
Globalization, SMEs, and Digitalization: The Role of Marketing and
Entrepreneurial Behavior
Sunil Kumar Vohra
1
, Shashi Kant Gupta
2
, Susheel Kumar Singh
3
and Prabhdeep Singh
4
1
Amity University, Noida, India
2
Eudoxia Research University, New Castle, U.S.A.
3
Heera Lal Yadav Balika Degree College, Lucknow, India
4
Shri Ramswaroop Memorial University, Lucknow, India
Keywords: Small and medium-sized enterprises, Digitalization, Marketing, Entrepreneurial performance, Globalization.
Abstract: Digitalization is not a new phenomenon, but it is evolving and altering in ways that affect businesses
worldwide and open doors for Small and medium-sized enterprises(SMEs) to participate in the global
economy. Although digitalization, globalization and SMEs are major concerns for global and European
corporations alike, Digitalization and SMEs' international strategic choices, which have not been thoroughly
explored, are critical to investigate. Both globalization and the increase of SMEs with an international
presence are significant developments on a global scale.The multidimensional behavior of an entrepreneur
who is imaginative, proactive, independent, proactive, and willing to compete aggressively to capitalize on
market possibilities is known as entrepreneurial behavior. This research investigates at marketing and
entrepreneurial behavior have a role in the effects of digitalization and globalization on SMEs.To help SME
managers, this research offers hypotheses data and conclusions on the crucial roles of moderating the effect
of entrepreneurial behavior and marketing.
1 INTRODUCTION
SMEs are crucial to the growth and development of
both established and developing economies,
particularly when it comes to creating jobs, raising
gross domestic product (GDP), redistributing wealth,
and other factors (Mpi, D.L. 2019). Yet, survival and
improved SME performance rely on supportive
government policies, superior organizational
cultures, and entrepreneurial behavior that may
advance and build a nation's SME sector (Park, et al.,
2020).
The entrepreneurial orientation is a reflection of
the entrepreneurial behaviors of creativity, initiative,
and risk-taking. Entrepreneurial orientation (EO)
enables small organizations to find new business
prospects, and the finding of new chances strengthens
their distinction from other companies (Rajagopal, et
al., 2022).
In this sense, marketing leadership entails the
development of original marketing plans, the
utilization of professional sales associates, and the
vigilant administration of channels of distribution.
Since it often sits at the center of a company's overall
strategic plan, a strong marketing strategy may be the
most crucial element to success for most businesses
(Irudayasamy, et al., 2022).
The term "globalization reaction" is used to
characterize how seriously businesses take the
benefits and risks brought about by globalization.
Changes in corporate strategy, advertising methods,
and other quick fixes are all the result of
management's initiative (Naradda Gamage, et al.,
2020). In this Study, the impact of digitalization and
globalization on SMEs is studied, along with the role
played by marketing and entrepreneurial behavior.
Vohra, S., Gupta, S., Singh, S. and Singh, P.
Globalization, SMEs, and Digitalization: The Role of Marketing and Entrepreneurial Behavior.
DOI: 10.5220/0012908000003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 623-627
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
623
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Table 1: Insights into SME Success: Marketing, Entrepreneurship, and Diversity Dynamics.
Author Findings
Nuseir, et al.,
2020
Empirical evidence linking digital marketing strategies to increased revenue generation among UAE's
SMEs.
Agyapong, et
al., 2020
Investigates how a global perspective might shape the connection between entrepreneurial behaviour and
financial success.
Al-Hakimi, et
al., 2022
Aims to examine the moderating role of marketing ethics and competitive intensity on the correlation
b
etween cost and
p
rofit.
Arzubiaga, et
al., 2018
Explored the moderate impacts of two primary sources of board diversity in family enterprises, family
engagement level and gender diversity, as possible strategies for boosting family firms' performance
when utilizing entrepreneurial ideas.
Genc, et al.,
2019
Investigates whether or not there are mitigating elements in the connection between EO and the success
of SMEs.
