
A Descriptive Study on Productivity of Generation Z Employees in
Call Centers of Bhopal
Marrium Khan
1
, Sumit Kishore Mathur
2
, Nileshwari Yadav
3
, Om Prakash Kumar
1
and Chintan Rajani
4
1
Department of Business Management and Studies, IES University, Bhopal, M.P. 462044 India
2
Oriental College of Management, Bhopal, M.P 462021 India
3
Department of Management, Truba Institute of Science and Commerce, M.P. 462044 India
4
School of Management, RK University, Gujarat India
Keywords: Generation Z, Call Centers, Workforce Productivity.
Abstract: This study examines the productivity of Generation Z employees within selected call centers in the Bhopal
Division, recognizing the pivotal role of this generation in the modern workforce landscape. Those who are
born in between 1990 and early 2010, Generation Z brings forth distinct characteristics, expectations, and
work methodologies, warranting a focused investigation into their contributions to workplace productivity.
With this generation increasingly entering the workforce, particularly in dynamic settings like call centers,
there is a pressing need to comprehend their impact on productivity. The study is prompted by the realization
that the workforce is undergoing a notable generational transition, with Generation Z gradually replacing or
collaborating with previous generations across industries. By delving into the productivity of Generation Z
within call centres, this research, with a sample size of 100 respondents, aims to furnish employers and
managers with valuable insights necessary for formulating effective strategies to leverage the potential of this
emerging workforce where key findings suggest a consistent approach to productivity across different age
groups within the Generation Z cohort, emphasizing the stability of productivity-related values and behaviours
among younger employees in the workforce.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, scholars have redirected their
research focus from Millennial, who have been
extensively studied for decades, to Generation Z—the
demographic born between 1997 and 2013 (Michael
D, 2019). This transition stems from the
acknowledgment that each generation (Chillakuri B,
2020; Thach L, Riewe S, and Camillo A, 2020),
including Millennials and Generation Z, harbors
distinct expectations related to work and aspirations,
in spite of exhibiting some shared behaviours
(Schroth H, 2019). It is imperative for organizations
aiming to attract this cohort to comprehend the unique
anticipation of Generation Z job seekers. Notably, the
expectations of Gen Z job seekers differ from those
of their predecessors, and yet, they constitute a
significant portion of the global population,
comprising of about one-third from 7.7 billion people
worldwide, with a substantial presence in emerging
countries (Thach L, Riewe S and Camillo A, 2020).
As organizations prepare for this influx of new
employees, it becomes imperative to adapt to the
distinct characteristics and expectations that
Generation Z brings to the workforce.
The modern workplace landscape is undergoing a
transformative shift, driven by the influx of a fresh
cohort entering the workforce—Generation Z, born
between the mid-1990s and early 2010s, arrives with
a distinct skill set, values, and attitudes that
significantly influence the dynamics of various
industries. In the realm of call centers, where
efficiency, communication, and adaptability are
paramount, understanding the productivity of
Generation Z employees is crucial for optimizing
operations and ensuring organizational success. In
contrast to earlier generations, Generation Z came of
age in a digital era characterized by rapid
technological advancements and unprecedented
access to information. This exposure has not only
542
Khan, M., Mathur, S., Yadav, N., Kumar, O. and Rajani, C.
A Descriptive Study on Productivity of Generation Z Employees in Call Centers of Bhopal.
DOI: 10.5220/0012878800003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 542-545
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

shaped their communication styles but has also
cultivated a strong inclination toward innovation. Call
centers, as hubs of customer interaction, benefit from
these characteristics as Generation Z employees
effortlessly navigate diverse communication channels
and leverage advanced tools to enhance productivity.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Generation Z encompasses individuals born between
1995 and 2010, a span characterized by the
widespread expansion of the World Wide Web.
