
Cultivating Contemporary Professional Personnel: Evaluating Higher
Education Standards and Reform Measures for Enhancement
Nasiba Jumaniyozova, Nilufar Nazarova, Khadicha Chulpanova
and Isakova Mokhinur
Tashkent State Transport University, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Higher Professional Education, Education Policy, Modernization, International Mobility, Human Capital.
Abstract: The purpose of this article is aimed at its research, since there is a need for research in the modern system of
socio-humanitarian knowledge on educational modernization, integration of regional and national cultures
and the need to separately study the mental characteristics of people. Design/methodology / approach: the
article uses techniques such as comparison, analysis and synthesis, comparative analysis, sociological inquiry,
and the principles of objectivity, historicity, logic. The process of the higher education system of Uzbekistan
was taken as the object of the study. Originality / value: as a result of the essence of higher education being
able to respond to the worldview of the educational person in response to the internal (introversive), external
extroversive (external) needs of a person, to reflect on the mechanism of "Science – Education – production",
harmonizing the elements of upbringing, to perform a capacitive function in society, reflect constant changes
and innovations as a social phenomenon.
1 INTRODUCTION
The main goal of the state government in the field of
higher education is to form a step-by-step model of
education that meets the challenges of the 21st
century. The scope and quality of higher education in
Uzbekistan is subject to constant attention and
improvement.
“The formation of human capital, the realization
of the capacity of the individual is counted from the
responsible tasks of the state. Whatever goals the state
sets for itself, it is necessary to create an educational
system accordingly”.
Focusing on education at the state level is a key
factor in the development of education, as well as a
positive impact on the level of knowledge of the
younger generation.
We can also know from the opinions and
decisions made by President Shavkat Mirziyoev in
this regard that modernizing higher education in
Uzbekistan is officially recognized as a strategic
direction of state policy. This, of course, requires
further improvement of the higher professional
education system of Uzbekistan. One of the most
visible results of innovative changes in education is,
in our opinion, the acceleration of the "aging" of
knowledge acquired in the process of obtaining
education in higher educational institutions, as well
as the incompatibility of theoretical knowledge with
the needs of the practical sphere of society's life.
Accordingly, the need to constantly update and put
this knowledge into practice is increasing. In this
regard, the transition of the educational system of our
country to a two-stage system has become a necessity
for the period of combining specialists in all fields
with practice in professional training and further
development of science. The radical improvement of
the educational policy carried out in this regard and
the further strengthening of the legal framework led
to the integration of international educational
templates. The preparation for the growing accession
of Uzbekistan to the Bologna Convention
predetermined the need to form a single educational
space, accordingly, the same as the European criteria
for the quality of education, compliance with uniform
technological and humanitarian standards and the
requirements for training specialists of all spheres. At
the same time, this approach helps to train
competitive professionals in the modern labour
market at all levels, expands the possibility of
influencing the content, forms and methods of
organizing the educational process, even helps to
choose the type of educational institution. On the one
hand, this approach helps to train professionals of all
levels who are competitive in the modern labour
486
Jumaniyozova, N., Nazarova, N., Chulpanova, K. and Mokhinur, I.
Cultivating Contemporary Professional Personnel: Evaluating Higher Education Standards and Reform Measures for Enhancement.
DOI: 10.5220/0012871600003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 486-492
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
market. In fact, these parameters affect the indicators
of the quality of education.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
Philosophical teachings on education are found in the
works of the ancient Greek and Roman philosophers
Plato, Aristotle, Cicero, Seneca, and later in the
teachings of the German classical philosophers of the
Renaissance. Even in the new era, scientific research
was carried out on the formation of education, global
culture and educational trends, scientific literature
was created.
D. Hell, D.Pobeptc, P.Pobeptcon, C.Huntington,
E. Cmit in the work of scientists such as inclusion and
renewal of higher education, global education,
transnational education, Education is scientifically
studied in the same direction as for everyone.
Problems such as national education,
democratization, education and culture in the higher
education system, CIS scientist A.P. Valitskaya, V.V.
Kpaevckiy, Studied by V.M. Pozin, B.M. Bid-Bam.
In the study of the formation of modern higher
education in Uzbekistan, its philosophical, economic-
political, socio-legal, spiritual and ideological
foundations, the philosophers of our country J.
Ramatov, N. The works of the Shermuhammedovs
occupy a special place. In particular, P.D. Yuldashev
in his research revealed the improvement and
development of the theoretical and conceptual
foundations of the development of the educational
process from a philosophical point of view. Professor
B.A. Amanov studied the political and philosophical
aspects of conceptual models of modernization of
society. Y. Namozova studied the philosophy of
education at the beginning of the 19th – end of the
20th century AD.
