
Analysing Healthcare App Satisfaction: Predictive Analytics Using
Stepwise Regression to Identify Key Factors
Arun Mittal
1a
, Nirmal Singh
2
, D. D. Chaturvedi
2
and Priyank Kumar Singh
3
1
Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra Ranchi, Off Campus: Noida, Noida, India
2
Sri Guru Gobind Singh College of Commerce, University of Delhi, New Delhi, India
3
School of Management, Doon University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
Keywords: Healthcare App, Customer Satisfaction, COVID-19 Pandemic.
Abstract: Healthcare applications have become essential tools for individuals seeking diverse health-related services.
These applications span from tracking fitness and reminding users to take medication to provide telemedicine
services. Their importance has been highlighted, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, where these
apps played a vital role in improving user satisfaction with public health management. A contented user is
more inclined to consistently interact with the app, follow prescribed treatment plans, and promote its use
among their circle of friends and family. The researcher considered 297 healthcare app users to conduct the
study survey and know the different factors that determine Customers' Satisfaction with Healthcare Apps
usage and the impact of different factors determining healthcare app usage on customers' satisfaction. The
study concludes that providing intuitive guidance, Value for money, saving time, user-friendly interfaces, and
Privacy protection have a significant impact on customers' satisfaction with healthcare apps usage.
1 INTRODUCTION
Healthcare apps have become indispensable tools for
users seeking various health-related services, with
applications ranging from fitness tracking and
medication reminders to telemedicine services. Their
significance has been further underscored during the
COVID-19 pandemic, where these apps played a
crucial role in enhancing users' contentment with
public health governance (Cao et al., 2022). However,
not all healthcare apps are equally successful in
attracting and retaining users. A satisfied customer is
more likely to engage with the app consistently,
adhere to prescribed treatment plans, and advocate for
its use among friends and family. Therefore,
exploring the multifaceted elements that contribute to
customer satisfaction is essential for healthcare
providers, app developers, and policymakers alike.
In understanding the determinants of customer
satisfaction for healthcare app usage, the importance
of functionality and intended health effectiveness
emerges as a central theme (Alnsour et al., 2017).
When healthcare apps effectively fulfil their intended
purpose while maintaining simplicity and appeal,
they tend to garner positive evaluations from users.
At the same time, overly complex functionalities that
are not seamlessly integrated can lead to negative
evaluations. Striking the right balance between
adding functionalities and preserving user appeal is
crucial for long-term user engagement and
satisfaction.
The proliferation of mobile health applications
(mHealth apps) in the healthcare landscape highlights
the critical factors influencing user satisfaction.
Usability, scientific validation, and ethical
considerations play pivotal roles in shaping user
satisfaction. Usability factors such as user-friendly
interfaces and reliable data recording are vital, as is
the assurance that information provided is
scientifically validated (Pires et al., 2020). Adherence
to ethical principles, like privacy protection and
trustworthiness, is also important in fostering user
confidence and satisfaction. Features such as plans or
orders, export of data, usability, and Value for money
affect user ratings. Users highly value apps that save
time, provide intuitive guidance for condition
management, and allow data sharing with designated
individuals. Interestingly, the tracker feature, while
negatively correlated, is positively linked with the
export of data and usability features, suggesting that
an efficient tracking process and meaningful output
display are essential for users' evaluation (Mendiola
et al., 2015).
514
Mittal, A., Singh, N., Chaturvedi, D. and Singh, P.
Analysing Healthcare App Satisfaction: Predictive Analytics Using Stepwise Regression to Identify Key Factors.
DOI: 10.5220/0012874200003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 514-518
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

By exploring the role of mHealth apps during
critical public health concerns like the COVID-19
pandemic, assessing functionality and appeal,
examining usability, scientific validation, and ethical
considerations, and delving into specific app features,
this paper aims to provide valuable insights for
healthcare app development and marketing.
Understanding and enhancing these elements is
pivotal for fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty
in the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare apps.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The study by Wu et al. (2022) reveals that perceived
reliability and online reviews significantly impact
users' intention to continue using healthcare apps,
particularly mobile health applications (mHealth
apps). These factors positively influence users' e-
satisfaction, with e-satisfaction playing a mediating
role. Habit formation is identified as crucial in
sustaining mHealth app usage, emphasizing the
importance of fostering user habits for app success. A
strong habit reinforces the connection between e-
satisfaction and the willingness to continue using
these healthcare apps. Online reviews and perceived
reliability are key elements influencing continued app
usage due to the availability of reliable health
information.
