
Analysing the Relationship Between Security and Migration
Categories
Durdona I. Madaminova
a
Tashkent State University of Oriental Studies, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Migrant, Securitization, Human Security, Identity, and Societal Security.
Abstract: The article analyses the theoretical and practical aspects of migration processes and their regulation. Even
though migration is formed under the influence of various factors and becomes an objective reality, it is
justified that it is becoming one of the main risks and problems within the national security system of the
states. While studies related to migration and its impact on the economic security of states, it is appropriate to
recognize that several studies have been carried out regarding the assessment of migration through the prism
of security. Therefore, studying the theoretical and practical aspects of migration processes and their
regulation today is important. From the point of view of the interrelationship of migration and security, the
concept of ‘human security’ and the issue related to the personal security of migrants within it are studied
separately. In this research, priority is given to a more civilized approach in studying migration as a security
threat. The analyses show that to improve the efficiency of the migration management system and ensure the
national security of states, an integrated approach to solving the migration problem is necessary. As part of
the issue of migration securitization, it was determined that there is a threat to a certain object by a political
actor, and it was explained that emergency political measures should be taken to eliminate it.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of globalization, the increase in
differences observed in the indicators of socio-
economic development between countries creates the
basis for the intensification of international migration
processes. As a result, in recent years there has been
a sharp increase in the flow of migrants, and the
factors influencing it acquired a structurally new
meaning. While studies related to migration and its
impact on the economic security of states, carried out
to date, have received relative priority, it is
appropriate to recognize that a number of studies have
been carried out regarding the assessment of
migration (especially illegal migration) through the
prism of security (national, regional and
international). Therefore, it is important to study the
theoretical and practical aspects of migration
processes and their regulation today.
In recent years, within the framework of domestic
and international studies, special attention has been
paid to the study and analysis of migration processes,
in particular, illegal migration from the point of view
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7029-2107
of national security and international stability. In the
conditions of modern international relations, in
connection with various risks arising from the
acceleration of the processes of technological
modernization and globalization, there is an
increasing need for the formation of effective
methods and means of protecting the national
interests of states, ensuring national security and
achieving competitiveness and their practical use.
One of the existing risks is associated with migration
processes, which play one of the main roles in the
socio-political changes observed in society today, and
their importance is expected to increase shortly. In
addition to the fact that the social, economic,
demographic, and political consequences of
migration are significant, it is natural that there are
many uncertainties in this regard.
Princeton scholar D. A. Baldwin links the various
definitions of security to two important aspects. First,
it promotes rational policy analysis by making it
relatively easy to compare one security policy with
another. Secondly, by creating points of contact
80
Madaminova, D.
Analysing the Relationship Between Security and Migration Categories.
DOI: 10.5220/0012672300003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 80-86
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

between people with different views, the activation of
scientific communication is achieved.
Egyptian researcher Nazli Shukri, while not
denying the connection between migration and
security, casts doubt on it. Recognizing that
migration, security and interaction are inherently
subjective concepts, the scholar concludes that the
relationship between migration and security is
problematic and complex. According to a group of
researchers, the relationship between migration and
security is two-way: on the one hand, if we consider
the problem through the prism of the security of
society and countries affected by migration flows, on
the other hand, it is appropriate to consider migrants
from the point of view of their security.
It is known that the main reason for emigration
observed in some countries is related to political
motives. Today, the situation associated with the
formation of the flow of refugees in the world occurs
precisely at the heart of the political situation. Most
of them are trying to obtain the status of political
emigrants in the territory of the host country. In our
opinion, this is where the implications of migration
for security (at the national and individual level)
begin.
The events of September 11, 2001, in the United
States, the non-democratic regime, and the activities
of immigrants in Western countries with non-
democratic ideas have led to a broader understanding,
assessment, and analysis of the problem of security in
Western studies. The fact that existing threats involve
non-state actors and networks has raised the issue of
security to a new level. In particular, the well-known
researcher of the Copenhagen Security School B.
Buzan in his monograph “People, States and Fear:
The Problem of National Security in International
Relations” also expands the scope of security research
and can be caused by non-state actors, which include
individuals and social groups, as well as also states,
the importance of studying possible threats is
determined.