We witnessed that in Japan, getting acquainted
with the literature and research work that reflected the
problems of the higher education system, the general
content of the higher education system, the prospects
and problems of the development of the higher
education system were paid much attention.
3 RESULTS
As you know, the only indicators of the quality of
education do not depend on the presence of a formed
professional mind. It is not for nothing that in modern
world practice, various conceptual and practical
approaches are used to assessing the quality of work
of higher educational institutions for the training of
specialists for various fields. Among them, attention,
effective and general approaches can be noted
separately.
We can also know this from the results of the
sociological study carried out. For example, the
respondents ' question "What do you want to do after
graduation?", analysing the answers to our question,
we will see the following indicators (Table 1).
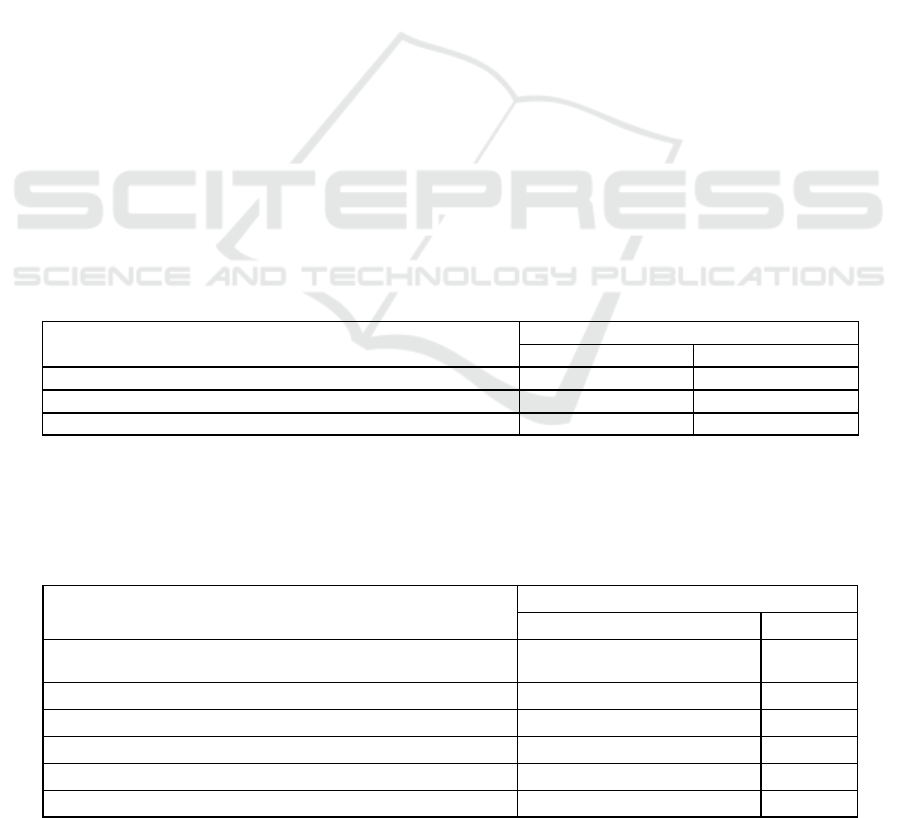
Table 1: What do you want to do after graduating from the High School?
What do you want to do after graduating from the University:
Selection group (in % account)
n-855 %
I work in government agencies (organizations) 425 50
I work in commercial institutions (organizations) 17 2
Continuing education (doctoral, second-higher education) 162 19
I am engaged in teaching activities 25 3
I am engaged in research activities 8 1
I'll start my own business 100 11.7
I dedicate myself to home, to my family 8 1
I will go abroad (to study). 175 20.5
The highest percentage, 50%, is held by government
organizations. 25% of respondents, on the other hand,
chose the post-tertiary stage, the basic doctorate. It
can be seen that the number of young people who
want to engage in scientific activities is also
increasing in later times. Those wishing to work
abroad were 20.5%.
According to the opinions of its researchers, an
Expert Mechanism is used to assess the professional
level of educational programs and educational
institutions. It is based on the measurement of
Cultivating Contemporary Professional Personnel: Evaluating Higher Education Standards and Reform Measures for Enhancement
487
quantitative indicators of university activity. The
general approach is based on the principles of
"universal quality Management " (TQM) and the
requirements for the quality management systems of
the International Organization for Standardization
(International Organization for Standardization,
ISO). This approach exists within two historically
formed quality assessment models. The first is based
on the internal self-esteem of the University academic
community. In France, it is based on the external
assessment of the University in terms of
responsibility for society and the state.
