
Identification and Analysis of Factors of Construction Schedule
Delays in Indian Construction Industry
Chinmay Shingare, Deva Dutta Dubey and Rajesh Joshi
RICSSBE, Amity University, Maharashtra, India
Keywords: Project Delays, Construction.
Abstract: Delays in project schedules can have far-reaching consequences, often leading to time and cost overruns,
disputes, legal proceedings, and in some cases, project abandonment. According to Sambasivan and Soon
(2007), these delays are insidious and can wreak havoc on project timelines and budgets. Clough (1986)
further emphasises the detrimental effects of delays, noting that clients may suffer financial losses or hardships
if projects exceed their specified completion times. Additionally, contractors bear the brunt of delay-related
costs, including standby expenses for idle workers and equipment, disruptions to construction and material
delivery schedules, and increased overhead expenses. The collective findings highlight the multifaceted
impacts of schedule delays on both clients and contractors, underscoring the importance of proactive
management strategies to mitigate their adverse effects.
1 INTRODUCTION
Delays in construction project schedules pose
significant risks, impacting both cost and time
overruns, as well as intangible factors such as
damaging organisational reputation. To mitigate
these risks, it's crucial to identify the root causes of
delays through continuous analysis, monitoring, and
control of project schedules.
Excusable delays, not under the regulation of the
owner or contractor, and non-excusable delays, which
are within their control, are both significant. Critical
delays jeopardise project deadlines, while
compensable delays involve compensation for the
delay. Concurrent delays occur when multiple parties
contribute to schedule delays.
Understanding these types of schedule delays -
excusable, non-excusable, critical, compensable, and
concurrent - is essential for effective project
management. By recognising and addressing these
delays promptly, project managers can minimise their
adverse effects and ensure successful project
completion within stipulated timeframes and budgets.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The significant repercussions of schedule delays on
construction and real estate projects, especially in
Gulf countries, demand a thorough investigation to
comprehend their adverse effects on project time,
cost, scope, and quality. As evidenced by Aibinu and
Jagboro (2002), these delays often lead to time
overrun, cost overrun, disputes, arbitration, total
abandonment, and litigation. Addressing this critical
issue is imperative to ensure timely project
completion while adhering to predefined quality
standards and specifications.
3 RESEARCH OBJECTIVE
• To identify the gap in the research done on
schedule delays in construction sector.
• To identify different factors which influence
delays.
• To analyse the probability and severity of the
schedule delay factors in the construction sector.
• To gauge relative index, to highlight various
critical delay factors.
• To prepare Framework screening Ranking of
Schedule Delay factors according to Highest to
Lowest affecting.
Shingare, C., Dubey, D. and Joshi, R.
Identification and Analysis of Factors of Construction Schedule Delays in Indian Construction Industry.
DOI: 10.5220/0012858700003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 397-403
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
397
• To identify of Top 5 Critical schedule delay
factors amongst all of them as per the basis of
relative index
• To identify factors which have a high
correlation with the identified top five RII
factors. Conclusion
4 LITERATURE REVIEW
Henry Agboola (1997) explored the causes and
effects of schedule delays in Nigerian housing
projects through questionnaire surveys, highlighting
loss and expense claims resulting from such delays.
Al-Momani (2000) investigated schedule delays on
public projects in Jordan, identifying key factors such
as design changes, weather, and late deliveries.
Aibinu (2001) focused on Nigerian construction
delays, confirming time and cost overruns as major
effects. AI-Tabtabai (2002) analysed schedule delay
factors in Kuwaiti projects, while Manavazhia (2002)
studied cost overruns in Nepalese highway projects.
