
Analysis of Green Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation
in Upper-Middle-Income ASEAN Countries
Fradya Randa and Mirza Ayunda Pratiwi
Faculty of Maritime Economics and Business, Maritim Raja Ali Haji University, Tanjungpinang, Indonesia
Keywords: Strategy, Promotion, E-Commerce Trends.
Abstract: The objective of this research is to examine the connection between green economic growth and
environmental degradation in upper-middle-income nations within the ASEAN region (specifically, Indonesia,
Malaysia, and Thailand) throughout the years 2000 to 2020, using a simultaneous panel model. The key
findings of this research can be categorized into two analytical models. First, cleaner energy has a positive
effect on green economic growth, while technological innovation has a negative effect. The positive impact
of trade openness and population on environmental degradation is evident. Green growth and environmental
degradation do not affect each other in upper-middle ASEAN countries. A different finding in this research
is that green growth and environmental degradation do not have any influence on each other in ASEAN upper
middle-income countries. The problem is believed to stem from the policy direction and focus on
technological innovation that has not been optimal for green economic development. The policy implication
that can be implemented is increasing the use of renewable energy in developing a green economy.
1 INTRODUCTION
The increase in CO2 emissions due to economic
activities in ASEAN member countries has an impact
on environmental degradation. Although there are
abundant natural resources and strong economic
performance. ASEAN countries face challenges in
creating environmentally sustainable economic
activities.
The rapid economic acceleration in ASEAN
nations is driving up the usage of fossil fuels,
resulting in elevated pollution levels and increased
emissions of CO2. Increasing energy consumption
has increased environmental degradation (Afridi et
al., 2019; Jian et al., 2019). Especially in ASEAN
upper-middle income countries, which are currently
spurring economic performance by increasing
economic growth. The heightened CO2 emissions
render the ASEAN region increasingly susceptible to
challenges posed by climate change (Sandu et al.,
2019).
The ASEAN region was found to contribute 3.6%
of global greenhouse gas emissions in 2013, partly
because of its strong economic growth and population
growth. (Chontanawat, 2018). The growth of the
economy has accelerated deforestation, resulting in a
swift exhaustion of natural resources. The 2017
edition of the fifth ASEAN Environmental
Economics Report affirms that the rise in energy
consumption is the primary driver behind the
escalating CO2 emissions, and it is projected to surge
by 61% between 2014 and 2025. (ASCCR, 2021).
According to a 2015 report from the Asian
Development Bank, it is projected that greenhouse
gas emissions from the energy sector in ASEAN
economies will see a threefold increase by the year
2050 (ADB, 2015).
This phenomenon is of particular concern in
ASEAN countries, especially upper-middle-income
countries (Indonesia, Thailand, and Malaysia). The
country is persistently striving to implement
measures aimed at sustaining natural resources in an
environmentally responsible way, with the aim of
boosting economic growth and curbing
environmental degradation. One of them is through
an agreement in the formulation of Sustainable
Development Goals (SDGs) (Alam et al., 2007;
Janoušková et al., 2018; Rosati & Faria, 2019).
Previous literature studies have proven that there
are many factors that influence the growth of green
economics and environmental degradation.
Analyzing the impact of energy consumption on
sustainable growth in China from 1997 to 2016, the
Randa, F. and Pratiwi, M.
Analysis of Green Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation in Upper-Middle-Income ASEAN Countries.
DOI: 10.5220/0012697100003798
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Maritime, Economics and Business International Conference (MEBIC 2023) - Sustainable Recovery: Green Economy Based Action, pages 37-43
ISBN: 978-989-758-704-7
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
37

research revealed that green growth was primarily
driven by natural gas consumption and other forms of
energy use, while the utilization of coal and oil acted
as impediments to green growth (Hongxian, 2018).