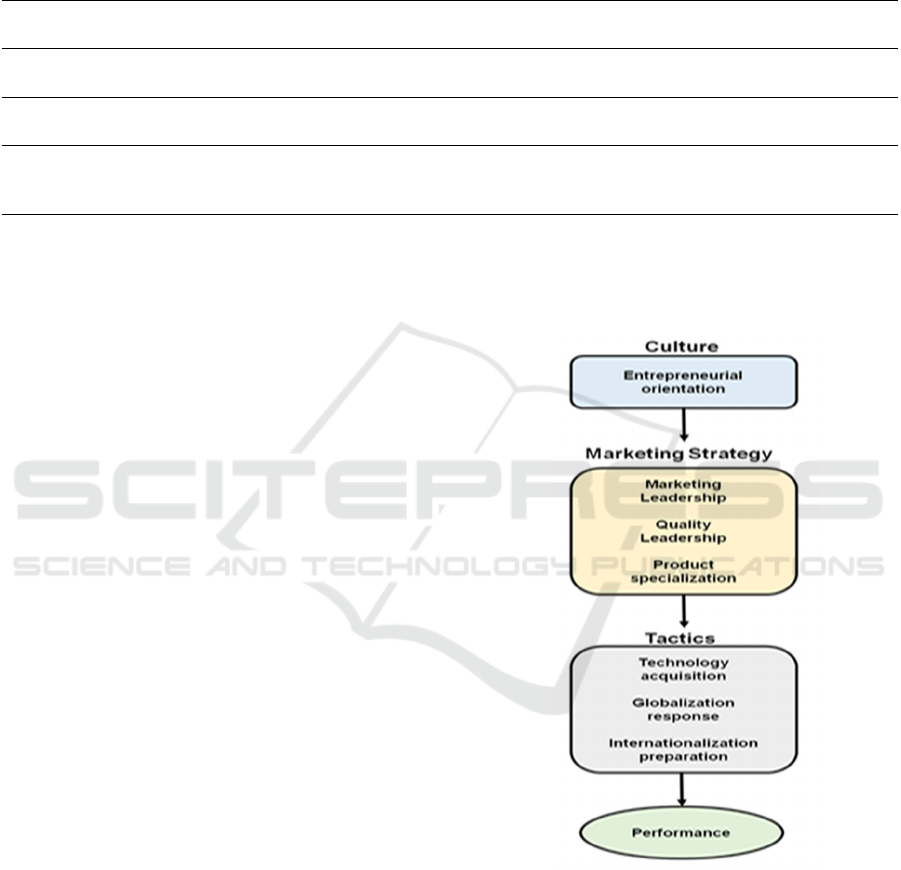
3 HYPOTHESIZED
RELATIONSHIPS
According to Webster's (1992) theory, an
entrepreneurial perspective predates Marketing plans,
which come before results. Figure 1 suggests the
hypothesized links.
H1: Marketing leadership strategy, quality
leadership strategy, and product specialization
strategy are all more likely to be pursued by a
company with a higher entrepreneurial orientation
than they are otherwise.
H2: The more aggressively a company pursues a
marketing leadership approach, the more likely it is to
acquire new technologies, adapt to the effects of
globalization, and make preparations to enter
overseas markets.
H3: There is a positive correlation between a
company's pursuit of a quality leadership strategy and
its interest in acquiring new technologies.
H4: The greater the company's emphasis on
product segmentation, the more likely it is to actively
seek out and acquire cutting-edge technological
capabilities.
H5: The performance of the firm improves as it
adds more technology.
H6: The firm performs better the more it adapts to
globalization, in general.
H7: The performance of the company improves as
it makes more preparations in advance to access
international markets.
Figure 1: Predicted Correlations Among Research
Hypotheses.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The data collection process for this study occurred in
three distinct stages. Initially, semi-structured
interviews were conducted with a range of
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
624

stakeholders, including business leaders,
policymakers, and industry advocates. These
interviews served to refine the research topics and
develop appropriate survey instruments. Following
this, a pilot test of the questionnaire was undertaken
involving 100 companies to ensure its effectiveness
and clarity. Subsequently, the finalized questionnaire
was distributed to 800 randomly selected
manufacturers operating within industries affected by
globalization. These industries were chosen based on
their relevance to electronic systems.
