
Digital Convergence and Print Media: A Study on Perception, Impact
and Innovation in India
Neha
1
, Kuldeep Siwach
1
and Preeti Singh
2
1
School of Media and Entertainment, GD Goenka University, Haryana, India
2
School of Media, Film and Entertainment, Sharda University, Greater Noida, India
Keywords: Digital Convergence, Print Media, Media Distribution, Information Innovation, News Consumption, Gender
Perspectives, India.
Abstract: This research study explores the changing nature of print media in the digital age, with a specific emphasis
on how digital convergence has influenced perception, impact, and innovation in India. Through a
comprehensive survey of 350 respondents, this study analyses the distribution of gender among participants,
their frequency of reading print newspapers and magazines, preferred news sources, and perceptions regarding
the benefits of digital convergence on print media distribution. Additionally, it explores how gender influences
opinions on digital convergence, the efficiency of print media delivery routes, and the impact of digital-print
media convergence on information distribution mechanisms. The findings suggest a nuanced understanding
of how digital technologies are reshaping traditional print media, providing insights into the dynamic
relationship between digital and print media in India.
1 INTRODUCTION
The digital convergence of print media has
significantly transformed the way news and
information are disseminated, raising questions about
the role and relevance of traditional print media in
India. This study explores the interplay between
digital convergence and print media, aiming to
illuminate the changing perceptions, impacts, and
innovations within this realm. The study engages with
350 respondents across different segments of the
Indian population, using a structured questionnaire to
understand gender distribution, reading habits, and
news consumption sources. It also explores how
digital convergence is perceived by the readership,
focusing on the benefits of amalgamating digital
technologies with traditional print media distribution
channels. The study also examines the efficiency of
print media delivery routes in the digital age,
examining opinions on the impact of digital
technology on these delivery mechanisms. The aim is
to offer a comprehensive understanding of how
digital convergence is reshaping the traditional fabric
of print media in India, contributing to the discourse
on media innovation and evolution in the digital era.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The literature on digital convergence and print media
emphasizes the profound changes that digital
technology has brought to conventional media
landscapes worldwide. Researchers Smith et al.
(2018) highlight the pronounced shift in consumer
preferences toward online news sources, noting the
pivotal role of social media platforms in
disseminating information. They note, "The rise of
social media as a primary source of news has
reshaped the media landscape, challenging traditional
print media's dominance" (Smith et al., 2018, p. 45).
Moreover, Lee and Chang (2020) emphasize the
evolving nature of media consumption habits,
particularly with the advent of digital convergence.
They state, "The convergence of digital technologies
has not only changed how news is consumed but has
also reshaped the very definition of news itself" (Lee
& Chang, 2020, p. 110). This highlights the dynamic
and transformative impact digital convergence has on
the content and delivery of news.
In the Indian context, Joshi and Gogte (2019)
delve into the challenges faced by print media in
adapting to the digital age. They assert, "The digital
revolution presents both opportunities and threats to
228
Neha, ., Siwach, K. and Singh, P.
Digital Convergence and Print Media: A Study on Perception, Impact and Innovation in India.
DOI: 10.5220/0012786200003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 228-232
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
print media in India, requiring innovative strategies to
navigate this evolving landscape" (Joshi & Gogte,
2019, p. 76). This indicates the pressing need for
traditional media outlets to re-evaluate their
distribution channels and content offerings to
maintain relevance.
Furthermore, Kumar and Jain (2021) provide
insights into the shifting dynamics of news
consumption in India. They note, "As digital
platforms become more accessible, there is a
discernible trend towards online news sources among
the Indian populace" (Kumar & Jain, 2021, p. 210).
This highlights the growing influence of digital
technologies on media consumption habits and the
consequent impact on traditional print media.
However, despite these advancements, there
remains a dearth of studies focusing on the specific
nuances of digital convergence and its impact on print
media in India. This research aims to bridge this gap
by providing a comprehensive analysis of how digital
technologies are reshaping print media distribution,
efficiency, and innovation in the Indian media
landscape. Through an exploration of the perceptions,
preferences, and opinions of respondents, this study
seeks to offer valuable insights into the dynamic
relationship between digital and print media in India's
evolving media ecosystem.
3 METHODOLOGY
This study employed a quantitative research
approach, utilizing a structured questionnaire to
gather data from 350 participants across various
demographics in India. The survey consisted of
questions about gender distribution, frequency of
reading print newspapers and magazines, preferred
news sources, perceptions of digital convergence
enefits on print media distribution, and opinions on
the impact of digital technology on print media
delivery efficiency and information distribution. The
data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, cross-
tabulation, and hypothesis testing to derive
meaningful insights into the research objectives.