English researchers J. Huysmans and V. Squires
put forward the idea that it is necessary to analyse the
relationship between migration and security in two
directions, that is, from the standpoint of security
studies and migration studies. Indeed, security and
migration research is inherently complex and
multifaceted. Within security studies, security can be
approached as a strategic imperative. Within
migration studies, migration can be approached from
a relatively narrow economic perspective, including
forced migration. At the same time, refugees and
labour migration make academic research a broader
object of study. In the current situation, it is
noticeable that the concepts of migration and security
are very contradictory in their meaning. As a result,
they can be used to identify multiple practices
representing different foundations.
Many analysts argue that illegal migration
threatens national security. According to researcher
Khalid Kozer, the notion that migration is one of the
main threats to national security is due to the increase
in the number of "illegal" migrants. However,
existing views are not supported by reliable research
on how immigrants pose a threat to national security.
Since the events of 9/11, which had a major
impact on US national security and immigration, the
emphasis on securing the existing process has become
even more important. American scientist Patrick J.
According to Buchanan, uncontrolled migration will
doom the state to extinction. The scientist also puts
forward the idea that the chaotic association of
peoples who have almost nothing in common with
each other in terms of history, folklore, language,
culture, and faith poses a significant threat to
America. In his opinion, this is a kind of new
Balkanization policy. P. Buchanan believes that in
order to prevent existing mistakes, it is necessary to
introduce a complete moratorium on immigration for
a long time, to abandon any amnesty for illegal
immigrants in the United States, and to strengthen
laws.
The American scientist Myron Weiner raised the
issue of how international migration poses a threat to
the security of the state and citizens, paying special
attention to how interconnected the security problems
of the sending and receiving countries are from a
transnational point of view. In practice, migrants face
many challenges due to the prevailing security
situation in sending and receiving countries. M.
Weiner believes that the growth of uncontrolled mass
migration, causing violence in host countries, will
lead to its transformation into a security threat.
Researcher Anna Kissinger advocates tougher
immigration policy, based on the assumption that
immigrants pose a threat to social security,
demographic stability, cultural identity, and the social
security system. However, the available evidence
from the scientists is groundless.
According to the Russian scientist A.
Kucherenko, migrants pose several threats to the
national security of host countries. The scientist
considers it appropriate to divide the existing threats
into three groups, which are general and complex in
their significance. It is worth noting here that the
author, as a representative of the host country,
expresses an anxious attitude towards migrants,
Analysing the Relationship Between Security and Migration Categories
81

which can be observed by the example of his
following comments:
Firstly, there are changes in the ethno-cultural
composition of the recipient countries. In addition,
the number of people among immigrants who respect
the existing values of this society is decreasing. The
worst thing is that their children and grandchildren
become citizens of this country and in most cases feel
like strangers in her life. As a result, they tend to
protest and act violently. In developed countries, such
an environment contributes to the growth of such
evils as international terrorism and crime.
Secondly, illegal migration is becoming one of the
most important security threats. Today, due to the fact
that corruption has become a global problem, the
process of combating it is becoming increasingly
complex. Human trafficking, which is carried out
with the aim of using countries with a relatively low
level of development as cheap labour and for sexual
purposes, is not only immoral but also causes the
spread of various diseases.
Thirdly, from time to time, legal and illegal
migrants commit mass terrorist attacks based on
nationalist sentiments and ethnic conflicts in certain
countries. The current situation has been observed in
recent years in many EU countries (France, Austria,
and the Netherlands) and to some extent in Russia.
Today, international migration remains one of the
most discussed but highly controversial areas of the
security agenda. Aspects of migration security have
been widely studied since the Cold War. According
to Islam Ahmed, a researcher at the Nohud Center for
Research and Studies in Doha, migration studies is
still a relatively new and small area of international
relations as a research field. This can be explained
primarily by the fact that in the period from 1945 to
1980, migration policy and issues related to
immigrants were considered an internal problem of a
particular host/host country, and their impact on
international security was underestimated. It is known
that during the Cold War, migration policy did not
have a significant impact on the balance of power,
especially on the socio-political situation in the
United States. Therefore, in these years, the security
of migration aspects has been studied as an internal
problem based on a state-centric approach, which
occupies an important place in this regard. In the
years after the end of the Cold War, security studies
began to draw attention to the existence of other
security-related issues in addition to military issues.
The analysis of migration in the context of
security in the context of modern international
relations was studied from a scientific point of view
by representatives of the Copenhagen Institute for
Peace Research Barry Busan and Ole Wever. In
particular, B. Buzen states that the security problem
is not limited to military threats between states, like
traditional security studies, and that there is a need for
more comprehensive security studies from the point
of view of multiple threats that have arisen in the
context of globalization and the changing
international situation.
