
Empirical Analysis of Financial Inclusion: Case Study of Madhya
Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
Reshma Udhani
1
, Sunita Ramchandani
2
and Marrium Khan
1
1
Department of Business Management & Studies, IES University, Bhopal, M.P. 462044, India
2
Sant Hirdaram Institute of Management, Barkatullah University, Bhopal, India
Keywords: Financial Exclusion/Inclusion, Financial Services, Credit, Saving.
Abstract: The sustainable growth requires a holistic approach, where all members of the society grow equally. This
study compares two states—Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh in an effort to analyze financial inclusion,
including the use of banking and other regulated products at an affordable price. To support the study, primary
data has been gathered from different rural areas in both states during 2023. Primary information was collected
from 200 households for each state. Financial inclusion is receiving attention from all around the world since
it has been identified as one of the main causes of poverty. The findings of the study show Madhya Pradesh
has performed a little better as compared to Chhattisgarh in making the population of the state financially
inclusive.
1 INTRODUCTION
Financial inclusion refers to offering conveniently
accessible and reasonably priced financial services to
commercial and retail clients who are shut out of the
system. The financial sector, which includes banks
and other financial organizations like the post office,
insurance providers, brokers, investment funds, and
so forth, is responsible for providing the majority of
financial services. Although there are many different
definitions of financial inclusion, the majority of
research focused on using basic banking services such
deposits, loans, microfinance, payment services,
money transfers, insurance, and financial literacy.
Madhya Pradesh, which has the 10th largest
economy in India, ranks 26th in terms of per capita
income, with an annual gross domestic product
(GDP) of $9.17 trillion (US$130 billion). The state's
growth rate for GDP is 8.22%. One of the Indian
states with the quickest rates of growth is thought to
be Chhattisgarh. With a GSDP per capita of
Rs.102,762, its Gross State Domestic
Product (GSDP) is currently *3.63 lakh crores.
Despite significant progress, many populations in
these states remain underserved by formal financial
institutions due to geographical remoteness,
inadequate infrastructure, low literacy rates, and
cultural barriers. However, governmental policies,
technological innovations, and collaboration between
public and private stakeholders have led to significant
advancements.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Radhika K. and Dr. P. Indrasena Reddy (Oct’2021) in
their study, they came to the conclusion that the
Indian government is committed to raising the
country's financial inclusion. Initiative programs
from the government and RBI are improving people's
access to financial services.
Usha Srivastava, (Feb’2018), evaluated the
expanding financial literacy initiatives in
Chhattisgarh and found that HDFC Bank Ltd.
launched its rural financial literacy program in the
Chhattisgarh village of Jamgaon under the direction
of the RBI.
C. Annamalai and K.Vijayarani (2014) the study
came to the conclusion that, in spite of the scheme's
strong social objective of financial inclusion, the
partial inclusion of the plan had prevented the tribal
community region's understanding of financial
inclusion from being fully converted into satisfactory
action.
546
Udhani, R., Ramchandani, S. and Khan, M.
Empirical Analysis of Financial Inclusion: Case Study of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
DOI: 10.5220/0012879100003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 546-550
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
2.1 Objectives of the Study
1. To study the variables responsible for Financial
Inclusion in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
2. To assess the progress and impact of Financial
Inclusion measures at ground level in Madhya
Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
2.2 Data Collection
For the purpose of this study, the population consists
of all adults in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
Since, it is not possible to collect the data regarding
financial inclusion from all the citizens of Madhya
Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Random and convenient
sampling technique was used for collecting Primary
Data.
The method used for the present study is
probabilistic sampling method, in which the chosen
population for the study is randomized and surveyed
is not known to the researcher. Five districts were
selected from each state, two villages from each state,
were selected randomly and 20 questionnaires were
got filled from every village selected. Table - 1
elaborates in detail the districts and villages selected
for data collection.
2.3 Population and Sample Design
The present research analysis, therefore, is an attempt
to carry out a comprehensive household survey to
assess the various dimensions of financial
inclusion/exclusion.
