
Factors that Affect Fishermen's Income with Fuel Cost as Moderating
Variable
Inge Lengga Sari Munthe, Fatahurrazak, Rizki Yuli Sari, Ronia Tambunan and Jack Febriand Adel
Faculty of Economics and Business Maritime, Accounting Department, Tanjungpinang, Indonesia
jackfebriandadel@umrah.ac.id
Keywords: Fishermen's Income, Work Experience, Consumption Costs, Labour Costs, Fuel Costs.
Abstract: This research discusses factors influencing fishermen's income with fuel costs as a moderating variable.
Sampling used a purposive sampling technique and obtained 52 research samples. Data collection was carried
out by collecting primary data with interviews, surveys and observations. The statistical test used is Moderated
Regression Analysis. The results of this research are (1) work experience simultaneously and partially
influences fishermen's income, (2) consumption costs simultaneously and partially influence fishermen's
income, (3) labour costs simultaneously and partially influence fishermen's income, (4) Fuel costs
simultaneously and partially influence fishermen's income. (5) Fuel costs can moderate the influence of
consumption costs on fishermen's income. (6) Fuel costs can moderate the influence of labour costs on
fishermen's income. (7) Fuel costs cannot moderate the effect of work experience on fishermen's income. Our
findings can provide insight into increasing fishermen's income.
1 INTRODUCTION
The total land area of the Bintan Regency is
88,038.54 km2. The oceans surrounding Bintan cover
an area equal to 86,092.41 km2 of the island's total
land area. It means that Bintan's water area is 98% of
the total. The district of Bintan spans a total size of
88,038.54 km2 in its entirety. However, its land area
is only 2.21%, equivalent to 1,946.13 km2. The
remaining 86,092.41 km2 is water. With the vastness
of Bintan's waters, fishermen can catch more marine
products.
According to Act No. 45/2009, fishermen are
people whose livelihood is fishing. Fishermen play a
crucial role in the community as they fulfil animal
protein intake at all levels of society. It concerns the
fulfilment of animal protein intake at all levels of
society. In order to maximize the catch, the welfare of
fishermen also needs to be considered. Fishermen's
income depends on the potential exploitation of
marine and fish resources in the ocean. Fishing is the
main source of income for his family.
The income of fishing communities influences,
directly or indirectly, the quality of life of fishermen.
Fishermen's income level has a big impact on their
lives. It is also related to environmental management
and coastal development based on existing local
wisdom that has long been rooted in fishing
communities.
Fishermen usually catch fish at night. Around 6
p.m., they went out to sea and waited for the fish.
Then come home at dawn. So, morning and afternoon
is the time for fishermen to rest. According to
(Munthe et al., 2018), there are also certain days of
fishing—only some days to catch fish. During the
"dark moon", fishermen only go to sea to fish. If it is
a "bright moon", fishermen will not go to sea. It also
depends on the weather. If the weather is not good,
the fishermen will also be unable to go to sea.
Fishermen can catch a variety of catches. The
catches of fishermen in Bintan are as follows: various
fish such as pomfret, mackerel, boren, red, worm trap,
goli jebung kaci, coral, grouper, selar selikur, cob,
and tamban. In addition, the catch is in the form of
shrimp, crabs and barks. Some fishermen catch only
one type of fish. Some fishermen catch more than one
species. Fishermen who catch more than one species
have a higher income than other fishermen. To carry
out their work, some fishermen have subordinates.
The catch and the money increase in proportion to the
number of subordinates who assist. According to
(Norlinda, 2022), those who have researched the
influence of labour on the revenue of fishermen in the
Munthe, I., Fatahurrazak, ., Sari, R., Tambunan, R. and Adel, J.
Factors that Affect Fishermen’s Income with Fuel Cost as Moderating Variable.