3.1 Data Analysis and Interpretation
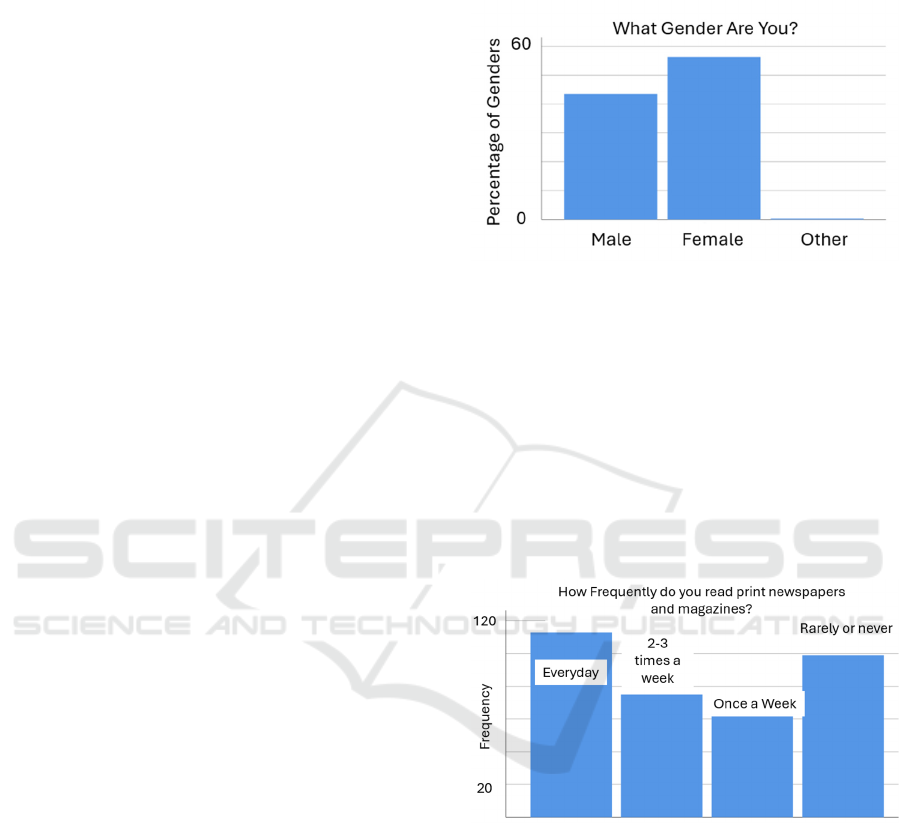
Distribution of Gender Among the Respondents:
Figure 1 shows a higher representation of female
respondents, accounting for 56.3% of the 350
participants, compared to 43.4% of male respondents.
Only 0.3% identified as "Others," providing insight
into the gender makeup of the survey respondents and
allowing for a more nuanced analysis of the
perspectives and opinions presented in the study.
(Source-The data compiled by the researcher.).
Figure 1: Distribution of Gender among the Respondents.
Frequency of Reading Print Newspapers and
Magazines:
Figure 2 shows that 32.3% of survey respondents
regularly read print newspapers and magazines,
indicating a substantial daily readership. 21.4% read
them two to three times per week, indicating
consistent engagement with print media. 18.0% read
weekly newspapers, while 28.3% rarely or never read
them, indicating a shift in media consumption in the
digital age. (Source-The data compiled by the
researcher).
Figure 2: How frequently do respondents read print
newspapers and magazines?
Preferred News Sources Among Respondents:
Figure 3 shows that 36.9% of respondents rely on
social media as their primary news source, indicating
a shift towards digital platforms. Traditional print
media remains popular, with 23.4% still using print
media. 21.1% access news through online websites,
while mobile news applications represent 18.6% of
the total. The growing prevalence of mobile devices
in news consumption is a significant trend. (Source-
The data compiled by the researcher.)