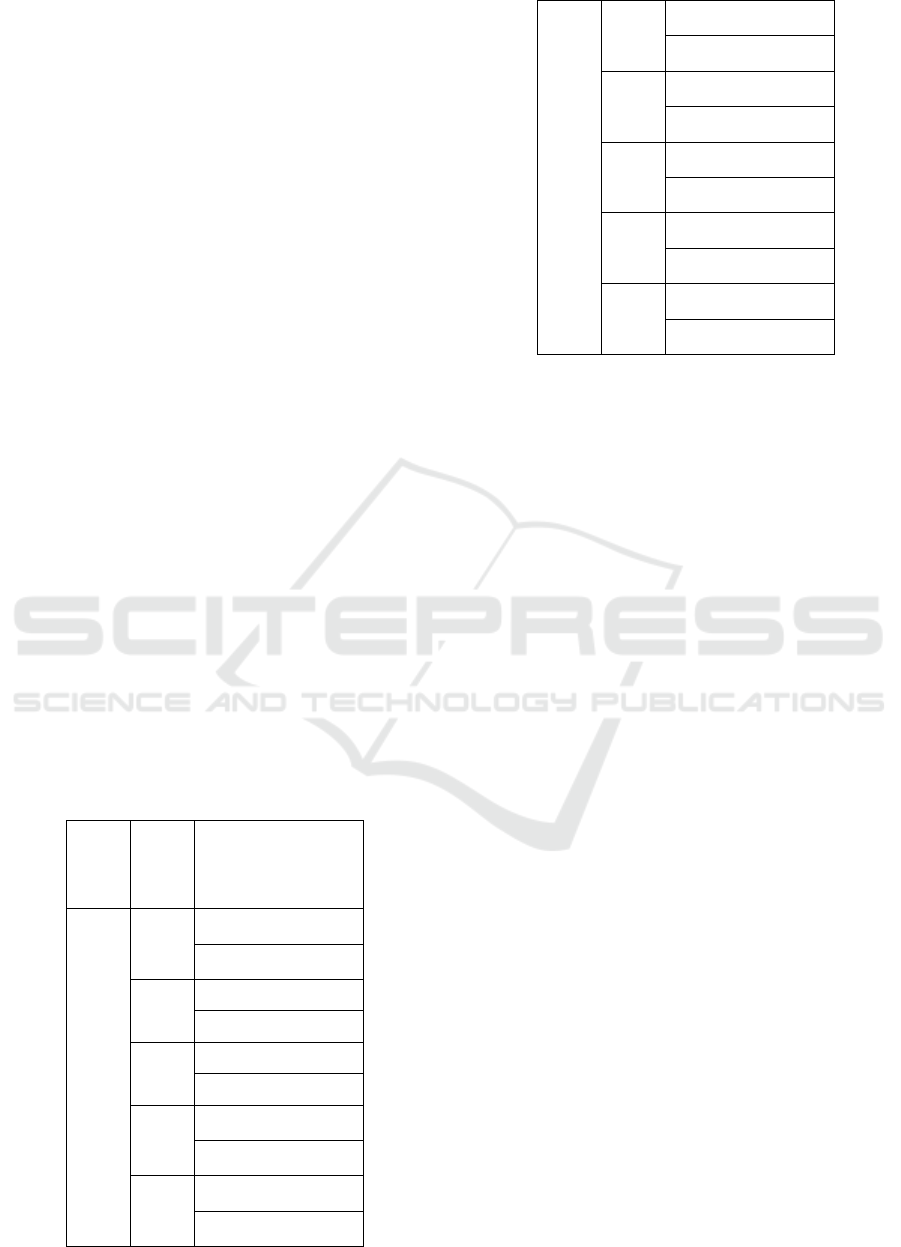
Table 1: Details of primary data collection locations.
States
Districts
Villages
MP
Bhopal
Barkheda Salam
Bairagarh Kalan
Indore
Madhopur
Jamalpura
Ujjain
Budhaniya
Hathod
Sehore
Devli
Magarda
Jabalpur
Jhurjhuru
Mohniya
CG
Raipur
Sarora
Hathkhoj
Bilaspur
Chakarbhatha
Amtara
Korba
Girari
Basin
Dhamtri
Akla Dongri
Barari
Durg
Piperchedi
Gorpa
The study covers five districts of each state i. e.
Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh. Since the study
aims at looking at the reality of financial inclusion
and its determinant at ground level, villages nearby
the districts have been selected. Two separate lists of
villages from the five districts were first prepared and
then the villages have been numbered and a random
draw of two villages each from the five districts has
been selected for survey. 20 households have been
selected on random basis for primary survey from
each village. Primary information was collected from
200 households for each state. The primary data on
number of saving and loan accounts, Kisan Credit
Card, Money Transfer, health, life and general
insurance, Mutual Fund Scheme, and Post office
Banking, were collected from the sample households
of both the states.