DOI: 10.5220/0012649600003798
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Maritime, Economics and Business International Conference (MEBIC 2023) - Sustainable Recovery: Green Economy Based Action, pages 25-31
ISBN: 978-989-758-704-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
25

hamlets of Ambahai, more labour and cooperation
with each other, the greater the catch, so the income
will also increase. Generally, fishermen sell their
catch to Toke. Then, Toke will sell again to the
merchant. Ship crew can be paid regularly per month
or day. It is also possible for subordinates to get profit
sharing from the sale of fish.
Experience in the sea will determine a fisherman's
skill in getting fish catches. Fishermen with more
experience can find it easier to determine where to
catch and the most effective way to get more catches.
According to (K. Cahyandi, 2021), having prior
experience at sea has a major impact on whether or
not one chooses to travel to sea again. Small-scale
fishing activities rely only on work experience at sea
and do not depend on guidelines or technology to
determine fishing locations. The length of time
fishermen go to work varies. In a month, fishermen
can work 20 days or even every day. Fishermen are at
sea for 4 to 5 hours. They usually go at night. Coming
home from the sea is tomorrow afternoon. Some
fishermen can spend 4 or 5 days at sea. Fishermen's
fishing gear can be in the form of traps, handlines,
nets, and trawls. If the fishing gear is damaged, new
fishing gear must be purchased. Fishing lines should
always be replaced when going out to sea.
Consumption will play an important role,
especially for fishermen who go to sea. For fishermen
to go to sea, they consume food, drinks, and even
cigarettes. Fishermen go to sea after 6 p.m. until the
next morning. From the results of (A. Widodo, 2019),
each additional ransom (food) at sea will affect
fishermen's catch in Medan Belawan District.
Fuel oil is a supporting factor in going to sea.
Fishermen-used boats must be filled with fuel. The
amount of fuel oil used depends on the size of the
ship, which ranges from 15 to 1,000 litres per month.
Based on the research results by (Lasut et., al, 2016),
fuel significantly affects fishermen's income in the
Tuminting sub-district of Manado.
Fishermen's catches have a significant impact on
increasing their income and overall well-being.
Various factors influence fishermen's income,
encompassing both social and economic aspects.
These factors include consumption costs, the
number of boats, the number of workers, the distance
travelled, and experience (Sujarno, 2008). In
alignment with this, the current research aims to
observe and assess the factors affecting income of
fishermen from a socioeconomic perspective,
specifically focusing on consumption costs, work
experience, labour costs, and fuel expenses and how
these factors influence fishermen's income in Bintan
Regency.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Production Theory
As outlined by Joesron and Fathorrozi (2003),
production refers to the outcome of an economic
process or activity that utilizes various inputs with the
aim of enhancing the utility, or usage value, of a
product. The utility of a product increases when it
provides new or added benefits compared to its
original form.
More precisely, production is an enterprise's
activity that involves combining diverse inputs to
generate output at the lowest possible cost. Hence, the
production function is an equation that illustrates the
maximum output achievable through a specific
combination of inputs.
Each input has a distinct function and is
interconnected with others, meaning that if one factor
is unavailable, it can disrupt the production process.
Increased production will increase fishermen's
income. Income fishermen is income earned by
fishermen who have been reduced with costs
(Sukirno, 2006). The factors that influence
fishermen's income levels are as follows:
1. Work experience
Work experience is defined as an activity or the
process that someone has experienced when
earning a living to meet his life needs (Rofi,
2012).
2. Labour
Labour is everyone who can work to produce
goods or services for their own needs and society
(Mulyadi, 2003).
3. Consumption
Consumption is generally interpreted as using
goods and services directly fulfilling human
needs, such as cigarettes, rations, Etc. (James,
2001).
4. Fuel Oil Expenses
Fuel oil expenses are from fishermen catching
fish/sea products (Sukirno, 2006).
3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Sampling and Data Collection
Within the framework of sampling and data
collection, the statistical population of the present
study initially encompassed a total of 132 fishermen.
Thus, the final sample became 52 fishermen.