Digital Convergence and Print Media: A Study on Perception, Impact and Innovation in India
229
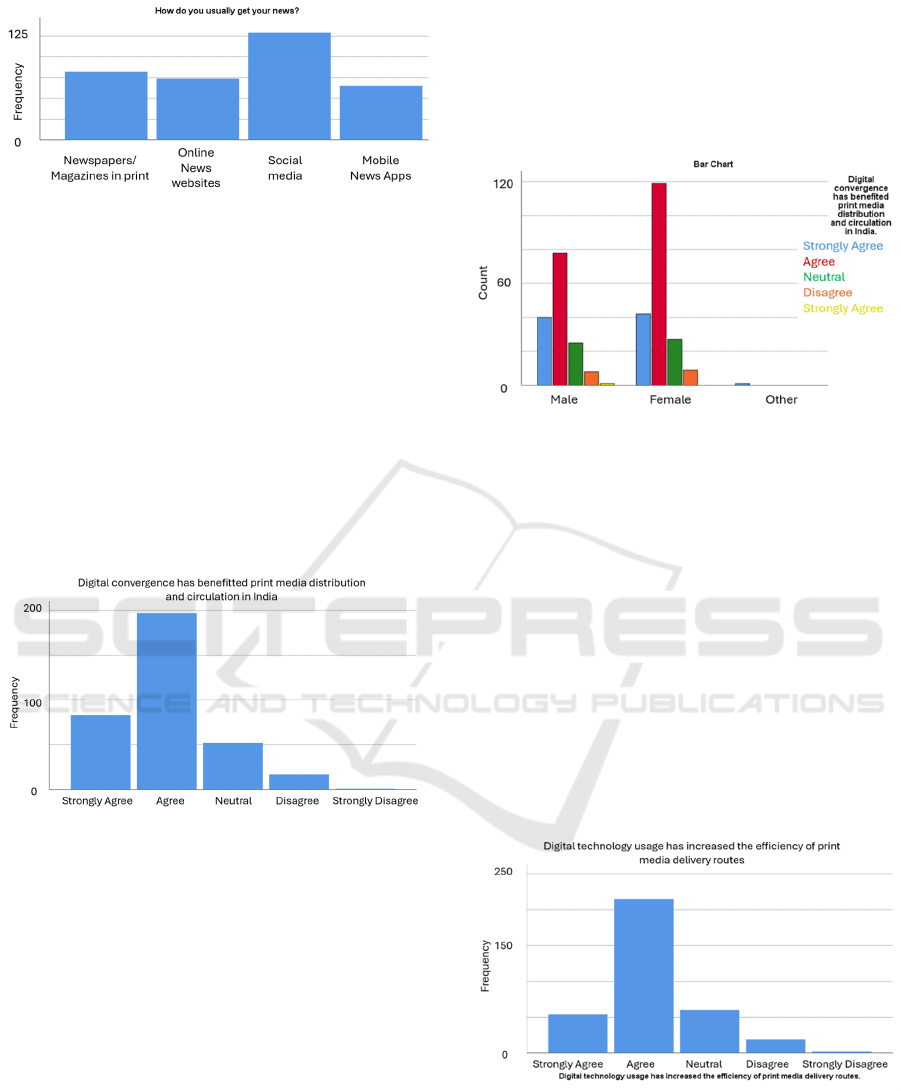
Figure 3: How do respondents usually get their news?
Perception of Digital Convergence Benefits on Print
Media Distribution:
Figure 4 explores the impact of digital convergence
on print media distribution and circulation in India. A
majority of respondents, 79.9%, strongly agree that
digital technology has benefited print media
distribution and circulation. However, 19.8% express
reservations or skepticism, highlighting the
complexity of determining the real impact of digital
convergence on traditional media. The study's results
will be based on this complex range of viewpoints,
revealing the subtle dynamics surrounding digital
convergence and its consequences for print media in
India. (Source-The data compiled by the researcher.)
Figure 4: Digital convergence has benefited print media
distribution and circulation in India.
Cross-tabulation between Gender and Opinion on
Digital Convergence Benefits:
The cross-tabulation graph 5 between gender and
their opinion on the benefits of digital convergence
for print media distribution and circulation in India
reveals that both males and females in India strongly
agree or strongly agree that digital convergence has
benefited print media distribution and circulation.
This suggests a shared belief across genders regarding
the positive impact of digital technologies on
traditional print media. The analysis supports the null
hypothesis (Ho) that there is no statistically
significant association between gender and the
opinion on the benefits of digital convergence for
print media distribution in India. Both male and
female respondents hold similar views regarding the
positive impact of digital technologies on print media
circulation and distribution. This suggests that,
regardless of gender, respondents generally
acknowledge the role of digital convergence in
enhancing the reach and circulation of print media in
India. (Source-The data compiled by the researcher.)