An examination of green growth in Turkey from
1980 to 2017, employing the ARDL methodology,
indicated that sustainable growth in the long term is
predominantly steered by cleaner energy sources and
technological advancement. Conversely, long-term
green growth is negatively affected by militarization
(Sohag et al., 2019)
Other studies have been conducted to investigate
the impact of economic expansion, energy utilization,
and CO2 emissions in nations categorized as
developed, developing, and those in the MENA
region from 2001 to 2017. The finding is that in
developed and developing countries, economic
growth rises in tandem with heightened energy
consumption, whereas in MENA countries, it
experiences a decline (Muhammad, 2019).
An empirical study on the impact of energy
consumption and economic growth on environmental
deterioration in the Asian region between 1991 and
2013. The panel causality analysis using VECM
confirms the existence of a bidirectional causal
relationship between energy consumption, economic
growth, and environmental deterioration. (Jamel,
2016).
The primary cause of environmental degradation
is rapid industrialization due to the consumption of
natural resources to fuel economic expansion. (Burki
& Tahir, 2022). Environmental deterioration,
particularly in developing nations undergoing swift
industrialization, is driven by energy consumption
(Afridi et al., 2019; Al-mulali & Binti Che Sab, 2012;
Jian et al., 2019).
Environmental degradation is caused by many
factors (Jan et al., 2021; Shah et al., 2021). Increased
environmental degradation can also be caused by
trade openness. The impact of international trade on
environmental degradation is determined by the
volume, quantity, and production technique
employed. (Grossman & Krueger, 1991). A
substantial increase in the production of goods and
services resulted in a greater use of resources,
resulting in increased pollution (Liobikienė &
Butkus, 2019).
The influence of trade on heightened
environmental deterioration is a result of its impact
on the magnitude and composition (Halicioglu, 2009;
Nasir et al., 2021; Nguyen et al., 2021). However, the
effect of using production technology has a negative
impact on environmental degradation (Tachie et al.,
2020).
In Pakistan, environmental degradation is also
affected positively and significantly by population,
energy consumption, and industrialization.
Meanwhile, economic growth contributes negatively
to environmental degradation (Ur Rehman & Zeb,
2020). Other research has explored the causal link
between carbon dioxide emissions, energy usage, the
adoption of renewable energy, population expansion,
and economic growth in five ASEAN nations
(Indonesia, Myanmar, Malaysia, the Philippines, and
Thailand) from 1971 to 2014. The unidirectional
causal effect of economic growth on renewable
energy consumption, CO2 emissions, and energy
consumption in Indonesia is found (Vo, 2019)Click
or tap here to enter text.
At the beginning, economic growth has a negative
impact on the environment, but as time goes on, it
leads to environmental improvement. (Rahman et al.,
2020). The N-shaped Environmental Kuznets Curve
(EKC) demonstrates that as growth progresses, it
initially heightens environmental degradation,
subsequently diminishes it, and then exhibits a
renewed increase in degradation (Afridi et al., 2019;
Ahmad et al., 2019; Allard et al., 2018). This study
aims to contribute to new and comprehensive
literature on the determinants of green growth and
environmental degradation in the economies of
ASEAN upper-middle-income countries. This study
also discusses the possible consequences for future
generations due to environmental degradation and
policy measures to promote green growth and reduce
environmental degradation in ASEAN upper-middle-
income countries.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The data used in this study consists of secondary data
that has been published by specific organizations or
authorities. The data employed in this analysis is
panel data, encompassing a time series spanning 21
years from 2000 to 2020, and covering three ASEAN
upper-middle-income nations, namely Indonesia,
Thailand, and Malaysia. The study encompasses both
internal and external variables. The variables that
control the economy are green economic growth and
environmental degradation. The variables that are
outside of the system include technological
innovation, clean energy, militarization, health
spending, population, and trade openness.
Each of the endogenous variables utilized in this
research also serves as an exogenous factor in other
equations. The connection between these variables is
illustrated in Figure 1, displayed below.