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
26

3.2 Data Analysis
The current research uses content analysis techniques
to explore the factors influencing fishermen's income
levels. Data were collected using the questionnaire
method, which fishermen have filled out.
The present study utilizes descriptive statistics for
data analysis, wherein the acquired data is described
without the aim of drawing overarching conclusions
or generalizations. The results of the data tabulated in
Excel are then processed in SPSS. The analysis model
used is the Moderated Regression Analysis model
(Ghozali et al., 2018).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSS
4.1 Classic Assumption Test
Before conducting the regression analysis, this study
first tested the classical assumptions. The testing of
classical assumptions using the SPSS program in this
research encompassed the following:
4.1.1 Normality Test
The purpose of the normality test in this investigation
was to determine whether or not the regression model
adheres to the normal distribution. The Kolmogorov-
Smirnov test was employed for this purpose.
According to the normality test results, the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov significance value was
discovered to be 0.200, which is higher than the 0.05
threshold required for statistical significance.
Because of this, data of this study is normally
distributed, indicating that the normality assumption
is met.
4.1.2 Multicollinearity
The intent of the multicollinearity test undertaken in
this study was to investigate the possibility of
correlation among the independent variables within
the regression model. Multicollinearity has not an
impact on the desirability of a regression model. The
existence of multicollinearity in the dataset was
evaluated by employing the Variance Inflation Factor
(VIF) and Tolerance values. The outcomes from the
multicollinearity test revealed that the Variance
Inflation Factor (VIF) value was below 10, reflecting
a low level of multicollinearity. Furthermore, the
tolerance value exceeded 0.1, further supporting the
absence of significant multicollinearity. As a result,
the data used in this study is free from
multicollinearity, indicating that the independent
variables do not exhibit high correlations.
4.1.3 Autocorrelation
Examining for autocorrelation conducted in this
research aimed to examine whether a regression
model exhibits correlations between the error terms in
period 't' and the error terms in the previous period, 't-
1.' The Durbin-Watson test was employed for this
autocorrelation analysis. Based on the results of the
autocorrelation test, it was determined that the
Durbin-Watson statistic falls within the range of 'dU
< DW < 4 - dU,' which suggests that the proposed
regression equation model does not suffer from
autocorrelation.
4.1.4 Heteroscedasticity
The objective of the heteroscedasticity test performed
in this study had been to detect the presence of
unequal variance among residual data within the
regression model. If the variance of residuals remains
consistent across observations, it indicates
homoscedasticity, whereas differing variances
suggest Heteroscedasticity.
A desirable regression model does not exhibit
Heteroscedasticity. Based on the outcomes of the
heteroscedasticity test, it was noted that the p-value
for each independent variable, specifically work
experience, consumption, labour, and fuel oil costs,
exceeded 0.05. Consequently, the regression model in
this study does not suffer from Heteroscedasticity,
indicating that the variances of residuals across
observations are relatively consistent.
4.2 Descriptive Statistics
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics.
Source: processed SPSS results, 2023.
