
Analysis of Determinants Human Development Index in ASEAN
Countries
Khubbi Abdillah
1
, Alfin Maulana
1
and Aminatuzzuhro
2
1
Department of Economic Development, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Wijaya Putra, Indonesia
2
Departement of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Wijaya Putra, Jl. Raya Benowo 1-3
Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Human Development Index, ASEAN Countries, Panel Regression.
Abstract: The Human Development Index (HDI) is an important variable in improving people's quality of life, measured
by the level of education, health, and income per capita. This research considers aspects of economic
variables, such as foreign direct investment (FDI), unemployment, and economic growth, with the aim of
analyzing the determinants of HDI in 11 ASEAN countries from 2018 to 2021. The analysis technique of this
study uses panel data regression with the help of eviews software version 12. The results of the study
concluded that economic growth, FDI have a significant positive effect on HDI. while the unemployment rate
has no significant effect on HDI. The policy recommendation in this study is that the government should
increase employment opportunities by opening new jobs through foreign direct investment, which will
increase GDP and subsequently improve HDI.
1 INTRODUCTION
Human development index (HDI) is an indicator used
to measure the progress of a country in terms of social
and economic dimensions (Shah, 2016). The social
and economic success of a country's development
hinges on human development. Human development
is not only about increasing human choices such as
human rights, freedom of speech, ability to work, and
the opportunity to live longer with good health, and
think creatively. UNDP developed the HDI concept
to assess human well-being from a broader
perspective, beyond the income generated by society
(Sofilda et al., 2015).
Previous studies have been conducted by previous
researchers on the Human Development Index in
several journals. With the existence of previous study
so that authors make rationale for compiling this
study. The results of studies by Handalani (2018),
Fadillah & Setiartiti (2021), and Dzulqornain & Iriani
(2022) conclude that economic growth has a
significant impact on the human development index.
According to study Rohmah & Wicaksana (2021), to
increase the human development index, it is
necessary to identify the problems faced and make
policies to increase the human development index by
encouraging higher economic growth. The study of
Sumiyarti and Handayani (2022) revealed various
outcomes. the research results show that economic
growth has not been able to drive growth in 34
provinces in Indonesia. Sumiyarti & Handayani
(2022) adds that the success of building welfare
(HDI) is determined by how much the government's
commitment as a regulator and provider of
infrastructure to achieve a modern economy, improve
the quality of life and human resources.
The results of the study conducted by Sumiyarti
and Handayani (2022) concluded that foreign
investment has a positive and significant impact on
the human development index. while studies
Sumiyarti & Handayani (2022), Arisman (2018),
show that the unemployment rate has significant
negative effect on the human development index. But,
Sofilda et al., (2015) conclude that the unemployment
rate has no significant effect on the human
development index. according to Sangaji (2016),
public policies implemented by the government must
be able to reduce the poverty rate by creating jobs
through pro jobs so that the unemployment rate
decreases.
The findings from Elistia & Syahzuni (2018)
show that economic growth as measured by GDP per
capita has a very strong positive correlation above 0,8
142
Abdillah, K., Maulana, A. and Aminatuzzuhro, .
Analysis of Determinants Human Development Index in ASEAN Countries.
DOI: 10.5220/0012649100003798
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Maritime, Economics and Business International Conference (MEBIC 2023) - Sustainable Recovery: Green Economy Based Action, pages 142-146
ISBN: 978-989-758-704-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

and significant at the α = 1% level with the Human
Development Index which is an indicator of welfare
in 10 ASEAN countries from 2010 to 2016, except
Brunei Darussalam which has a strong positive and
significant correlation of 0,76. In contrast to
Simamora et al., (2022) who conducted research on
the relationship between HDI and economic growth
in districts/cities of East Kalimantan Province in 2010
– 2021 using the Klassen Typology approach,
cointegration, and Granger causality relationships.
The research results concluded that only 3 regions
consisting of 1 district and 2 cities were in quadrant I
of the Klassen Typology, namely the correlation
between growth and HDI was positive. The long-term
relationship between economic growth and HDI is
evident. In addition, the Granger causality results
show a one-way relationship, namely that HDI has an
impact on growth.
