Digital Payment Dynamics in Gig Economy Integration
V. Shobha and B. Vinnarasi
CHRIST (Deemed to be University), Bengaluru, India
Keywords: Digital Payment Systems, Gig Economy, Implementation, Integration, Technological Infrastructure.
Abstract: The gig economy, characterized by short-term employment and a reliance on independent workers, has
witnessed significant growth in recent years, making the integration of digital payment systems a vital aspect
of its functioning. This review paper critically examines the multifaceted factors that influence the adoption
and integration of digital payment systems within the gig economy. Drawing upon a comprehensive analysis
of 30 selected research papers out of 88, this review explores the key drivers and implications related to the
implementation of digital payment systems. The synthesis of these findings provides a holistic understanding
of the complexities surrounding the adoption of digital payment systems in the gig economy and offers
insights into their future development and implications.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the modern era of technological advancements and
digitalisation, the nature of work and the demand for
workers have profoundly transformed. On one hand,
the introduction of artificial intelligence, algorithms,
robots, and machine learning has certainly improved
the efficiency and ease of many tasks for human
workers. However, it has also led to the displacement
of certain jobs as machines increasingly take over,
reducing traditional job opportunities within the
economy adapt to these changes, companies have
been reevaluating their workforce models. The
demand for full-time workers has, in many cases,
shifted towards independent workers or gig workers.
This shift represents the emergence of a "gig
economy," where a significant portion of work is
performed by gig workers or freelancers (Altenried,
2021). These individuals work as independent, short-
term contractors and are compensated based on each
specific task or project they undertake. The Gig
economy, often described as a free market system,
revolves around the execution of temporary contracts
with independent workers for short-term
engagements. However, what sets this economic
model apart is its profound reliance on digital
technologies for both work arrangements and
payments. Platforms like Uber, which provide ride-
sharing services, epitomize this digital shift. In such
ecosystems, drivers not only receive work but also
payment through digital channels (Behl et al., 2022).
Consequently, the integration of digital payment
systems assumes a pivotal role, while also raising
significant concerns. The endeavour to streamline
these payment mechanisms encompasses a
multifaceted challenge, addressing technological,
security, human resource, and economic
considerations.
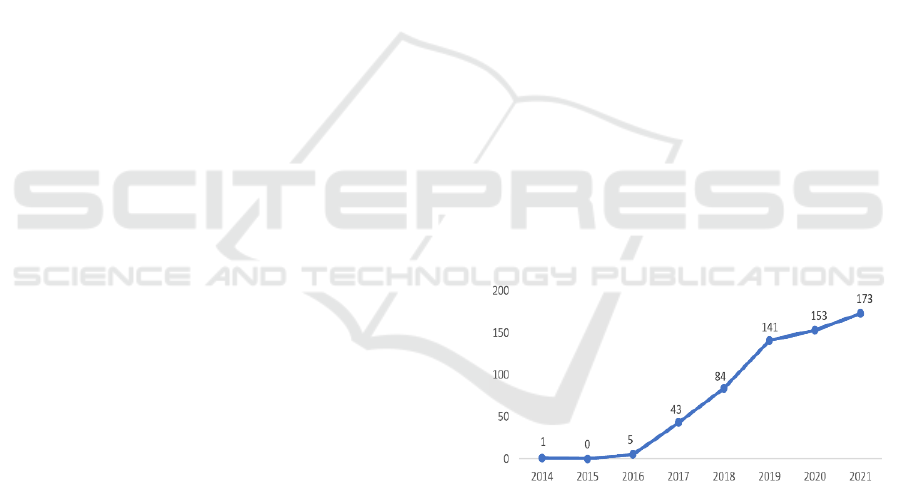
Figure 1: The rise of the Gig Economy in India (Source:
MDPI, 2022).
India's gig economy boasts a staggering 15 million
workers, involved in various sectors, according to a
report by the Boston Consulting Group. The 2019
report by the India Staffing Federation positions India
as the fifth-largest country globally in flexi-staffing,
indicating substantial growth. However, a significant
urban-rural digital divide is apparent, making the gig
economy predominantly urban-centric. With
regulations still in the drafting stage, there's a pressing
need for authorities to establish robust digital
payment systems to bridge the divide and foster
Shobha, V. and Vinnarasi, B.