Table 1 shows the summary descriptive statistics of
the variables. The analysis shows that the average
labour cost is 55.59, meaning that the costs
influencing fishermen's income are generally labour
costs. The standard deviation of labour costs is 87.47
above the average (55.59), meaning that labour costs
have high data variations. The range of work
Factors that Affect Fishermen’s Income with Fuel Cost as Moderating Variable
27
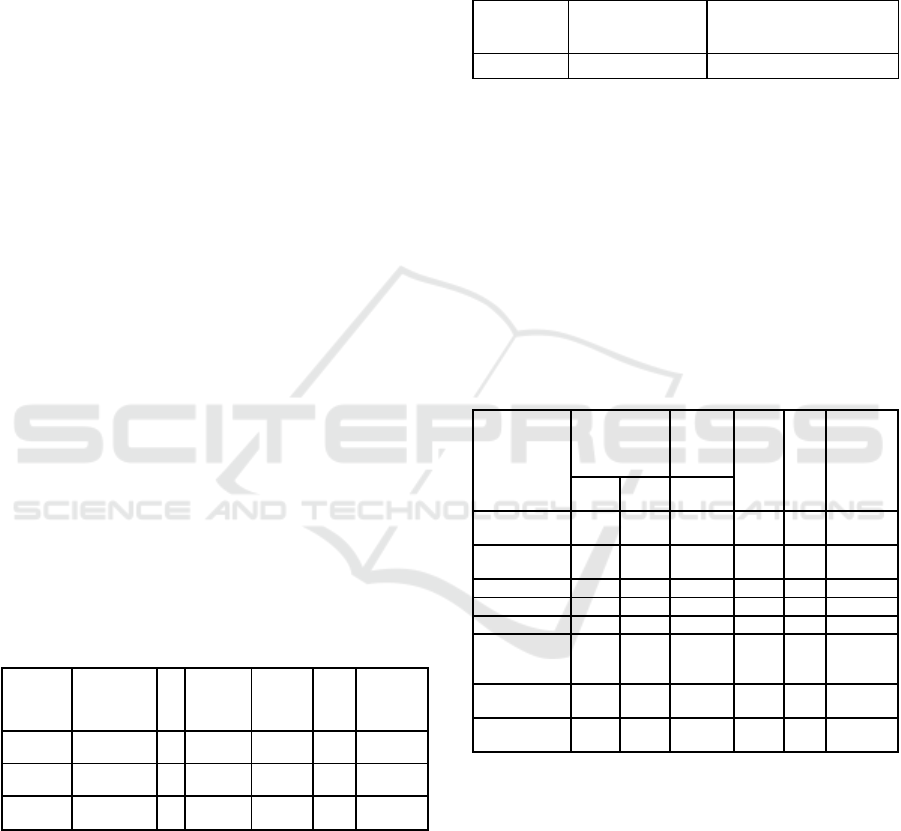
experience comprises a minimum value of 2 to a
maximum value of 42, with a mean value of 18.37.
This average exceeds the standard deviation of 7.48,
indicating a significant degree of variability in the
data pertaining to work experience. Consumption
costs have the uppermost limit of 144 and a lower
bound of 5.59 with an average value of 11.89, which
is lower than the standard deviation (19.45), meaning
that consumption costs have low data variation. Fuel
oil costs have a maximum value of 48 and a minimum
value of 6.27 with an average value of 16.79, which
is higher than the standard deviation (14.85), meaning
that fuel oil costs have high data variations. The
income level of fishermen has a maximum of 576 and
a lower of 62.72 with a middle value of 151.31, which
is lower than the standard deviation (72.06), meaning
that the income level of fishermen has low data
variation.
4.3 Regression Analysis
The statistical model used to test the hypothesis is
Moderated Regression Analysis (MRA). Moderated
Regression Analysis (MRA) in this study is intended
to see how work experience, consumption, labour,
and fuel costs affect fishermen's income. In order to
assess the viability of the regression model, various
factors can be taken into consideration, as outlined
below:
4.3.1 F Test
The F test shows whether all the independent
variables included in the model can be explanatory or
predictor variables.
Table 2: ANOVA Test Results (Simultaneous Test).
Model
Sum of
Squares
Df
Mean
Square
F
Sig.
Informatio
n
Regression
264860,343
4
66215,08
608,083
0,000
b
Significant
Residual
5226.796
48
108,892
Total
270087.139
52
Source: processed SPSS results, 2023.
Table 2 shows that the calculated F value of
608.083 has a probability (sig) of 0.000, which is less
than 0.05. Work experience, consumption, labour,
and fuel costs can become explanatory variables.
Hence, the conclusion is that the regression model is
feasible to predict fishermen's income. Thus, the
regression model is a good fit for research.
4.3.2 Coefficient of Determination
The percentage of independent variables explaining
fishermen’s income in the research model is shown
by the magnitude of the coefficient of determination.
Table 3: Results of Analysis of the Coefficient of
Determination.