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
38
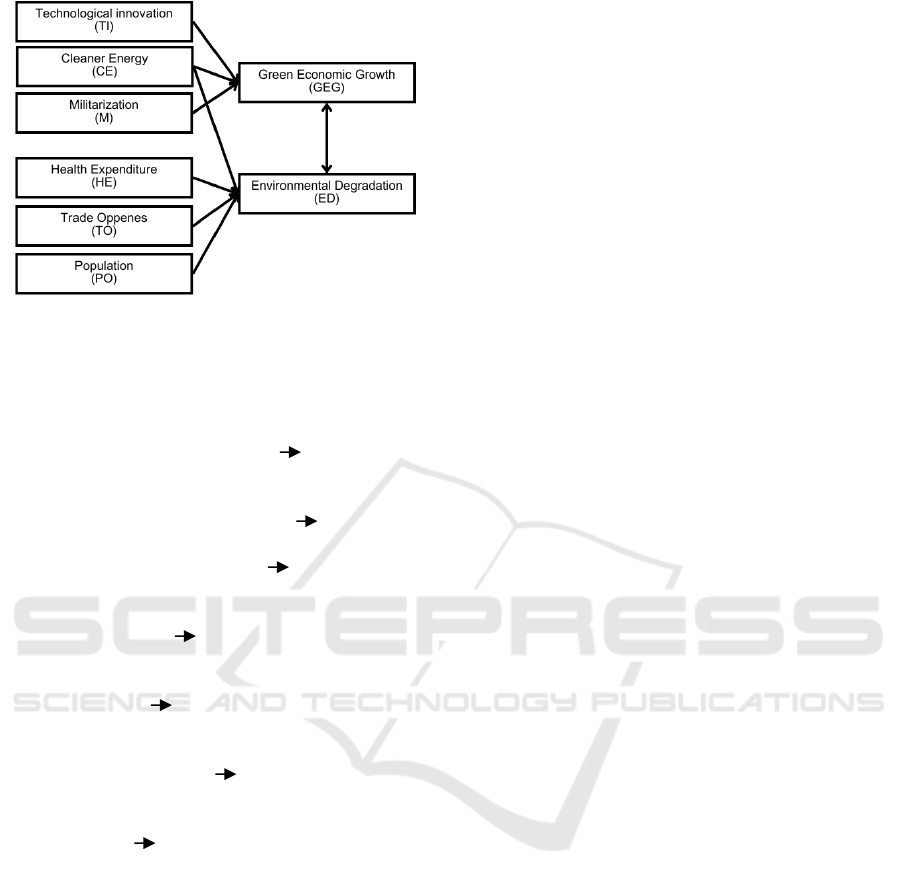
Figure 1: The conceptual framework of the research.
In accordance with the research's conceptual
model presented in Figure 1, the study utilizes
specific indicators to measure the variables being
investigated.
Environmental Degradation (ED) CO2 emissions
resulting from the use of petroleum-derived fuel as an
energy source are expressed in kilotons.
Green Economic Growth (GEG) Renewable
energy supply, percentage of total energy supply
Technological Innovation (TI) Development of
environment-related technologies, percentage all
technologies
Cleaner Energy (CE) Renewable energy's share in
the overall final energy consumption is expressed as
a percentage.
Militarization (M) The capital spending allocated
to the military is measured as a percentage of the
Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Health Expenditure (HE) The present healthcare
expenditure is represented as a percentage of the
Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Population (PO) The total population is determined
using the de facto population definition, which
includes all residents, regardless of their legal status
or citizenship.
Using the conceptual framework depicted in
Figure 1, this research employs two analytical
models, encompassing green economic growth and
environmental degradation. The econometric
equations for these models are presented as Equations
(1) and (2) below:
GEG
it
= α
1.0
+ β
1.1
Log(ED
it
) + β
1.2
TI
it
+
β
1.3
CE
it
+ β
1.4
M
it
+ ε
1it
(1)
Log(ED
it
) = α
2.0
+ β
2.1
GEG
it
+ β
2.2
CE
it
+
β
2.3
HE
it
+ β
2.4
Log(PO)it + β
2.5
TO
it
+
ε
2it
(2)
In this context: α represents the parameter, i
signifies the cross-sectional dimension, t denotes the
time-series component, and ε signifies the error term.