This approach was further developed in the book
"Security: A New Structure of Analysis" by Barry
Buzen, Ole Wever, and Yap de Wilde. According to
him, researchers have identified the concept of "soft"
security, which is much broader than the scope of
military threats to the national interests of the state,
and on this basis a new "security theory"
("securitization theory") has been created. it was
formed in the 1990s. The purpose of the "security
theory" is to embody the views of proponents of an
expanded security concept covering all areas of
security, and representatives of the traditional
approach that reveals the level of security against
security threats. In a word, it is an intermediate theory
based on the measurement of large-scale
determinants of security, equally suitable for
representatives of traditional and modern schools of
security.
Securitization is a complex political process
wherein a political actor identifies a threat to a
specific object and advocates for urgent political
measures to address it. In securitizing a problem or
threat, the actor elevates it from the realm of regular
political discourse to a security concern of the highest
priority. Consequently, actions to address the issue
occur outside the established political procedures,
often involving emergency measures that deviate
from the actor's usual activities. The key distinction
lies in the use of exceptional political measures,
implying that securitizing (or desecuritizing) a
problem has significant political implications.
The core of securitization theory doesn't mandate
the imposition of emergency measures but rather
assesses the threat as a platform that can justify the
legitimization of such measures. This process can be
dissected into three integral components: 1) the
identification of a threat; 2) the delineation of the
threat as the object of danger; and 3) the
implementation of emergency measures against the
threat, often involving the general population.
Visualizing the securitization process reveals a
dynamic interplay between these components.
Understanding securitization provides insights into
how political entities navigate and manipulate
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
82

perceived threats, emphasizing the political nature of
emergencies and the consequential impact on
governance and societal responses.
Figure 1: Successful securitization.
It should be noted that scientists such as Barry
Buzen, Ole Wever, and Yap de Wilde believe that
new threats, such as illegal and uncontrolled
migration, should be highlighted among the problems
associated with social, economic, and climate change.
For this reason, scientists have introduced the concept
of "migration securitization" into scientific
circulation. As mentioned above, according to the
theory of securitization, an event can become a type
of security as a result of certain actions and can be
perceived by society as a threat. Securitization of
migration restricts the rights of migrants, linking this
phenomenon with insecurity.
The Center for Conflict Studies, Paris, researchers
A. Ceyhan and A. Tsukalalar, who studied the issue
of securitization of migration, analyzed the evidence
and views of a group of politicians, law enforcement
agencies, and the media who assessed migration as a
security threat, analyzing them, they divided them
into four axes (parts):
1. socio-economic axis, in which migration is
associated with unemployment, the rise of the
informal economy, the crisis of public welfare, and
the deterioration of the urban environment;
2. securitarian axis, migration is associated
with the erosion of control over sovereignty, borders,
internal and external security issues;
3. an identitarian axis in which migrants are
seen as a threat to national identity and the
demographic balance of the host society;
4. a political axis, in most cases, in the fight
against migration, racism, and xenophobia are used as
a tool to achieve political goals.
The analyses show that within the framework of
the relationship between migration and the security
system, its negative impact on the existing social
relations in society acquires a relative priority. As an
example, we can cite cultural, that is, civilizational
differences between migrants and the host country.
Here it is important to pay special attention to the
views of the American scientist S. Huntington, who
scientifically substantiated the future order of
international relations on the basis of a civilizational
approach. It is well known that the article published
in 1993 by S. S. was of worldwide importance in this
regard. Huntington's "Clash of Civilizations", made a
significant contribution to the development of the
neo-Atlantic concept. According to him, conflicts
between civilizations are at the heart of the unstable
situation and contradictions taking place in the world.
The scientist expressed the following thoughts about
the flow of Muslim migrants arriving in Europe from
the Middle East and North Africa, and their impact on
the social life of society: "... rapid population growth
in Arab countries, especially in North Africa, and the
migration flow to Western European countries is
increasing even more. The current situation requires
increased political vigilance in Western Europe when
implementing actions aimed at minimizing internal
borders. In recent years, racism in Italy, France, and
Germany has become more visible. This can also be
seen in the growing political opposition and violence
against Arab and Turkish immigrants since 1990.
