
Opportunities to Ensure Competitiveness Through the Improvement
of Higher Education Institutions Quality
Ochilova Dilobar
Navoi Innovations University, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Education, Higher Education, Quality of Education, Educational System, Competitiveness, Labor Market,
Financial Resources, Innovation, Organizational Economic Mechanism.
Abstract: The present paper examined the status of the tertiary education system in Uzbekistan, drawing on an analysis
of developed countries' strategies for enhancing the quality of education and maintaining higher education
institutions' competitiveness. Proposed were organizational and economic strategies aimed at boosting the
quality of education and the competitiveness of universities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Institutions of higher education (HEI) are operating
under intense competition to strengthen and expand
their position in the world education market, and the
education system is rapidly developing, and
competition in the global education market is
increasing today. HEIs strive to increase
competitiveness by developing their scientific and
pedagogical potential, quality of education, and
international cooperation. In this article, we analyze
the possibilities of improving the competitiveness of
HEIs and make suggestions based on the quality of
education, educational services, science, and
innovation, as well as rating indicators.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
During this research, we reviewed the main literature
covering topics related to improving the
competitiveness of HEIs, quality of education,
educational services, science and innovation, as well
as rating indicators. D.G. Bajutkin.
Core formation and development of the higher
education market: theory and methodology, V.S.
Bazhenova, the issues of continuous education in the
context of changes in the economic system, A.N.
Boeva, ways to evaluate and increase the
effectiveness of the educational activities of state
higher education institutions and the competitiveness
of higher education programs E.N.Letiagina,
J.A.Grinevich, A.V.Gutko , problems of educational
services marketing, G.N.Akhunova, D.Kh.Nabiev,
problems of increasing the efficiency of training
management of highly qualified personnel,
A.Ochilov who covered in detail in their scientific
works.
In particular, the article "High Participation
Systems of Higher Education" by S. Marginson, a
foreign researcher, analyses the intercontinental
development and competitiveness of tertiary
education systems. The author discusses the
necessary strategies of increasing the place and
competitiveness of the globe’s tertiary education
institutions.
J. Hemsley-Brown, I. Oplatka in the scientific
article on the topic "University ranking systems for
marketing and management decision making"
considered the role of university ranking systems in
marketing and management decision making. The
authors analyse strategies for improving ranking
indicators and their impact on the competitiveness of
higher education institutions.
Author D. Bock's "Higher education in America"
analyses the country's higher education system and
highlights the value of research, creativity, and high-
quality instruction. It provides strategies for
enhancing educational offerings and enhancing the
social function of universities.
"From National Systems and 'Mode 2' to a Triple
Helix of university-industry-government relations:
the dynamics of innovation" by H. Etzkowitz, L.
Leydesdorff. The authors use the triple helix model to
examine the dynamics of innovation across academia,
Dilobar, O.
Opportunities to Ensure Competitiveness Through the Improvement of Higher Education Institutions Quality.
DOI: 10.5220/0012904500003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 571-578
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
571

business, and government. They will talk about how
to further research and develop initiatives, and boost
their economic impact.
It was studied how to make higher education
institutions more competitive, but not how to train
highly qualified personnel or how to assess the
efficacy of educational activities. Instead, theoretical
issues like the nature, content, and development
characteristics of the market of educational services
were examined.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
We used methods of qualitative and quantitative
research methods, questionnaires and interviews,
SWOT and PESTLE analysis, etc. in the research.
4 ANALYSIS AND RESULTS
Ensuring the competitiveness of the higher education
system in global practice is based on specific
attributes and development models of education
quality improvement.
Evaluation of intramural HEIs, with an emphasis
on efficient extramural HEI evaluation through state
and public institutions, serves as the foundation for
the French model. In addition to Germany and most
of the Scandinavian nations, France was the country
that introduced the "English (Anglo-Saxon)" model.
The model states that HEIs' internal self-evaluation is
very important and that the standard of expert
evaluations of their exterior social and professional
education is also considered. This is a prevalent
scenario in the majority of industrialized and
emerging countries, including Taiwan, the
Philippines, Great Britain, the USA, Ireland, and
Latin American countries.
The principles of the "continental" model of
managing educational institutions build ground for
the "French model" of higher education quality
assurance systems:
By the authorities towards the country of tertiary
education.
