
Users Satisfaction with Electronic Health Records: Experience of the
Rheumatology Department at CHU Ibn Rochd of Casablanca
Zakaria El Ouali
1 a
, Samy Housbane
2 b
, Khadija Azzabi
2
, Kawtar Nassar
1 c
and Saadia Janani
1 d
1
Department of Rheumatology, CHU Ibn Rochd, Casablanca, Morocco
2
Medical Informatics Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, Hassan II University of Casablanca, Morocco
Keywords: Electronic Health Records, Users Satisfaction.
Abstract: The medical record plays a key role for patients care and monitoring. It is considered as an indicator of the
quality of care. The adoption of electronic health records requires a real strategy of implementation and needs
constant monitoring to improve its function. The aim of this study was to evaluate the users’ satisfaction of
electronic health records in the Rheumatology Department at the CHU Ibn Rochd of Casablanca. A
descriptive cross-sectional study was carried out among all health professionals of the department to evaluate
the satisfaction of the users in March 2022, after 18 months of using the electronic health records. The staff
had an overall satisfaction of 96%, 84% felt that it improved the traceability of data, 88% found that it allowed
easy access to patient data and 80% admitted that it improved the feeling of professionalism and was a
teaching tool. Despite some constraints expressed by the department's staff, the overall high satisfaction and
contributions of the electronic health records indicate that this experience holds promise for widespread
implementation throughout the entire university hospital via the Hospital Information System.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Electronic Health Record (EHR) is a key element
in the quality of care. It allows easy acess to the
patient's medical history, performed examinations,
and prescribed treatments, thus promoting the
continuity of care (Bourdillon, 2006). It is a central
element in the care process and its evolution,
reflecting the broader evolution of medical practice
(Bourdillon, 2006).
The Rheumatology Department of the Ibn Rochd
University Hospital has been engaged in the
experience of implementing the EHR within its care
units since July 2020.
This work aims to study the satisfaction of EHR
users in their daily practice.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4997-6464
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3973-9123
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1879-2363
d
https://orcid.org/0009-0002-6226-8312
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Study Type
A descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted
among all healthcare staff in the Rheumatology
Department of Ibn Rochd University Hospital in
March 2022.
2.2 Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2.1 Inclusion Criteria
All the staff working in the Rheumatology
Department of CHU Ibn Rochd who have used the
EHR in 2021.
2.2.2 Exclusion Criteria
No exclusion criteria have been identified/selected.
El Ouali, Z., Housbane, S., Azzabi, K., Nassar, K. and Janani, S.
Users Satisfaction with Electronic Health Records: Experience of the Rheumatology Department at CHU Ibn Rochd of Casablanca.
DOI: 10.5220/0012769500003854
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 1st International e-Health Forum (IeHF 2023), pages 21-24
ISBN: 978-989-758-711-5
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
21

2.3 Data Collection
Data collection was conducted using a self-
administered anonymous questionnaire, completed
through two methods:
• An electronic questionnaire via Google
Forms sent to all resident doctors and interns
in the department.
• A paper questionnaire for the department's
secretaries.
The questionnaire (see Appendix) was developed
based on two user satisfaction questionnaires
regarding EHR found in the literature (Liu et al.,
2013), translated into French using 'Deepl'. It consists
of four parts:
• Sociodemographic criteria
• Questions regarding professional practice
and computer use
• Evaluation of EHR satisfaction using a five-
level Likert scale (strongly disagree,
disagree, neither agree nor disagree, agree,
strongly agree) concerning overall
satisfaction, EHR use, use of structured
forms, technical and time-related aspects,
impact on the doctor-patient relationship,
and patient safety
• Feedback and secondary use
The questionnaire also includes an open-ended
question to gather comments from users about their
experience with the EHR.
2.4 Data Analysis
A descriptive analysis of the data was conducted.
Quantitative variables (age, years of practice) were
represented by mean and standard deviation, as well
as minimum and maximum values. Qualitative
variables were presented by the count and percentage
of their categories.