(Wood, 2013). This cohort is recognized by a
multitude of names, many of which underscore their
close association with technology, the internet, and
social media. Some commonly employed labels
include Internet Generation or IGen (Dorsey, 2016),
Post Millennials, Centennials (Dorsey, 2016), Digital
Natives (Mohr & Mohr, 2017; Seemiller & Grace,
2016), Plurals, Gen Wii, and Generation Text
(Flippin, 2017). The adoption of such nomenclature
for Generation Z stems from the fact that they are the
first generation born into a world characterized by
global connectivity, where the Internet has been
omnipresent throughout their lives, deemed an
essential tool for daily lives (Turner, 2015).
Additionally, the behaviours of learning and work
among Generation Z are shaped by various influences
by unique experiences inherent to their upbringing,
such as they enter into the job place with limited
experience, the extra use of gadgets and social
platforms, participation in social justice movements,
and exposure to a culture that gives importance to
safety as a priority. (Schroth, 2019). As Generation Z
enters the workforce, they bring forth unique
characteristics that manifest in their skills, needs,
expectations from employers, and workplace
behaviour.
P.S. Sibi's (2023) study explores how personal
traits and the influence of social life affect Generation
Z's loyalty to tourism websites. Unlike previous
models, it considers factors like perceived
compatibility and innovativeness, alongside
subjective norms, in shaping trust and usefulness.
This research highlights the crucial role of the
personal characteristics and social influence in
Generation Z's e-loyalty toward tourism websites,
offering insights into technology adoption in this
demographic.
Thang Nguyen's (2022) study highlights
understanding the anticipation and career aspirations
of Generation Z seeking for job is crucial for
organizations. Focused on Vietnam, the study aims to
bridge research gaps in transition and emerging
economies. It investigates the preferences of
Vietnamese Generation Z job seekers, revealing a
greater emphasis on intangible attributes like office
atmosphere and workplace ethics over physical
features when evaluating job
Meilani, Tan, Murwani, Bernarto, and Sudibjo
(2021) undertook a study focusing on Generation Z
faculty members in private Indonesian universities.
The research delved into the individual motivations,
job satisfaction, and organizational commitment of
these faculties, examining their impact on overall
performance. Employing an exploratory research
approach, structured interviews were conducted to
gather data from 10 faculty members and their
respective supervisors in five private universities
across Indonesia. The study yielded managerial
implications, emphasizing the importance of
providing clear targets and procedures, granting
autonomy, and establishing clear career guidelines to
retain Generation Z faculty members.
Alexandra Broennimann's (2017) research
centered on Generation Z within the hospitality
management student population in Switzerland. The
study investigated their evolving needs, upbringing,
characteristics, and job preferences, emphasizing the
impact of digitalization. Notable findings included
limited multitasking proficiency and a desire for
societal change. Broennimann provided valuable
insights and recommendations for the hospitality
industry to better engage and manage Generation Z.
2.1 Research Objectives
1. To understand and profile the Gen Z through their
characteristics, values & Behavior.
Hypotheses
H01: There exists no notable contrast in the
characteristics Values &Behaviour of Gen-Z Male
and Female Employees towards the Productivity.
H02: There exists no notable contrast in the
characteristics, Values &Behaviour of Gen-Z
Employees’ age group between 18-23 Years and 24-
28 Years towards the Productivity.
Data Analysis
For the examination of the demographic profile of
Generation Z employees of Bhopal Division and the
identification of the variables most closely linked to
productivity within Generation Z, descriptive
statistics were employed. The overall means and
standard deviations of all constructs were computed,
test, ANOVA, Regression are applied in utilizing the
Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) to
fulfil this objective.
A Descriptive Study on Productivity of Generation Z Employees in Call Centers of Bhopal
543
3 RESULTS
H01: There exists no notable contrast in the
characteristics Values & Behaviour of Gen-Z Male
and Female Employees towards the Productivity
With a p-value of .825 exceeding the .05
threshold (at a 5% level of significance), it suggests
acceptance of the null hypothesis for the
Characteristics of Gen-Z Male and Female
Employees, for the Values of Gen Z male and female
employees is also not significant at .802, likewise
Behaviour of Gen Z male and female employees is
not significant at .837. Therefore, H01 (There exists
no notable distinction in the Characteristics, Values
&Behavior of Gen-Z Male and Female Employees
towards the Productivity) is accepted. Hence, it may
be concluded that Characteristics, Values &Behavior
of Gen-Z Male and Female Employees do not differ
for the Productivity.