Digital Payment Dynamics in Gig Economy Integration.
DOI: 10.5220/0012909500003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 657-660
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
657

economic growth. Major food delivery platforms like
Zomato and Swiggy rely on gig workers for food
deliveries, utilizing digital payments for transactions.
Fostering financial inclusion requires simplified
processes for gig workers to access banking services
and dedicated apps for managing insurance, social
security, and taxes. Robust digital integration on the
customer side is vital for transparency, security, and
accessibility. To overcome geographical disparities,
integrating digital payment systems with apps
supporting offline digital payments will enhance
inclusivity in the gig economy.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Table 1: Digital Payment Revolution: Transforming the Gig Economy.
Author
Findings
Harvard Business
Review (2021)
Integrating digital payments in the gig economy can free up resources for other business aspects.
Altenried (2021)
Digital payment integration should occur at all levels of the gig economy.
World Bank (2022)
Digital payments streamline processes, ensuring timely compensation for gig workers and
reducing administrative burdens.
Álvarez Cuesta (2018)
Digital payments enhance financial security for gig workers and reduce administrative burdens
for employers.
Behl et al. (2022)
Evolving digital payment systems require substantial investments in technology to keep pace
with security advancements and transaction volumes.
Vyas (2020)
Regulators must adapt to emerging technologies and business models as digital payments
become more integrated into daily life.
3 OBJECTIVE
• To Identify Key Factors Influencing the
Adoption of Digital Payment Systems in the
Gig Economy.
• To Assess the Impacts and Implications of
Digital Payment System Integration in the
Gig Economy.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
For this review paper, a comprehensive research
methodology was employed, involving the initial
selection of 88 relevant papers. A careful screening
process based on key keywords led to the inclusion of
50 papers. Subsequently, 30 of these papers were
meticulously examined to analyze the multifaceted
factors influencing the implementation and
integration of digital payment systems in the gig
economy. The review laid a robust foundation for
understanding the interconnections among these
factors and their profound implications for the gig
economy and its stakeholders.
5 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
According to Behl et al. (2022), the gig -economy has
been a fruit of disruptive innovation where the digital
revolution has created access to on-demand services
like Food delivery and transport logistics like Uber,
and OLA. However, the product of disruptive
innovations, like start-up culture, has been highly
questioned for its unstructured network and
sustainability (Basadur,2016). The integration &
implementation of a digital payment system creates
the scope for discussion on its effect on the various
aspects of the gig economy (Álvarez Cuesta, 2018).
Hence the coming sections will discuss the issues in
the Gig economy from various perspectives and its
prospective resolution with the integration and
implementation of a digital payment system.
5.1 Factors Influencing the Adoption of
Digital Payment Systems in the Gig
Economy
Kim, L. (2018) in the artcile, “Capability Building in
Catching-up at Hyundai Motor & Gig Economy” has
argued that the initialization is the foundation of the
gig economy. Hence the adoption of digital payment
should be at various levels for a holistic inclusivity
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
658

and sustainability of the gig culture. Hence following
factors have been considered for discussion on digital
payment integration in the Gig economy based on the
review of journal papers (Cherry et al.,2020).
Technological Infrastructure
The backbone for seamless digital fund exchange, its
challenges include ensuring universal access and
sustainability, addressing digital divide issues, and
considering environmental concerns. Future
expansions like 5G, IoT, and edge computing present
opportunities and data security challenges.
Regulatory Framework
Clear regulations fostering trust and security while
encouraging innovation are vital. Striking a balance
between safety and innovation is key, as overly
complex regulations may hinder growth.
International cooperation in regulating cross-border
payments might become more crucial.
Trust and Security
Paramount in digital payment adoption, trust is
established through robust security measures such as
encryption, two-factor authentication, and fraud
detection systems. Users need to feel confident that
their financial data is secure.
User Experience
A positive user experience through intuitive design,
functionality, and excellent customer support
encourages adoption. Conversely, poor user
experiences, like confusing interfaces or glitches, can
deter users from embracing digital payments.