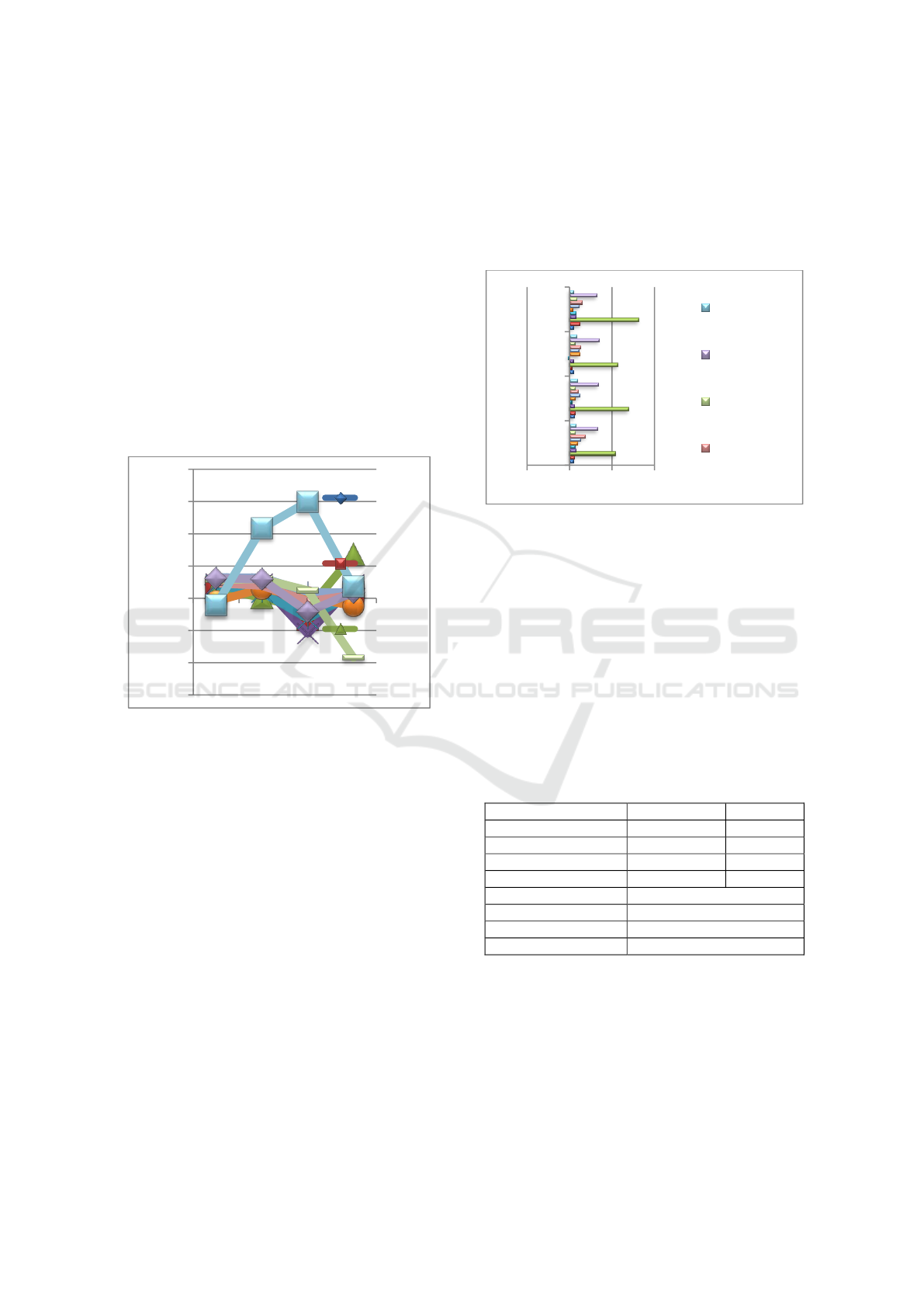
Source: UNDP (2023), Processed Data.
Figure 1: Human Development Index in ASEAN 2018 –
2021.
Based on Figure 1, the Human Development
Index in ASEAN countries varies and increases
yearly, except for 2021. Almost all ASEAN countries
experienced a decline in Human Development Index
(HDI), except for Singapore. Singapore is an ASEAN
country that has the highest average HDI score,
followed by Brunei Darussalam, Thailand, Malaysia,
and Indonesia. While the lowest HDI is owned by
Timor Leste.
