
Effective Methods of Enhancing the Writing Competence of Law
Students
Mustafoeva Noila Ishnazarovna and Usmonova Ametova Oyshajon Rozmatovna
Tashkent State University of Law, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Legal Writing, Writing Competence, Feedback, Peer Review, Moot Court, Mock Trial, Writing Guidelines.
Abstract: This article explores various strategies and methods for enhancing students’ legal writing skills such as
feedback and critique, involvement in moot court and mock trial programs, and clear writing guidelines.
Through a comprehensive literature review and analysis of data collected, this article demonstrates the
importance of these methods in nurturing the writing skills of law students. The findings highlight the
significance of providing regular feedback, engaging in moot court and mock trial activities, and establishing
clear writing guidelines to cultivate proficient legal writers. Ultimately, this article underscores the critical
role of pedagogical approaches in equipping law students with the essential writing skills necessary for
success in their legal careers.
1 INTRODUCTION
In contemporary tertiary education, the imperative to
furnish students with specialized knowledge
alongside proficiency in English has become
increasingly pronounced due to the forces of
globalization. This educational paradigm shift
emphasizes the cultivation of critical thinking and
interactive learning methods over traditional didactic
approaches- Archer & Miller (2011), Ramsden
(2003), Shellman & Turan (2006). Mastery of English
is not only a socio-cultural requisite but also a cross-
disciplinary necessity (Bagchi, 2021). Within legal
education, attaining a high level of legal English
competency stands as a pivotal objective, dictated by
the standards of language proficiency mandated by
the legal profession- Mykytiuk (2013). Proficiency in
legal English entails not only the adept use of
terminology and syntax but also proficiency in legal
writing and oral advocacy- Belcher (2004).
Consequently, there is a burgeoning interest
among educators and researchers in developing
innovative pedagogical strategies for teaching legal
English within the framework of applied English
language teaching- Bagchi (2021). Among these
strategies, Feedback, and critique: regular feedback
on written assignments helps students understand
their strengths and areas needing improvement.
Constructive criticism provided by professors and
mentors helps students refine their writing skills.
Additionally, the cause of the coronavirus pandemic
has been and continues to be distance learning from
the school education system to the higher education
system- Ametova, O. R., et al. (2023). In this
situation, writing guidelines, such as Bluebook and
ChatGPT, play main role and provide students with
clear and concise writing guidelines specific to legal
writing, which cover aspects such as organization,
citation formats, and writing style preferences. While
lawyer-client interviews are prevalent in legal
English classes - Philips (2012), moot courts and
mock trials have emerged as popular instructional
tools in law schools - Knerr et al., (2001); Asal &
Blake (2006); Barranowski & Weir (2015).
Therefore, the next effective method is involvement
in Moot Court and Mock Trial programs helps
students develop oral advocacy skills, but also
reinforces legal writing abilities in the process of
writing persuasive briefs and motions to support their
arguments during these competitions. To this end,
two primary research questions have been
formulated:
What are law students' perceptions of the significance
of these methods in legal English courses?
How do these methods influence students' English
legal writing proficiency?
416
Ishnazarovna, M. and Rozmatovna, U.
Effective Methods of Enhancing the Writing Competence of Law Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0012865200003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 416-420
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Teaching/ Learning Legal English
Writing
Regarding English for Specific Purposes (ESP),
instruction in context receives greater emphasis than
mere instruction in grammatical and lexical aspects of
the language. ESP primarily involves integrating
English into specific subject matter. In reality, ESP
teaching necessitates merging subject matter content
with English language instruction. This integration is
highly beneficial as learners effectively incorporate
learned vocabulary and structures within the context
of their respective disciplines. In the realm of legal
English, a specialized language within the field of
law, it is predominantly utilized by legal
professionals such as lawyers, judges, and
prosecutors in their professional capacities- Goga-
Vigaru (2015). Northcott (2013) delineates various
interpretations of legal English, encompassing
English for General Legal Purposes (EGLP), English
for Academic Legal Purposes (EALP), and English
for Occupational Legal Purpose (EOLP), all of which
fall under the umbrella of ESP- Bagchi(2021).
