
Specific Characteristics of Formation of Attitude Motivation Related
to Study Activity in Primary Class Students
L. Z. Koraeva
Navoi Innovations University, Karmana, Navoiy, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Social Attitude, Subjective Attitude, Educational Activity, Motive, Person, Motivation, Individual.
Abstract: In this article, in the framework of social relations in the educational process of elementary school students,
the motivation of attitude to learning activity in children of junior school age, learning, research, methods of
doing and In primary school students, the motivation of the attitude to the educational process, interest in
school life, the feeling of school life, and the ways of formation of certain beliefs about school life were
thought about.
1 INTRODUCTION
Personal education, its social and psychological
maturity is one of the main strategic issues of any
country. It is impossible to build a society capable of
achieving perfection in all aspects without educating
a person based on certain noble ideas, socio-
psychological, and high intellectual requirements.
Naturally, the concept of attitude is a comprehensive
and wide-ranging concept, and its interpretation is
equally wide and diverse. From this point of view,
philosophers, psychologists, sociologists,
psychophysiologists, pedagogues, and
representatives of several social sciences, who
researched social psychological criteria in various
fields of attitude, scientifically justify one or another
direction of attitude category. Educational activity
relies on the same research directions and is important
for the formation of personal activity. Here, Professor
E. A lot of scientific opinions were expressed by
Ghaziev. For example, to socially solve the problem
of subjective attitude towards a person, it is necessary
to adhere to the hierarchy of "man-human-person-
individuality-subject-perfection" and abandon the
erroneous theory that subjective attitude towards a
person, that is, all characteristics can be formed
equally in him as a robot transition, creating a
"subject-subject" relationship, solving the problem
that any subject is a person, but not every person is
subject, recognizing that a person needs
independence, personal position, determination,
worldview and the possibility of their implementation
in life (E. G'oziev, I. Tursunov) have an important
place in the interpretation of the motivation of
personal relationships. K. Obukhovsky interprets the
motive as "a goal program that directs a certain
activity", while H. Heckhausen justifies that "the
motive is a process that explains directed actions
within the framework of the individual-environment
relationship". The analysis of scientific literature
shows that worldviews, beliefs, ideals, and
behavioural motives, which play an important role in
the formation of a person, are based on one or another
values. moreover, values are formed based on social
experience - Andreeva [1996].
From this point of view, it is necessary to
conditionally interpret the scientific literature on
attitude motivation into the following groups and
define research tasks based on this interpretation.
1. The motivation of the relationship is based on
the individual's interests. The system of internal
impulses, which ensures the instability or stability of
these interests, also determines to some extent the
system of attitudes.
2. At one level or another, the influence of
personality orientation on attitude motivation is
shown. In the process of this influence, some
manifestations of the combination of personality
orientation and attitude motivation occur.
3. Attitude motivation is also formed based on
certain institutions. In particular, the regulations
related to educational activity serve to determine the
factors related to the social development of the
student's personality.
Koraeva, L.
Specific Characteristics of Formation of Attitude Motivation Related to Study Activity in Primary Class Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0012905600003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 593-597
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
593

4. At the base of attitude motivation, it is possible
to assess the influence of the scale of values at one or
another level.
2 OBSERVATIONS AND
SCIENTIFIC ANALYSES
It has shown that the process of reaction to educational
activity has a unique hierarchical system in the
psychological direction of the individual, and based on
this system, it is possible to research the manifestation
sign, result, and dynamics of the individual's activity.
The following direction, which serves to form the
motivation of attitude to educational activity, was
selected and these directions were integrated into the
general purpose of the research: in the first direction,
to study the motivation of attitude to school, in the
second direction, to study the levels of formation of
educational components, and in the third direction,
methods aimed at researching the motivation of
attitude to educational activities by studying the
orientation of the person complex was selected and the
task of putting it into practice was set. In the scale of
the attitude system, the scale of "active-positive",
"positive", and "indifferent" relational motivation to
the process of choosing the educational activity
formed in the activity of students is included. enables
analysis. the following three areas that serve to form
the motivation of attitude to educational activities
were selected and a complex of methods focused on
these areas was developed. Including, in the first
direction, the methods of researching the motivation
of the general attitude to school and educational
activities, in the second direction, the methods of
studying the motivation of the attitude based on the
components of the educational activity, in the third
direction, the methods of researching the motivation
of the attitude to the educational activity by studying
the orientation of the person; the complex was selected
and a plan for its implementation was developed.