The development regulations governing tertiary
education are consolidated under the Ministry of
Education, a governmental administrative body.
Independence of HEIs in terms of finance and
academics.
Government’s property becoming dominant in
education.
In this case, education quality improvement is
implemented by the competent state bodies and
financed by the government. Systems of quality
improvement in HEIs are controlled by the state.
They are licensed, accredited, and certified by the
state, compared within different HEIs indicators, and
financed.
"England (Anglo-Saxon) model is organized on
the basis of the principles of the "Atlantic" model in
house:
Independence of the country of higher education
(development of universities).
A liberal approach to strategy.
Higher education institutions have great
autonomy, including rational financial and
intellectual independence of each university.
The service of the higher education system is
paid.
The share of non-state property in the education
system is high."
Based on the accreditation of HEIs and
educational programs, the "American model" of
enhancing quality in the tertiary education system is
seen as a successful fusion of the "French" and
"English" models. In the modern era, American
universities have established a self-evaluation
system, and HEIs now have solid authority over the
country's higher education system. The accreditation
of universities is carried out by the association of
regional universities and colleges. Within these
associations, specialized commissions of the
postsecondary education system work and grant
regional HEI certification. The intricate group
management structure that accredits higher education
institutions in the United States ensures that their
responsibilities to the public are consistent while
upholding the right to academic freedom. based on
the United States' self-control system
Tasks completed in Austria are coordinated with
the Ministry of Education and the university's
administration. Based on research of the demand for
professionals in the market of higher education
services in the fields important for the country's
socioeconomic growth, the Ministry of Higher
Education of Austria orders and pays the training of
specialists in these areas at the universities. In
Austria, universities organize and are responsible for
the development of the necessary training programs
that cover the innovation achievements necessary for
the training of highly qualified specialists based on
market demands.
The following are core concepts of higher
education system quality: freedom to participate and
the preservation of national identity, as well as the
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
572
convergence of national tertiary education systems.
Its essential guidelines are established in the Bologna
Declaration, which was ratified by 29 European
countries in 1999. The goal of this strategy is to gain
entry to the European school system and improve its
international reputation and competitiveness.
The "Bologna Process Model" is based on the
following principles:
Centralized control of HEIs' academic and
research activities, leading to increased
independence and responsibility.
Educational institutions and higher education
evaluation organizations independent from the
structure of state education supervision.
Convenient parameters for assessing the quality
of higher education.
Full participation of HEIs in evaluation.
After following this approach, the self-
assessment report should be compared to the
external auditor's expert view.
In our opinion, higher educational institutions
operating in the market of educational services of our
country should be strengthened in all aspects with
international HEIs.
In recent years, Uzbekistan has focused on significant
reforms in research and education. On October 8,
2019, the President of the Republic of Uzbekistan
issued Decree No. PF-5847 "On approval of the
concept of development of the Republic of
Uzbekistan's higher education system until 2030".
This concept envisages such strategic directions as
"developing public-private partnership in the field of
higher education, increasing the level of higher
education coverage by 50 percent based on the
organization of activities of state and non-state higher
education institutions in the regions, and creating a
healthy competitive environment in the field."
Ensuring stable economic growth in the new
Uzbekistan, as one of the strategic directions, the
formation of a new continuous education system was
defined as one of the priority tasks.
As a result of major changes adopted in our nation
to ensure the long-term development and
competitiveness of the higher education system, the
number of HEIs has increased significantly in recent
years.
Uzbekistan now has 154 higher education
institutions, a 2.2-fold increase over the previous
years. In the studied years, the number of students
studying in HEIs increased from 268.3 thousand in
the 2016/2017 academic year to 808.0 thousand in the
2021/2022 academic year, in proportion to the
number of HEIs. Higher education is not only
considered a social necessity, but also shapes the
supply of specialists at the national and regional
levels. At the next stage of the analysis, we carried
out the distribution of OTM by regions.
The number of regional tertiary education
institutions in Uzbekistan was merely 70 in the
2016/2017 academic year, and this figure increased to
154 in the 2021/2022 academic year. As can be seen
from the table, the number of HEIs has increased
several times in almost all regions except Navoi and
Namangan. In the city of Tashkent - from 39 to 67, in
Samarkand region - from 6 to 14, in Fergana region -
from 3 to 11. Such a situation can be evaluated
positively.