The percentage of agreement was calculated as
the sum of the percentage of users responding with
agree and strongly agree.
3 RESULTS
3.1 User Characteristics
Twenty-six users responded to our EHR user
satisfaction survey (60% of the personnel in the
Rheumatology Department, constituting 100% of
EHR users).
3.1.1 Age of Participants
The average age of the users was 30.5 years with a
standard deviation of 5 years. The minimum age was
26 years and the maximum was 49 years.
3.1.2 Sex of Participants
Ninety-two percent of the participants were females,
while 8% were males.
3.1.3 Profile of Participants
There were 22 physicians (85%) and 4 (15%)
secretaries who participated in the study.
3.1.4 Seniority of Participants
The average seniority of the EHR users who
responded to our satisfaction survey was 3 years with
a standard deviation of 2.5 years. The minimum
seniority was 9 months, and the maximum was 9
years.
3.1.5 Computer Usage Level
Out of the EHR users, 14 individuals (54%) had an
average level of computer usage, 9 (34.6%) had a
basic level, and 3 (11.5%) had a high level of
computer usage.
3.1.6 Duration of EHR Usage
Two individuals (8%) have been using HER for less
than 3 months, 1 individual (4%) between 3 and 6
months, 5 individuals (18%) between 6 months and 1
year, while 18 individuals (69%) have been using
EHR for more than one year.
3.2 User Satisfaction
The results of user satisfaction survey are presented
in Table 1.
Twenty-five users (96%) are generally satisfied,
among which 8 (32%) are highly satisfied. Twenty-
one users (84%) believe that the computerized patient
file allows for better traceability. Nineteen users
(86%) confirm that semi-structured forms are suitable
for the specialty. However, 25% still prefer writing
on paper, and 46% prefer free text. This preference is
explained by the physicians' need to compose
paragraphs in certain sections.
IeHF 2023 - International e-Health Forum
22
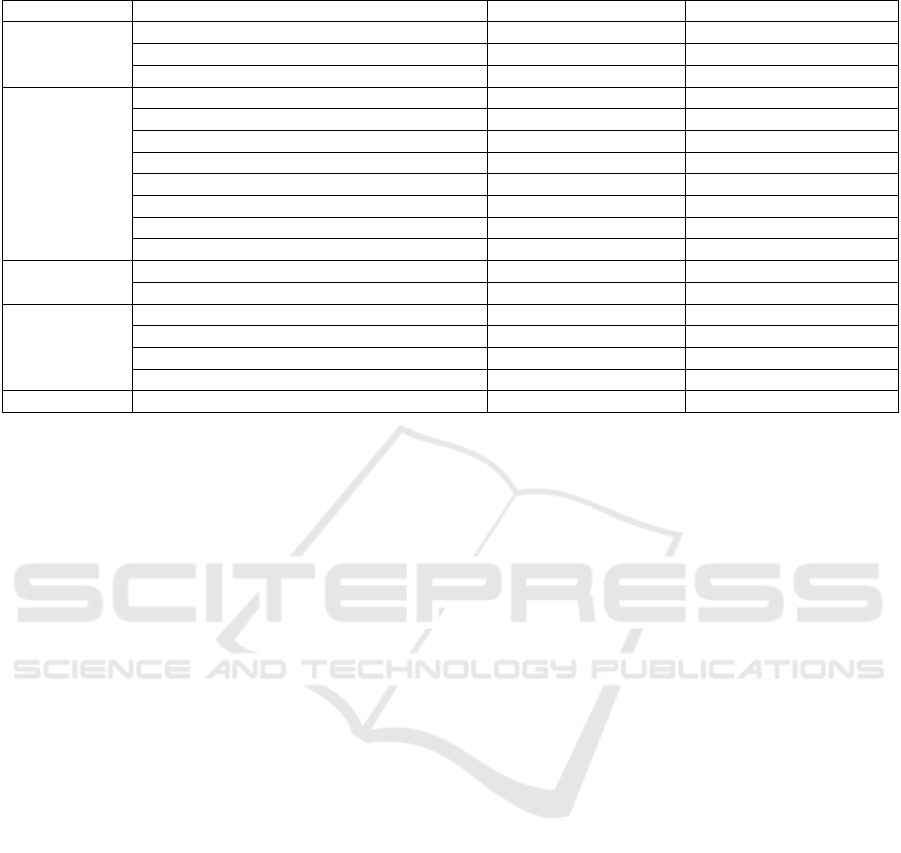
Table 1: User satisfaction with the EHR in the Rheumatology Department of the Ibn Rochd University Hospital in Casablanca.