Feriyanto (2016) examined how labor, growth,
and investment (both domestic and foreign) affect
HDI in 33 provinces from 2006 to 2013 using a fixed-
effect model. The research results concluded that
labor, domestic investment, FDI have a positive effect
on HDI. Meanwhile, economic growth hasn’t effect
on HDI. Furthermore, Anindhita and Hasbi (2022)
examined the causality relationship and multiple
regression between economic growth and HDI in
Gorontalo Province between 2011 and 2022 using 40
samples. The findings conclude that economic growth
and HDI are stationary at the 1
st
difference level and
have a cointegration relationship at the α = 5% level.
The results of the causality test show that economic
growth and HDI have a two-way relationship or
influence each other.
The aim of this study is to examine the factors that
affecting the Human Development Index in 11
ASEAN countries in 2018 – 2021. For this aim, panel
data regression can be used, along with a combination
of time series and cross-sectional data. Independent
variable in this study, include economic growth,
foreign direct investment, and unemployment rate.
2 RESEARCH METODOLOGY
The data secondary used taken from World
Development Indicators (WDI) and United Nations
Development Programme (UNDP). Research objects
taken from 11 countries namely: Indonesia, Malaysia,
Singapore, Philippines, Thailand, Brunei
Darussalam, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia,
Timor Leste. The data required include: Human
Development Index (HDI) from UNDP (2023), GDP
per capita growth (annual %), Foreign Direct
Investment (FDI) net inflows (% of GDP),
unemployment rate (% of total labor force) (World
Bank, 2023).
Panel data regression was used to analyze
relationships between dependent and independent
variables using pooled data. HDI was the dependent
variables. While the independent variables in this
study were economic growth, FDI, and
unemployment. This study sample from 2018 until
2021. Panel data regression has three model stages:
common effect model (CEM), fixed effect model
(FEM), and random effect model (REM). CEM has
explanatory variables that are not influenced by error
term. Meanwhile, FEM assumes different intercepts
and REM has error term that are not correlatied with
each other and more consistent than CEM.
However, in panel data regression, there are two
tests, namely Chow test (to select CEM nad FEM)
and Hausman test (to select FEM and REM). The best
model is chosen to interpret the analysis results based
on the existing test results. The mathematical
equation that used in this study as follow:
HDI
it
= α
0
+ β
1
GDP
it
+ β
2
FDI
it
+ β
3
UNEMP
it
+ ε
it
(1)
Where:
HDI = Human development index
0
0,2
0,4
0,6
0,8
1
2018 2019 2020 2021
Indonesia
Malaysia
Singapore
Philippines
Analysis of Determinants Human Development Index in ASEAN Countries
143
GDP = Economic Growth
FDI = Foreign direct investment
UNEMP = Unemployment rate