From this point of view, the first set of methods is
based on the methodology "Assessment of the
motivation of attitude to school" developed and
recommended by N.G. Luskanova. of course, in
addition to this methodology, the results of individual
interviews, answers to questionnaire questions,
special observations, and content analysis were used -
Barotov [1992].
The method consists of 10 situation-specific
questionnaire questions, and the answer to each
question serves to determine the levels of attitude
motivation in a certain sense. Therefore, first,
questionnaire questions are prepared and distributed
to the participants. There are 3 answer options in each
of the distributed questionnaire questions, and the
participant is asked to select the one that is closest to
him. To find out the correctness of the questionnaire
answers, the experimenter repeats the questions and
their content once again and records the results of
individual interviews with each participant within the
chosen answer direction. When everything is
finished, the experimenter collects the completed
questionnaires and begins to process the data.
3 - points - shows the student's willingness and stable
interest in the educational process of the school.
1 - point - neutral answer, i.e., answers like "I don't
know", "it happens", "sometimes", and "I can't say for
sure", it is understood that some superficiality and
indifference towards school education are expressed.
0 - 0-point - means no positive attitude towards school
and school education.
Table 1: Answer options in questionnaire questions are evaluated in the following order.
Question no Amount of points for answer
1
Amount of points for answer
2
Amount of points for answer
3
1 1 3 0
2 0 1 3
3 1 0 3
4 3 1 0
5 0 3 1
6 1 3 0
7 3 1 0
8 1 0 3
9 1 3 0
10 3 1 0
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
594
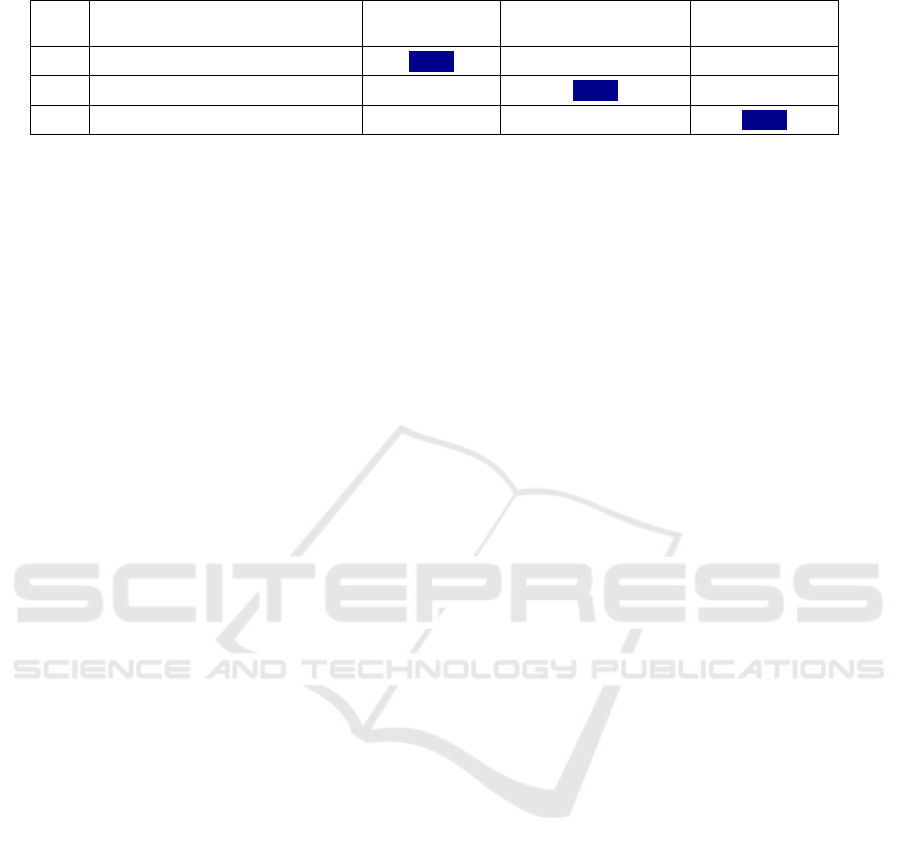
Table 2: The key to the method.