Alwi (2003) ranked schedule factors in correlation
with delays. Alaghbari (2007) identified delay factors
in Malaysian projects, and Le-Hoai (2008) assessed
Vietnamese construction delays. Agyakwah-Baah
(2010) investigated project suspensions in Ghana, and
Hamzaha (2011) defined delay terminologies in
Malaysian projects. Kikwasi (2012) analysed
interruptions in construction projects, and Aziz
(2013) studied delays in Egyptian projects. Muhwezi
(2014) examined delays in Ugandan construction, and
Marzouk (2014) identified delays in civil
construction. HOSSEN (2015) assessed delay risks in
nuclear projects, and Srdić (2015) proposed models
for mitigating delays. Senoucia (2016) analysed cost
overruns in Qatari projects, and Arya (2016)
investigated Indian delays. Alzaraa (2016) studied
delays in Saudi projects, and Muhamad (2016)
utilised delay analysis methodologies. Niazia (2017)
identified influences on Afghan cost overruns, and
Naqash (2019) examined delays in Northern Indian
projects. Odeh identified factors causing cost
overruns in traditional contracts, emphasising
contractor perspectives. Abd El-Razek analysed
schedule delays in Egyptian projects, focusing on
contractors, consultants, and owners through
interviews and questionnaires.
5 DATA ANALYSIS
At the top level, the 28 factors were distributed into 6
categories as under. 110 responses were received
Figure 1: Broad Distribution of factors.
Table 1: indicates the constituent factors for each category
of factors.
Category / Code Factor Category /
Code
Factor
Owner Contractor
O1 Delay in progress
payments
C1 Ineffective
Project planning
and schedulin
g
O2 Slowness in
decision making
p
rocess
C2 Poor Financial
control of site
O3 Poor
communication and
coordination
C3 Rework due to
errors
O4 Delay in approving
Desi
g
n Documents
C4 Delays in sub-
contractors wor
k
Consultant Material
Co1 Delay in approving
major changes in
scope of wor
k
M1 Poor procurement
of construction
materials
Co2 Inaccurate site
investigation and
survey before