In general, there is no single system of institutional
evaluation of university activities in Europe. Each
country has its own approach to ensuring and
evaluating the quality of Higher Education. The main
elements of the quality assessment system in
Uzbekistan are standardization, licensing, certification
and accreditation of educational institutions. At the
same time, the basics of quality assessment are, first
of all, state educational standards and state
requirements. Educational standards of the
educational process in higher educational institutions
of Uzbekistan include requirements for all
components of the educational process, including
personnel, educational-methodological, material and
technical and information equipment. This was also
known in the results of the sociological survey. Will
you be given a variety of guides (guide, study
calendar, selection science catalogues, etc.)? when
asked, 39.8% of respondents specified that "not all
manuals are available to students". Also, 36.3% of
respondents answered Yes. Almost percentages are
close to each other, but opposite answers are felt. This
is a sign that the problem has not found a complete
solution (Table 2).
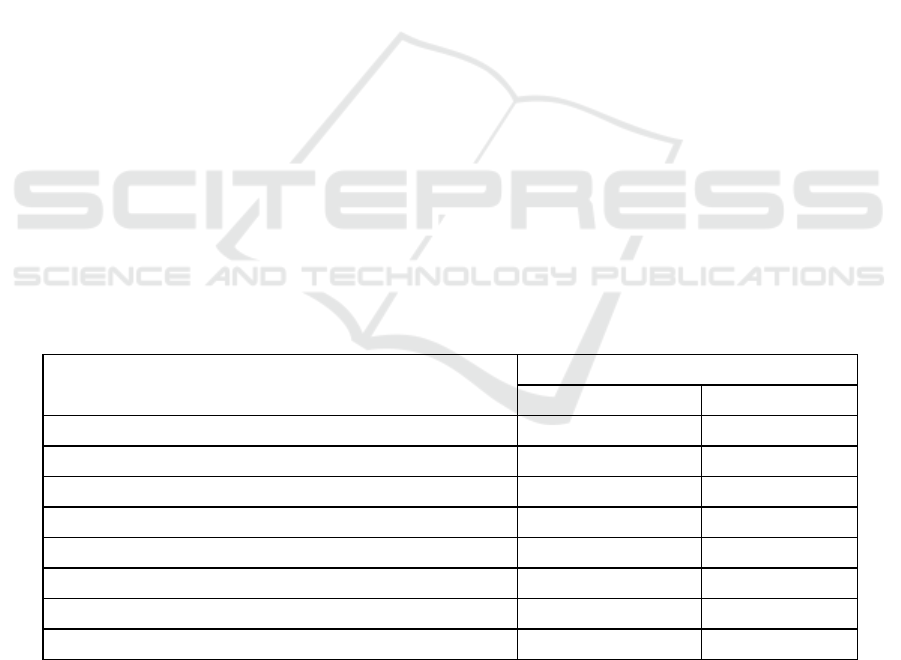
Table 2: Will you be given a variety of guides (guide, study calendar, selection science catalogues, etc.)
Will you be given a variety of guides (guide, study calendar,
selection science catalogs, etc.)?
Selection group (in % account)
n-855
Yes 310 36.3
Not all student guides are available 340 39.8
The package is issued for the Academic Team 50 5.9
Not provided 162 19
Diagram 1: Will you be given a variety of guides (guide, study calendar, selection science catalogues, etc.)?
With all the differences in approaches to the problem
of ensuring the level and effectiveness of Education,
Uzbekistan today focuses on the quality of education
in terms of its participation in the Bologna Process. A
number of regulatory legal acts adopted in recent
years are confirmation of this. One of the most
important tasks of the higher professional education
system is to develop a system for assessing the quality
of education and increase the demand for educational
services. After all, it is important. The concept of
long-term socio-economic development of
Uzbekistan for the period up to 2025 focuses on the
priority features of Higher Education.
0
10
20
30
40
36.3
39.8
5.9
19
Will you be given a variety of guides (guide, study calendar,
selection science catalogs, etc.)?
Yes, 100%
Not all student guides are available
The package is issued for the Academic Team
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
488
This shows that there are hundreds of problems
related to the quality of education waiting to be
solved.