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
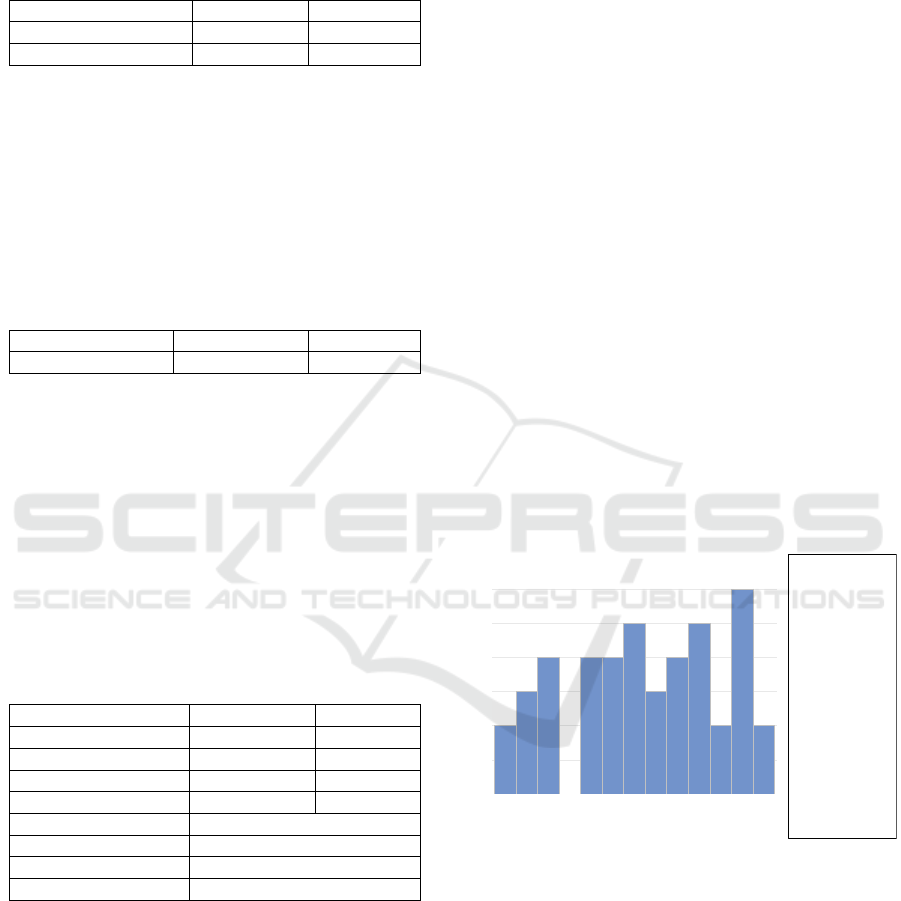
According to Figure 2, economic growth in ASEAN
countries tends to fluctuate, and even decline,
especially during the COVID-19 outbreak. Almost all
countries experienced minus (-) growth during covid
in 2020, except Brunei Darussalam and Vietnam.
Timor Leste has the highest average economic growth
of 29,93 percent. The reason for this is that the
country is considered a new country and is currently
in the process of development.
Figure 2: FDI in ASEAN 2018 – 2021.
Based on Figure 2, Foreign Direct Investment
(FDI) in ASEAN tends to increase. The country with
the highest average FDI is Singapore, with 26.17
percent. Then, followed by Cambodia, Lao, and
Vietnam. The remaining 8 countries have an average
FDI below 4 percent. The country that has the lowest
average FDI is Thailand. FDI is an important
component in encouraging an increase in HDI.
According to Todaro and Smith (2020), the
Human Development Index (HDI) is a proxy for
social welfare and has a positive relationship with
income per capita. This means that the higher GDP
per capita, the higher the social welfare. The increase
in job opportunities and income will be accompanied
by more capital inflows into the country. Because of
the production goods and services increases, social
welfare increases.
Todaro and Smith (2020) added that economic
growth only results in improvements in income
distribution if two conditions are met, namely
expanding employment opportunities and increasing
productivity. The more job opportunities expand, the
greater the opportunity for people to get a job. In
order for people to earn more income, in this case
workers must continue to increase productivity by
increasing working hours rather than leisure time.
Source: World Bank (2023), Processed Data.
Figure 3: Foreign Direct Investment in ASEAN 2018 –
2021.
This study uses panel data regression to analyze
the relationship between independent variables and
the dependent variable in panel data. Panel data is
combination of time series dan cross-section. The
first step in this study we estimate using common
effect model. We can see empirical results common
effect model in Table 1. The result shows that
economic growth, foreign direct investment had
impact on human development index (HDI) at α=1%.
But, GDP hadn’t impact on HDI.
Table 1: Empirical Results Common Effect.
Variable
Coefficient
Prob
C
0.616647
0.0000*
GDP
-0.002573
0.1907
FDI
0.006758
0.0012*
UNEMP
0.021718
0.0032*
R-squared
0.342141
Adjusted R-squared
0.292801
Prob (F-statistic)
0.000723*
Durbin-Watson stat
0.143300
Source: Eviews 12, Processed.
Table 2 show the results of Chow Test. The Chow
test is utilized to determine which common effect or
fixed effect model is the most suitable for estimating
panel data. The results of chow test indicated that the
probability of cross-section chi-square is 0,000 less
than α=1% so that Ho is rejected and H1 is accepted.