design
M2 Shortage of
construction
materials
Co3 Late in reviewing
and approving
desi
g
n documents
M3 Delay in material
delivery
Co4 Delays in producing
design documents
M4 Poor quality of
construction
materials
Equipment Others
E1 Equipment
allocation problem
Ot1 Complexity of
project (Project
type, Project
scale etc
)
E2 Shortage of
e
q
ui
p
ment
Ot2 Additional Work
E3 Slow mobilization
of equipment
Ot3 Delay in
obtaining permits
E4 Low efficiency/
Productivity of
e
q
ui
p
ment
Ot4 Global financial
crisis
E5 Low level of
equipment-
o
p
erator's skill
Ot5 Unfavorable
weather
conditions
Ot6 Accident during
construction
Ot7 Low productivity
of labo
r
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
398
6 RESULTS & DISCUSSIONS
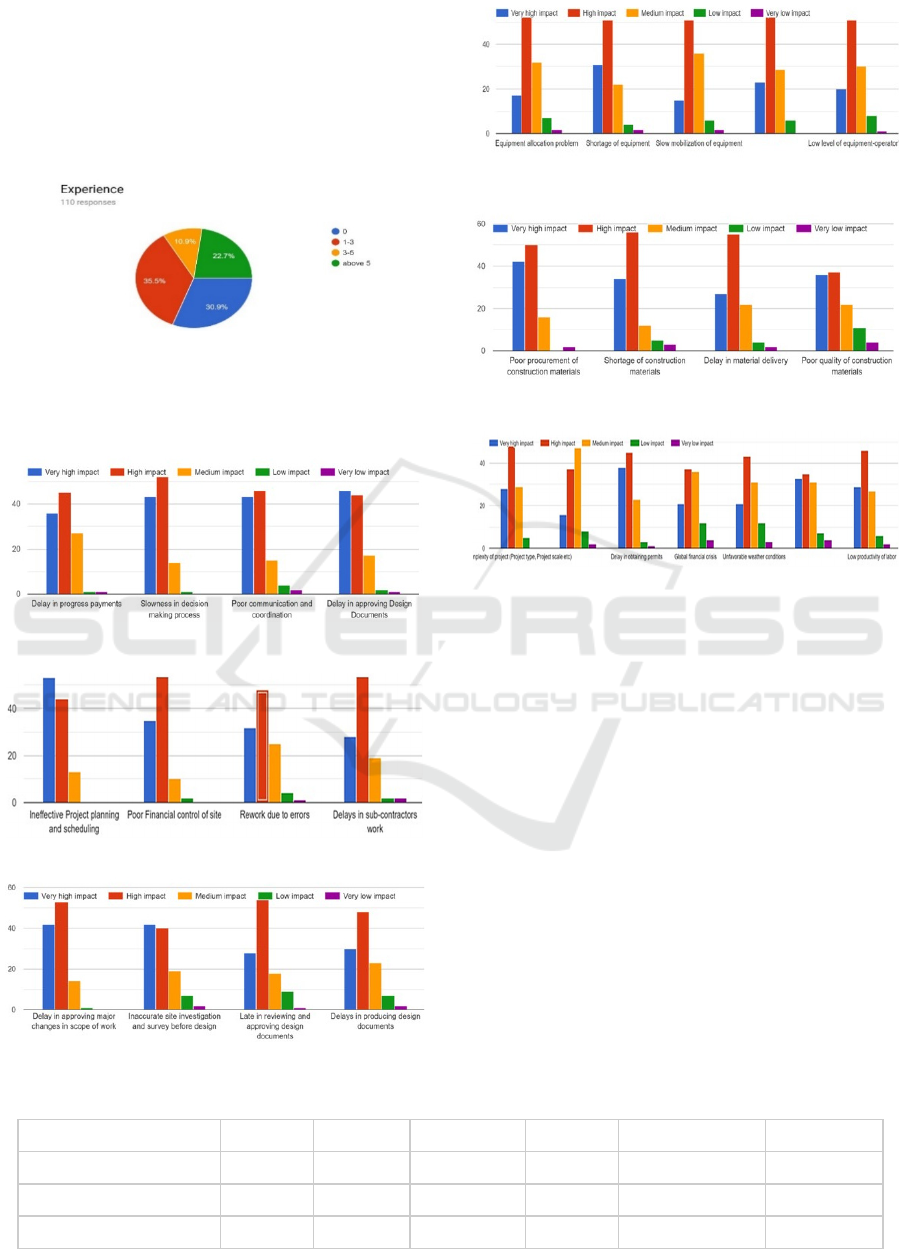
Demographic profile indicators of respondents
showed that 70% of the respondents had one or more
years of experience in the industry. 30% of the
professionals had experience of a few months to 1
year.
Figure 2: Experience of Respondents (in years).
Then we present scores for each factor in different
categories identified for the analysis. These are
presented in Figures 3 – 8.
Figure 3: Responses for Owner Related Factors.
Figure 4: Responses for Contractor Related Factors.
Figure 5: Responses for Consultant Related Factors.
Figure 6: Responses for Equipment Related Factors.
Figure 7: Responses for Materials Related Factors.
Figure 8: Responses for Other Factors.
In order understand the scores and the factors that
they influence, further analysis was conducted. This
would help us to find out the root cause of schedule
delay which may be addressed by continuous
analysis, monitor & control of the project schedule.
First and foremost, average scores of different
categories of factors was studied by taking simple
averages of scores across the different categories.
Descriptive statistics pertaining to average scores of
groups of factors is as under:
Table 1: Descriptive Statistics of Average Values of Responses to Factor.