Today, the status of a university is determined not
only by the traditional multiplier, but also by the
presence of a system of employment of graduates in
higher education, the possibility of continuing
education and improving the qualifications of
graduates, etc.
Modernization of the higher education system
makes it possible to see some incorrect calculations
in the implementation of the process of modernization
and implementation of a new system of assessing the
quality of Education. At the same time, effective
work is underway to develop and implement new
competency-based basic education programs for all
levels of education related to new legislation in the
field of Education. The implementation of work
aimed at practical results is one of the most important
indicators of the quality of education in terms of a
competent approach. For example, "how satisfied are
you with the different aspects of the educational
process?", 37.4 percent of respondents showed partial
satisfaction. 9.1% reported being unhappy (Table 3).
So, it follows from this that the organization of the
educational process does not correspond to the
requirements of today's reforms and modernization.
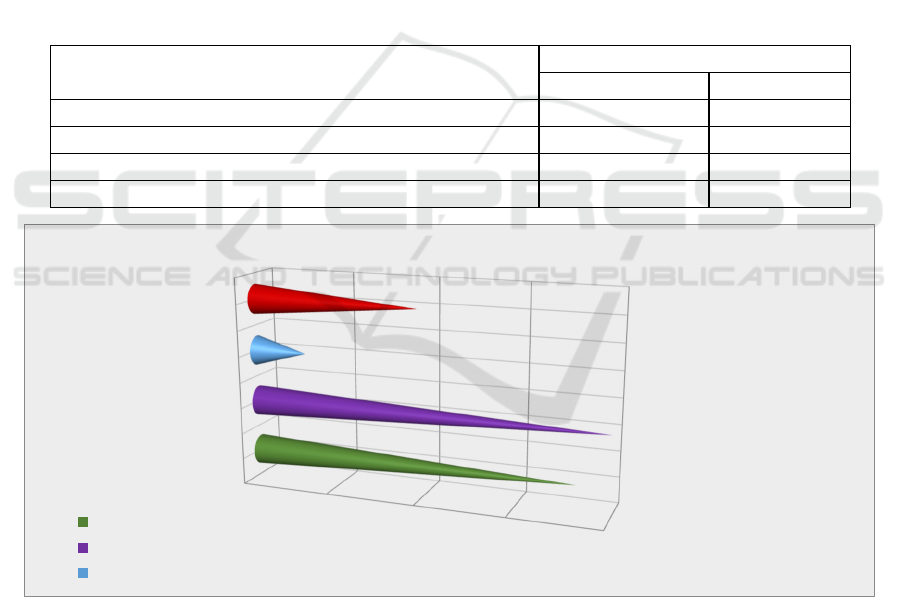
Table 3: How satisfied are you with the different aspects of the educational process"?
Selection group (in % account)
n-855
Lesson content 165 19.3
Using visual elements and tutorials 72.6 8.5
Awareness of changes in the educational process 102.6 12
Very pleased 117.1 13.7
Partially satisfied 319 37.4
Not satisfied 77.8 9.1
That is why there are now increasing demands for the
development of a plan of measures aimed at
supporting, financing institutions of Higher
Education.
Diagram 2: How satisfied are you with the different aspects of the educational process?
When preparing this report, industrial employers
noted a low level of satisfaction with the knowledge
and skills of university graduates. Almost half (49%)
of industrial firms show difficulties in finding
qualified professionals with higher education, and
only a third (33%) believe that today the skills of
university graduates are higher than ten years ago
(36% of respondents believe). Nor are there any
suggestions that knowledge and skills have declined.
It is worth noting that graduates of the higher
education system often do not work in their
specialties, for example, ".... only 57% of graduates
of pedagogical universities are employed in the field
of education, and in the field of construction,
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
Content of
the lesson
Using
visual
elements
and
tutorials
Awareness
of changes
in the
educational
process
very
satisfied
Partially
satisfied
Not
satisfied
n-855
165 72.6 102.6 117.1 319 77.8
%
19.3 8.5 12 13.7 37.4 9.1
Cultivating Contemporary Professional Personnel: Evaluating Higher Education Standards and Reform Measures for Enhancement
489
construction occupies three-quarters of all positions
intended for graduates of higher educational
institutions"[7]. Low coverage rates and poor
relationship between employers, industries, and
universities also limit the economy's potential for
innovation, technology customization, and value
added. Obviously, a lot of work needs to be done to
eliminate the gap between demand and supply,
preparing universities to meet the requirements of a
changing economy.