The selection criteria for these sectors
encompassed various factors such as the number of
workers, annual sales activity, market dominance,
and the duration of presence in the market. The aim
was to encompass a diverse range of companies
within the study sample. Upon analysis, no significant
differences were found across these industry
classifications, suggesting that contextual variables
within the industries did not substantially influence
the study's findings. The questionnaire distribution
was staggered into three waves, each separated by
approximately two weeks. Respondents were
incentivized to participate, resulting in a response rate
of 32%.
Out of the 273 completed questionnaires
received, 268 were deemed valid for analysis. To
assess nonresponse bias, comparisons were made
between the characteristics of responding businesses
and those of a random sample of 50 non-responding
businesses. This analysis found no statistically
significant differences, indicating that nonresponse
bias was unlikely to impact the study outcomes.
Measures were presented on a 7-point scale to elicit
granular responses. Exploratory factor analysis was
employed to derive dimensions within the marketing
strategy construct scale. Factors such as leadership in
marketing, quality, and product specialization
emerged from this analysis.
The study also employed various performance
metrics to assess the overall health of each company.
These measures underwent validation through factor
analysis in LISREL 8 structural equations
computational modeling, ensuring their construct
validity. A high level of fit was observed across all
models, indicating the robustness of the measures
used. Additionally, Cronbach's alpha tests
demonstrated that the multi-item measures were
either highly reliable or sufficiently reliable. Overall,
the comprehensive approach to data collection,
analysis, and validation employed in this study
provides confidence in the reliability and validity of
the findings presented.
5 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The hypotheses were subjected to rigorous
examination through three distinct model testing
approaches. Initially, t-tests were employed to
scrutinize the primary study construct scores,
discerning disparities between highly globalized and
less globalized enterprises. Subsequently, a
combination of multivariate regression and
correlation analyses was employed to scrutinize and
substantiate our hypotheses. Finally, a comparative
analysis of the hypotheses testing outcomes for the
two categories of companies was conducted, enabling
a nuanced understanding of the impacts of
globalization on various business models. A subset of
Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs) with an
international footprint (n = 216) was initially selected
for analysis. These enterprises boasted an average
workforce of 143 individuals, with employee counts
ranging from 5 to 500. With an annual revenue
generation of $100 million, they exhibited export
activities to three countries, with approximately 25%
of their revenue stemming from exports. This subset
was subsequently bifurcated into two groups of equal
size (n = 108 each), based on a median globalization
score. All statistical analyses were predicated upon
these classifications, offering a structured framework
for assessing the hypotheses.
Furthermore, SMEs grappling with the challenges
of globalization may derive substantial benefits from
embracing an entrepreneurial mindset. Businesses
imbued with such a spirit are predisposed towards
employing innovative marketing tactics to penetrate
unexplored markets and navigate complex business
landscapes adeptly. This is particularly pertinent for
SMEs, as deploying imaginative advertising
strategies, prioritizing product quality, and carving
out a niche through product specialization are
strategies likely to yield favourable outcomes. The
findings of subsequent studies, delving into the
validation of the study's hypotheses, are presented in
Table 1. Evaluation of hypotheses H1–H4, all centred
on bivariate relationships, was conducted through
correlation analysis utilising Pearson's correlation
coefficient. With respect to hypotheses H5–H7,
which share a common dependent variable, the
necessity to test only one regression equation arose.
Both hypotheses H1a and H1b, asserting a significant
linkage between an entrepreneurial mindset and
success in marketing and quality management,
garnered substantial support (p < .01). Hypothesis
H1c, positing a positive correlation between an
entrepreneurial mindset and product specialization,
received moderate backing (p < .05). Notably,
Globalization, SMEs, and Digitalization: The Role of Marketing and Entrepreneurial Behavior
625

responses to globalization and proactive market
readiness emerged as pivotal strategies, as identified
by managers, in navigating the challenges posed by
globalization.