No Component
questions
Cognitive Emotional and
volitional
His assessment
I 1,4,7,10,13,16,19,22,28 \\\\\\\\\
II 2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23, \\\\\\\\\
III 3,6,9,12,15,18,21,24 \\\\\\\\\
The method is mainly carried out by analysing the
questions of the questionnaire and the answers given
to it. For example, 24 pairs of educational tasks are
presented to the student in the form of an alternative
questionnaire. That is, the performance of each
recommended task determines the indicator of one or
another level of attitude motivation, which is
characteristic of the student's activity. For example,
the presence of a tendency to participate more in
situations indicated by the letter "A" (selection of this
or that situation) indicates the superiority of the
motivation of an indifferent (superficial) attitude
towards educational activity, while the selection of
situations in the situation "V" is due to the formation
of motivation of an active-positive attitude to
educational activity. testifies. Briefly, the procedure
for applying the method is as follows:
1. To acquaint students in detail with the content of
questionnaire questions in an alternative way, in
which situations directed to specific goals are
expressed.
2. Presenting 24 pairs of situations for students to read
and study and providing additional explanations to
help them fully understand each situation.
3. Each participant chooses and marks the one that is
best for him, having deeply imagined both situations
in each pair. In this way, 24 situations are studied in
detail and 24 answers are selected.
4. The teacher collects the answer sheets and, after
making sure of their authenticity, enters each piece of
information for primary processing.
All the answer options mentioned in the questions of
the questionnaire are determined according to the
system of educational components in the above order.
As mentioned earlier, the selection of situation "A" in
each alternative question number is determined by 0”
by " points, and the selection of situation "B" is 5”
determined by " points. The maximum score for a
total of 24 situations is 120 points. Also, 8 situations
are offered for each component. That is, the
maximum score for each component is a total of 40
points. No marks will be assigned to "A" situations
selected in all components. All presented "A"
situations are based on the absence of active-positive
attitude motivation based on the relevant component,
and in "B" situations, the presence of active-positive
attitude motivation is based on attitude motivation.
Primary Data Processing
1. The amount of points characteristic for each
participant is determined.
2. The determined number of points are placed
according to conditionally accepted forms of attitude
motivation (active-positive, positive, indifferent).
3. The number of points obtained from the
participants of each object is combined into a set of
average-general indicators. The average total interest
amount is also determined.
4. For the students of each class (2nd and 4th class)
characteristic distance (range) indicators are also
determined in the example of all objects, and general
conclusions are made.
Secondary Data Processing
1. Indicators of motivation towards school are re-
considered for correlation analysis and included in
special tables.
2. The results of the correlation between the
available empirical data, and the reliability value of
the data are re-examined using specially adopted
statistical criteria. (Using SPSS software).
3. General laws are determined based on
mathematical statistical results collected on all data.
Thus, with the help of this set of methods of the first
direction, average-general and comparative-typical
indicators of attitude motivation characteristic of
elementary school students are analysed. Based on
these analyses, relevant scientific and practical
conclusions can be drawn by the purpose of the
research. First of all, it should be said that this set of
methods serves to determine the extent to which
educational components are included in the student's
activity. Because at the root of any activity are certain
factors. In our opinion, the participation of
educational components (cognitive, emotional-
volitional, evaluation) is important in the motivation
of educational activity or the attitude towards the
manifestation of educational activity. That is, it is
possible to talk about educational activity by forming
an educational component at an appropriate level.