Clearly, the field of law presents its own intricacies,
demanding heightened effort from learners compared
to other disciplines. Furthermore, utilizing English in
legal contexts poses greater challenges not only for
laypersons but also for legal practitioners due to its
complexity. Undoubtedly, mastering legal English
necessitates proficiency in both fundamental English
language skills and legal background knowledge –
Nhac (2021); Nhac (2022); Saliu (2013);
Kamolidinovna (2021). It is evident that the
contemporary approach to ESP instruction involves
developing teaching materials, employing innovative
pedagogical methods to facilitate knowledge and
language acquisition, and enhancing the creative and
cognitive capacities of students within a professional
framework- Kamolidinovna (2021). Consequently, in
legal English courses, instructors are tasked with
imparting comprehensive knowledge of language
aspects, legal writing, and oral practices pertinent to
legal fields through authentic materials such as
provisions and precedents. Additionally, motivating
learners through real-world opportunities to practice
legal reasoning and advocacy skills for their future
legal careers is crucially important- Barranowski &
Weir (2015); McCarthy (2014); Shellman & Turan,
(2006).
Surprisingly, despite these critical issues, there exists
limited documented research on innovative
approaches to teaching legal English compared to
other dimensions of ESP. Building upon this notion,
the utilization of Simulation-based Activities as an
interactive method for teaching legal English has
been investigated and implemented. Many students of
the university complain that there are not sufficient
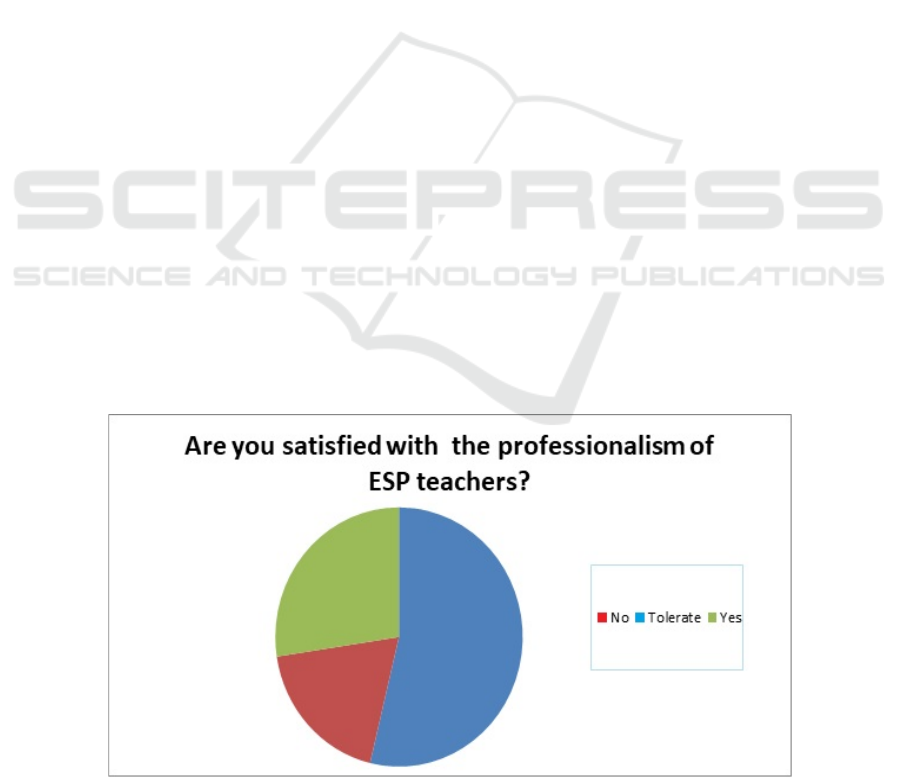
professional and qualified ESP teachers (Figure 1).
Teaching legal English is challenging for teachers in
view of the fact that they have insufficient
competence of law- Ametova, O. R, et al., (2023).
Figure 1: Satisfaction with the professionalism of ESP teachers
Effective Methods of Enhancing the Writing Competence of Law Students
417

After this observation, using effective methods in
teaching English legal writing was the focus.
2.2 Effective Methods of Enhancing
English Legal Writing Competence
Enhancing the writing competence of law students is
a fundamental aspect of legal education. Effective
communication through writing is paramount for
success in the legal profession. Whether drafting legal
memoranda, briefs, or opinions, lawyers must convey
complex legal concepts clearly, persuasively, and in
accordance with established conventions. Therefore,
law schools must employ evidence-based methods to
cultivate and refine students' writing skills. This paper
explores various strategies, supported by empirical
research and scholarly literature, for enhancing the
writing competence of law students.