This research employs a simultaneous panel
model methodology to accomplish the established
research goals. The description of the econometric
phases within this model approach consists of:
Selection of the appropriate model for the regression
model estimation method using panel data can be
done through three approaches, including:
First, the Common Effect Model (CEM) is the
most straightforward panel data approach, as it
simply merges time series and cross-sectional data. It
neglects the temporal and geographical dimensions,
assuming uniform data behavior within a country
across different time periods.
The Fixed Effect Model (FEM) argues that
differences in intercepts can be responsible for
variations between countries.
Third, the Random Effects Model (REM)
calculates panel data in which the disturbance
variables can related associations across time and
among different countries.
Furthermore, the panel analysis model that was
most suitable was chosen from the three models. The
model is selected through testing as follows:
First, the Chow test was performed to ascertain
the suitability of using either the CEM or FEM model.
The selection was carried out by comparing the p-
values obtained from the cross-sectional chi-square
test with a significance level of <unk> = 0.05.
In the second step, should the Chow test favor the
FEM as the preferable model, the Hausman test will
be conducted. This additional examination will
determine whether FEM or REM is the more suitable
choice. The decision will be based on comparing the
p-value of the random cross-section test at a
significance level of α = 0.05
Next, in the event that the Hausman test favors
REM as the preferred model, the Lagrange multiplier
test will be performed. Additional analysis will
determine whether REM or CEM is the more suitable
model. The decision will be based on comparing the
p-value of the cross-sectional test hypothesis for
Breusch-Pagan at a significance level of α = 0.05.
Simultaneous equation models are models that
have more than one equation that are interrelated and
have a causal relationship between endogenous and
exogenous variables. Obtaining the numerical value
for each parameter in each equation is unfeasible due
to the indistinguishable nature of the equations or
their strong resemblance to each other. Hence, it is
essential to perform an identification test utilizing the
order condition as depicted in Equation (3) below:
Analysis of Green Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation in Upper-Middle-Income ASEAN Countries
39
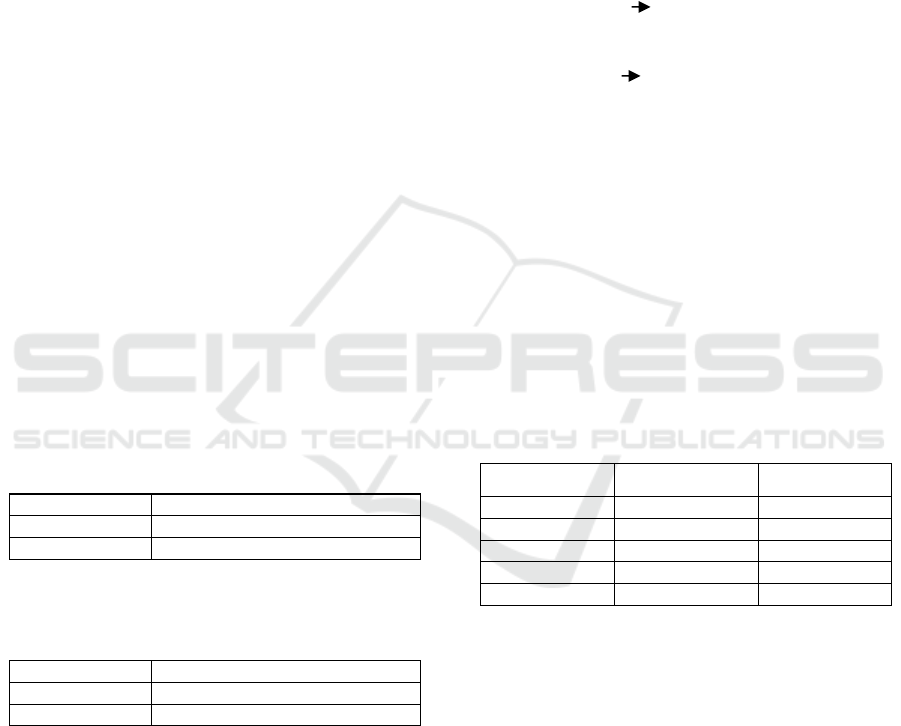
K – k ≥ m – 1 (3)
Where: M represents the quantity of endogenous
variables within the model, while m represents the
count of endogenous variables in the equation. K
indicates the total number of predefined variables in
the model, and k represents the number of variables
predetermined in the equation.