Health apps have the potential to contribute to
senior health promotion, yet they often struggle with
low user retention rates. To enhance continued usage
of health apps among them it is important to foster
health technology self-efficacy and self-evaluative
outcome expectations. Knowledge about technology
and better usage of it can enable older adults to get
better accessible healthcare and promoting senior
friendly app design for health apps can improve long
term health behaviours in this demographic (Kim &
Han, 2021).
Anderson et al. (2016) investigated the factors of
consumer engagement with healthcare apps,
emphasizing the factors shaping customer
satisfaction, and found that key elements influencing
user behaviour and satisfaction are app usage
patterns, engagement themes, gamification, medical-
purpose apps, device convenience, perceived self-
management benefits, and integration with healthcare
professionals. With a growing demand for self-care,
especially among the elderly managing chronic
conditions, it's crucial to understand how users
interact with these electronic self-monitoring tools.
In a study by Pal et al. (2023), the focus was on
user experiences and satisfaction with mobile health
(mHealth) platforms, which gained prominence
during the COVID-19 pandemic. They identified key
factors influencing user experiences, including time,
cost, convenience, responsiveness, and availability.
These factors were categorised into two dimensions:
strategic adoption and motivational association. They
also highlighted the significance of review sentiment
in shaping brand perception and enjoyable
motivation, especially in aspects like online booking
and video consultations.
User satisfaction with healthcare apps,
particularly during public health crises like COVID-
19, relies on factors such as functionality,
performance, and meeting expectations, with a
specific focus on features like vaccination. This
satisfaction significantly impacts app usage. App
developers and policymakers must prioritise
improving aspects like functionality, information,
performance, security, design, and overall quality to
ensure user satisfaction and effective app utilization,
especially during such critical times (Samsuri et al.,
2022).
Users share their app experiences through various
types of reviews, including bug reports, feature
requests, performance evaluations, and user interface
feedback. It is important to identify categories like
bugs, usability, and performance, which are key
factors in determining user satisfaction with
healthcare apps as by improving these aspects based
on user feedback, app developers can enhance
customer satisfaction (Al Kilani et al., 2019).
Yu & Huang (2020) studies how to enhance user
experiences and satisfaction in yoga apps, particularly
the Daily Yoga app and identified sense, feel, think,
act, and relate as key factors that influences user
satisfaction. This highlights the significance of an
attractive interface, data record, and yoga classes in
improving user satisfaction.
Reddy et al. (2022) examined factors impacting
consumer satisfaction with healthcare apps in the
context of telemedicine during the COVID-19
pandemic in India and found high user satisfaction
but also the need for app interface improvements.
Critical factors influencing consumer attitudes
include reliability, proximity to health services, and
overall user experience, with age, education, and
income influencing perceptions. These apps have
reduced patient exposure and enabled remote care,
emphasizing their importance.
Fu et al. (2023) explored the complex landscape
of user satisfaction and continued usage intention of
m-health management apps, an area that is
increasingly vital in the context of modern health
assistance programs and found that the factors driving
m-health app success and customer loyalty mostly
depends on aligning app features with genuine user
desires. Ultimately, these insights have significant
practical implications for businesses and researchers,
guiding them in making informed decisions to
Analysing Healthcare App Satisfaction: Predictive Analytics Using Stepwise Regression to Identify Key Factors
515
enhance app functionality and better meet user needs,
thereby ensuring long-term business success in the
ever-evolving m-health landscape.
As people become more health-conscious,
healthcare apps have become popular and it has
become important to consider social factors like
subjective norms and personal factors such as how
users feel while using the app, their awareness of
health, and strategies for changing behaviour while
analysing user response to these apps. The extent to
which users find the apps useful and easy to use
directly influences their experience using them, and
the behaviour-changing techniques all affect whether
they'll keep using the app. Satisfaction plays a role in
this too. How health-conscious someone is can affect
how useful and easy they find the app, and how
satisfied they are with it (Yan et al., 2021).
The perception of vulnerability positively affects
users' belief in their abilities and the effectiveness of
protective actions, shaping their attitudes and
continued app usage. The presence of network
externalities, both direct and indirect also plays a vital
role in determining user attitudes, which, in turn,
impact ongoing app use. Direct network externalities
indirectly affect usage behaviour through attitudes
that serve as a key mediator between psychological
factors and continued usage, although other mediators
may exist. Demographic factors such as age and
education level also influence users, with older and
more educated individuals exhibiting higher self-
efficacy, response efficacy, and a stronger intention
to keep using m-health apps (Luo et al., 2021).