R
R Square
Adjusted R Square
0,990
a
0,981
0,979
Source: processed SPSS results, 2023.
Based on Table 4, it is known that the adjusted R2
is 0.990. This value indicates that the variation in
fisherman’s income can be explained by 99% by
variations in the independent variables, and the
remaining 1.00% is explained by the causes of
variables outside the model so that this model is
considered capable of explaining the dependent
variable.
4.3.3 T Test
Table 4: Results of Partial Analysis.
Variable
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardi
zed
Coefficien
ts
T
Sig.
Information
B
Std.
Error
Beta
(Constant)
116.01
4
11.694
9.921
0, 000
Work
experience
0.704
0.255
0. 073
2.755
0,008
Significant
Consumption
-5.977
1.118
-1.613
-5.347
0,000
Significant
Labour
0.494
0.197
0.599
2.508
0,016
Significant
Fuel cost
1.898
0.494
0.392
3.842
0,000
Significant
Work
Experience*
Fuel cost
-0.014
0.008
-0.068
-1.622
0,112
No
Significant
Consumption*
Fuel cost
0.211
0.025
2.525
8.267
0,000
Significant
Labor * Fuel
cost
-0.027
0.011
-0.664
--2.475
0,017
Significant
Source: processed SPSS results, 2023.
Based on table 3 it can be explained as follows:
1. The Effect of Work Experience on Fishermen's
Income
According to the results obtained from SPSS
calculations, a t-value of 2.755 was computed, and its
associated significance value was determined to be
0.008, which is less than the threshold of 0.05. This
result indicates that work experience has a
statistically significant effect on fishermen's income.
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
28

2. The Effect of Consumption on Fishermen's
Income
Based on the results obtained from calculations using
SPSS (as shown in Table 3), a t-value of -5.347 was
observed, and the associated significance value was
determined to be 0.000, which is less than the
significance threshold of 0.05. This result suggests
that consumption has a statistically significant impact
on fishermen's income.
3. The Influence of Labour on Fishermen's
Income
Based on the results of calculations using SPSS (as
presented in Table 3), a t-value of 2.508 was obtained,
and the associated significance value was found to be
0.0016, which is less than the significance threshold
of 0.05. This result implies that labour has a
statistically significant impact on fishermen's income.
4. The Effect of The Fuel Cost on Fishermen's
Income
Based on the calculations using SPSS, specifically
from Table 3, a t-value of 3.842 was determined, with
an associated significance value of 0.000, which is
less than the significance threshold of 0.05. This
result indicates that fuel costs have a statistically
significant impact on fishermen's income.
5. The Interaction Effect of Working Experience
with The Fuel Cost on Fishermen's Income
Based on the information presented in Table 3, it is
evident that the interaction between work experience
and fuel costs (Work Experience * Fuel Costs) on
fishermen's income yields a t-value of -1.622, and the
corresponding probability (sig) is 0.112. This
probability value (sig) is greater than the significance
level of 0.05 (0.112 > 0.05), indicating that the
interaction between work experience and fuel costs
does not have a statistically significant effect on
fishermen's income.
6. The Interaction Effect of Work Experience
with the Fuel Cost on Fishermen's Income
Based on the data provided in Table 3, it is evident
that the interaction between consumption and fuel
costs (Consumption * Fuel Cost) concerning
fishermen's income yields a t-value of 8.267, and the
corresponding probability (sig) is 0.000. This
probability value (sig) is less than the significance
level of 0.05 (0.000 < 0.05), signifying that the
interaction between consumption and fuel costs has a
statistically significant effect on fishermen's income.
7. The Effect of The Interaction of Labour with
the Fuel Cost on Fishermen's Income
Based on the information provided in Table 3, it is
evident that the interaction between labour and fuel
costs (Labor * Fuel Costs) concerning fishermen's
income yields a t-value of -2.475, and the
corresponding probability (sig) is 0.017. This
probability value (sig) is smaller than the significance
level of 0.05 (0.017 < 0.05), indicating that the
interaction of labour and fuel costs has a statistically
significant effect on fishermen's income.