In selected villages almost all selected households
studied have reported their awareness of the existence
of bank branch in their village or in nearby districts.
A similar response is also observed in the case of
awareness of saving facility and awareness of loan
facility. But opposite response is observed in case of
awareness to access loan are low in Chhattisgarh as
compared to Madhya Pradesh, so it can also be said
that people are less interested for loan facility when it
comes to financial inclusion. As regards awareness of
the money transfer facility, mutual fund schemes,
post office banking and other banking facility less
than 50 per cent of the respondents from both the
states Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh.
Empirical Analysis of Financial Inclusion: Case Study of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
547
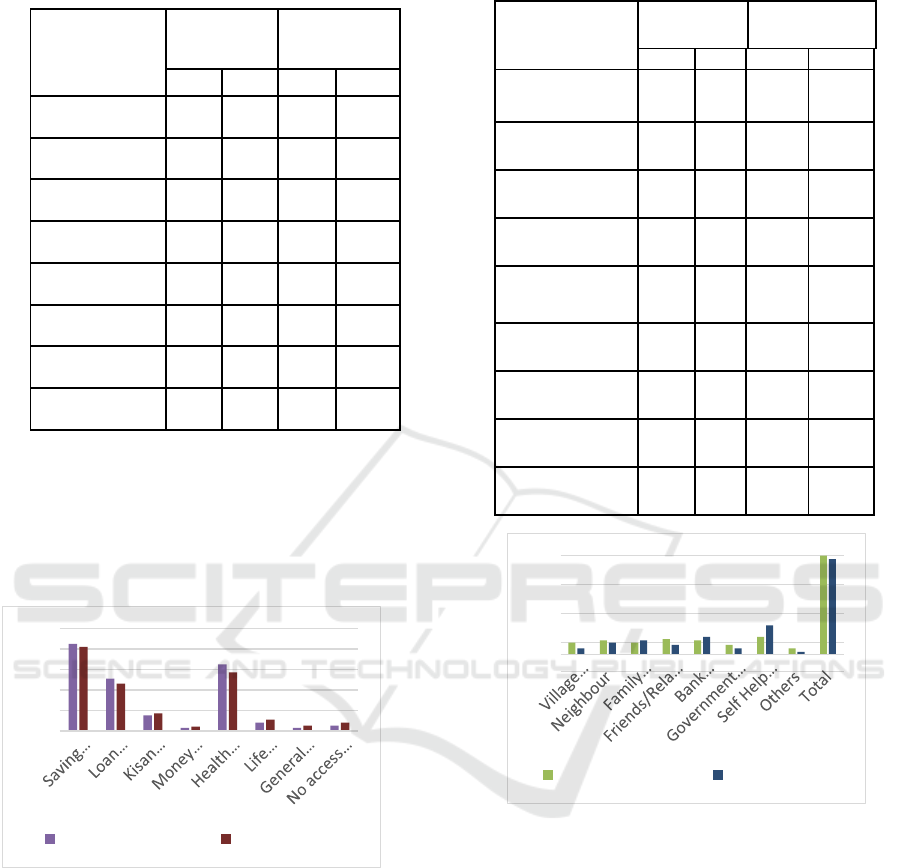
Table 2: Access to and Availability of Financial Services
in Survey Areas.
Access to and
Availability of
Financial Service
Madhya
Pradesh
Chhattisgarh
No. % No. %
Saving Account 170 85 164 82
Loan Borrowed 102 51 92 46
Kisan Credit Card 30 15 34 17
Money Transfer 6 3 8 4
Health Insurance 130 65 114 57
Life Insurance 16 8 22 11
General insurance 6 3 10 5
No access to any 10 5 16 8
Source – Field survey
The analysis of the data presented in the Table above
discloses that, there are very minor differences in
access problems in both the states and for different
products. But savings and loan products, 5% of the
respondents in Madhya Pradesh and 8% of the
respondents in Chhattisgarh have no access problem.
Figure 1. Field survey results- Access to financial services.
As regards access to other financial
products/services, while in Madhya Pradesh, 15% of
the households have reported access to Kisan Credit
Card (KCC), in Chhattisgarh 17% of the households
had access to KCC. In the case of all other financial
products and services except insurance the majority
of households have indicated access problems, as
majorly have reported about the Ayushman Bharat
Heath Insurance Scheme is utilised by them.