3 OBJECTIVES
• To explore the factors determining customer
satisfaction for healthcare app usage.
• To ascertain the impact factors determining
healthcare app usage on customers'
satisfaction.
4 METHODOLOGY
The researcher considered 297 healthcare app users to
conduct the study survey and know the different
factors that determine Customers' Satisfaction with
Healthcare app usage and the impact of different
factors determining healthcare app usage on
customers' satisfaction.
5 DATA ANALYSIS
Table 1: Factors determining customers' satisfaction.
S. No
Factors determining customers'
satisfaction
1. Fitness tracking
2. Reliable data recording
3. User-friendly interfaces
4. Scientifically validated information
5. Privacy protection
6. Trustworthiness
7. Value for money
8. Save time
9. Provide intuitive guidance
10.
Allow data sharing with designated
individuals
Table 2: Model Summary.
Model R R Square
Adjusted R
Square
Std. Error of the
Estimate
1 .723
a
.522 .520 .57752
2 .747
b
.558 .555 .55664
3 .758
c
.575 .571 .54645
4 .764
d
.584 .579 .54140
5 .769
e
.591 .584 .53791
To evaluate the necessity of dimensions of different
factors in predicting customer satisfaction, stepwise
multiple regression was applied. Table 2 shows
multiple linear regression model summaries and
overall fit statistics for the dependent variable
customer’s satisfaction with healthcare app usage.
The multiple correlation coefficient of model 1 is
.723, indicating approximately 52% of the variance of
customer satisfaction could be accounted for Provide
intuitive guidance. The multiple correlation
coefficient of model 2 is .747, indicating
approximately 55% of the variance in customer
satisfaction could be accounted for by providing
intuitive guidance and Value for money. The multiple
correlation coefficient of model 3 is .758, indicating
approximately 57% of the variance in customer
satisfaction could be accounted for by providing
intuitive guidance, value for money, and Saving time.
The multiple correlation coefficient of model 4 is
.764, indicating approximately 58% of the variance in
customer satisfaction could be accounted for by
providing intuitive guidance, Value for money,
Saving time, and User-friendly interfaces. The
multiple correlation coefficient of model 5 is .769,
indicating approximately 59% of the variance of
customer satisfaction could be accounted for by
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
516
providing intuitive guidance, Value for money,
saving time, User-friendly interfaces, and Privacy
protection.
The results of ANOVA indicate that the
dependent variable (customer satisfaction) is
statistically and significantly predicted by the
independent variables (Providing intuitive guidance,
Value for money, saving time, User-friendly
interfaces, and Privacy protection) across all the
models.
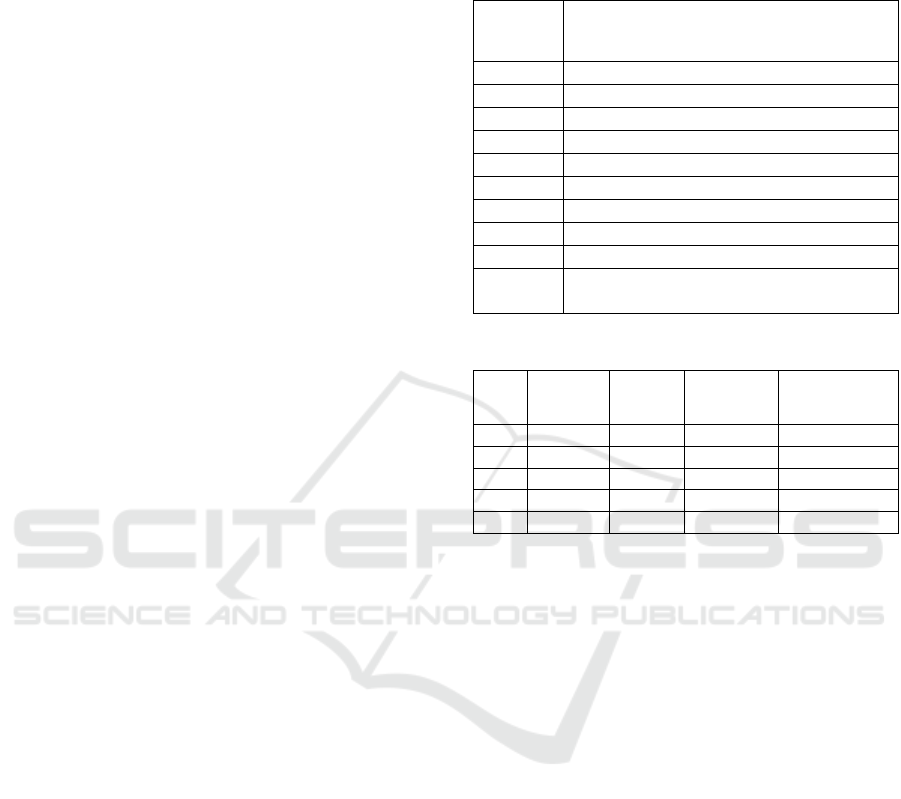
Table 3: Coefficients.