Specific Characteristics of Formation of Attitude Motivation Related to Study Activity in Primary Class Students
595
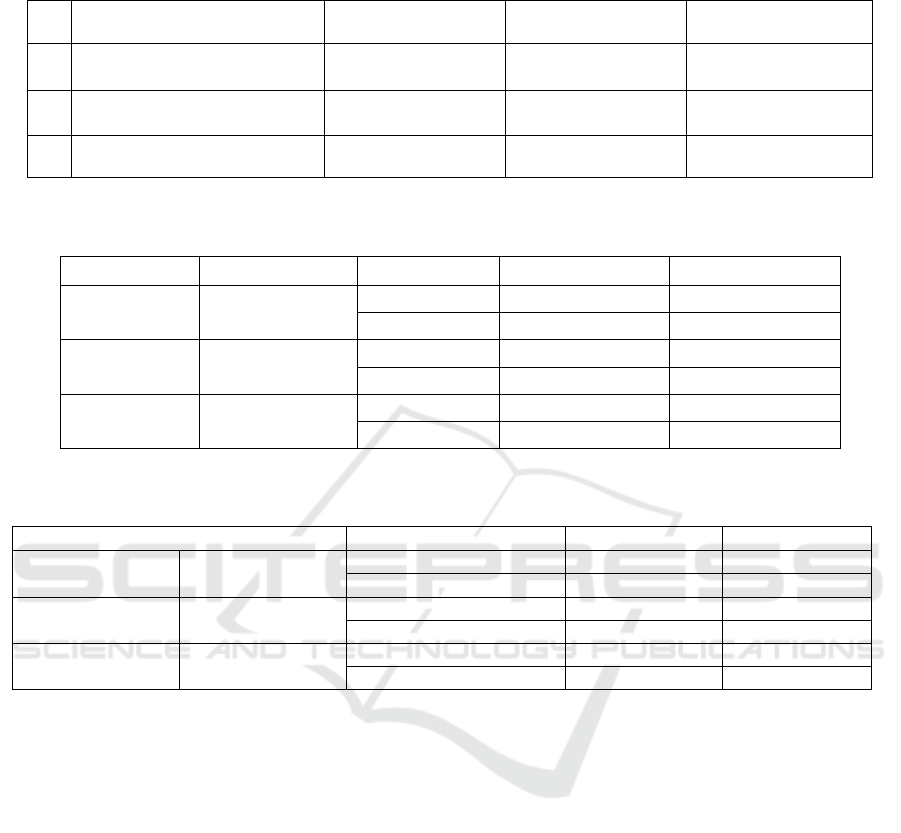
Table 3: Average-general comparative typical indicators of the visibility of school motivation, ranges of indicators, and places
in relation to the total number of participants.
No Communication system
ob
j
ect
Actively positive
ran
g
e %
Positive
Intermediate %
Indifferent
Intermediate %
n 1 =1000 (grade 4 ) Places: 22.2 - 30.5
3rd place
35.2 – 45
1st place
30.8 - 38.8
2nd place
n 2 = 1000 (4 classes) Places: 26.7 - 35.2
2nd place
33.5 - 43.1
1st place
22.5 - 40
3rd place
Total
n 1 = n2
22.2 - 35.2
3rd
p
lace
33.5-45
2nd
p
lace
22.5 - 40
1st
p
lace
Table 4: Correlation results on the average general indicators of manifestation of motivation of attitude to school in elementary
school students (grade 2).
Active positive positive Indifferent
Active positive X 2 (Pearson)
1 0.313 0.400
- 0.546 0.432
Ijobiy X 2 (Pirson)
0.313 1 0.650
0.546 - 0.162
Indif ferent X 2 (Pirson)
0.400 0.650 1
0.432 0, 162 -
Table 5: Correlation results on the average general indicators of the manifestation of school motivation in elementary school
students (4th grade).
( n 2 =1000) Active positive positive indifferent
Active positive X 2 (Pearson)
1 0.985 (**) 0.052
- 0.000 0.923
Ijobiy X 2 (Pirson)
0.985 (**) 1 0.046
0,000 - 0.930
indifferent X 2 (Pirson)
0.052 0.046 1
0.923 0.930 -
Indifferent attitude towards educational activity
somewhat hinders the effective use of opportunities
for the social and intellectual development of the
student's personality. Observations indicate that the
growth of indicators of indifferent attitude leads to a
decrease in educational activity, or on the contrary, a
decrease in indifferent attitude leads to an increase in
educational activity. This identified situation requires
the constant attention of elementary school students
and school psychologists. These obtained data once
again confirm the objectivity of the previous data
analysis by the content of the methodology.
So, as it can be seen from the above analysis, the
motivation of primary school students' attitude to
educational processes is directly related to the
formation of certain beliefs about school life, first of
all, interest in school life, and feeling of school life.
Empirical data obtained based on Luskanova's
methodology indicate the different levels of attitude
to school among elementary school students.
Additional methods and special content - the results
of the analysis show that the course of this process
depends on certain social and psychological factors.
For example, the child's ability to perform one or
another task as a student for the first time, to work in
cooperation with peers, to be kind to the teacher, to
develop self-esteem and self-development by
following the traditions of the family and school, to
develop his own worldview and social life for the first
time. such situations as having activity serve as an
important basis for the formation of attitude
motivation in the student.