H02: There exists no notable distinction in the
Characteristics, Values &Behaviour of Gen-Z
Employees’ age group between 18-23 Years and 24-
28 Years towards the Productivity.
Given that the p-value of .078 exceeds the .05
threshold (at a 5% level of significance), the null
hypothesis is retained for the Characteristics of Gen-
Z Employees’ age group between 18-23 Years and
24-28 Years, for the Values of Gen Z employees’ age
group between 18-23 Years and 24-28 Years is also
not significant at .223, likewise Behaviour of Gen Z
employees’ age group between 18-23 Years and 24-
28 Years is not significant at .227. Therefore, H02
(There exists no notable distinction in the
Characteristics, Values &Behaviour of Gen-Z
Employees’ age group between 18-23 Years and 24-
28 Years towards the Productivity) is accepted.
Hence, it may be concluded that Characteristics,
Values &Behaviour of Gen-Z Employees’ age group
between 18-23 Years and 24-28 Years do not differ
for the Productivity.
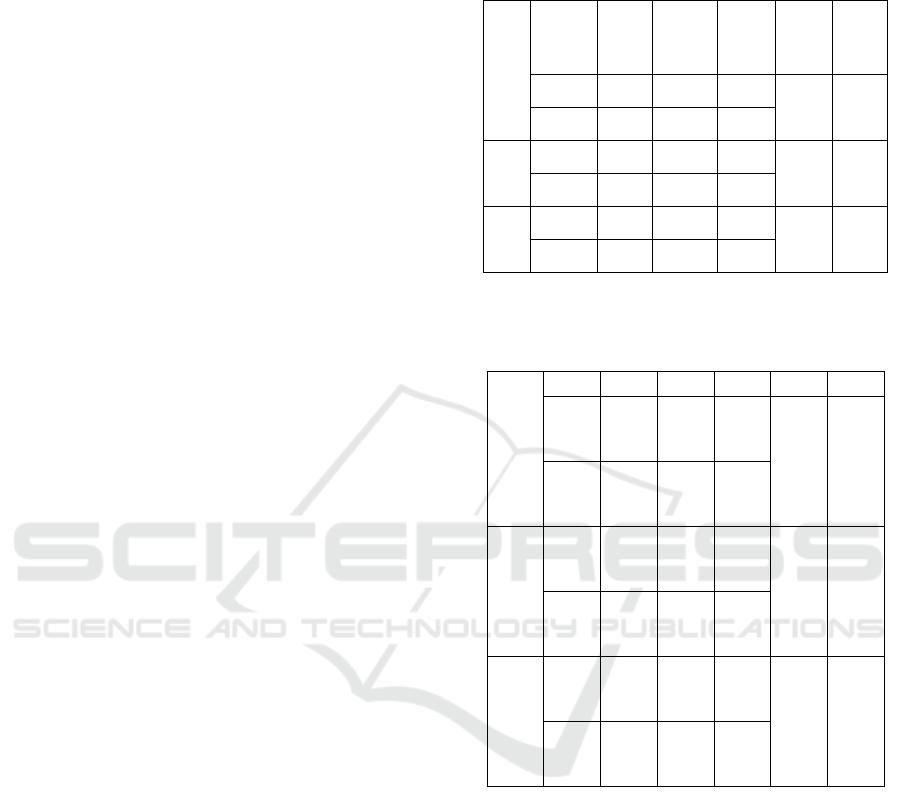
Table 1: Showing t -test for significant difference in
characteristics, values & behaviour of gen-z male and
female employees.
Characteristics
Gender
N
Mean
SD
t-
Value
p-
value
(0.05)
F
123
10.56
3.59
.221
.825
M
377
10.47
3.65
Values
F
123
10.54
3.71
.251
.802
M
377
10.44
3.83
Behavio
ur
F
123
10.83
3.80
.205
.837
M
377
10.74
3.92
Table 2: Showing T -Test For Significant Difference In
Characteristics, Values & Behaviour Of Gen-Z Employees’
Age.