In the case of money transfer, 3% households of
Madhya Pradesh and 4% households of Chhattisgarh
have reported easy access to money transfer (because
of they are educated).
Table 3: Sources of Information for Financial Inclusion.
Sources of
Information
Madhya
Pradesh
Chhattisgarh
No. % No. %
Village Panchayat
Officials
20 10 10 5
Neighbour 24 12 20 10
Family members 20 10 24 12
Friends/Relatives 26 13 16 8
Bank
employee/Insurance
agen
t
24 12 30 15
Government
officials
16 8 10 5
Self Help Group
(SHG)
30 15 50 25
Others 10 5 4 2
Total 170 85 164 82
Figure 2. Sources of financial inclusion.
Above table 2 provides details of the source of
information which led the household’s entry into the
financial sector, it is important to note that only 13%
respondents in Madhya Pradesh and 8% in
Chhattisgarh reported friends/ relatives as their
source of information about financial services and
products. On the other hand 10% in Madhya Pradesh
and 12% households of Chhattisgarh reported family
members / acquaintance as the source of information
about financial inclusion. 5% and 2% households in
both the states have reported other sources as the main
source of information about financial services
respectively. The major and important source of the
information mentioned is Self-help Group which
0
20
40
60
80
100
Madhya Pradesh % Chhattisgarh %
-15
10
35
60
85
Madhya Pradesh % Chhattisgarh %
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
548
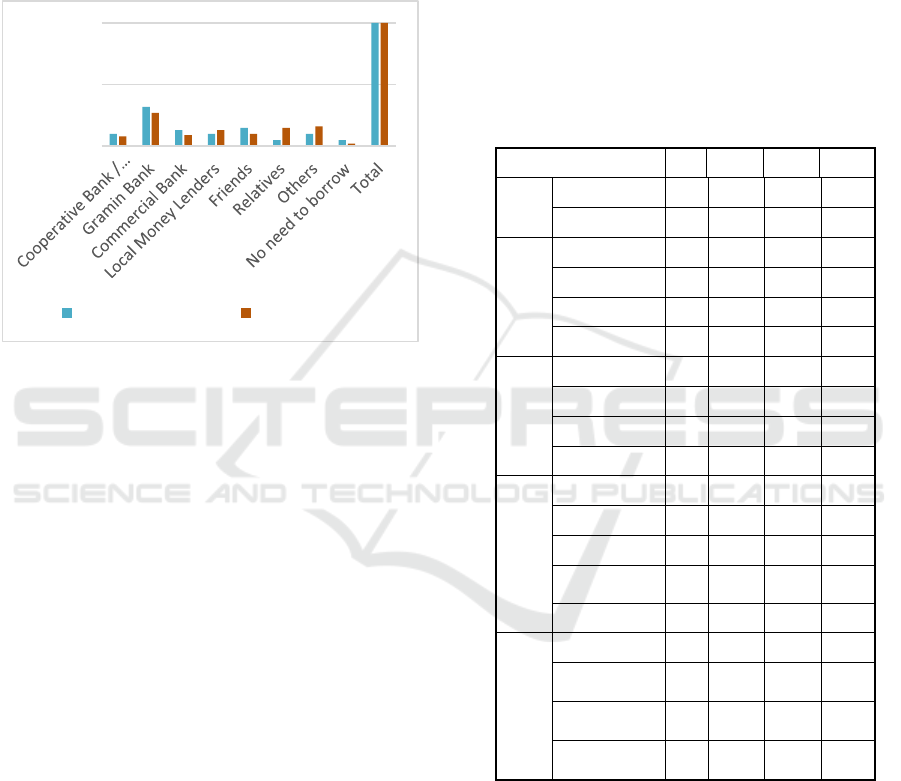
contributed 15% in Madhya Pradesh and 25% in
Chhattisgarh.
Figure 3. Sources of financial inclusion(extended).
At the onset, it should still be noted that the access of
the household to loan facility depends upon the nature
of work of the household, mentality of the members
of household, intensity of need (it is high at the time
of medical emergency) and also the easy availability
of credit facility.
The above Table no – is, an attempt
made to evaluate the responses of the households
relating to the agencies from which they have
borrowed for their credit requirements. From the
table, it appears that Gramin Banks have good
network in Madhya Pradesh as compared to that in
Chhattisgarh. Access to informal sources for loan is
higher in Chhattisgarh as compared to Madhya
Pradesh.