5 CONCLUSION
1. Work Experience Affects Fishermen's
Income in Bintan
Experience is the best teacher. According to the study
results, the experience of working fishermen ranged
from 2 years to 55 years. The age range of fishermen
ranges from 18 to 70 years. There are even fishermen
who have gone to sea since they were small, i.e.,
around the age of 10. The right pattern has been
formed for capturing the catch. This study is by
research (Norlinda, 2022). With the experience they
have, it can help fishermen know the right point to
place fishing gear, such as fishing nets, to produce
many catches. Also, experience is very important
because, with experience, we can find out which
locations have many results and which do not.
2. Consumption Costs Affect Fishermen's
Income in Bintan
Fishermen usually spend a long time at sea. They
need food, drink, and even cigarettes. Consuming
much delicious food will make fishermen enthusiastic
about looking for catches. As a result, the higher the
consumption costs, the more powerful the fishermen
should be at catching more fish. This will increase the
income of fishermen. However, the consumption that
is brought about could be better now. Fishermen may
bring homemade dishes such as rice and side dishes
cooked at home. So it does not taste good anymore.
This study is by (Dahen et al., 2016), although it
differs in its effect. The study's results (Dahen et al.,
2016) show that working capital's homemade dishes
(consumption costs) can increase fishermen's income.
Meanwhile, the results of this study show that
consumption costs harm income.
Factors that Affect Fishermen’s Income with Fuel Cost as Moderating Variable
29

3. Labor Cost Affects Fishermen's Income in
Bintan
The number of workers can make fishermen catch
many fish. Reasonable and tempting wages will
encourage workers to work harder. This study is by
research (Norlinda, 2022). When they work together,
they will both benefit, and the probability of getting a
catch will increase, which in turn will generate
income as well. In addition, some fishermen still have
to lift their nets themselves or with manual labour. If
more people help, the work will be faster, and the
catch will be greater. This study is by (Sakti et al.,
nd). Labour is needed in catching fish, and for lifting
nets, manual labour is needed directly from the labour
itself to maximize the catch from businesses in
Semidang Alas Maras District, Seluma Regency.
4. Fuel Costs Affect Fishermen's Income in
Bintan
Ships need fuel. If the distance to the sea is close, then
the catch is also a little. The farther the fishermen go
to sea, the deeper the sea, so the catch is also higher.
For this reason, fishermen need much fuel so they can
go further out to sea. This result is by research
(Sofiana et al., 2017). The wider the fish catch, the
variety of fish caught and the size of the catch. The
fishermen can expand their catch because fishermen
can provide more fuel, and the ship's condition is well
maintained. With a longer time at sea, fishermen can
catch more fish.
5. Fuel Costs Cannot Moderate the Effect of
Work Experience on Fishermen's Income in
Bintan
The longer working experience will not affect
fishermen's income, even if supported by adequate
fuel. More experienced fishermen can estimate the
exact time needed to go to sea. So fishermen can save
fuel and will be bolder to go to sea. According to
research (Ibrahim, et al., 2021), the more a fisherman
understands the sea conditions and fish
characteristics, the easier it is for him to catch fish.
The longer the experience, the more sensitive
fishermen are to the fish's position, making it easier
for fishermen to catch fish in the sea so that the time
they use becomes faster and saves fuel.
6. Fuel Cost Can Moderate the Effect of
Consumption Cost on Fishermen's Income in
Bintan
Much fuel will be able to increase consumption costs
and increase fishermen's income. Fishermen may
spend days at sea. Besides that, it is a long journey.
For that, it takes much fuel and much consumption as
well. This study is by research (Sofiana et al., 2017).
Fuel and consumption are fishermen's working
capital. The amount of working capital used will
increase the fishermen's income opportunities.
Because of working capital, the fishermen's catch
area will be expanded, and the time at sea will be
longer.