Characteristics
Age
N
M
e
a
n
SD
t
-
V
a
l
u
e
p
-
v
a
l
u
e
(
0
.
0
5
)
18-23
310
10.7
2
3.5
3
1.766
.078
24-28
190
10.
13
3.7
9
Values
18-23
310
10.
63
3.6
6
1.221
.223
24-28
190
10.
20
4.0
0
Behaviour
18-23
310
10.
93
3.8
1
1.209
.227
24-28
190
10.
49
4.1
1
4 FINDINGS
The findings of the study indicate that there is no
statistically meaningful contrast in the productivity-
related traits between male and female employees of
Generation Z. The analysis encompassed various
aspects of professional traits, work habits, and
personal attributes, and the results indicate a
consistent pattern of similarity between male and
female employees belonging to Generation Z. It is
found that both male and female Gen-Z employees
exhibited comparable levels of professionalism in
their work. This includes factors such as punctuality,
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
544

adherence to company policies, and commitment to
their roles.
The study findings indicate that there is no
statistically noteworthy distinction in the traits of
Generation Z employees within the age groups of 18-
23 years and 24-28 years concerning their
productivity. This implies that, within the context of
the studied parameters, the productivity-related
characteristics of Generation Z employees remain
relatively consistent across the specified age brackets
of 18-23 years and 24-28 years.
The study's results suggest that there is no
statistically meaningful variation in the productivity-
related values between two distinct age groups within
the Generation Z employee cohort. Specifically, the
comparison between individuals aged 18 to 23 years
and those aged 24 to 28 years reveals a lack of
substantial variance in their attitudes, beliefs, and
perspectives concerning productivity. This suggests a
consistency in the values embraced by Generation Z
employees across these age brackets when it comes to
their approach and commitment to work output.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The study on Generation Z productivity in Bhopal
Division call centers reveals valuable insights into
this emerging workforce. Notably, Generation Z's
digital proficiency matches the technological
demands of call centers, highlighting a shift in work
preferences towards remote options. Adapting
organizational structures to embrace digital
transformation and flexibility can enhance
productivity and job satisfaction among Generation Z
employees.
REFERENCES
Dimock, M. (2019). Defining generations: Where
Millennials end and Generation Z begins. Pew
Research Center, 17.
Dorsey, J. (2016), IGEN Tech Disruption, The Center for
Generational Kinetics. Retrieved from:
https://genhq.com/wpcontent/uploads/2016/01/iGen-
Gen-Z-Tech-Disruption-ResearchWhite-Paper-c-2016-
Center-for-Generational-Kinetics.pdf
Flippin, C.S. (2017). Generation Z in the Workplace:
Helping the Newest Generation in the Workforce Build
Successful Working Relationships and Career Path.
Candace Steele Flippin, New York
Goh, E., &Okumus, F. (2020). Avoiding the hospitality
workforce bubble: Strategies to attract and retain
Generation Z talent in the hospitality workforce.
Tourism Management Perspectives, 33, 100603.
Gomez, S. C. (2019). Generation Z in the Workplace: A
Study of Productivity in Call Centers. Workplace
Trends.
Meilani, Y. F. C. P., Tan, J. D., Murwani, F. D., Bernarto,
I., & Sudibjo, N. (2021). Motivating and retaining
Generation Z faculty members in private universities.
Journal of Educational and Social Research, 11(1), 245-
245.
Mohr, K.A. J. & Mohr, E.S. (2017). Understanding
Generation Z Students to Promote a Contemporary
Learning Environment. Journal on Empowering
Teaching Excellence, 1(1), 84-94
P.S. Sibi (2023) E-loyalty formation of Generation Z:
Personal characteristics and social influences. Journal
of Tourism, Heritage & Services Marketing, Vol. 9, No.
1, pp. 3-14
Schroth, S. (2019). Are You Ready for Gen Z in the
Workplace? California Management Review, 61(3), 5-
18
Seemiller, C. & Grace, M. (2016). Generation Z Goes to
College, Jossey-Bass, San Francisco.
A Descriptive Study on Productivity of Generation Z Employees in Call Centers of Bhopal
545