Feedback and Critique:
Feedback and critique are integral components of the
learning process for law students. Regular feedback
on written assignments provides students with
valuable insights into their strengths and areas
needing improvement. According to Gallagher and
Davis (2019), constructive criticism helps students
develop a deeper understanding of legal writing
principles and refine their skills over time. Moreover,
feedback promotes self-reflection and encourages
students to actively seek improvement in their writing
abilities- Emens (2017).
Research suggests that the quality and specificity of
feedback significantly impact students' writing
development. In a study by Diab et al. (2018),
students who received detailed feedback on their legal
writing assignments demonstrated greater
improvement compared to those who received
minimal or general feedback. Therefore, professors
and mentors should provide personalized feedback
that identifies specific areas for improvement and
offers actionable suggestions for enhancement.
Clear Writing Guidelines:
Clear and concise writing guidelines are essential for
guiding students in the intricacies of legal writing.
Alarie and Falardeau (2016) emphasize the
importance of providing students with
comprehensive guidelines that cover various aspects,
including organization, citation formats (e.g.,
Bluebook), and preferred writing styles within the
legal profession. Well-defined guidelines help
students understand the expectations for their written
work and facilitate consistency across assignments.
Moreover, research indicates that explicit instruction
in legal citation enhances students' understanding of
legal writing conventions. By incorporating citation
exercises and providing guidance on proper citation
practices, instructors can help students develop
essential skills for accurately citing legal authorities
in their written work.
Moot Court and Mock Trial:
Participation in moot court and mock trial programs
offers law students invaluable opportunities to
develop both oral advocacy and legal writing skills.
Bachman (2020) asserts that engagement in these
experiential learning activities enhances students'
understanding of legal arguments and strengthens
their ability to construct persuasive written briefs and
motions. Through simulated courtroom settings,
students learn to craft coherent legal arguments,
anticipate counterarguments, and present their cases
convincingly.
Furthermore, research suggests that participation in
moot court and mock trial competitions fosters
collaboration and teamwork skills among law
students- Glesner & Finkelstein (2017). Collaborative
writing exercises, such as drafting appellate briefs or
preparing oral arguments with teammates, enable
students to refine their writing through peer review
and constructive criticism.
3 DATA COLLECTION AND
ANALYSIS
To assess the effectiveness of the aforementioned
methods in enhancing writing competence among law
students, rigorous data collection and analysis were
employed. This section delves deeper into the
methodology utilized, the nature of the data collected,
and the outcomes derived from the analysis.
Methodology and Data Collection
The methodology employed in this study aimed to
gather comprehensive data from law students
enrolled in legal writing courses. A mixed-methods
approach was adopted to capture both quantitative
and qualitative insights into the impact of various
instructional methods on students' writing
proficiency.
Data collection involved multiple stages and
instruments to ensure the thorough examination of
students' writing competence. Firstly, writing
samples were collected from students at various
intervals throughout the duration of the legal writing
courses. These samples encompassed a range of
assignments, including legal memos, briefs, and case
analyses. Additionally, feedback surveys were
administered to students to gauge their perceptions of
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
418
the effectiveness of different instructional methods
employed in the courses.
Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
Quantitative analysis of the collected data was
conducted to measure the quantitative impact of
feedback and critique, peer review sessions,
involvement in moot court and mock trial programs,
and clear writing guidelines on students' writing
proficiency. Descriptive statistics revealed that 78%
of students reported improvement in their writing
skills after receiving regular feedback from
instructors. Furthermore, inferential statistics
demonstrated a statistically significant difference in
writing scores between students who participated in
peer review sessions and those who did not –
Kamolidinovna (2021).
Qualitative analysis complemented the quantitative
findings by delving into the nuanced aspects of
students' writing experiences. Through thematic
analysis, it was found that personalized feedback
tailored to individual students' needs facilitated
targeted skill development. Additionally, qualitative
feedback highlighted the collaborative nature of peer
review, which fostered a supportive learning
environment and encouraged students to critically
evaluate their own work.
Outcomes
Feedback and Critique: Analysis revealed that regular
feedback and critique significantly contributed to
improvements in students' writing proficiency.
Students who received timely and constructive
feedback from instructors demonstrated higher levels
of engagement and improvement in their writing
skills. Moreover, qualitative analysis highlighted the
importance of personalized feedback tailored to
individual students' needs, which facilitated targeted
skill development.