Chapter 8 of S. Huntington's monograph "The
Clash of Civilizations and the Restructuring of the
World Order", published in 1996, is devoted to many
aspects of migration processes, in particular, the
socio-economic situation in Western countries and
their civilizational identification of settled migrants.
it reveals the role of many immigrants who do not
belong to Western civilization in the life of these
countries, and the growing hatred of Muslims and
Africans among representatives of the host society.
For information, it should be noted that in recent
years, right-wing parties against immigrants have
become more active in European countries. In
addition, the issue of the connection of Muslim
immigrants with terrorist organizations has become
the center of broad academic and public discussions.
It is important to note that the main risk associated
with migration does not come from external migrants
but from internal social relations. For example,
despite the fact that the descendants of Muslim
immigrants who have lived in France for many years
have grown up on the territory of this country, they
are unable to negotiate with the local population.
According to the data, the unemployment rate among
the second-third generation of immigrants without
immigrant status is 80% higher than among the
French. The current situation allows us to imagine
how complex the crisis is associated with people
currently working as migrants. In the case of France,
the focus is on domestic issues, as terrorism is
associated with people coming from countries such as
the Middle East and Africa. Although the terrorist
attacks in Paris seem to have established a link
between the migration crisis and terrorism,
historically this connection has proved difficult to
maintain. A 2015 article in Charlie Hebdo claimed
that European citizens descended from Muslim
immigrants were behind every attack, including the
November terrorist attacks. Illegal migrants are also
Analysing the Relationship Between Security and Migration Categories
83
seen as a security threat in the United States.
According to the report of the US Department of
Homeland Security on the assessment of internal
threats for October 2020, "illegal migration" is one of
the seven main threats to the country.
At the moment, the attention of Russian
researchers is focused on the category of "migration
security". By its nature, this category assesses
migration as a threat to national security and serves to
reduce the risk of threats arising from migration and
to combat them within the framework of an effective
migration policy. Accordingly, we can say that the
categories "migration security" and "migration
securitization" are mutually compatible.
Since migration flows threaten the social relations
of the host State and its ethnic homogeneity, the
concept of "public security" has been developed in
Western studies (mainly by the Copenhagen School
of Security). This term cannot be used as a synonym
for the Uzbek term "social security". Social security,
at its core, means that members of society are
protected from the point of view of social security.
"Social security" means the state of preservation of
the identity of society. According to Ole Weber,
"social security" is the ability of a society to preserve
its identity (character) in changing conditions and
possible and real threats. In the context of integration
processes, when threats to the identity of society are
threatened, but it is known that the state cannot
protect it, a dilemma arises between the state and
society regarding security. In this case, the state
protects its sovereignty, and social security protects
the identity of society. Therefore, conflicts in many
societies were assessed using the civilizational factor.
Indeed, the social security concept of the
Copenhagen School has certain drawbacks. In
particular, Tobias Tyler, a professor at the University
of Dublin, pointed out three main shortcomings of the
concept: 1) shortcomings related to the definition of
the status of society as an independent social
institution; 2) the presence of significant uncertainties
in the definition of "uniqueness" (identity); 3) the
significance of the issue of social security for the
individual is not sufficiently disclosed.
Later, the French academic scientist Dede Bigot
and his Scandinavian followers created a new
alternative to the concept of social security to avoid
existing shortcomings. According to him, the main
problem faced by developed countries is the massive
and unregulated influx of migrants from different
civilizations and the threat of social integration of
society. In a word, the main essence of the concept of
social security is to protect important functions of
society and prevent the spread of a crisis that has
arisen in a certain area to the whole society through a
chain reaction.
In addition to the above, from the point of view of
the relationship between migration and security,
special attention should be paid to the concept of
"human security" and the personal security of
migrants within its framework. Later, the French
academic scientist Dede Bigot and his Scandinavian
followers created a new alternative to the concept of
social security to avoid existing shortcomings.
According to him, the main problem faced by
developed countries is the massive and unregulated
influx of migrants from different civilizations and the
threat of social integration of society. In a word, the
main essence of the concept of social security is to
protect important functions of society and prevent the
spread of a crisis that has arisen in a certain area to
the whole society through a chain reaction.
In addition to the above, from the point of view of
the relationship between migration and security,
special attention should be paid to the concept of
"human security" and the personal security of
migrants within its framework.