Min Max Mean SD Median Mode
Count 110 110 110 110 110 110
Owner 2 5 4.15 0.51 4.25 4
Contractor 2.75 5 4.13 0.47 4 4
Identification and Analysis of Factors of Construction Schedule Delays in Indian Construction Industry
399
Consultant 2 5 4.01 0.64 4 4.25
Equipment 2 5 3.99 0.63 4 4.25
Materials 2 5 3.99 0.63 4 4.25
Others 1.57 5 3.75 0.64 3.86 4
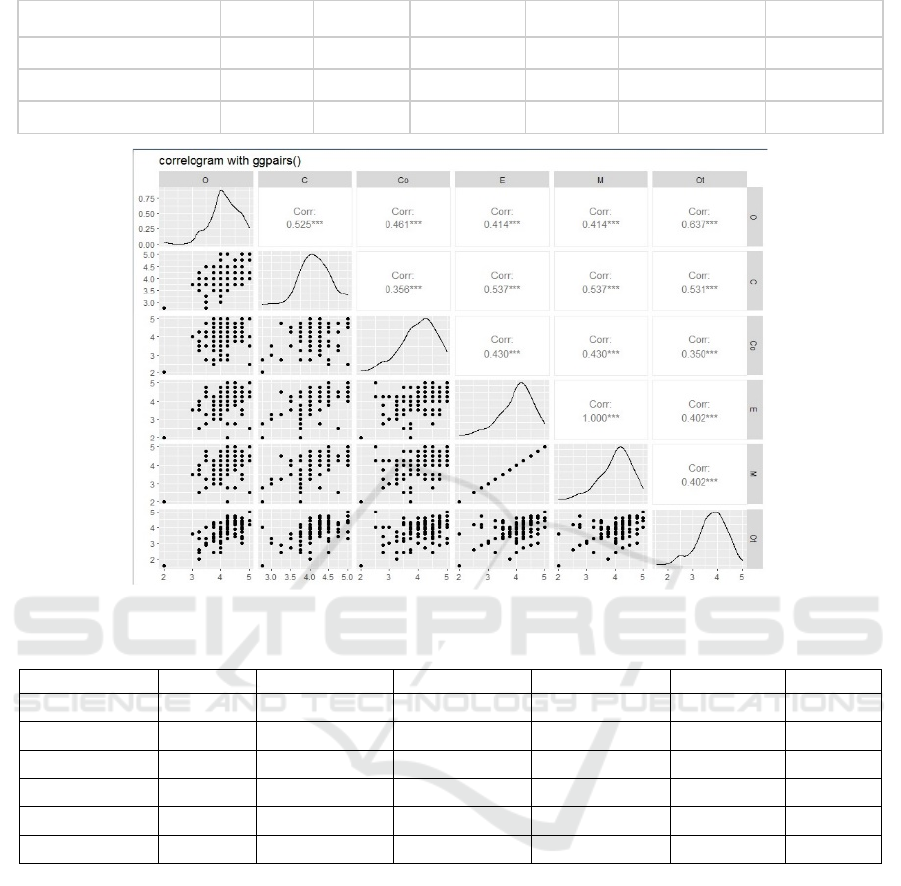
Figure 9: Plots of Pairwise Correlations of groups of factors.
Table 2: Pairwise correlation amongst different groups of factors.
Owner Contractor Consultant Equipment Material Others
Owner 1
Contractor 0.52 1
Consultant 0.46 0.36 1
Equipment 0.41 0.54 0.43 1
Material 0.41 0.54 0,43 1 1
Others 0.64 0.53 0.35 0.4 0.4 1
Pairwise correlations of the average scores were
obtained using R and Stata and the following table
show the correlations amongst the groups of factors.
Further, pairwise correlations amongst different
groups of factors was examined. These are presented
in Table 2.
The highest correlation is observed between
Owner and Others at 0.64. The next highest one is
between Contractor & Equipment and Contractor &
Machinery at 0.54. This is followed by Owner and
Contractor at 0.52, which is followed by correlation
between Owner and Consultant at 0.46. The next
highest is between Consultants & Equipment and
Consultants & Materials at 0.43. This is then followed
by Owner & Equipment and Owner & Materials.
Owner, Contractor and Consultants are key players in
the construction projects as they have a good
understanding of the project from all angles.
We then identified key factors affecting the
schedule delays based on Relative Importance Index
using the following formulation.
RII = ∑ (Wi * Xi) / ∑ Xi (1)
Where,
i represents category index
Wi represents weight of the ith response relating
to any factor.
Xi represents frequency of the ith response given
as a percentage of total responses for each factor
The RII obtained for all the factors is presented in
Table 3 below.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
400
Table 3: Computed Relative Important Index for each delay
factor.
Sr.