If K – k = m – 1, this equation is identified.
Simultaneous equation estimation using the indirect
least squares (ILS) method
If K – k > m – 1, this equation is overidentified.
Simultaneous equation estimation using the two-
stage least square (2SLS) method.
If K – k < m – 1, this equation is not identified.
Equations that can be solved using a system of
simultaneous equations are equations that result in
identified and over-identified order conditions.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Panel Analysis Results
Following the execution of the Chow and Hausman
tests to ascertain the most suitable model for this
study, the results show that the Fixed Effect Model
was selected as the best panel model. The analytical
findings have been presented in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1: The results of the Chow test for the panel analysis
model.
Equation
Prob. Cross-Section Chi-Square
GEG
0.0000
ED
0.0000
Table 2: The results of the Hausman test for the panel
analysis model.
Equation
Prob. Cross-Section Random
GEG
0.0000
ED
0.0000
Table 1 shows that for all models, the probability
values are low, having a chi-square value of 0.05.
Consequently, the Fixed Effect Model (FEM) is
appropriate the most model use choice across all
analysis models. Next, the Hausman test was
conducted to determine the appropriate model
selection between the Fixed Effect Model (FEM) and
Random Effect Model (REM). The data presented in
Table 3 reveals that all models have probability
values with a small chi-square value of 0.05.
Therefore, the Fixed Effect Model (FEM) is the most
suitable choice for all analytical models, and there is
no need to proceed with the Lagrange Multiplier test.
3.2 Simultaneous Equation Analysis
Results
The necessary prerequisite test for conducting
simultaneous equation analysis involves performing
an identification test based on the order conditions
outlined in Equations (4) and (5) provided below.
Equation GEG 6 – 3 > 2 – 1
3 > 1 (overidentified)
(4)
Equation ED 6 – 4 > 2 – 1
2 > 1 (overidentified)
(5)
The identification test result indicates that all
analytical models employed in this study are
estimated using the two-stage least square (TSLS)
approach due to the over-identification of all
equations.
Drawing from the conclusive outcomes of both
panel analysis and simultaneous equation analysis
conducted in accordance with predefined steps, the
result of the simultaneous panel model analysis for
each analysis model is shown in Tables (3) and (4)
provided below:
Table 3: Results of simultaneous panel estimation of the
green economic growth model.
Variable
Coefficient
Prob.
C
-15.40643
0.6197
LOG(ED)
1.591296
0.4763
TI
-0.077794
0.0474
CE
0.643581
0.0000
M
1.024559
0.2584
Table (3) provides a summary of the outcomes
from estimating the simultaneous panel model for the
equation related to green growth.
This study revealed that environmental
degradation did not exhibit an impact on green
growth. Furthermore, the limited contribution of
renewable energy sources in clean energy
management, leading to environmental harm, does
not influence green economic growth (Panayotou,
1993).
Technological innovation was found to have a
negative and significant effect on green economic
growth in ASEAN upper-middle-income countries (
β1.4 = - 0.077794, P <0,05 ). This negative impact is
most likely caused by the type of technology being
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
40
developed that is not integrated with efforts to utilize
environmentally sustainable resources. Sometimes,
technological innovations can have undesirable side
effects, such as air pollution or hazardous waste,
which can harm the environment (Huesemann, 2011).
Technological innovation often enables greater
exploitation of natural resources. Overexploitation of
these resources can damage ecosystems and create
negative impacts on the green economy (Dernis,
2017).
The study revealed a noteworthy positive impact
of clean energy on green economic growth (β1.4 =
0.643581, P < 0.001). Clean energy involves the
utilization of renewable energy through efficient
technology. The effective deployment of clean energy
relies on a substantial contribution from renewable
sources, ensuring that an expansion of clean energy
leads to an enhancement of green economic growth.