Harukhiko Kuroda, president of the Asian
Development Bank, said: "Uzbekistan's
achievements in social and humanitarian
development are admirable... Uzbekistan is
consistently advancing towards the achievement of
the Millennium Development Goals in the primary,
secondary and higher education sectors... The
educational model of Uzbekistan is not limited to the
establishment of educational institutions that meet the
most modern requirements. This model is primarily
based on quality, i.e., teachers, students, curricula
and, ultimately, improving the quality of knowledge.
In addition, this educational model, developed taking
into account the needs related to globalization, serves
as a means of ensuring that Uzbekistan occupies a
worthy place in Asia, in the world community as a
whole,", he noted.
Of course, this was a matter of several years ago.
In the following years, the higher education system is
constantly working to improve the standards and
requirements of Education. To this end, modern
forms of education, effective methods, new
information and educational technologies have been
developed and brought to life by higher education.
How much his social image has changed and how
reforms are working, we have analyzed similar issues
through our studies of the effects of serious changes
over the next five years and have witnessed a great
difference in certain aspects.
For example, "are professors creative and
enterprising in class?", 58.2 percent of respondents
gave the answer "yes, not all professors", and from
37.1 percent of the answers, we know that there are
not many teachers with skills and abilities that direct
creative, enterprising and students to work in
cooperation, to correctly assess the situation. Of
course, this is a sad situation. It is a sign that those
who get lost in a higher education institution or with
the support of someone will also meet. This does not
adversely affect the most important issues, such as the
implementation of the reforms that our country is
implementing and confidence in the future. 4.7% of
respondents claimed that teaching and tutoring
professors had no creativity at all, did not work on
themselves, and did not Research in the field. It can
be said that in the lecture or practical classes of such
people, students are bored and cannot concentrate,
and their coldness towards science also gradually
increases. The descendants of the new age and New
Age society will never forgive such a situation.
Table 4: Will professors be creative and enterprising in the lesson?
Will professors be creative and enterprising in the lesson?
Selection group (in % account)
n-855
Yes, most of the teachers 497.6 58.2
Few teachers 317.2 37.1
No 40.1 4.7
The period and age of information covering all areas,
as well as higher education, can be judged as the
greatest achievement. On this basis, in order to find
out the opinions of students, we addressed the
following question (Table 5).
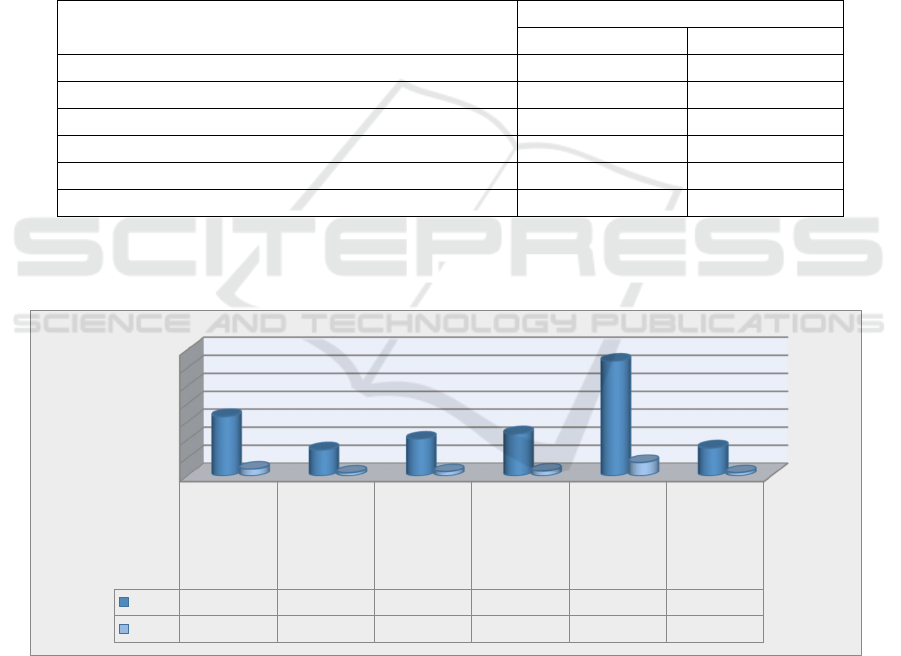
Table 5: How satisfied is it to provide information support to the educational process?
« How satisfied is it to provide information support to the
educational process »?
