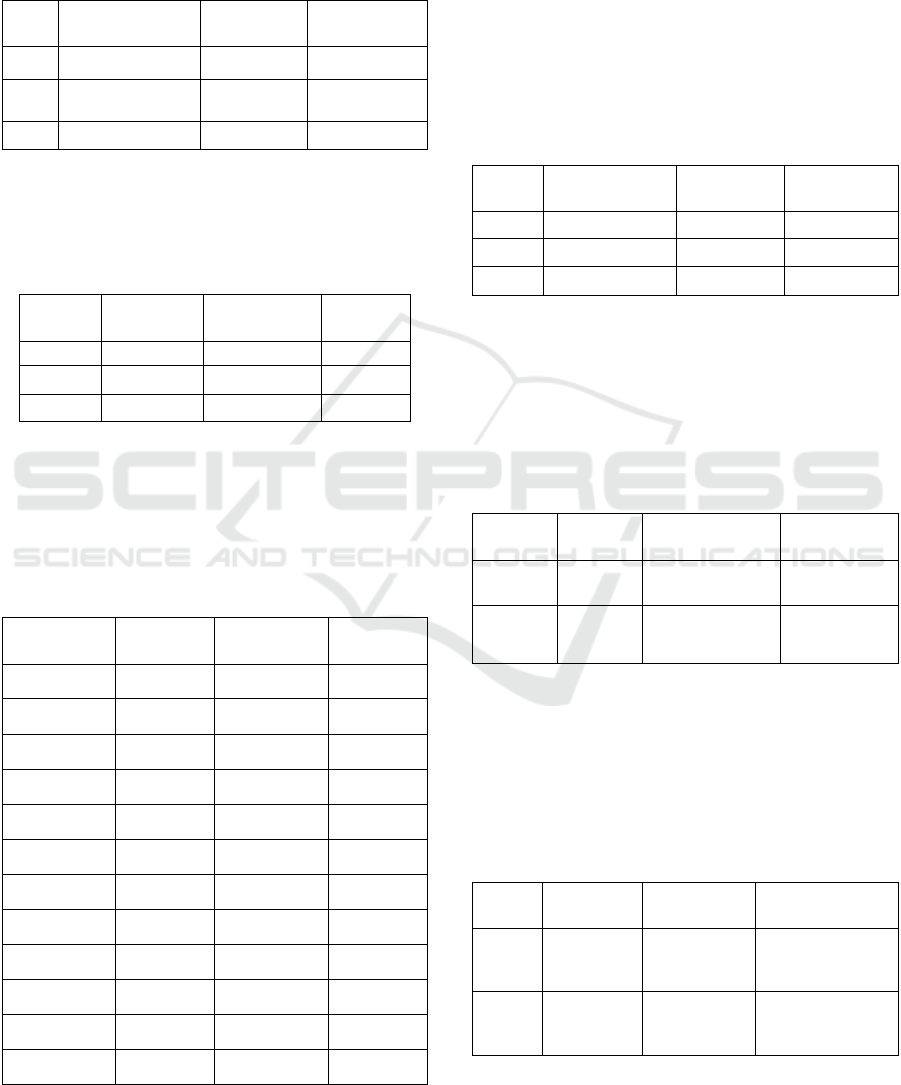
The value of the Outer Loading variable in the table
above is more than 0.700, indicating that the data
utilized can be considered valid sample size (Irwan
Khaeyna, 2015).
Table 2: Average Variance Extracted (AVE).
Average Variance
Extracted (AVE)
Standard
Value
Information
X1
0.617
0.500
Valid
X2
0.647
0.500
Valid
Y
0.655
0.500
Valid
Based on the table data above, the Average Variance
Extracted (AVE) value is above 0.500, which means
the data used is valid (Irwan Khaeyna, 2015).
Table 3: Fornell Larcker.
X1
X2
Y
X1
0.785
0.671
0.688
X2
0.671
0.804
0.777
Y
0.688
0.777
0.809
By using the Fornell Larcker, based on the results of
the table above, the root value of the AVE variable is
greater than the correlation between the other
variables. This indicates that the overall discriminant
validity evaluation is fulfilled.
Table 4: Cross Loading.
X1
X2
Y
X1.1
0.776
0.533
0.547
X1.2
0.744
0.512
0.523
X1.3
0.831
0.419
0.472
X1.4
0.789
0.615
0.599
X2.1
0.523
0.821
0.647
X2.2
0.469
0.742
0.534
X2.3
0.616
0.846
0.683
Y1
0.517
0.609
0.753
Y2
0.517
0.609
0.811
Y3
0.623
0.696
0.863
Y4
0.621
0.706
0.861
Y5
0.485
0.542
0.751
According to the Cross Loading results in the table
above, the correlation of the loading value of each
item to the construct is greater than the cross loading
value. This signifies that the discriminant validity
evaluation has been completed (Irwan Khaeyna,
2015).