Today, the formation of a specific national-
cultural, religious, and ethnic attitude towards
immigrants in host countries does not fully guarantee
their safety. In recent years, the activity of ultra-right
movements and parties has been observed in the
example of various countries. At the same time,
criminal activity related to human trafficking is
becoming more global, and the activity of groups
engaged in the transportation of migrants by illegal
and unsafe routes is increasing. As a result, many
migrants become victims of forced labor and sexual
slavery, are subjected to violence, and many of them
are killed and missing. According to the Missing
Migrants Project of the International Organization for
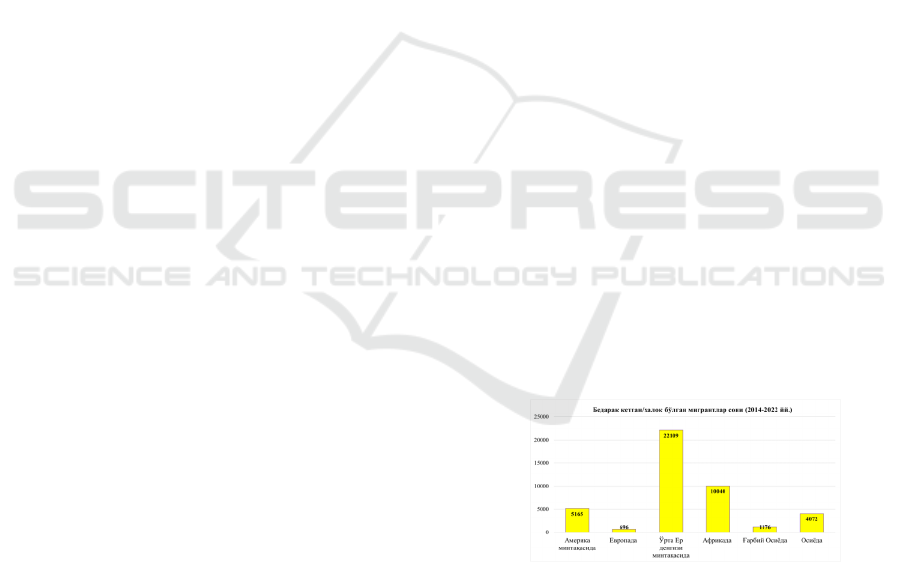
Migration, 43,258 migrants died or went missing
worldwide between 2014 and 2022 (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Missing Migrants Project Data(2014 to2022).
Based on the data presented above, it can be seen
that North Africa and the Middle East region are
leading in the number of missing/dead migrants.
According to Human Rights Watch, more than 1,200
migrants died in the Mediterranean Sea from January
to September 2022. Their total number in the period
from 2014 to 2022 will exceed 25,000 people. The
available figures show how important it is to
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
84

investigate the safety of migrants from the point of
view of human security.
The conceptual formation of the problem of
human security can be associated with the Human
Development Report 1994 (Human Development
Report 1994) of the United Nations Development
Programme (UNDP). This document defines new
dimensions of human security and reveals its
connection with 7 important security components:
1) economic security (economic security); 2) food
security (Food security); 3) health security (Health
security); 4) environmental security (Environmental
security); 5) personal security (Personal security); 6)
public security (Community security); 7) political
security (Political security).
Based on the concept of "human security", it is
planned to organize effective public administration in
the social, economic, and political spheres and
actively use preventive diplomacy in preventing
crises in the life of society. Therefore, support for the
concept of human security is considered an important
factor in preventing and regulating illegal and illegal
mass migration. We can see this in the example of
unstable and crisis countries.
The concept of "human security" is based on the
criteria of social justice to national security. This
imposes additional responsibility on States. The State
should pay attention not only to the borders of
territorial integrity but also to the issue of ensuring
the security of its citizens. Researcher at the
Portuguese Institute of International Relations Zh.
Estevens emphasizes the need to develop a new
approach to ensuring the safety of migrants (a
migrant-centered approach) from the point of view of
the relationship between migration and security
within the framework of the concept of human
security. For example, the migrant factor is not taken
into account in the policy of states to ensure the
security of their citizens and citizens, that is, this issue
is not reflected in the national security system. In his
opinion, donor countries, transit, and recipient
countries should coordinate the fight against crime
and human trafficking to organize safe and legal
routes for migrants.
In short, in the XXI century, in the context of
globalization, the strengthening of interdependence
between States has opened a wide path for the
development of active cooperation between States
and peoples. This once again confirms the massive
influx of migration flows to developed countries.