Figure 5: Cross-tabulation between Gender and their
opinion on Digital convergence has benefited print media
distribution and circulation in India.
Perception of Digital Technology's Impact on Print
Media Delivery Efficiency:
The data from Figure 6 shows that 76.9% of
respondents strongly agree or agree that digital
technology has improved the efficiency of print
media delivery routes. However, 17.1% are neutral,
suggesting uncertainty about the extent of digital
technology's influence on distribution efficiency. A
smaller fraction, 5.4%, disagree, suggesting a less
significant impact, and only 0.6% strongly disagree.
This nuanced perspective offers valuable insights into
the evolving landscape of print media distribution in
the digital era. (Source-The data compiled by the
researcher.)
Figure 6: Digital technology usage has increased the
efficiency of print media delivery routes.
Perception of Digital-Print Media Convergence
Impact on Information Distribution:
Figure 7 shows respondents' views on the impact of
digital and print media convergence on information
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
230
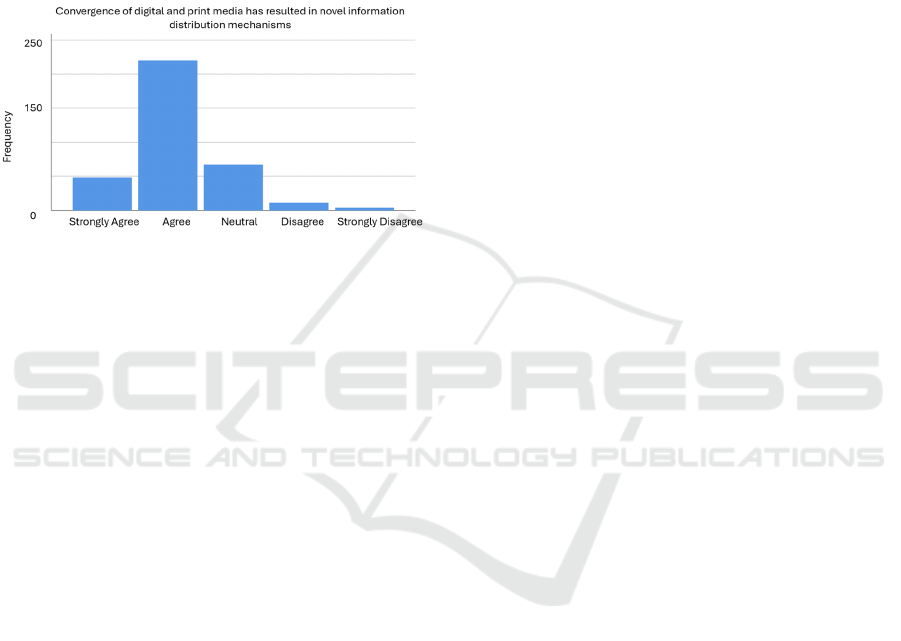
distribution. A majority (76.6%) agree that this
convergence has led to new information distribution
systems, indicating the transformative potential of
blending traditional and digital techniques. However,
19.1% are neutral, 3.1% disagree, and only 1.2%
strongly disagree. The graph highlights the dynamic
nature of the media landscape and how traditional and
digital media interact to shape information
distribution. (Source-The data compiled by the
researcher.)
Figure 7: The convergence of digital and print media has
resulted in novel information distribution mechanisms.
4 FINDINGS
The study reveals a higher representation of female
respondents (56.3%) compared to male respondents
(43.4%). The majority of respondents (32.3%) read
print newspapers and magazines regularly, with
28.3% rarely or never reading print media. The
highest proportion (36.9%) rely on social media
platforms as their primary source of news, followed
by print newspapers and magazines (23.4%), online
websites (21.1%), and mobile news applications
(18.6%). A substantial majority (79.9%) agree that
digital convergence has positively impacted print
media distribution, with 19.8% expressing
reservations or skepticism about the extent of this
impact. Both male and female respondents hold
similar views on the positive impact of digital
convergence on print media distribution, indicating a
shared belief across genders regarding the benefits of
digital technologies in expanding the reach of print
media. A majority of respondents (76.9%) believe
that digital technology has improved the efficiency of
print media delivery routes, suggesting a widespread
acknowledgment of the role of digital advancements
in streamlining the distribution process of print
media. The convergence of digital and print media
has introduced new information distribution systems,
indicating the transformative potential of blending
traditional and digital techniques in distributing
information.