The main implication emerging from
this analysis of the data shows that formal and
informal both agencies are equally important source
in providing financial services in remote areas, which
should be a matter of concern as for achieving
Financial Inclusion we need to increase the scope of
formal sector in money lending in rural areas.
Madhya Pradesh is showing results of more formal
sources preferred for borrowing i.e. 50% whereas
Chhattisgarh is showing 44% of formal sources of
borrowing.
It is clear from the above figures 1-3 that there is very
minute difference between the sexual ratio of the
respondents in both states, Madhya Pradesh and
Chhattisgarh.
The table 4 shows that majority of the respondents
belong to 20-40 years of age group that is 40% in
Madhya Pradesh and 60% in Chhattisgarh. Similarly,
Madhya Pradesh has more senior citizen respondents
as compared to Chhattisgarh i.e. 30% and 10%
respectively.
From the above charts it can be clearly concluded that
majority of the respondents that is 62.5% in Madhya
Pradesh and 55% in Chhattisgarh are farmers and
second major that is 25% in Madhya Pradesh and
40% in Chhattisgarh are from labour class. Business
and other occupation is followed by very a smaller
number of respondents. The chart above shows that
the respondents are not well educated, majority of the
respondents from both the states have only completed
primary education.
Table 4: Socio-Economic Profile of Respondents
Indicators MP % CG %
Sex
Male 125 62.5 140 70
Female 75 37.5 60 30
Age
0-20 20 10 10 5
21-40 80 40 120 60
41-60 40 20 50 25
above 60 60 30 20 10
Occup
ation
Laboure
r
50 25 80 40
Farme
r
125 62.5 110 55
Business 5 2.5 2 1
Others 20 10 8 4
Literac
y
None 25 12.5 30 15
upto Primary 75 37.5 80 40
upto Middle 20 10 40 20
upto High
School 70 35 45 22.5
Graduate 10 5 5 2.5
Annua
l
Incom
e
Below 70,000 90 45 95 47.5
70,000-
100,000 80 40 80 40
100,000-
1,50,000 20 10 20 10
Above
1,50,000
10 5 5 2.5
3 CONCLUSIONS
States like Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh are
examples which can prosper economically and
socially, provided their less fortunate populations can
achieve financial independence. Because of this,
financial inclusion plays a crucial role in accelerating
the process of growth and development.
0
50
100
Madhya Pradesh % Chhattisgarh %
Empirical Analysis of Financial Inclusion: Case Study of Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
549

It can also be concluded that there is a significant
connection between literacy rates and financial
exclusion. It is observed that money transfer, 3%
households of Madhya Pradesh and 4% households of
Chhattisgarh have reported easy access to money
transfer (because of they are educated). Madhya
Pradesh is showing results of more formal sources
preferred for borrowing i.e. 50% whereas
Chhattisgarh is showing 44% of formal sources of
borrowing. In recent years, the government and other
responsible authorities have launched numerous
initiatives aimed at achieving financial inclusion,
which has created a strong foundation and created a
strong demand for additional research on the topic.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, M., & Agrawal, N. (2019). Basic Income and
Financial Inclusion. Research Journal of Humanities
and Social Sciences, 10(2), 433-435.
C. Annamalai and Dr. K. Vijayarani (2014). Awareness of
financial inclusion on tribal people in Dharmapuri
district. Asia Pacific Journal of Research Vol: I Issue
XVII.
Das, D. and Tiwari, R. K., (2012), Fundamentals of
Microfinance. India, Global Publishing House, New
Delhi.
Lalitagauri Kulkarni and Anandita Ghosh,
(Jul’2021).Gender disparity in the digitalization of
financial services: challenges and promises for women
& financial inclusion in India. Gender, Technology and
Development.
NABARD, (2012), Status of Microfinance in India,
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development,
Mumbai.
Planning Commission. (2009). Report on Financial Sector
Reforms. (Chairman: Raghuram G. Rajan).
Government of India, New Delhi.
Radhika K. and Dr. P. Indrasena Reddy (Oct’2021).
Progress and Status of Financial Inclusion in India – A
Study International Journal of Research Culture
Society.
Usha Srivastava, (Feb’2018). Financial Literacy in
Chhattisgarh-An overview of growing efforts.
International Journal of Latest Engineering and
Management Research.
Vaishali Waikar, Yamini Karmarkar (2018). Financial
Inclusion- A Study of Awareness Level of People in
Indore District. Asian Journal of Management.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
550