Selection group (in % account)
n-855 %
Availability of necessary scientific and educational literature in
the librar
y
322.5 37.7
Talim zharaenida foidalaniladigan computlar sony 70 8.2
Number of places in the study hall 47 5.5
Жудa мaмнунман 110 12.9
Partially satisfied 272 31.9
Not satisfied 75 8.8
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
490
As you know, information and resource centres are
organized in all SMS messages. From the answers to
questions about whether the situation in them is
suitable for today's demand, it turned out that 37.7%
of young people "have the necessary scientific and
educational literature in the library. "While 5.5%
reported few locations, 12.9% were very satisfied,
while 31.9% reported partial mannequin, 8.8% said
the state of the library was not satisfied at all. Such
aspects also reduce confidence in going to an
Information Resource Centre, learning something
there. And later, the attitude towards books can lead
to drastic changes if one cannot fully master a
particular subject and achieve the goal, irritability,
mental tension, and this can also cool down from
education.
Diagram 3: How satisfied is it to provide information support to the educational process?
Typically, there would be individuals or disciplines in
particular responsible for issues related to spirituality
and enlightenment. The situation is currently
changing. In order to clarify the educational work
carried out in addition to the auditorium in the
institution of Higher Education, the question "Are
you satisfied with the areas of extracurricular
activities and training carried out at the University
(Institute, Academy)?"with the question. Analysing
the results obtained, 37.4% determined that young
people were fully satisfied, while 43% gave a partial,
14.3% no response. 5.3% of the participants gave the
answer "No, at all". The conclusion follows that
sports training, clubs, reading hours, scientific circles,
competitions are not properly and rationally
established. The issue of youth leisure does not
correspond to the demand of the Times (Table 6).
Active youth around the world enrich their social
lives with the likes of going to orphanages with
disabilities to read books, organizing fun quiz games,
or going to a nursing home to volunteer to help them
explore their needs, in addition to organizing poetry
days at university leisure.
When we analysed the demographics of the
students of the higher education institution involved
in our studies, 67.8% were male and 32.2% were
female. This, of course, does not mean that women
are inferior in the Uzbek higher education system, nor
does it prove that there is a problem of gender
equality. Because in the higher education institutions
that we have researched, depending on the
professional orientation, we see that mainly men are
educated and that they are actively involved. For
example,"... men make up 60% of the students
entering universities (in the following years, the
proportion of women in universities decreased in
contrast to other countries in the Region)".
4 CONCLUSION
As a conclusion, it should be said that for the future
success of industrialized countries in the field of
knowledge and services, it is necessary not only to
improve higher education, but also to more clearly
understand that higher education is required,
combined with international actions of governments
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
Availability
of necessary
scientific
and
educational
literature in
the library
The number
of
computers
used in the
educational
process
Number of
seats in the
study hall
Very
satisfied
Partially
satisfied
Did not
satisfy
%
37.7 8.2 5.5 12.9 31.9 8.8
n-855
322.5 70.1 47 110.2 272.7 75.2
Cultivating Contemporary Professional Personnel: Evaluating Higher Education Standards and Reform Measures for Enhancement
491

and the private sector. The problem is that this
integration must be achieved while maintaining the
traditional universal goals of Higher Education.
When it comes to the international aspects of
university activities, they use different terms
"International Education", "internalization of
education", its "globalization", "transnational
education", etc. The term" international education " is
sometimes used to refer to international student
exchange programs, to attract foreign students, and to
send students to study abroad. Instilling in the youth
of our country the mood and idea of not getting an
education for a diploma, but of being a real,
competitive modern specialist, leads to the
achievement of significant achievements.
REFERENCES
Aristotle. On the Parts of Animals. Moscow: GIBML, 1998.
Alimardonov, T. National Education: Criticism and
Proposal. Tafakkur, Tashkent: Ma'naviyat, 2019. No.2.
p. 19.
Amanov, B.A. Sociophilosophical Analysis of the
Conceptual Models of Society Modernization: Ph.D.
diss., Tashkent, 2019. 250 p. Retrieved from
http://diss.natlib.uz/
Bim, Bad B.M. Philosophy of Education. Pedagogical
Encyclopedic Dictionary. Moscow, 2002.
Valitskaya, A.P. Russian Education: Modernization and
Free Development. Pedagogy, 2001. No. 7.
Data from MVSO, data from EdStats of the World Bank,
2013.
Kesaeva, P.E., Byazrova, T.T., Kantemirova-Kanukova,
G.A. Modernization of the Higher Professional
Education System in Russia. Fundamental Research,
2014. No. 9-6. pp. 1339-1342. URL:
http://www.fundamental-
research.ru/ru/article/view?id=35066.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
492