No
Delay Factors
Relative
Importance
index
1 Owner Related factors [Delay in progress payments] 0.8073
2 Owner Related factors [Slowness in decision making
p
rocess]
0.8491
3 Owner Related factors [Poor communication and
coordination]
0.8255
4 Owner Related factors [Delay in approving Design
Documents]
0.84
5 Contractor Related factors [Ineffective Project
p
lanning and scheduling]
0.8727
6 Contractor Related factors [Poor Financial control of
site]
0.8382
7 Contractor Related factors [Rework due to errors] 0.7927
8 Contractor Related factors [Delays in sub-contractors
work]
0.7982
9 Consultant Related factors [Delay in approving
ma
j
or chan
g
es in sco
p
e of work]
0.8473
10 Consultant Related factors [Inaccurate site
investi
g
ation and surve
y
before desi
g
n]
0.8055
11 Consultant Related factors [Late in reviewing and
a
pp
rovin
g
desi
g
n documents]
0.78
12 Consultant Related factors [Delays in producing
desi
g
n documents]
0.7764
13 Equipment related factors [Equipment allocation
p
roblem]
0.7364
14 Equipment related factors [Shortage of equipment] 0.7909
15 Equipment related factors [Slow mobilization of
e
q
ui
p
ment]
0.7291
16 Equipment related factors [Low efficiency/
Productivit
y
of e
q
ui
p
ment]
0.7673
17 Equipment related factors [Low level of equipment-
operator's skill]
0.7473
18 Material related factors [Poor procurement of
construction materials]
0.8364
19 Material related factors [Shortage of construction
materials]
0.8055
20 Material related factors [Delay in material delivery] 0.7836
21 Material related factors [Poor quality of construction
materials]
0.7636
22 Other related factors [Complexity of project (Project
type, Project scale etc)]
0.78
23 Other related factors [Additional Work ] 0.7036
24 Other related factors [Delay in obtaining permits] 0.8109
25 Other related factors [Global financial crisis] 0.7073
26 Other related factors [Unfavorable weather
conditions]
0.7218
27 Other related factors [Accident during construction] 0.7564
28 Other related factors [Low productivity of labor] 0.7709
Construction Schedule Deferrals are continuously
proving to be the crucial influencing and negatively
affecting factors of construction projects. These
should be scrutinized on priority basis to finish the
project under the specified duration and under the
predefined cost. All the three aspects of construction
project management are affected due to these
schedule delays. Ranking of the delay factors was
done and the top five results we obtained are
presented in Table 4 as under.
Table 4: Top five RII Factors.
S No Factor / Description RII
1 C1 [Ineffective Project planning and scheduling] 0.8727
2 O2 [Slowness in decision making process] 0.8491
3 Co1 [Delay in approving major changes in scope
of work]
0.8473
4
O4 [Delay in approving Design Documents]
0.84
5 C2 [Poor Financial control of site] 0.8382
These five high RII factors were further analysed on
the basis of correlation amongst factors to in-turn
determine component factors which demonstrated
high correlation with these factors. These are
presented in the following table. The table shows the
factors which have high correlation with other
factors.
Table 5: Constituent factors having high correlation with top five RII Factors.
Factor/Description Correlated factor Correlated factor Correlated factor Correlated factor Correlated factor
C1
[Ineffective Project
planning and
scheduling]
Ot4
[Global financial
crisis]
(0.24)
O2
[Slowness in deci-
sion making process]
(0.19)
O3
[Poor communicati-
on and coordination]
(0.19)
C4
[Delays in sub-
contractors’ work]
(0.19)
Ot2
[Additional Work]
(0.18)
O2
[Slowness in
decision making
process]
M1
[Poor procurement of
construction
materials] (0.30)
C2
[Poor Financial
control of site]
(0.29)
Ot4
[Global financial
crisis]
(0.24)
E3
[Slow mobilization of
equipment]
(0.24)
E1
[Equipment
allocation problem]
(0.22)
Co1
[Delay in approving
major changes in
scope of work]
M1
[Poor procurement of
construction
materials] (0.34)
E2
[Shortage of
equipment]
(0.24)
Ot1
[Complexity of pro-
ject (Project type,
Project scale etc.)]