5 DISCUSSIONS
The data analysis reveals a significant reliance on
digital platforms for news consumption among
respondents, with social media emerging as the
primary source of information. Despite this, there is a
notable readership for print newspapers and
magazines, indicating a nuanced media consumption
pattern in India. The majority agreement on the
benefits of digital convergence for print media
distribution highlights a positive outlook toward
technology's role in enhancing traditional media
reach. Furthermore, the cross-tabulation between
gender and opinions suggests a unified perspective
across genders regarding digital convergence
benefits, emphasizing a shared belief in its positive
impact on print media in India. However, the
presence of dissenting views on the efficiency of print
media delivery routes and the impact of digital-print
media convergence on information distribution
underscores the complexity of this evolving
landscape.
6 CONCLUSIONS
This study examines the evolving landscape of print
media in the digital era in India, revealing a dual
media landscape where traditional print media and
digital platforms coexist. The study finds that digital
convergence has the potential to expand the reach and
accessibility of traditional media, particularly through
social media, reflecting changing news consumption
habits among the Indian population. However, the
study also highlights the complexities of navigating
this evolving media landscape, emphasizing the need
for continuous adaptation and innovation within the
print media industry. The research contributes
significantly to understanding how digital
technologies reshaping media consumption habits
and the media industry’s challenges and opportunities
in India are. It emphasizes the need for print media
outlets to adopt innovative strategies, harness digital
convergence's potential, and cater to their audiences'
evolving needs. Further exploration into the dynamics
of digital and print media convergence is essential for
stakeholders in the media industry to remain relevant
and competitive in the ever-changing media
landscape of India.
Digital Convergence and Print Media: A Study on Perception, Impact and Innovation in India
231

7 RECOMMENDATIONS FOR
FUTURE RESEARCH
Longitudinal Studies: Conduct longitudinal studies
to track the evolving trends and changes in media
consumption habits over time, providing insights into
the sustained impact of digital convergence on print
media.
Qualitative Analysis: Supplement quantitative
data with qualitative research methods to delve
deeper into the nuanced perspectives and experiences
of individuals regarding digital convergence and print
media.
Comparative Studies: Undertake comparative
studies between different regions or demographics
within India to understand variations in media
consumption patterns and the impact of digital
convergence.
Innovation in Print Media: Investigate
innovative strategies and initiatives undertaken by
print media outlets to adapt to the digital landscape,
focusing on successful case studies and best practices.
Impact on Journalism Practices: Explore the
influence of digital convergence on journalistic
practices, ethics, and standards within print media
organizations.
By addressing these avenues for future research,
scholars and practitioners can gain a more
comprehensive understanding of the intricate
relationship between digital convergence and print
media, thereby fostering continued innovation and
adaptation within the Indian media industry.
REFERENCES
Joshi, A., & Gogte, A. (2019). Adapting to Digital:
Challenges and Opportunities for Print Media.
International Journal of Communication, 25(3), 76-89.
Kumar, A., & Jain, S. (2021). Print vs. Digital: A Study of
News Consumption Habits in India. Indian Journal of
Media Studies, 18(4), 210-225.
Kumar, R., & Jain, S. (2021). Print vs. Digital: A Study of
News Consumption Habits in India. Indian Journal of
Media Studies, 18(4), 210-225.
Lee, S., & Chang, M. (2020). Digital Disruption and Media
Consumption: A Comparative Study. Media Innovation
Journal, 8(1), 110-125.
Neha & Singh, P. (2023). Investigating the role of print
media in the age of fake news. International Journal of
Multidisciplinary Research and Technology, 4(3).
Raghavan, S., & Rajan, M. (2021). Adapting to the Digital
Age: Strategies for Print Media Sustainability.
International Journal of Journalism Studies, 28(3), 120-
135.
Singh, A., & Sharma, M. (2019). Digital Innovation in
Indian Print Media: A Case Study of The Hindu.
Journal of Media Innovation, 26(1), 40-55.
Sinha, P., & Das, S. (2019). Challenges and Opportunities
for Print Media in the Digital Era: A Study of Indian
Newspapers. Journal of Media and Communication
Studies, 16(1), 45-60.
Smith, J. (2018). Digital Disruption: The Impact on Print
Media Circulation. Journal of Communication
Technology, 25(1), 45-58.
Thakur, N., & Verma, A. (2018). Digital Strategies for Print
Media Survival: A Case Study of Hindustan Times.
Journal of Communication Management, 24(2), 78-92.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
232