Furthermore, the Cronbach Alpha value can be
used to measure the reliability. Because the Cronbach
Alpha value in the table below is more than 0.700, it
can be claimed that all variables are reliable
(Febrianawati, 2018).
Table 5: Cronbach Alpha.
Cronbach Alpha
Standard
Value
Information
X1
0.793
0.700
Reliable
X2
0.727
0.700
Reliable
Y
0.867
0.700
Reliable
The next test is hypothesis testing. Hypothesis testing
was carried out to see if there was an influence from
X1 on Y and X2 on Y. Based on the following table,
the P values of X1 and X2 are smaller than 0.05 so it
can be concluded that X1 has an influence on Y, and
X2 also has an influence on Y.
Table 6: P Value.
P Value
Standard Value
Information
X1->Y
0.005
< 0.05
X1 has an
Effect on Y
X2->Y
0.000
< 0.05
X2 has an
Effect on Y
The next test is hypothesis testing. Hypothesis testing
was carried out to see if there was an influence from
X1 on Y and X2 on Y. Based on the following table,
the P values of X1 and X2 are smaller than 0.05 so it
can be concluded that X1 has an influence on Y, and
X2 also has an influence on Y.
Table 7: Cross Loading.
T Statistics
Standard
Value
Information
X1->Y
2.781
> 1.96
X1 has a
Significant Effect
on Y
X2->Y
6.345
> 1.96
X2 has a
Significant Effect
on Y
A Comprehensive Study of the Effects of User Competence and Internal Control on the Quality of Accounting Information Systems
119

Furthermore, to see whether variables X1 and X2
have a positive or negative effect on variable Y, it can
be seen through the value of the Original Sample.
Table 8: Cross Loading.
Original Sample
Information
X1->Y
0.303
Positively
Influence
X1->Y
X2->Y
0.574
Positively
Influence
X2->Y
Through the table above, the value of the Original
Sample X1 on Y is positive, so X1 has a positive
effect on Y, as well as the value of the Original
Sample X2 on Y which is positive, so X2 also has a
positive effect on Y. This means that if X1 or X2
increases, Y will increase as well.
6 DISCUSSION
Based on the discussion mentioned above, it appears
that the first hypothesis is accepted. To improve the
quality of information systems, banks must increase
user competence because it has a significant and
positive influence on them. This conclusion is
supported by previous research conducted by Nisa &
Citra (2020) which showed that the ability of users
has a positive and significant influence on the quality
of information systems. Information systems are
intended to improve decision-making by streamlining
procedures and providing important insights. The full
potential of users who are proficient in using these
systems can be realized by making educated
judgments and reaping the benefits of these systems.
Competent users are more likely to enter trustworthy
and correct data into information systems. The overall
quality of the provided information can be lowered by
erroneous analysis and incorrect conclusions caused
by wrong or missing data.
If an information system's users are familiar with
its features, they can use it more effectively and finish
tasks faster. With higher productivity and quicker
answers to company demands, this enhanced
efficiency also benefits businesses. Competent users
can discover and repair technical problems or
mistakes, thereby reducing downtime and
interruptions. They may also troubleshoot small
issues without the need for expert assistance.
Advanced users may frequently change and adjust
information systems to better meet their individual
needs. This adaptability can lead to more specialized
and effective solutions that satisfy specific company
objectives. The common user may not be aware of a
variety of features and capacities that many
information systems have.
Competent users are more likely to investigate
and make use of these features, increasing the value
they get out of the system. Understanding data
security best practices is essential for user
competency. Competent users are more likely to
adhere to security measures, lowering the risk of data
breaches and illegal access to sensitive data.
Competent users can save companies both time and
money by requiring less training. Training sessions
can include more complex subjects, which will help
users improve their abilities and system competency.
Users have a more favorable experience when they
are skilled and can properly use the technology. As a
consequence, the information system and its overall
performance have increased user satisfaction. The
functioning, user interface, and features of an
information system are often better understood by
competent users who are often better positioned to
give constructive input. This input may be used to
create enhancements and updates that will improve
the system's quality over time.