When we investigated the reason for this situation
through specially directed additional individual
interviews and other methods, it became clear that
when students of junior school age are more likely to
complete an academic task, they, first of all, perform
this task with a certain enthusiasm and pleasure, while
they also have a feeling of hearing praise from
the
teacher. they try harder and spend willpower to
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
596
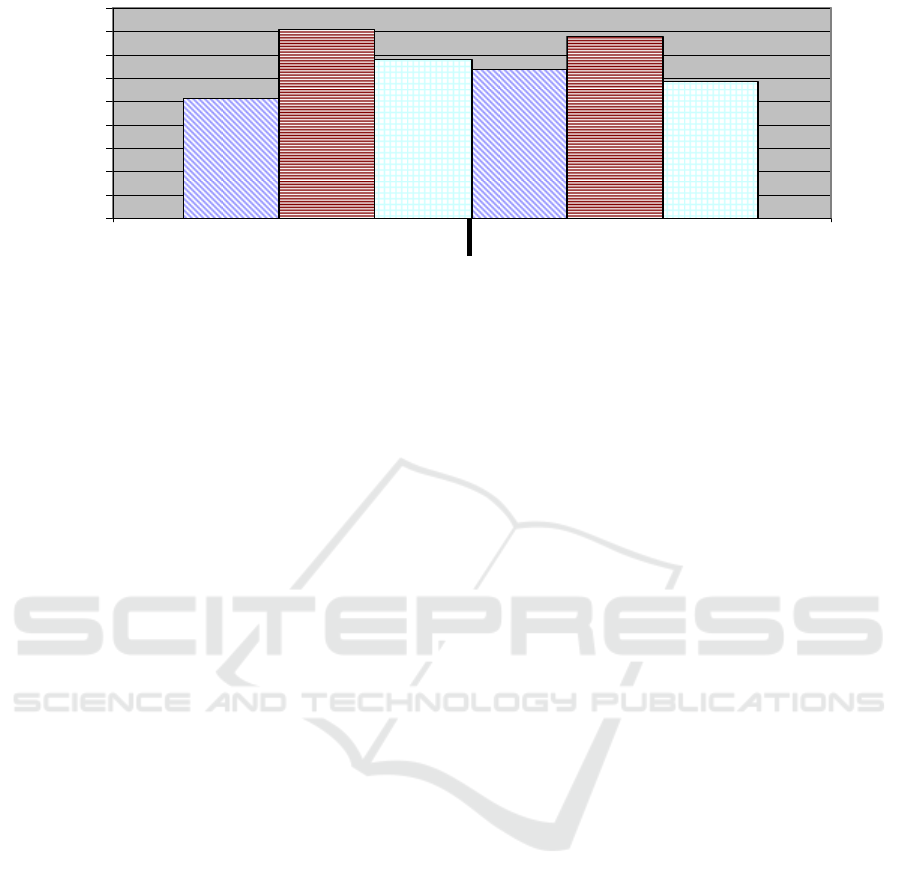
Figure 1: Diagrams of indicators of motivation of attitude to school (in %).
complete any educational task. More precisely, in
most cases, their emotional-volitional qualities serve
to form the motivation of an active-positive attitude
to educational activity.
3 CONCLUSION
The formation of motivation of the attitude system
(active-positive, positive, indifferent) to educational
activity in students at junior school age and its
manifestation at one or another level depends on the
personality of the student, psychologically
influencing "interests", "personal orientation",
"certain level educational institutions" is directly
related to "values". More precisely, based on the
analysis of empirical data, it can be said that
depending on whether these qualities are unstable or
stable in the personality of the student, it is possible
to form an idea about the active-positive, positive, or
indifferent attitude of the student towards the
educational process.
REFERENCES
Andreeva G.M. Social Psychology. - M., 1996.
Baratov Sh.R. Social-psychological and scientific-practical
foundations for creating a psychological service in
Uzbekistan. (Author's abstract of dissertation, doctor of
psychological sciences). – T., 1998.-37 p.
Barotov Sh.R. Evaluating the activity of young students. -
T.: "Teacher", 1992. - 48 p.
Psychological foundations of personality formation in
conditions of public education. - M., 1979.
Goziev E. Psychology. study manual. - T.: " Teacher ",
1994. - 224 p.
KorayevaL.Z. (2023). Relation Is As A Social
Psychological Problem. Genius
25,6
40,4
34
31,8
38,9
29,3
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
1
2 синф n1 = 1000 4 синф n1 = 1000
Specific Characteristics of Formation of Attitude Motivation Related to Study Activity in Primary Class Students
597