7. Fuel Costs Can Moderate the Effect of
Labour Costs on Fishermen's Income
Much fuel will reduce labour costs and increase
fishermen's income. Fishermen use diesel and petalite
for their boats. Some fishermen buy fuel oil at official
Pertamina dealers. Some buy at wild stalls. When
buying at an official kiosk, the price of diesel fuel is
Rp. 6.800 per litre. However, if Fishermen buy it at
an illegal kiosk, then the price of diesel is Rp. 10.000
per litre. The amount of fuel oil used depends on the
size of the ship, which ranges from 15 to 1,000 litres
per month. Fuel is an important factor in fishermen's
activity. Fishermen very much need the availability
of fuel by authorized dealers. When buying at illegal
kiosks, the fuel price can be higher than it should be.
The government, in this case, Pertamina, should
provide more authorized dealers. Also, fishermen can
avoid linger at sea if the fuel price is high. Expensive
fuel will reduce labour costs. This study is by research
(Lasut et al., 2016) that shows rising fuel prices have
a major impact on fishermen's income. The
government's active role as power holders and
policymakers must pay greater attention to this
problem. As the institution responsible for the
division and distribution of fuel oil, the government
must pay greater attention to the availability of fuel
oil supplies and the ease of access to obtain them.
REFERENCES
I. L. S. Munthe, M. Sofia, “Pencatatan Transaksi Akuntansi
Beserta Fungsi Manajemen Untuk Menunjang
Pengelolaan Kelong di Desa Malang Rapat, Kecamatan
Gunung Kijang, Kepulauan Riau”, Journal of Maritime
Empowerment, 1, no.1, (2018)
Norlinda, “Pengaruh Modal, Tenaga Kerja, Pengalaman
dan Tehnologi terhadap Pendapatan Nelayan di Desa
Ambahai Kecamatan Paminggir Kabupaten Hulu
Sungai Utara”, 151 Kindai, 18, no.1,150-164, (2022)
K.Cahyandi, “Pengaruh Pengalaman dan Jarak Tempuh
Melaut Terhadap Pendapatan Nelayan di Kabupaten
Cilacap” jurnal Saintara,.5, no.2, (2021)
A.Widodo, “Faktor Sosial Ekonomi yang Mempengaruhi
Pendapatan Nelayan Tradisional di Kecamatan Medan
Belawan”, skripsi Universitas Muhamadiyah Sumatera
Utara, (2019).
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
30

S. J. Lasut, D. C.Rotinsulu, D. S. M. Engka, “Analisis
Harga Bahan Bakar Minyak dan Perubahan Cuaca
Terhadap Pendapatan Nelayan di Kecamatan
Tuminting, Manado”, Jurnal Ekonomi dan
Pembangunan, 18, no.1, (2016).
I. Ghozali, “Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate dengan Program
IBM SPSS 25”, Universitas Diponegoro, 9, (2018)
L. D. Dahen, “Analisis Pendapatan Nelayan Pemilik
Payang di Kecamatan Koto Tangah Kota Padang”,
ECONOMICA Journal of Economic and Economic
Education, 5, No.1, (2016)
B. Sakti, H. Dayanti, “Analisis Faktor-faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Pendapatan Nelayan Kecamatan
Semidang Alas Maras Kabupaten Seluma”, EQUITY,
06, no. (02)
N. Sofiana,Yanto,” Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Pendapatan Nelayan Kecamatan Mlonggo, Kabupaten
Jepara (Studi Nasabah PT. Bank Tabungan Pensiunan
Nasional Syari’ah Tbk)”, JURNAL REKOGNISI
AKUNTANSI, 1, no. 1, (2017)
J. Ibrahim, D. Renjaan, “Analisis Pendapatan Nelayan
Tangkap di Desa Mafututu”, Jurnal Pendidikan
Ekonomi, 3, no.1, (2021)
Factors that Affect Fishermen’s Income with Fuel Cost as Moderating Variable
31