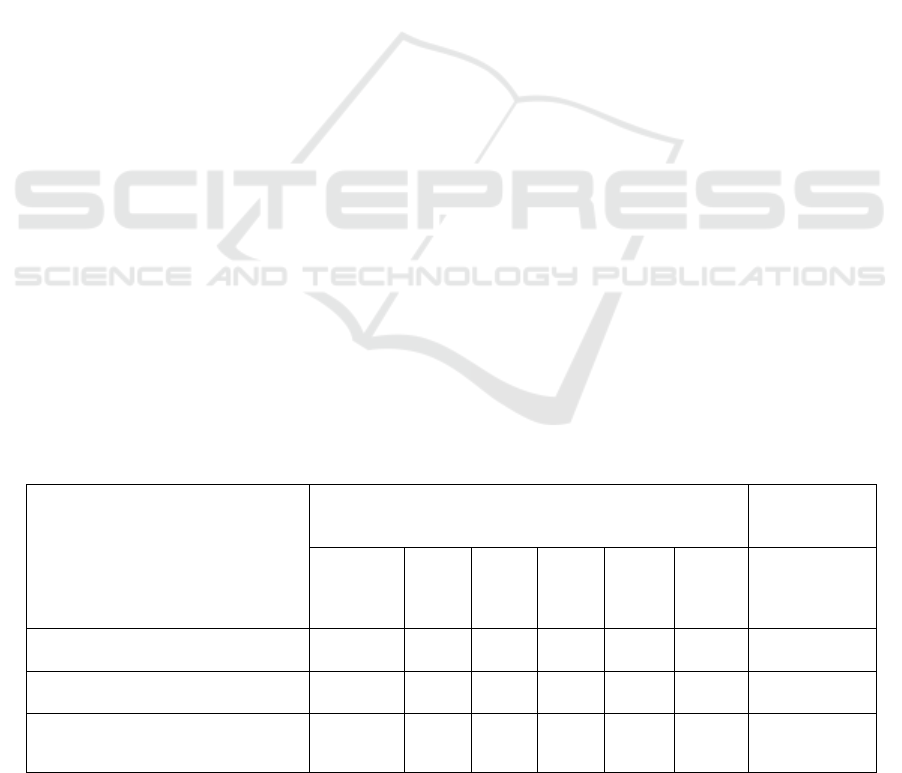
Table 1: Number of higher education institutions operating in Uzbekistan (per academic year, unit).
Indicators
Years
Growth in
2016-2022,
times
2016/
2017
2017/
2018
2018/
2019
2019/
2020
2020/
2021
2021/
2022
Number of higher education
institutions, unit
70 72 98 119 127 154 2.2 times
Including branches of foreign
higher education organizations
7 7 9 18 20 25 3.8 times
They have a thousand students 268.3 297.7 360.2 441.0 571.5 808.0 3.0 times
Opportunities to Ensure Competitiveness Through the Improvement of Higher Education Institutions Quality
573
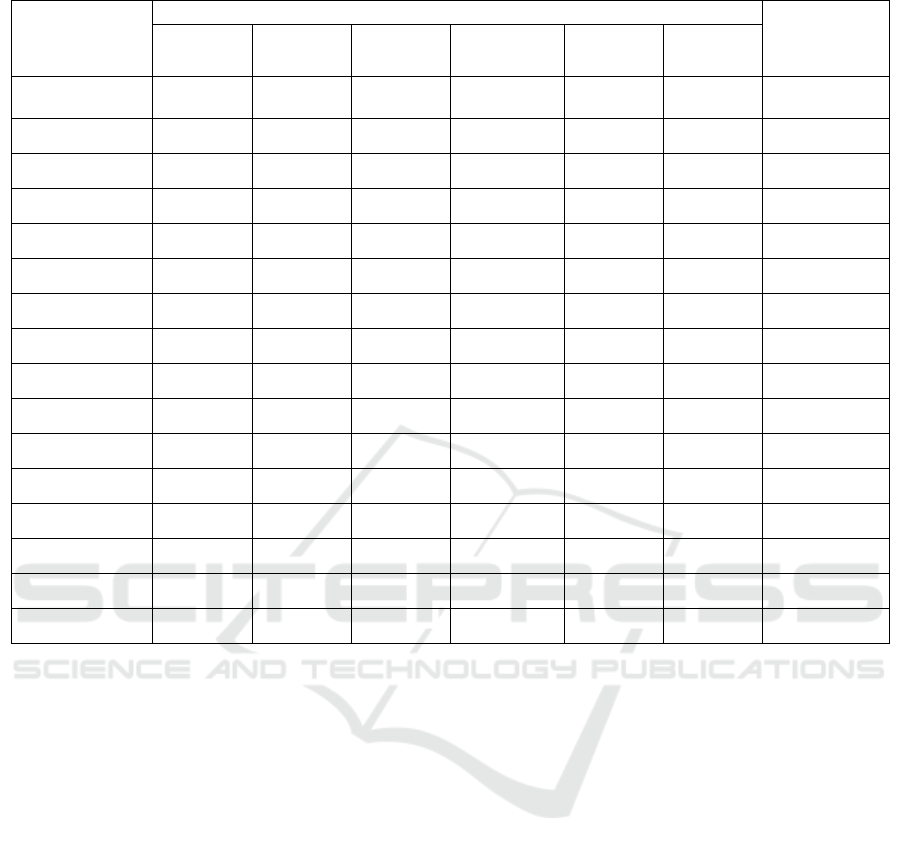
Table 2: Number of higher education institutions by region in the Republic of Uzbekistan (per academic year, unit).
The name of the
areas
Years
2016-20 22
y.y. increase,
times
2016/2017 2017/2018 2018/2019 2019/2020 2020/2021 2021/2022
Republic of
Karakal
p
akstan
2 2 6 9 9 10 5.0 times
regions:
Andijan 4 4 4 5 6 8 2.0 times
Bukhara 3 4 5 5 5 6 2.0 times
Jizzakh 2 2 2 3 3 4 2.0 times
Kashkadarya 2 2 3 6 6 6 3.0 times
Navoi 2 2 2 2 2 2 100.0
Namangan 3 3 3 3 3 3 100.0
Samarkand 6 6 8 11 12 14 2.3 times
Surkhandarya 1 1 7 7 7 7 7.0 times
Syr Darya 1 1 1 2 2 2 2.0 times
Tashkent 1 2 5 5 8 8 8.0 times
Ferghana 3 3 7 10 10 11 3.7 times
Khorezm 1 1 3 3 3 6 6.0 times
Tashkent s. 39 39 42 48 51 67 172.0
by republic 70 72 98 119 127 154 2.2 times
Currently, the main tasks of HEIs are the
development of innovative activities, the
determination of the future demand for specialists, the
development of effective integration processes
between education and business, the expansion of
external sources of financing of scientific research
and experimental constructional developments in
HEIs, and the widespread use of modern methods of
cooperation with foreign HEIs.
While innovative development of the economy is
witnessed, one of the issues is to achieve a balance of
supply and demand for qualified specialists for
modern economic sectors. All these are management
(structure and management, scale and number of
educational organizations), cognitive (knowledge,
thinking, professional knowledge and skills),
methodological (organization of the educational
process based on modern educational technologies
and tools), values (the content of the educational
process, the role of HEIs and revising its activities at
the international, national, regional levels) requires a
serious transformation.
Currently, as a result of the commercialization of
higher education services, the higher education
system is emerging as part of the market. Financial
instruments have an important place in higher
education institutions, and a correct and smooth
transition from resource management to results
management, that is, from "control at entry" to
"control at graduation" of students in higher
education institutions is taking place. The
representation of higher education services as an
economic resource that supplies qualified personnel
to the market of specialists, the introduction of
economic factors, methods and effective mechanisms
into the educational system strengthens the
integration of the labor market of specialists and the
market of educational services.