(0.23)
M4
[Poor quality of
construction materials]
(0.22)
E3
[Slow mobilization
of equipment]
(0.22)
O4
[Delay in approving
Design Documents]
O3
[Poor communication
and coordination]
(0.49)
Ot3
[Delay in obtaining
permits]
(0.46)
Ot5
[Unfavorable
weather conditions]
(0.43)
C4
[Delays in sub-
contractors’ work]
(0.41)
Co4
[Delays in produ-
cing design
documents] (0.38)
C2
[Poor Financial
control of site]
E3
[Slow mobilization of
equipment]
(0.33)
Ot1
[Complexity of proje-
ct (Project type, Pro-
ject scale etc.)] (0.30)
O2
[Slowness in
decision making
process] (0.29)
E4
Low efficiency/
Productivity of
equipment] (0.27)
Ot4
[Global financial
crisis]
(0.28)
*Figures in parentheses indicate correlation amongst the factors.
Identification and Analysis of Factors of Construction Schedule Delays in Indian Construction Industry
401

• All component factors for the top five RII
factors were analysed based on their frequency
of occurrence.
• Constituent factors were presented alongside
their descriptions, with those having high
correlation with multiple top RII factors
displayed in bold font.
• Notably, the high RII factors belonged to
Owner, Contractor, and Consultant groups, with
two factors each attributed to Owner and
Contractor groups, and one to Consultant group.
• For instance, Owner Factor O4 had the highest
correlation with another Owner factor, O3
(0.49), along with significant correlations with
Contractors, Consultants, and other factors.
• Similarly, Consultant Factor Co1 correlated
highly with materials and equipment related
factors, while Contractor Factor C2 correlated
significantly with Equipment, Others, and
Owner factors.
• The contributory factors for the top five
important factors were discussed, leading to a
total of 17 overall factors considered for greater
managerial attention.
• These factors could serve as recommendations
for project managers to ensure project success
and minimise delays.
• Managerial implications were drawn from the
above findings, offering recommendations for
project managers.
• Factors impacting one or more of the top five
high RII factors were categorised as Exogenous
Factors.
• Examples of such factors included the Global
Financial Crisis, Unfavourable Weather
Conditions, and Delay in Obtaining Permits.
• While beyond direct control, suitable techniques
or methods could mitigate the impact of
unfavourable weather conditions, requiring
project managers to anticipate and prepare
accordingly.
• Factors under managerial control, impacting
more than one of the top five high RII factors,
were identified.
• These included Project Management factors
such as Complexity of project, Delay in sub-
contractors work, and Slowness in decision-
making process.
• Communication Skills factors like Poor
Communication and Coordination also
warranted attention to improve project-related
information dissemination.
• Further factors impacting one of the top five
high RII factors were highlighted, including
Poor Financial control of site and Delays in
producing design documents.
• Recommendations for addressing these factors
included enhancing communication skills,
improving financial control, and streamlining
decision-making processes.
• By identifying key metrics and implementing
suitable action plans, project managers could
minimise delays and optimise project outcomes.
7 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the comprehensive analysis of
schedule delay factors in construction projects
provides valuable insights for project managers
aiming to enhance project success and minimise
delays. By examining the frequency of occurrence
and correlation of constituent factors, we identified
key contributors to schedule delays, spanning across
Owner, Contractor, and Consultant domains. The
delineation of factors under managerial control
underscores the importance of proactive management
strategies in mitigating delays. Furthermore, the
identification of exogenous factors highlights the
need for strategic planning to anticipate and mitigate
external challenges. The managerial implications
drawn from this analysis offer actionable
recommendations for project managers,
encompassing areas such as project management,
communication skills, and procurement practices.
Implementing these recommendations can empower
project managers to navigate complexities, streamline
processes, and optimise project outcomes.
Ultimately, this study underscores the critical role of
effective management practices in achieving project
success amidst dynamic project environments.