The second hypothesis is also supported by the
study findings, which reveal that internal control has
a considerable and favorable impact on the quality of
information systems. Banks must strengthen their
internal controls in order to increase the quality of
their information systems. The quality of information
systems is affected by internal control, as explained
in Treyani (2019)'s previous research. Internal
controls contribute to the accuracy and integrity of
data in information systems. Organizations can
prevent unwanted access, data tampering, or mistakes
that might jeopardize the quality of the information
being processed and stored by instituting checks and
balances.
Internal control is a corporate policy process that
is influenced by the board of directors, management,
and other employees of a company. This was done to
ensure confidence about a number of
accomplishments, including operational performance
and efficiency, financial report correctness, and
compliance with applicable rules. The effectiveness
of internal control affects the quality of accounting
information systems because the effectiveness of
internal control is perceived to be weak by the parts
that utilize it, particularly in inventory control, and
there is still a lack of data security.
The auditability of information systems is
improved by a strong internal control architecture.
The quality of information given can be enhanced by
auditors checking controls to ensure that procedures
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
120

are sound and reliable. The protection of information
systems against cyber assaults and breaches requires
the use of internal controls. They develop procedures
for encrypting data, managing access, and other
security measures that guarantee the integrity and
confidentiality of the system's data. Effective internal
controls aid in the simplification of procedures within
the information system. Organizations can increase
data processing efficiency and speed by reducing
superfluous stages and automating regular tasks,
resulting in higher-quality outputs.
Internal controls are in place to ensure that
information is processed and reported as soon as
possible. This is especially vital for decision-making,
since current and accurate information is essential for
making educated decisions that contribute to the
overall quality of corporate operations. Internal
controls often involve monitoring and feedback
methods. The ability to identify system flaws and
opportunities for improvement enables businesses to
make iterative improvements that improve system
quality over time.
7 CONCLUSION
The validity of various findings was demonstrated by
testing two hypotheses: the impact of user
competence on information system quality and the
impact of internal control on information system
quality.
1. User competence has a large and beneficial
influence on the quality of the information system.
Thus, to improve the quality of the information
system at the Bank, it is necessary to carry out
trainings that support the competence of the User.
To enhance user competence should provide
structured and planned training for users of
information systems. Adjust training to suit the
level of knowledge and skills of users, from basic
to advanced. Ensure that the training material
includes an in-depth understanding of the features
of the information system, its usage patterns, and
best practices in its use. Consider repetitive
training and advanced training to help users
deepen their understanding over time.
2. This study also revealed that internal control has
a significant and positive influence on the quality
of information systems, implying that banks must
strengthen their internal controls in order to
increase and improve the quality of information
systems. To enhance internal control in the use of
information systems must carry out a thorough
assessment of the risks associated with the
information system, identifying potential threats
to data security, information integrity, and
possible regulatory violations. Determine the
possible impact of each identified risk. This helps
in determining priorities and resources to be
allocated to address the risk. Implement designed
controls into information systems and related
business processes. Make sure that each control is
enabled and works as expected. Improving
internal control is a continuous effort involving
various aspects of the organization. With a
structured approach and a high awareness of the
importance of managing risk and security, you can
ensure that your information system operates with
a better level of control.
REFERENCES
R T Mardia, A Karim, M Ismail, 2021. Sistem
Informasi Akuntansi Dan Bisnis (Yayasan Kita
Menulis, Medan.)
Suprihatin, N Sri, 2022. Sistem Informasi Akuntansi
2 (Penerbit Qiara Media, Purworejo.)
K Safitri, 2022. LapKeu Bukalapak SalCat, Akuisisi
Rp 14,3 M Ditulis Rp 14,3 T (Kompas.com)
https://money.kompas.com/read/2022/03/25/113
000126/laporan-keuangan-bukalapak-salah-catat-
akuisisi-rp-143-miliar-ditulis-rp-143.
A A Nisa, Citra, V, Nisa, 2020. Pengaruh
Kemampuan Pengguna dan Pengendalian Internal
Terhadap Kualitas Sistem Informasi Akuntansi
pada Salah Satu Perusahaan Manufaktur di Kota
Bandung. The 11th Industrial Research Workshop
and National Seminar.
S P Robbins, T A Judge, 2013. Organizational
Behaviour, 12 (Salemba Empat.)
Y M Basri, 2020. Kontrol Thd Kecurangan dlm SA
Berbasis Komp. Jurnal Akuntansi & Investasi,
1(1).
D Hasanuddin, 2020. Kasus Maybank Tunjukan
Lemahnya Pengawasan Internal Bank, Anis: OJK
Perlu Lakukan Mediasi (Tribunnews.com)
https://wartakota.tribunnews.com/2020/11/15/kas
us-maybank-tunjukan-lemahnya-pengawasan-
internal-bank-anis-ojk-perlu-lakukan-mediasi .