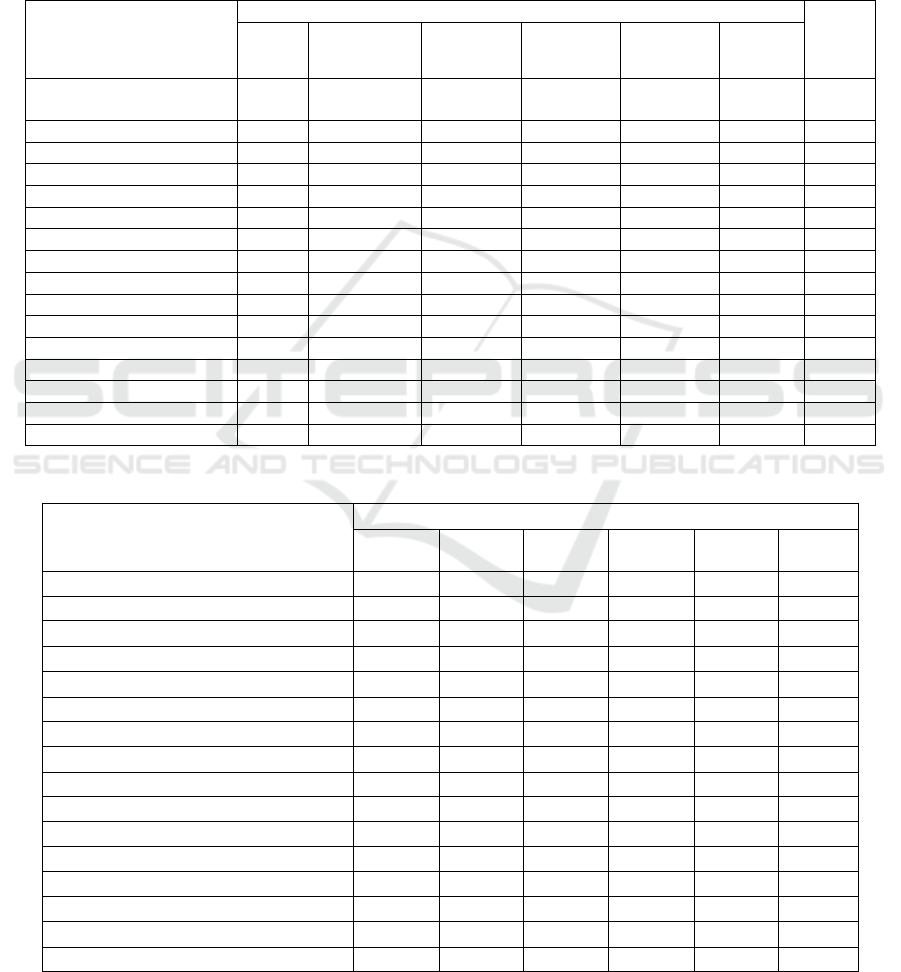
In recent years, the number of specialists
graduating from higher education institutions in our
republic has a trend of regular growth. In 2017, the
number of graduates was 64,100, and in 2021, it was
103,900. The number of graduates of higher
education institutions increased by 1.6 percent in the
analysed years at the national level (Table 3).
Graduate employment is a significant indicator of
a higher education institution's competitiveness in the
job market. As a natural continuation of Table 3, we
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
574
examined the level of competitiveness of graduates-
bachelors from higher education institutions on a
republic scale (Table 4).
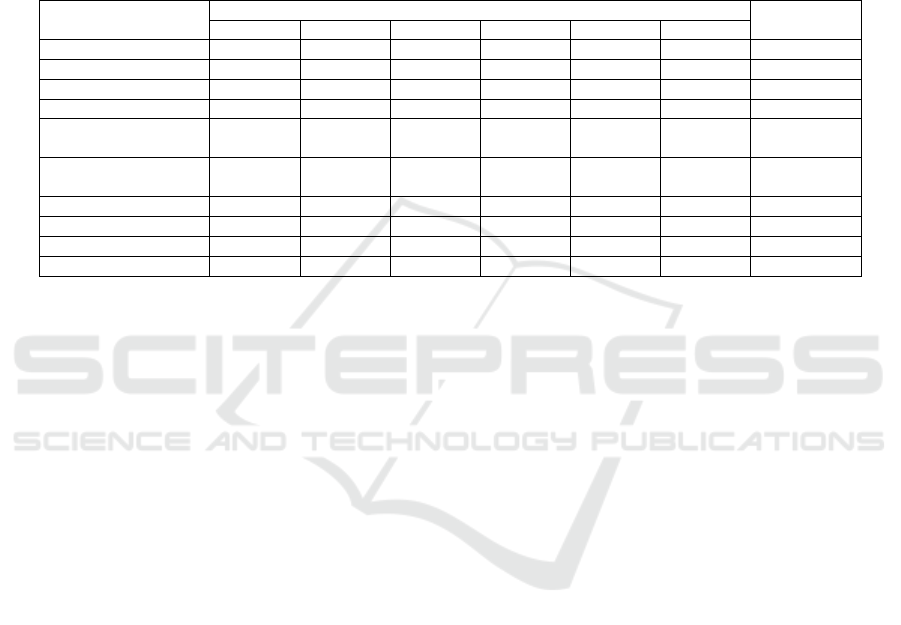
Table 4 shows the percentage of graduates of tertiary
education institutions who have employment, and
their competitiveness levels within the national level
has peaked in the academic year 2017/2018 (85.3%).