Today, despite the fact that migration is formed under
the influence of various factors and has become an
objective reality, it has become one of the main risks
and problems in the national security system of
countries. As a result, the issue of the relationship
between migration and security has become the
subject of many studies, and much attention is paid to
the study of the nature of migration as a security
threat.
2 CONCLUSIONS
Based on this, the following conclusions can be
drawn:
First, although the Copenhagen School of
Security has achieved relative success in researching
the relationship between migration and security, a
clear, consistent, and comprehensive theoretical
framework for the migration/security relationship has
not yet been fully developed.
Secondly, priority is given to a more civilized
approach in studying migration as a security threat.
Today, the problems between developed societies and
immigrants, arising precisely against the background
of the civilizational gap, attract the attention of the
general public.
Thirdly, instability in the world, various kinds of
separatism, the intensification of terrorist activities
form migrant phobia in various societies. Today,
there is a growing tendency on the part of society to
involve governments more widely in the issue of
migration securitization.
Fourth, there is an urgent need to pay attention to
the issue of ensuring the individual safety of migrants
within the framework of scientific and applied
research in the context of human security. Therefore,
research in this direction (migrant-centric approach)
is actively developing. When determining the
interdependence of migration and security and
assessing the scale of its threats, it is advisable to
conduct a study within the format: sending country -
migrant - receiving country.
Fifth, migration cannot be fully assessed as a
security threat. Because the existing approach is one-
sided and it cannot be called the right approach.
Security threats are mainly related to illegal and mass
migration. The analyses show that in order to improve
the efficiency of the migration management system
and ensure the national security of states, an
integrated approach to solving the migration problem
is necessary. Therefore, it is important to develop a
perfect system and legal framework for state
regulation of migration.
Analysing the Relationship Between Security and Migration Categories
85

REFERENCES
Ahmed, I. (2017). Migration and security: In search of
reconciliation. Migration Letters, 14(3), 371-383.
Baldwin, D. A. (1997). The concept of security. Review of
International Studies, 23(1), 5-26.
Bergh, H. (2020). Securitization of migration: A discourse
analysis of the Swedish migration policy during the
Syrian refugee crisis.
Buzan, B. (2008). People, states & fear: An agenda for
international security studies in the post-cold war era.
ECPR press.
Buzan, B., Wæver, O., Wæver, O., & De Wilde, J. (1998).
Security: A new framework for analysis. Lynne
Rienner Publishers.
Huntington, S. P., & Jervis, R. (1997). The clash of
civilizations and the remaking of world order. Finance
and Development-English Edition, 34(2), 51-51.
Sunderland, J. Endless Tragedies in the Mediterranean Sea.
URL: https://www.hrw.org/news/2022/09/13/endless-
tragedies-mediterranean-sea
Theiler, T. (2003). Societal security and social psychology.
Review of International Studies, 29(2), 249-268.
Wæver, O. (1993). Societal Security: The Concept. In
Buzan, Wæver, Kelstrup, and Lemaitre, Identity,
Migration and the New Security Agenda In Europe (pp.
17-40). London: Pinter.
Weiner, M. (1992). Security, stability, and international
migration. International Security, 17(3), 91-126.
Dyadyun, K. V. (2012). Migration and crime: The
interconnection of causes and conditions. Humanitarian
Research in Eastern Siberia and the Far East, 2(18),
109-114.
Lagutkin, O. Y., & Dyakov, O. Y. (2010). International
migration in the context of regional security. Strategy
for Sustainable Development of the Regions of Russia,
4, 209-214.
Lagutkin, O. Y., & Dyakova, V. V. (2011). Renewal of state
migration policy in the context of ensuring national
security. Current Problems of Humanities and Natural
Sciences, 12, 249-253.
Lebedeva, I. V., & Bicharova, M. M. (2015). Migrants in
Europe and cultural security. Caspian Region: Politics,
Economics, Culture, 3, 330-337.
Lelikov, V. A., & Azarova, I. V. (2016). Illegal migration
as a criminogenic factor. Bulletin of the Voronezh
Institute of the Ministry of Internal Affairs of Russia, 4,
54-62.
Troitskaya, O. V. (2012). Migration management and
security: The experience of developed countries.
Bulletin of Moscow University. Series 25. International
Relations and World Politics, 4, 97-112.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
86