Item
Question
Number of Agreements
Percentage of Agreement
Satisfaction
Generally satisfied
25
96
Favorable opinion of colleagues
19
76
Prefers writing on paper
7
25
Benefits
Improves healthcare provision
17
68
Allows better traceability
21
84
Reduces medical errors
9
44
Enables tracking of laboratory results
19
78
Enables good communication / coordination
16
64
Rapidly accessible patient history
23
88
Sense of professionalism
20
80
Represents a teaching tool
16
80
Structure
Forms adapted to the specialty
19
86
Prefers free text
11
46
Technical and
Practical
Aspects
Consumes more time than paper forms
12
48
Increases workload
13
52
Available technical support
10
40
Frequent breakdowns
7
28
Patient Safety
Compromises patient safety
5
20
Sixteen users (64%) find that the EHR enables
good communication and coordination among
healthcare professionals within the department, as
there is no sharing with other departments or at the
hospital level.
3.3 Feedback Meeting Assistance
Eight individuals (32%) assisted once to a feedback
meeting, while 1 individual (4%) assisted twice or
more. Sixteen individuals (64%) never assisted to a
feedback meeting.
3.4 Feedback from Hierarchical
Superiors
Fifteen (60%) of the users received feedback from
hierarchical superiors or colleagues after feedback
meetings.
3.5 Participation in Scientific Works
Twenty-four percent of the users participated in
scientific works issued from EHR, while 76% did not
participate in such works.
3.6 User Comments
Here are the user comments:
• Generalize the experience to all departments.
• Automatically record summaries/reports.
• Free up Wi-Fi for the use of other work-related
applications.
• Schedule multiple appointments for the same
patient on the same day.
• Increase the internet connection speed.
• Manage system failures.
• Educate patients about the system: explaining
that looking at the screen is simply the doctor
reviewing their medical record. Many patients
quickly feel that the doctor is paying more
attention to the screen.
• Avoid requiring identification for each session
closure (after a certain period of time).
4 DISCUSSION
This study confirms statements regarding the
satisfaction of the Rheumatology Department staff
with the EHR and its contributions to continuity of
care. Indeed, after 18 months of EHR use, the
Rheumatology Department staff reports an overall
satisfaction rate of 96% and believes that the EHR has
contributed to better data traceability (84% of users),
easy access to patient data (88% of users), and
improved professionalism (80% of users). These
findings are consistent with the literature: Alex G and
Paul Cohen reported in 2006 on the Valaisan EHR
user satisfaction evaluation that 70% of users
positively assessed the EHR effect on patient
information accessibility and improvement in
communication among healthcare professionals
Users Satisfaction with Electronic Health Records: Experience of the Rheumatology Department at CHU Ibn Rochd of Casablanca
23

(Gnaegi et al., 2006). These results are also consistent
with other studies in the literature (Liu et al., 2013)
Regarding medical data structuring, the staff
appreciates the use of semi-structured reports, finding
them suitable for the Rheumatology specialty (86%
of users) and considering them as a teaching tool
(80% of users).
However, there are several challenges and
discomforts related to EHR use. Our survey showed
that 25% of the individuals prefer writing on paper,
48% feel that the EHR increases workload and
consumes more time compared to paper patient
records, 46% prefer free-text format for clinical
descriptions in their reports, 28% report frequent
network-related issues accessing the EHR, 20%
believe that EHR compromises patient safety.