The increased adoption of clean energy serves as a
key driver in fostering long-term green economic
growth (Sohag et al., 2019).
The research revealed that militarization in upper
middle-income countries in ASEAN did not have a
significant effect on green economic growth. The
reason for this was the cautious and limited utilization
of natural resources for military purposes, which
minimized their broader environmental repercussions
and impact on green economic growth (Dincer,
2013).
Table 4: Results of simultaneous panel estimation of the
environmental degradation model.
Variable
Coefficient
Prob.
C
-33.21688
0.0000
GEG
-0.016726
0.6304
CE
0.002958
0.8638
HE
0.072542
0.0523
TO
0.003174
0.0001
LOG(PO)
2.496564
0.0000
Table (4) provides an overview of the findings
from the simultaneous panel model estimation related
to the environmental degradation equation. The
outcomes of this investigation confirm the hypothesis
that trade openness contributes positively to
environmental degradation (β2.5 = 0.003174, P <
0.001). The findings reveal that the upper-middle-
income countries in ASEAN are strongly inclined
towards trade openness, resulting in an increase in
environmental degradation. Greater trade openness is
associated with a heightened level of global
environmental deterioration (Le et al., 2016; Yu et al.,
2019).
The study uncovered a positive correlation
between population and environmental degradation
in upper-middle-income ASEAN countries (β2.6 =
2.496564, P < 0.001). Environmental degradation
increases with population growth due to an inverse
relationship between population and the environment.
The combination of rapid population growth and
sustainable economic development is likely to create
significant environmental challenges. Consequently,
countries should establish measurable economic
development strategies to manage and mitigate the
environmental impacts stemming from economic
activities (Ur Rehman & Zeb, 2020).
Green economic growth does not contribute to
reducing environmental deterioration, as it exhibits a
detrimental pattern in upper-middle-income ASEAN
countries. The considerable expenses associated with
environmental harm pose a substantial challenge to
fostering environmentally sustainable economic
development (Kang et al., 2019). The limited extent
of green economic growth suggests that the utilization
of natural resources hasn't adequately considered the
environmental consequences when advancing
sustainable economic development.
The empirical findings indicate that despite the
expectation that cleaner energy would promote
environmental sustainability, this is not the situation
in upper-middle-income ASEAN countries. There is
a need for enhancements in the management of eco-
friendly energy to genuinely foster environmental
quality (Pata et al., 2023)
Health expenditure was found to have a positive
but statistically insignificant relationship with
environmental improvement in upper-middle-income
ASEAN nations. To effectively address carbon
emission reduction and promote a healthier
environment, a reevaluation of the health expenditure
sub-policy program is warranted (Ganda, 2021).
4 CONCLUSIONS
According to the analysis performed, this research
suggests that promoting green economic growth can
be accomplished by boosting the adoption of cleaner
energy sources and curbing environmental
degradation through the regulation of both trade and
population.
The innovation of technology will contribute to
the promotion of environmentally sustainable
economic growth. The direction of developing
innovative technology can balance the benefits of
exploitation and prevention of environmental damage
if institutional and financial commitments are
Analysis of Green Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation in Upper-Middle-Income ASEAN Countries
41

supported. Health expenditure needs to be increased
in overcoming environmental degradation. Although
it does not have a significant impact, it is effective in
reducing environmental degradation.
The government should consider policy measures
to maintain environmental quality and foster
sustainable economic growth by implementing a
clean development mechanism that focuses on
advancing renewable energy.
The growth of renewable energy not only helps in
reducing CO2 emissions but also offers multiple
benefits. These advantages encompass lowering
investment expenses for nations in the upper middle-
income bracket, such as those in the ASEAN region,
facilitating technology transfer, and gaining access to
sustainable technologies. Renewable energy has
prospects for development in ASEAN upper middle-
income countries, due to the availability of sufficient
natural resources. The government is expected to be
able to encourage the clean energy development
mechanism with various policies such as subsidies, in
order for renewable energy to become cost-effective
and competitive with the development of fossil fuels.