Model
Unst.
Coeff.
St. Coeff.
t Sig.
B
Std.
Erro
r
Beta
(
Constant
)
.221 .198 1.116 .265
Provide
intuitive
g
uidance
.280 .080 .282 3.507 .001
Value for
mone
y
.190 .068 .182 2.794 .006
Save time .271 .082 .264 3.305 .001
User-friendly
interfaces
.083 .037 .092 2.246 .025
Privacy
p
rotection
.097 .044 .092 2.191 .029
DV: Customer Satisfaction
Table 3 shows that there is a significant impact of
Provide intuitive guidance, Value for money, saving
time, User-friendly interfaces, and Privacy protection
on customers' satisfaction with healthcare app usage.
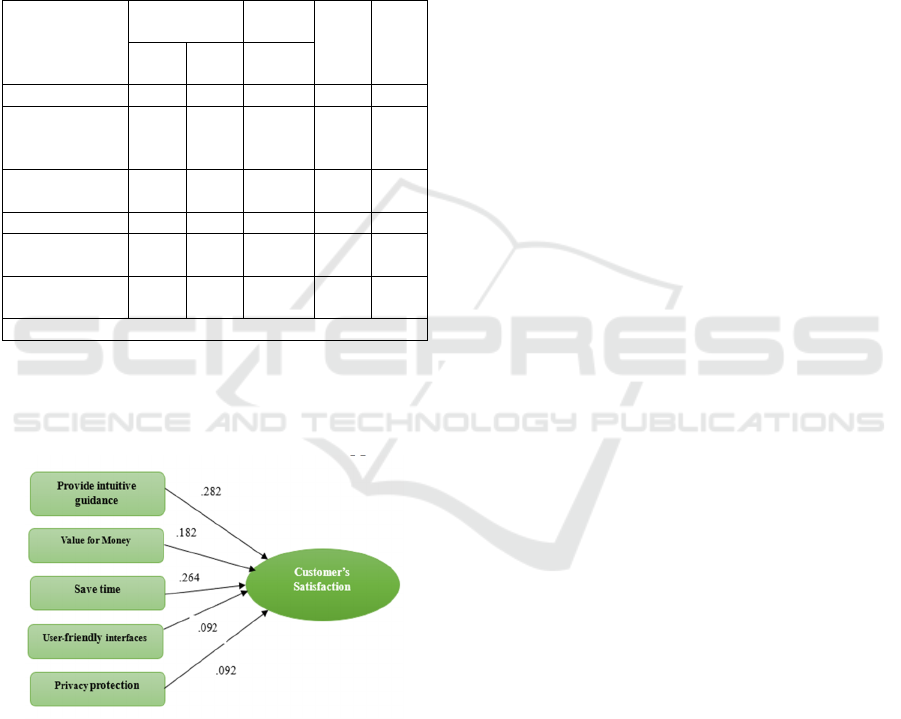
Figure 1: Impact of different factors determining
Customers' satisfaction for healthcare apps usage.
Figure 1 shows the unstandardized beta values for
each independent variable with its relationship to the
dependent variable. It may be interpreted from the
values that Provide Intuitive Guidance as the most
important variable with a beta value of .282 followed
by Save Time with (.264), Value for Money (.192),
User-Friendly Interface (.092) and Privacy Protection
(.092).