I Astria, E Halimatusadiah, N Nurhayanti, 2017.
Pengaruh Kompetensi Pengguna, PI thd Kualitas
SIA (Survey pada Bank Syariah di Kota
Bandung). Jurnal Akuntansi 3(2).
T Tresyani, 2019. Pengaruh Sistem Pengendalian
Internal Thd Kualitas SIA Yang Berdampak Pada
Kualitas Informasi Akuntansi (Survei Pada
A Comprehensive Study of the Effects of User Competence and Internal Control on the Quality of Accounting Information Systems
121

Satuan Kerja perangkat Daerah Kota Bandung),
Universitas Komputer Indonesia, Bandung.)
W Nugroho, Kristanto, 2019. Pengaruh SIA Dan
Sistem Pengendalian Internal Thd Kinerja
Karyawan Kspps Bmt Al Fataa Kabupaten
Pemalang, Jurnal Akuntansi Dan Sistem
Teknologi Informasi.
O Syahputra, 2022. The Effect Of IC And Quality Of
AIS On Quality Information On Pt. Pandu Siwi
Sentosa (Pandu Logistics), Enrichment: Journal
of Management, 12(2).
F Hafidz, Muhammad Fikru Rizal, 2022. Analisis
Efisiensi Fasilitas Kesehatan (UGM PRESS,
Yogyakarta.)
M F Bormasa, 2022. Kepemimpinan Dan Efektivitas
Kerja (CV. Pena Persada. Jawa Tengah,.)
Ir. F I Wijayanti, 2023. Entrepreneurship! Marketing!
Dalam Bisnis (Elex Media Komputindo, Jakarta.)
Marjulin, 2019. Pengaruh Kompetensi Pengguna
Thd Kualitas SIA Survei Bumn di Aceh, Jurnal
Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, 21(2).
K G Mejia, B B David, L C Robert, 2010. Managing
Human Resources, 6 (Pearson Education,
Canada.)
Dr S Simbolon,S. E. , M. Si. , CIMBA., 2022.
Manajemen SDM Dlm Meningkatkan Kinerja
Karyawan (CV. Bintang Semesta Media,
Yogyakarta.)
A Chaeruddin, I Hartaningtyas, V Alicia, 2020.
Sumber daya manusia : pilar utama kegiatan
operasional organisasi (CV Jejak (Jejak
Publisher), Yogyakarta.)
A Susanto, 2017. Sistem Informasi Akuntansi :
pemahaman konsep secara terpadu (Linggar Jaya,
Bandung.)
Dr. Ir. D Soelistya, M. M, CPHCM, CHRMP., 2021.
Kepemimpinan Strategis (Nizamia Learning
Center, Sidoarjo.)
Endraria, 2016. User Competence and Influence on
The Quality of Accounting Information System.
Journal of Theoretical and Applied Information
Technology 86(1).
R Fitrios, 2022. How Information Technologi and
User Competense Affect the Quality if
Accounting Information Through the Quality of
AIS. Quality – Access to Success 23(187)
Y Mulyanti, 2017. Pengaruh TI dan Pengendalian
Internal Thd Kualitas SIA, Jurnal Akuntansi,
Audit dan Sistem Informasi Akuntansi
Sugiyono, 2019. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif,
Kualitatif, Dan Kombinasi (Mixed Methods)
(Alfabeta.)
O Usman, T Monoarfa, M Marsofiyati, 2020. E-
Banking and M-banking effects on customer
satisfaction, Accounting, 6(6)
Irwan, A Khaeryna, 2015. Metode Partial Least
Square (PLS) dan Terapannya (studi kasus:
Analisis Kepuasan Pelangga terhadap Layanan
PDAM Unit Camming Kab. Bone), Jurnal
Teknosains 9(1).
Y Febrianawati, 2018. Uji Validitas dan Reliabilitas
Instrumen Penelitian Kuantitatif. Jurnal Tarbiyah:
Jurnal Ilmiah Kependidikan, 7(1).
M A Suswandera, N Nurhayati, E Halimatusadiah,
2018. Pengaruh Gaya Kepemimpinan dan
Pengendalian Internal Terhadap Kualitas Sistem
Informasi Akuntansi (Survey pada Bank Umum
Konvensional di Kota Bandung). Prosiding
Akuntansi 4(2).
A Kurniawan, M Purwanti, 2017. Pengaruh
Pengendalian Internal Terhadap Kualitas Sistem
Informasi Akuntansi dan Dampaknya Terhadap
Kualitas Informasi Akuntansi, 17(2)
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
122