REFERENCES
ADB. (2015). Southeast Asia and the Economics of Global
Climate Stabliization.
Afridi, M. A., Kehelwalatenna, S., Naseem, I., & Tahir, M.
(2019). Per capita income, trade openness,
urbanization, energy consumption, and CO2 emissions:
an empirical study on the SAARC Region.
Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 26(29).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06154-2
Ahmad, N., Du, L., Tian, X. L., & Wang, J. (2019). Chinese
growth and dilemmas: modelling energy consumption,
CO2 emissions and growth in China. Quality and
Quantity, 53(1). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-018-
0755-0
Alam, S., Fatima, A., & Butt, M. S. (2007). Sustainable
development in Pakistan in the context of energy
consumption demand and environmental degradation.
Journal of Asian Economics, 18(5).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asieco.2007.07.005
Allard, A., Takman, J., Uddin, G. S., & Ahmed, A. (2018).
The N-shaped environmental Kuznets curve: an
empirical evaluation using a panel quantile regression
approach. Environmental Science and Pollution
Research, 25(6). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-
0907-0
Al-mulali, U., & Binti Che Sab, C. N. (2012). The impact
of energy consumption and CO2 emission on the
economic growth and financial development in the Sub
Saharan African countries. Energy, 39(1).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.01.032
ASCCR. (2021). ASEAN State of Climate Change Report.
Burki, U., & Tahir, M. (2022). Determinants of
environmental degradation: Evidenced-based insights
from ASEAN economies. Journal of Environmental
Management, 306.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.114506
Chontanawat, J. (2018). Decomposition analysis of CO2
emission in ASEAN: An extended IPAT model. Energy
Procedia, 153.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2018.10.057
Dernis, H. , G. A. , & M. F. (2017). The environmental
Kuznets curve: A literature survey. OECD
Environment Working Papers, No. 123, OECD
Publishing, Paris.
Dincer, I. , & R. M. A. (2013). Sustainability assessment of
electricity generation technologies. Renewable and
Sustainable Energy Reviews, 15(3), 1228–1239.
Ganda, F. (2021). The impact of health expenditure on
environmental quality: the case of BRICS.
Development Studies Research, 8(1).
https://doi.org/10.1080/21665095.2021.1955720
Grossman, G. M., & Krueger, A. B. (1991). Environmental
Impacts of a North American Free Trade Agreement.
National Bureau of Economic Research. In NBER
working aper series (Issue 3914).
Halicioglu, F. (2009). An econometric study of CO2
emissions, energy consumption, income and foreign
trade in Turkey. Energy Policy, 37(3).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2008.11.012
Hongxian, X. (2018). Influences Energy Consumption has
on Green GDP Growth in China. IOP Conference
Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 113(1).
https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/113/1/012125
Huesemann, M. H. , & H. J. A. (2011). Techno-Fix: Why
Technology Won’t Save Us or the Environment. . New
Society Publishers.
Jamel, L. , D. A. (2016). Do energy consumptionand
economic growth lead to environmental degradation?
Evidence from Asian economies. Cogent Economics
&Finance, 4(1).
Jan, A. A., Lai, F. W., & Tahir, M. (2021). Developing an
Islamic Corporate Governance framework to examine
sustainability performance in Islamic Banks and
Financial Institutions. Journal of Cleaner Production,
315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128099
Janoušková, S., Hák, T., & Moldan, B. (2018). Global
SDGs assessments: Helping or confusing indicators?
Sustainability (Switzerland), 10(5).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su10051540
Jian, J., Fan, X., He, P., Xiong, H., & Shen, H. (2019). The
effects of energy consumption, economic growth and
financial development on CO2 emissions in China: A
VECM approach. Sustainability (Switzerland), 11(18).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su11184850
Kang, S. H., Islam, F., & Kumar Tiwari, A. (2019). The
dynamic relationships among CO2 emissions,
renewable and non-renewable energy sources, and
economic growth in India: Evidence from time-varying
Bayesian VAR model. Structural Change and
Economic Dynamics, 50.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strueco.2019.05.006
MEBIC 2023 - MARITIME, ECONOMICS AND BUSINESSINTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE
42

Le, T. H., Chang, Y., & Park, D. (2016). Trade openness
and environmental quality: International evidence.