Moreover, chow test produces the chosen model,
-30,000
-20,000
-10,000
0,000
10,000
20,000
30,000
40,000
2018 2019 2020 2021
Indonesi
a
Malaysia
Singapor
e
-20,0000,000 20,00040,000
2018
2019
2020
2021
Timor Leste
Cambodia
Myanmar
Lao
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
144
namely fixed effect model than common effect
model.
Table 2: The Results of Chow Test.
Effect Test
Statistic
Prob
Cross-section F
1812,9156
0,0000*
Cross-section Chi-square
281,8522
0,0000*
Source: Eviews 12, Processed.
Hausman test is a test used to determine whether
a fixed effect model or a random effect model is.
Based on Table 3, the results of Hausman test show
that probability of cross-section random is equal to
0,0784 less than α=10% so that H0 is rejected and H1
is accepted. So, the best model used is fixed effect
model in this study.
Table 3: The Results of Hausman Test.
Test Summary
Chi-square Stat
Prob
Cross-section random
6,805564
0,0784**
Source: Eviews 12, Processed.
Based on the test results and selection of the best
estimator then the model which is more precise in
estimating the analysis of determinant variables for
the human development index in ASEAN countries
by using fixed effect model. This model will then be
selected, interpreted, and analyzed in research. It can
be seen in Table 4. The fixed effect model equation
in this study can be explained as follow:
HDI
it
= 0,7193 + 0,0279 GDP
it
+ 0,0336 FDI
it
+
0,0142 UNEMP
it
+ ε
it
(2)
Table 4: Empirical Results Fixed Effect.
Variable
Coefficient
Prob
C
0,7193
0,0000*
GDP
0,027997
0,0002*
FDI
0,033615
0,0122**
UNEMP
0,014232
0,9592
R-squared
0,999786
Adjusted R-squared
0,999693
Prob (F-statistic)
0,0000*
Durbin-Watson stat
2,392593
Source: Eviews 12, Processed.
Table 4 show that fixed effect estimated model is
exists with probability or empirical statistical
significance F of 0,0000 less than α=1%,
simultaneously independent variables significant on
dependent variable. Coefficient of determination (R-
squared) which indicates that the variation of
independent variable can be explained by 99,9786%
of the dependent variable and the rest is influenced by
other variables outside the model by 0,0214%.
Economic growth (GDP) variable has a
regression coefficient value of 0,0279 with p-value of
0,0002 at significant effect on Human Development
Index (HDI) at α=1%. It means that if GDP increased
by 1%, the HDI will increase by 0,0279 or 2,79%. The
high level of economic growth will increase the
Human Development Index in ASEAN. The results
of this study is in line with previous study Handalani
(2018), Fadillah & Setiartiti (2021), Dzulqornain &
Iriani (2022) and rejected by Feriyanto (2016).
Based on from panel data regression results
with Eviews 12, coefficient of 0,0336 with p-value of
0,0122 at a significance α=5% then H1 is accepted
and Ho is rejected, which means that Foreign Direct
Investment (FDI) partially has a positive and
significant effect on Human Development Index
(HDI) in ASEAN period 2018 – 2021. It means that
if FDI increased by 1%, the HDI will increase by
0,0336 or 3,36%. It is consistent with the studies of
Feriyanto (2016), Handalani (2018), and Sumiyarvi
& Handayani (2022). On the other hand, with p-value
of 0,9592 less than α=10% then Ho accepted and H1
is rejected, which means unemployment rate
(UNEMP) has no significant on Human Development
Index (HDI). It is also in line with study conducted by
study Sofilda et al., (2015) and rejected by Feriyanto
(2016).
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
-0.006 -0.004 -0.002 0.000 0.002 0.004 0.006
Series: Standardized Residuals
Sample 2018 2021
Observations 44
Mean -3.01e-18
Median 3.68e-05
Maximum 0.005310
Minimum -0.006176
Std. Dev. 0.003527
Skewness -0.242376
Kurtosis 1.876252
Jarque-Bera 2.745954
Probability 0.253352
Source: Eviews 12, Processed.
Figure 4: The Results of Normality Test.