Also, in the following years, the level of
competitiveness of graduates and bachelors had a
relatively decreasing trend. A systematic increase in
the number of students in HEIs and the mismatch
between the demand and supply of highly educated
specialists in the labor market is considered as the
main reason for the above-mentioned pattern.
Table 3: The number of specialists who graduated from higher educational institutions in the Republic of Uzbekistan by
region, thousand people.
Name of regions
(provinces)
Years
2016 -
2022
growth,
%
2016 /
2017
2017 /
2018
2018 /
2019
2019 /
2020
2020/
2021
2021/
2022
Republic of
Karakal
p
akstan
3.9 4.3 4.5 4.3 5.5 6.5 1.7
re
g
ions:
Andijan 4.0 4.2 4.8 4.3 4.6 6.4 1.6
Bukhara 3.4 3.4 3.5 3.8 4.8 6.2 1.8
Jizzakh 2.3 2.7 2.9 2.9 3.9 3.6 1.6
Kashkadar
y
a 3.1 3.6 3.8 3.9 5.2 5.9 1.9
Navoi 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 3.1 3.9 1.9
Naman
g
an 2.7 2.9 3.0 3.2 4.1 5.5 2.0
Samarkan
d
6.0 6.4 6.9 6.8 7.2 8.5 1.4
Syr Darya 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.6 2.2 2.2
Surkhandarya 1.7 1.9 2.0 2.1 3.3 3.6 2.1
Tashkent 1.8 1.7 2.7 2.8 4.1 3.7 2.1
Fer
g
hana 4.6 4.8 4.6 4.8 5.8 9.3 2.0
Khorez
m
2.0 2.2 2.2 2.4 3.2 4.2 2.1
Tashkent s. 25.5 26.1 26.1 26.1 27.5 34.4 1.3
b
y republic 64.1 67.4 70.3 70.8 83.9 103.9 1.6
Table 4: The level of competitiveness of graduates and bachelors of higher education institutions by region (%).
Name of regions (provinces).
Years
2015 /
2016
2016 /
2017
2017 /
2018
2018 /
2019
2019 /
2020
2020/
2021
Republic of Karakalpakstan 75.8 78.4 82.4 83.0 74.8 74.3
regions:
Andijan 86.8 84.6 86.4 84.5 91.4 90.7
Bukhara 88.1 86.4 77.9 90.8 74.1 74.0
Jizzakh 96.9 91.2 98.6 90.4 74.0 74.5
Kashkadarya 89.9 89.5 86.2 79.2 85.5 86.5
Navoi 77.6 81.0 80.5 72.3 73.3 73.8
Namangan 70.0 74.5 84.8 83.6 90.4 90.2
Samarkand 85.1 85.5 90.5 83.4 88.7 88.4
Surkhandarya 88.9 87.1 94.8 96.4 88.9 88.1
Syr Darya 90.6 82.5 85.5 84.2 85.8 85.3
Tashkent 88.9 81.0 91.4 88.4 84.2 83.9
Ferghana 70.7 78.6 81.5 60.5 48.9 48.3
Khorezm 86.3 82.6 75.4 79.1 86.9 86.5
Tashkent s. 81.8 82.8 84.6 81.1 85.4 85.4
by republic 82.5 83.0 85.3 81.6 81.6 81.4
Opportunities to Ensure Competitiveness Through the Improvement of Higher Education Institutions Quality
575
The educational policy of higher education
institutions that have chosen the path of innovative
development is to solve the issue of modernizing
education, making it maximally compatible with the
requirements of the new "knowledge" economy.