Energy Policy, 92.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enpol.2016.01.030
Liobikienė, G., & Butkus, M. (2019). Scale, composition,
and technique effects through which the economic
growth, foreign direct investment, urbanization, and
trade affect greenhouse gas emissions. Renewable
Energy, 132.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2018.09.032
Muhammad, B. (2019). Energy consumption, CO2
emissions and economic growth in developed,
emerging and Middle East and North Africa countries.
In Energy (Vol. 179).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.03.126
Nasir, M. A., Canh, N. P., & Lan Le, T. N. (2021).
Environmental degradation & role of financialisation,
economic development, industrialisation and trade
liberalisation. Journal of Environmental Management,
277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.111471
Nguyen, D. K., Huynh, T. L. D., & Nasir, M. A. (2021).
Carbon emissions determinants and forecasting:
Evidence from G6 countries. Journal of Environmental
Management, 285.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.111988
Panayotou, T. (1993). Empirical tests and policy analysis of
environmental degradation at different stages of
economic development. International Labour
Organization (ILO).
Pata, U. K., Caglar, A. E., Kartal, M. T., & Kılıç Depren, S.
(2023). Evaluation of the role of clean energy
technologies, human capital, urbanization, and income
on the environmental quality in the United States.
Journal of Cleaner Production, 402.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136802
Rahman, A., Murad, S. M. W., Ahmad, F., & Wang, X.
(2020). Evaluating the ekc hypothesis for the bcim-ec
member countries under the belt and road initiative.
Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(4).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su12041478
Rosati, F., & Faria, L. G. D. (2019). Addressing the SDGs
in sustainability reports: The relationship with
institutional factors. Journal of Cleaner Production,
215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.12.107
Sandu, S., Yang, M., Mahlia, T. M. I., Wongsapai, W., Ong,
H. C., Putra, N., & Ashrafur Rahman, S. M. (2019).
Energy-related CO2 emissions growth in ASEAN
countries: Trends, drivers and policy implications.
Energies, 12(24). https://doi.org/10.3390/en12244650
Shah, S. Q. A., Lai, F. W., Shad, M. K., Konečná, Z., Goni,
F. A., Chofreh, A. G., & Klemeš, J. J. (2021). The
inclusion of intellectual capital into the green board
committee to enhance firm performance. Sustainability
(Switzerland), 13(19).
https://doi.org/10.3390/su131910849
Sohag, K., Taşkın, F. D., & Malik, M. N. (2019). Green
economic growth, cleaner energy and militarization:
Evidence from Turkey. Resources Policy, 63.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resourpol.2019.101407
Tachie, A. K., Xingle, L., Dauda, L., Mensah, C. N.,
Appiah-Twum, F., & Adjei Mensah, I. (2020). The
influence of trade openness on environmental pollution
in EU-18 countries. Environmental Science and
Pollution Research, 27(28).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09718-9
Ur Rehman, H., & Zeb, S. (2020). Determinants of
Environmental Degradation in Economy of Pakistan.
Empirical Economic Review, 3(1).
Vo, D. H., L. Q. T. T. (2019). CO2 emissions,
energyconsumption, and economic growth: New
evidence in the ASEAN countries. Journal of Risk and
Financial Management, 12(3).
Yu, C., Nataliia, D., Yoo, S. J., & Hwang, Y. S. (2019).
Does trade openness convey a positive impact for the
environmental quality? Evidence from a panel of CIS
countries. Eurasian Geography and Economics, 60(3).
https://doi.org/10.1080/15387216.2019.1670087
Analysis of Green Economic Growth and Environmental Degradation in Upper-Middle-Income ASEAN Countries
43