Normality tes result can be seen in figure 2,
which shows that data has been estimated is normally
distributed. The probability for Jarque Berra is
0.253352, which exceeds 10%, so H0 is accepted and
H1 is rejected, as shown in Figure 2. So, it can be
concluded that error term in this model is normally
distributed.
Analysis of Determinants Human Development Index in ASEAN Countries
145

4 CONCLUSION
The dependent variable used in the study results of 11
countries in ASEAN is Human Development Index
(HDI). Economic growth, Foreign Direct Investment
( FDI), unemployment are independent variables.
Panel data regression used in this study with fixed
effect model. The results of the study can be
summarized as follows: economic growth and foreign
direct investment have a positive and significant
impact on the Human Development Index (HDI) in
ASEAN. But, unemployment rate has no significant
effect on HDI. Policy recommendation in this study
is that the government needs to increase employment
opportunities by opening new jobs through FDI to
improve HDI. Apart from that, an increase in GDP
which is influenced by the size of output can result in
additional labor and better productivity. GDP that
continues to grow will increase people’s per capita
income and encourage the state to provide education
and health facilities through large tax collections from
the society so that HDI increases.
REFERENCES
Anindhita, F., & Hasbi, M. (2022). The Analysis of
Economic Growth and Human Development in
Gorontalo Province. Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan,
20(01), 1–9.
Arisman. (2018). Determinant of Human Development
Index in ASEAN Countries. Signifikan: Jurnal Ilmu
Ekonomi, 7(1), 113–122.
Bank, W. (2023). World Development Indicators.
databank.worldbank.org
Dzulqornain, R., & Iriani, R. (2022). The Effect of
Economic Growth, Regional Expenditures, and Poverty
Levels in East Kalimantan Province. Jurnal Ekonomi
Akuntansi, 7, 27–37.
Elistia, E., & Syahzuni, B. A. (2018). The correlation of the
human development index (HDI) towards economic
growth (GDP per capita) in 10 ASEAN member
countries. Jhss (Journal of Humanities and Social
Studies), 2(2), 40–46.
Fadillah, N., & Setiartiti, L. (2021). Analysis of Factors
Affecting Human Development Index in Special
Regional of Yogyakarta. Journal of Economics
Research and Social Sciences, 5(1).
https://doi.org/10.18196/jers
Feriyanto, N. (2016). The effect of employment, economic
growth, and investment on HDI: In provinces in
Indonesia. Journal of Economics, Business &
Accountancy Ventura, 19(1), 1.
Handalani, R. T. (2018). Determinan Indeks Pembangunan
Manusia di Asia Tenggara. Jurnal Kebijakan
Pembangunan Daerah, 2(2).
Rohmah, C., & Wicaksana, E. J. (2021). Factors Affecting
Inter-Regional Human Development Index in Jambi
Province. Jurnal Ekonomi Pembangunan,
19(December), 193–206. https://doi.org/10.29259/jep
Sangaji, J. (2016). The Determinants of Human
Development Index in Several Buddhist Countries.
Journal of Buddhist Education and Research, 2(1), 48–
60.
Shah, S. (2016). Determinants of Human Development
Index : A Cross-Country Empirical Analysis. SSRG
International Journal of Economics and Management
Studies (SSRG - IJEMS), 3(7), 40–43.
Simamora, J. P., Fahrulaji, F., & Martha, S. (2022).
Analysis of Relation Human Development Index and
Economic Growth Regency/City in the Province of
West Kalimantan: Analysis of Relation Human
Development Index and Economic Growth
Regency/City in the Province of West Kalimantan.
Jurnal Forum Analisis Statistik (FORMASI), 2(2), 72–
82.
Sofilda, E., Hermiyanti, P., & Hamzah, M. Z. (2015).
Determinant Variable Analysis of Human Development
Index in Indonesia (Case For High And Low Index At
Period 2004 – 2013). OIDA International Journal of
Sustainable Development, i.
Sumiyarti, S., & Handayani, K. (2022). Determinants of
Human Development Index : Case Study of Provinces
in Indonesia. LePALISSHE.
https://doi.org/10.4108/eai.3-8-2021.2315091
Todaro, M. P., & Smith, S. C. (2020). Economic
development. Pearson UK.
UNDP. (2023). Human Development Index Report.
data.undp.org
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
146