REFERENCES
Aibinu, A.A., & Jagboro, G.J. (2001). The effects of
construction delays on project delivery in Nigerian
construction industry.
Odeh, Abdalla M., & Battaineh, H.T. (n.d.). Causes of
construction delays- Traditional contracts.
Agyakwah-Baah, F. D. (2010, July). Delays in Building
Construction Projects in Ghana.
Senoucia, Ahmed A.I. (2016). Time Delay and Cost
Overrun in Qatari Public Construction Projects.
Ahmed, T. (2015, January). Delays in construction projects.
AI-Tabtabai, H. M. (2002). Causes for delays in
construction projects in Kuwait. Engineering Journal of
the University of Qatar.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
402

Alavifar, Amir Hossein, & Motamedi, Shadab. (2014).
Identification, Evaluation and Classification of Time
Delay Risks of Construction Project in Iran.
International Conference on Industrial Engineering and
Operations Management, Indonesia.
Srdić, Aleksander, & Šajn, J. (2015). Delays in
Construction Projects: Causes and Mitigation.
Al-Momani, A. H. (2000). Construction delay: a
quantitative analysis.
Arya, Aunradha, & Kausal, Rajeev. (2016). Analysing
Delays of Construction Projects in India – Causes and
Effects. International Journal of Science Technology
and Engineering, Vol 3, Issue 6.
Aziz, R. F. (2013). Ranking of Delay factors in construction
projects after Egyptian revolution. Alexandria
Engineering Journal, 52.
Sweis, G., & Sweis, R. (2008). Delays in construction
projects: The case of Jordan.
Niazia, Ghulam Abbas, & Naeem, N. (2017). Significant
Factors Causing Cost Overruns in the Construction
Industry in Afghanistan.
Agboola, Henry, & Akinloye, Y. (1997). The causes and
effects of construction delays on completion cost of
housing projects in Nigeria.
Kikwasi, G. J. (2012). Causes and Effects of Delays and
Disruptions in Construction Projects in Tanzania.
Australasian Journal of Construction Economics and
Building Conference Series.
Muhwezi, L., & Ahimbisibwe, J. (2014). An Assessment of
the Factors Causing Delays on Building Construction
Projects in Uganda. International Journal of
Construction Engineering and Management.
Le-Hoai, Long, & Lee, Y.D. (2008). Delay and Cost
Overruns in Vietnam Large Construction Projects: A
Comparison with Other Selected Countries.
Abd El-Razek, M. E., & Bassioni, H.A. (n.d.). Causes of
Delay in Building Construction Projects in Egypt.
Marzouk, Mohamed M., & El-Rasheed, T.I. (2014).
Analyzing delay causes in Egyptian construction
projects.
Manavazhia, Mohan R., & Karki, D. K. (2002). Material
and equipment procurement delays in highway projects
in Nepal.
Hossen, Muhammed Mufazzal, & Karim, S. K. (2015).
Construction Schedule Delay Risk Assessment By
Using Combined Ahp-Rii Methodology For An
International Npp Project.
Hamzaha, N., & Kamaruzzaman, M. (2011). Cause of
Construction Delay - Theoretical Framework.
Syed Mohammad Tahir, Naqash, & Singla, Sandeep.
(2019). Significant factors affecting delays in
construction projects in Northern Region of India and
their relation with cost. International Journal of
Scientific & Technology Research, Vol 8, Issue 11.
Muhamad, Nurul Huda, & Fathi, M. (2016). Delay Analysis
Methodologies (DAMs) in Delivering Quality Projects:
Contractors and Consultants’ Perceptions.
Wang, Shou Qing, & Fernandez, M. F. (2004, March). Risk
management framework for construction project in
developing countries.
Alwi, Sugiharto, & Khalid, H. (2003). Identifying the
important causes of delays in building construction
projects.
Alaghbari, Wa’el, & Rizwan, M. (2007). The significant
factors causing delay of building construction projects
in Malaysia.
Identification and Analysis of Factors of Construction Schedule Delays in Indian Construction Industry
403