Table 2: Discussion of the differences between the groups
and the study hypotheses.
Implied
Relationship Hypothesi
s
High-
Globaliza
tion
Group Low-
Globaliza
tion
Group Assessme
nt
Entrepreneurial
Behaviors
Marketing
leadership
H1a .41** 0.3
8
Support
e
d
Quality leadership H1b .26** 0.0
3
Support
e
d
Product
s
p
ecialization
H1c .21* .39
**
Support
e
d
Marketing
leadership
Technology
Acquisition
H2a .36** .31
**
Support
e
d
Globalization
res
p
onse
H2b .37** .22
*
Support
e
d
Internationalization
preparation
H2c 0.17 0.1
1
Not
signific
ant
Quality leadership
Technology
Ac
q
uisition
H3 0.15 .26
**
Support
e
d
Product
s
p
ecialization
Technology
acquisition
H4 .26** .25
**
Support
e
d
Technology
acquisition
Performance
H5 -0.7 0.1 Not
signific
ant
Globalization
response⇒Perform
ance
H6 .34** 0.1
3
Support
ed
Internationalization
preparation⇒Perfor
mance
H7 .25** 0.0
8
Support
ed
6 CONCLUSION
The study presents a cross-sectional snapshot of
business conditions, a method often criticised for
overlooking causal relationships in construct
interactions and failing to grasp the full complexities
of a dynamic system over time. Moreover, the
research was confined to a select few industries
directly impacted by globalization. Future
investigations should encompass a broader spectrum
of industries to validate the findings. Longitudinal
studies are recommended, comparing shifts in
business strategy with specific globalization
occurrences at defined junctures, offering insights
into the evolving relationship between marketing
strategies and performance over an extended
timeframe. Additionally, conducting in-depth
dialogues with industry leaders can yield valuable
insights for constructing case studies, enabling
thorough tracking of strategy and methodology
changes along with their underlying rationales.
REFERENCES
Al-Hakimi, M.A., Saleh, M.H., Borade, D.B., Hasan, M.B.,
& Sharma, D. (2022). Competitor orientation and SME
performance in competitive environments: the
moderating effect of marketing ethics. Journal of
Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, (ahead-of-
print).
Agyapong, A., Maaledidong, P.D., & Mensah, H.K. (2021).
Performance outcome of entrepreneurial behavior of
SMEs in a developing economy: the role of
international mindset. Journal of Strategy and
Management, 14(2), 227-245.
Rajagopal, N.K., Qureshi, N.I., Durga, S., Ramirez Asis,
E.H., Huerta Soto, R.M., Gupta, S.K., & Deepak, S.
(2022). Future of business culture: an artificial
intelligence-driven digital framework for organization
decision-making process. Complexity, 2022.
Irudayasamy, A., Christotodoss, P.R., & Natarajan, R.
(2022). Multilingual Novel Summarizer for Visually
Challenged Peoples. In Handbook of Research on
Technologies and Systems for E-Collaboration During
Global Crises (pp. 27-46). IGI Global.
Park, S., Lee, I.H., & Kim, J.E. (2020). Government support
and small-and medium-sized enterprise (SME)
performance: the moderating effects of diagnostic and
support services. Asian Business & Management, 19,
213-238.
Arzubiaga, U., Iturralde, T., Maseda, A., & Kotlar, J.
(2018). Entrepreneurial orientation and firm
performance in family SMEs: the moderating effects of
family, women, and strategic involvement in the board
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
626

of directors. International Entrepreneurship and
Management Journal, 14, 217-244.
Mpi, D.L. (2019). Encouraging Micro, Small and Medium
Enterprises (MSMES) for economic growth and
development in Nigeria and other developing
economies: The role of ‘the Igbo apprenticeship
system’. The Strategic Journal of Business & Change
Management, 6(1), 535-543.
Globalization, SMEs, and Digitalization: The Role of Marketing and Entrepreneurial Behavior
627