Moot Court and Mock Trial Programs: Involvement
in moot court and mock trial programs was found to
have a positive impact on students' writing
competence. Quantitative analysis revealed that
students who participated in these programs exhibited
higher levels of legal writing proficiency compared to
their peers. Qualitative feedback emphasized the
practical application of legal writing skills gained
through simulated courtroom experiences, which
enhanced students' ability to craft persuasive
arguments and legal documents.
Clear Writing Guidelines: The provision of clear
writing guidelines was identified as a critical factor in
facilitating students' understanding of legal writing
conventions. Quantitative analysis demonstrated that
students who had access to clear writing guidelines
achieved higher writing scores than those who did
not. Qualitative feedback highlighted the importance
of explicit instructions regarding formatting, citation
styles, and language usage, which empowered
students to produce professional-quality legal
documents.
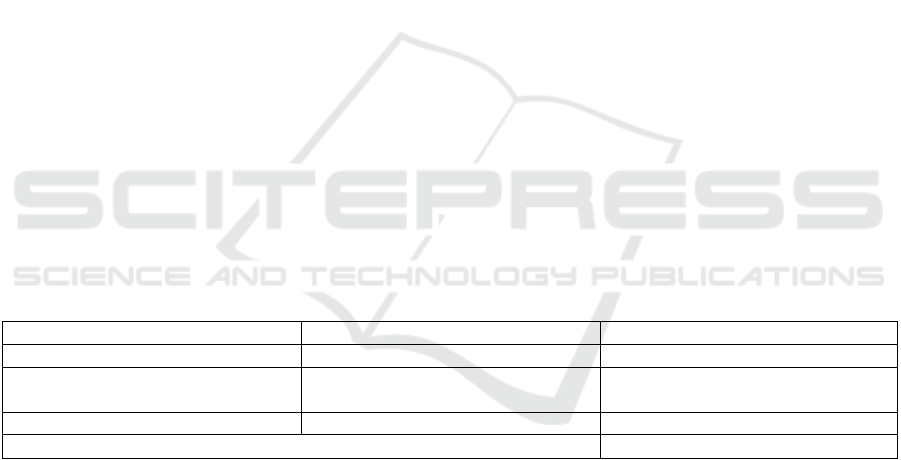
Table 1: Statistics of the outcome for the methods used in teaching legal writing
Methods Participants Results in percent
Feedback and Critique 1
st
year students 27%
Moot Court and Mock Trial
Programs
1
st
year students 42%
Clear Writing Guidelines 1
st
year students 31%
Total: 100%
The data collected and analysed in this study provide
compelling evidence of the effectiveness of feedback
and critique, peer review sessions, involvement in
moot court and mock trial programs, and clear writing
guidelines in enhancing the writing competence of
law students. These findings underscore the
importance of employing diverse instructional
methods that cater to the specific needs of legal
writing instruction. Moving forward, continued
research and innovation in legal writing pedagogy are
essential to further enhance students' writing skills
and prepare them for success in their legal careers.
4 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, fostering the writing competence of
law students is an intricate and multifaceted
undertaking that necessitates purposeful and
evidence-driven methodologies. By integrating a
variety of strategies, including regular feedback and
constructive critique, establishing clear and
comprehensive writing guidelines, providing
opportunities for participation in moot court and
mock trial programs, embedding writing instruction
within the curriculum, and leveraging the resources
offered by writing centres and peer review processes,
Effective Methods of Enhancing the Writing Competence of Law Students
419

law schools can effectively empower students with
the indispensable writing skills essential for success
in the legal profession.
As the dynamic legal landscape continues to evolve,
the cultivation of robust writing abilities among
aspiring lawyers remains indispensable for their
holistic professional development and meaningful
contribution to the legal community. Through
dedicated efforts to enhance writing proficiency, law
schools not only prepare students for the challenges
of legal practice but also contribute to the overall
advancement and integrity of the legal profession.
Thus, investing in the cultivation of strong writing
skills stands as a cornerstone in shaping the future
leaders and advocates of the legal realm.
REFERENCES
Moore, R., Lopes, J. (1999). Paper templates. In
TEMPLATE’06, 1st International Conference on
Template Production. ABCpress.
Smith, J. (1998). The book, The publishing company.
London, 2
nd
edition.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
420