Based on the distribution of students by academic
fields at higher education institutions in the Republic
of Uzbekistan, the following percentages apply: 46.9
percent are in the humanitarian sector; 1.1 percent are
in the social sector; 13.0 percent are in economics; 1.0
percent are in law; 22.3% are in development,
production, and technical sector; 4.8% are in
agriculture and water industry; 6.0% are in health
care; 0.3% are in social security; and 4.6% are in the
service sector.
Table 5: Distribution of students of higher education institutions in Uzbekistan by educational fields (per academic year,
thousand people).
Indicators
Years 2016-2022
growth, %
2016/2017 2017/2018 2018/2019 2019
/
2020 2020/2021 2021/2022
Humanitarian field 108.4 124.0 166.7 213.1 268.6 379.4 3.5 times
Social sphere 2.5 2.5 3.2 3.8 5.2 8.6 3.4 times
Economy 23.6 24.1 25.4 36.0 60.3 105.2 4.5 times
Righ
t
2.7 3.1 3.9 4.3 5.8 8.4 3.1 times
Production and
technical field
78.8 87.7 97.8 108.5 134.2 180.4 2.3 times
Agriculture and water
management
21.0 23.9 24.4 26.6 30.7 38.5 18 3.3
Health care 19.6 20.0 23.8 28.6 39 48.3 2.5 times
Social security 0.5 0.5 0.6 0.7 1.2 2.2 4.4 times
Services secto
r
11.2 11.9 14.4 19.0 26.2 37.1 3.3 times
Total 268.3 297.7 360.2 440.9 571.5 808.4 3.0 times
If we pay attention to the growth trend of the data
presented in Table 5 for the years under analysis, the
highest growth dynamics are in the economy (4.5
times), social security (4.4 times), the humanitarian
sector (3.5 times) and the social sector (3.4 times
times), the education sector with the lowest growth
was observed in agriculture and water management.
It was demonstrated, supported by the above-
mentioned analytical facts, that raising the standard
of instruction in higher education institutions is now
objectively necessary to maintain competitiveness.
Because of this, we think that improving the quality
of education greatly depends on HEIs' ability to
effectively organize and operate the following
organizational and economic mechanisms.
The higher education system is covered by these
organizational-economic processes, which when put
into practice offer the chance to improve education
quality and make HEIs more competitive by
producing workforce that satisfies labour market
demands. It is especially important to analyse the
present and future needs of the labour market to
periodically update higher education programs in
response to business requests. To increase internship
programs for students and internship opportunities for
professors and teachers, it is imperative to actively
involve companies in this process and work in
partnership with them.
In order to create more opportunities for students
to gain practical experience in their fields, higher
education institutions should create "practice
laboratories" for students, as well as establish practice
bases that will improve students' practical skills in
cooperation with educational institutions and
employers.
In order to modernize the educational content, it
is necessary to enrich the educational programs with
modern knowledge and technologies, and at the same
time bring the educational content to the level of
international standards. Due to this, it will be
appropriate to expand cooperation and exchange of
experience with foreign educational institutions.
The qualifications of teachers in "modern
innovative pedagogical technologies" must be
improved. They must also be given opportunities for
ongoing professional development, encouraged to
incorporate modern pedagogical technologies into the