6 CONCLUSION
Healthcare apps have evolved into indispensable
tools for individuals seeking a range of health-related
services. From monitoring fitness and sending
medication reminders to offering telemedicine
services, these applications play a crucial role. Their
significance became even more pronounced during
the pandemic, where they played a vital role in
enhancing user satisfaction with public health
management. A satisfied user is more likely to engage
consistently with the app, adhere to prescribed
treatment plans, and advocate for its use in their
network. The study was conducted to know the
impact of different factors determining healthcare app
usage on customers' satisfaction. It is found that
factors like Providing intuitive guidance, Value for
money, saving time, User-friendly interfaces, and
Privacy protection have a significant impact on
customers' satisfaction with healthcare app usage.
REFERENCES
Al Kilani, N., Tailakh, R., & Hanani, A. (2019). Automatic
Classification of Apps Reviews for Requirement
Engineering: Exploring the Customers Need from
Healthcare Applications. Sixth International
Conference on Social Networks Analysis,
Management and Security (SNAMS), 541–548.
Alnsour, Y., Hazarika, B. B., & Khuntia, J. (2017). Health
Apps’ Functionalities, Effectiveness, and Evaluation.
Lecture Notes in Business Information Processing,
296, 13–21.
Anderson, K., Burford, O., & Emmerton, L. (2016). Mobile
Health Apps to Facilitate Self-Care: A Qualitative
Study of User Experiences. PLOS ONE, 11(5), 1–21.
Cao, J., Zhang, G., & Liu, D. (2022). The Impact of Using
mHealth Apps on Improving Public Health
Satisfaction during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A
Digital Content Value Chain Perspective. Healthcare,
10(3), 1–19.
Fu, Y., Wang, Y., Ye, X., Wu, W., & Wu, J. (2023).
Satisfaction with and Continuous Usage Intention
towards Mobile Health Services: Translating Users’
Feedback into Measurement. Sustainability, 15(1101),
1–21.
Kim, E., & Han, S. (2021). Determinants of Continuance
Intention to Use Health Apps among Users over 60: A
Test of Social Cognitive Model. International Journal
of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(19),
1–19.
Luo, Y., Wang, G., Li, Y., & Ye, Q. (2021). Examining
Protection Motivation and Network Externality
Perspective Regarding the Continued Intention to Use
M-Health Apps. International Journal of
Analysing Healthcare App Satisfaction: Predictive Analytics Using Stepwise Regression to Identify Key Factors
517

Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(11),
1–17.
Mendiola, M. F., Kalnicki, M., & Lindenauer, S. (2015).
Valuable Features in Mobile Health Apps for Patients
and Consumers: Content Analysis of Apps and User
Ratings. JMIR MHealth and UHealth, 3(2), 1–14.
Pal, S., Biswas, B., Gupta, R., Kumar, A., & Gupta, S.
(2023). Exploring the factors that affect user
experience in mobile-health applications: A text-
mining and machine-learning approach. Journal of
Business Research, 156, 1–15.
Pires, I. M., Marques, G., Garcia, N. M., Flórez-Revuelta,
F., Ponciano, V., & Oniani, S. (2020). A Research on
the Classification and Applicability of the Mobile
Health Applications. Journal of Personalized
Medicine, 10(1), 1–30.
Reddy, L. K. V., Madithati, P., Narapureddy, B. R., Ravula,
S. R., Vaddamanu, S. K., Alhamoudi, F. H., Minervini,
G., & Chaturvedi, S. (2022). Perception about Health
Applications (Apps) in Smartphones towards
Telemedicine during COVID-19: A Cross-Sectional
Study. Journal of Personalized Medicine, 12(11), 1–
12.
Samsuri, A. S., Hussin, S. M., Badaruddin1, M. N. A.,
Arifin, T. R. T., Zainol, S. S., & Mohamad, Z. Z.
(2022). Antecedents of User Satisfaction and
Continuance Usage of Mobile Health Applications: A
Study on MySejahtera Apps in Malaysia. Asian
Journal of Behavioural Sciences, 4(2), 91–105.
Wu, P., Zhang, R., Zhu, X., & Liu, M. (2022). Factors
Influencing Continued Usage Behavior on Mobile
Health Applications. Healthcare, 10(2), 1–18.
Yan, M., Filieri, R., Raguseo, E., & Gorton, M. (2021).
Mobile apps for healthy living: Factors influencing
continuance intention for health apps. Technological
Forecasting and Social Change, 166, 1–13.
Yu, N., & Huang, Y.-T. (2020). Important Factors
Affecting User Experience Design and Satisfaction of
a Mobile Health App—A Case Study of Daily Yoga
App. International Journal of Environmental
Research and Public Health, 17(19), 1–16.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
518