Among the major challenges in EHR adoption is
data quality and the percentage of missing data,
making its exploitation difficult and sometimes
inefficient (Ta & Weng, 2019). The Rheumatology
Department staff is aware of the importance of data
quality in terms of traceability and completeness, as
well as the significance of data structuring. A policy
focusing on supervising data completeness and
quality, as well as adopting coding data standards,
will be implemented after fostering a culture of
digitizing care practices.
These challenges and discomforts in EHR user
satisfaction are commonly reported in literature.
Various explaining factors include user's personal
characteristics, organizational aspects of the system
(user involvement in the project, sustainable
communication), and the quality and continuous
presence of technical support (Frisina et al., 2022;
Janett & Yeracaris, 2020; Kalankesh et al., 2020;
Williams et al., 2019).
Regarding future perspectives for the
Rheumatology EHR, the transition to an interoperable
Hospital Information System (HIS) represents the
next step of medical records computerization process.
The Rheumatology Department staff, following their
local EHR experience, is looking forward to
extending the EHR to the entire university hospital,
and to integrating it into the new HIS recently adopted
by Ibn Rochd University Hospital in 2021. Sharing
data across different clinical services and existing
information systems aims at providing better
multidisciplinary patient care within the university
hospital and its affiliated hospitals.
Moreover, the EHR allows easy storage and
access to thousands of patient records, facilitating
case studies spanning several years. Secondary use of
this data is a secondary goal for the Rheumatology
Department professors and residents, allowing them
to assess their practice and contribute to scientific
research.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The local experience of EHR in the Rheumatology
Department at CHU Ibn Rochd of Casablanca shows
the great benefits for health professionals as well as
for the patients quality of care and follow-up. Despite
the constraints and discomfort expressed by the
department's staff, the overall high satisfaction and
contributions of the EHR in providing easy access to
patient data, along with its increasing adoption over
time, indicate that this experience holds promise for
widespread implementation throughout the entire
university hospital via the Hospital Information
System.
REFERENCES
Bourdillon, F. (2006). Le dossier du patient. EMC - Traité
de médecine AKOS, 1(1), 1–5.
Frisina, P. G., Munene, E. N., Finnie, J., Oakley, J. E., &
Ganesan, G. (2022). Analysis of end-user satisfaction
with electronic health records in college/university
healthcare. J of ACH, 70(3), 717–723.
Gnaegi, A., Cohen, P., Marey, D., Rivron, M., & Wieser, P.
(Eds.). (2006). Satisfaction des utilisateurs du dossier
patient informatisé valaisan. Swiss Medical
Informatics.
Janett, R. S., & Yeracaris, P. P. (2020). Electronic Medical
Records in the American Health System: Challenges
and lessons learned. Ciencia & Saude Coletiva, 25(4),
1293–1304.
Kalankesh, L. R., Nasiry, Z., Fein, R. A., & Damanabi, S.
(2020). Factors Influencing User Satisfaction with
Information Systems: A Systematic Review. Galen
Medical Journal, 9, e1686.
Liu, J., Luo, L., Zhang, R., & Huang, T. (2013). Patient
satisfaction with electronic medical/health record: A
systematic review. Scandinavian Journal of Caring
Sciences, 27(4), 785–791.
Ta, C. N., & Weng, C. (2019). Detecting Systemic Data
Quality Issues in Electronic Health Records. Studies in
Health Technology and Informatics, 264, 383–387.
Williams, D. C., Warren, R. W., Ebeling, M., Andrews, A.
L., & Teufel Ii, R. J. (2019). Physician Use of
Electronic Health Records: Survey Study Assessing
Factors Associated With Provider Reported
Satisfaction and Perceived Patient Impact. JMIR
Medical Informatics, 7(2), e10949.
IeHF 2023 - International e-Health Forum
24