classroom, and given access to contemporary
educational resources and literature. In addition,
there
has been a greater integration of contemporary
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
576
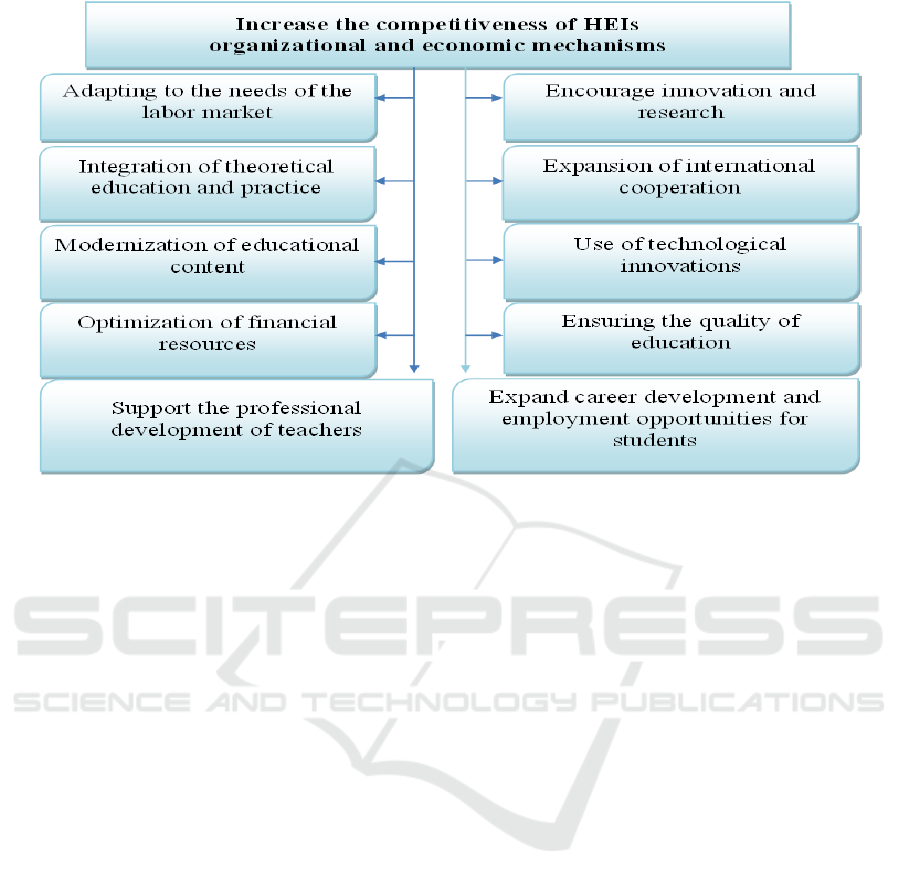
Figure 1: Organizational and economic mechanisms of increasing the competitiveness of HEIs and enhancing the quality of
education in them.
technologies like virtual tools and platforms for
remote learning into the educational process. The
instructional process will become more effective and
efficient as a result.
Higher education institutions should make sure
that they participate in international research projects
and arrange for teacher and student exchanges
through international cooperation programs. This
enhances the standard of instruction and enhances the
standing of educational establishments globally.
Establish and expand career centres for students,
providing them with advice and guidance on
employment and career development. Also,
strengthening of cooperation with employers on
employment of graduates, diversification of sources
of funding for grants, scholarships and scientific
research projects is of great importance to work on
the requirements and ensure the stability of the
quality of education.
5 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, it should be highlighted that
maintaining competition in postsecondary
educational institutions ensures a high concentration
of innovative, material, and technological potential,
which raises the quality of educational services.
The subject of the fundamental reformation of
the local education system is receiving the most
attention from the President of the Republic of
Uzbekistan, Sh. M. Mirziyoev. The rise in the
proportion of young people with higher education
from 9% in 2016 to 25% in 2025 explains the first
effect in this regard. This indication will eventually
be raised by 50–60%. Going forward, these figures
will rise even further. as a result of the creation of
pertinent terrain. After establishing competitiveness,
graduates of higher education institutions must
become more competitive, according to a summary of
the socioeconomic variables mentioned above.
REFERENCES
Akhunova G.N. Marketing problems of educational
services in Uzbekistan (monograph). - T.: Economy and
Finance, 2005. - 244 p.
Bazhenova V.S. Continuing education in the context of
transformation of the economic system. – M.:
Publishing house Ros. econ. acad., 2000.
Bazhutkin D.G. Formation and development of the market
for educational services of higher educational
institutions: theory and methodology: abstract of thesis.
dis. Doctor of Economics Sci. Samara, 2010.
Boeva A.N. Assessment and ways to increase the
effectiveness of educational activities of state higher
educational institutions: abstract of dissertation. ...
Ph.D. in Economics. – Vladivostok, 2011. – 23 p.
Vahabov A_V, Rakhmanov N. _ R. _ High education
quality increase abroad from experience Uzbekistan_
Opportunities to Ensure Competitiveness Through the Improvement of Higher Education Institutions Quality
577

higher education system isla h in reaching use
opportunities " Khal q aro finance and hisob” scientific
magazine. No. 4, August 2020.
Bock, D. (2013). " Higher education in America " Princeton
University Press.
Elena N. Letiagina, Julia A. Grinevich, Alexander V. Gutko
Ways to improve the competitiveness of higher
education programs // Human, Technologies and
Quality of Education, 2019. P.62-66.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
578