Financial Considerations
Affordability, transparency in transaction costs, and
accessibility are critical factors influencing adoption.
Users seek cost-effective alternatives to traditional
payment methods. Achieving reasonable transaction
costs while ensuring sustainable revenue streams for
service providers is a challenge.
In summary, the integration of digital payments
into the gig economy requires robust technological
infrastructure, balanced regulatory frameworks,
emphasis on trust and security, a positive user
experience, and addressing financial considerations
for affordability and transparency in transaction costs.
These factors together contribute to the holistic
inclusivity and sustainability of digital payment
adoption in the gig culture.
5.2 Impacts and Implications of Digital
Payment System Integration in the
Gig Economy
Economic Sustainability
Koutsimpogiorgos et al. (2020) emphasize economic
sustainability at micro and macro levels concerning
gig workers' reliance on digital payments for income
stability. For individuals, it provides predictable cash
flows, while on a broader scale, it increases financial
inclusion and stimulates economic growth.
Social Inclusivity
Langley (2021) highlight digital payments' role in
fostering social inclusivity by breaking traditional
barriers for individuals from diverse backgrounds,
including the underbanked and unbanked. It
contributes to gender inclusivity and transcends
geographical boundaries, enabling opportunities for
remote or rural dwellers.
Innovative Sustainability
Friedman (2021) stress how innovative features like
real-time tracking and digital wallets empower gig
workers. These tools address challenges such as
income volatility, offering better financial
management and control, ensuring sustainability in
the gig economy.
6 DISCUSSION
The Gig economy, reliant on technological
infrastructure for digital transactions, underscores its
vital role in shaping the landscape of digital payment
systems. Accessibility and reliability are crucial for
seamless transactions, essential for the thriving
existence of gig work ecosystems (Doucette,2019) .
Regulatory frameworks strike a balance between
innovation and user safeguarding, significantly
impacting the adoption of digital payments. Trust and
security are pivotal; any breach disrupts the entire gig
economy ecosystem.
Innovative sustainability features in digital
payments address income volatility for gig workers,
providing real-time tracking, budgeting aid, and
tailored financial services, ensuring economic
stability (Cherry,2016). Market dynamics,
Digital Payment Dynamics in Gig Economy Integration
659

intertwined with these factors, foster competition,
driving innovation and service enhancement. Yet, this
competition can lead to complexities and
fragmentation, necessitating a vigilant and adaptable
approach for the evolving gig economy's continued
relevance.
7 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, the implementation and integration of
digital payment systems in the gig economy are
subject to a multitude of interconnected factors.
These factors, including technological infrastructure,
regulatory frameworks, trust and security, user
experience, financial considerations, economic
sustainability, social inclusivity, innovative features,
and market dynamics, collectively shape the digital
financial landscape within the gig economy. Hence,
Continuous evaluation and adaptation are vital in this
dynamic landscape. The ever-evolving gig economy
necessitates a vigilant and flexible approach to ensure
the digital financial landscape's relevance and
effectiveness. Understanding the interconnected
nature of these factors is essential in crafting
strategies that leverage these elements to foster a
more resilient and inclusive gig economy, ensuring its
continued success in an ever-changing world of work.
REFERENCES
Altenried, M. (2021). Mobile workers, contingent labour:
Migration, the gig economy and the multiplication of
labour. Environment and Planning A: Economy and
Space, 2(5).
Álvarez Cuesta, H. (2018). The gig economy and the
obligation to coordinate the security and health of their
self-employed. Revista Jurídica de La Universidad de
León, 2(5), 83.
Basadur, M., & Hausdorf, P. A. (2016). Gig Economy &
Measuring Divergent Thinking Attitudes Related to
Creative Problem Solving and Innovation
Management. Creativity Research Journal, 9(1), 21–32.
Behl, A., Rajagopal, K., Sheorey, P., & Mahendra, A.
(2022). Barriers to entry of gig workers in the gig
platforms: exploring the dark side of the gig economy.
Aslib Journal of Information Management, ahead-of-
print(ahead-of-print).
Cherry, M. A. (2016). Gig Economy: Settlements Leave
Labor Issues Unsettled. SSRN Electronic Journal, 5(2).
Doucette, M. H., & Bradford, W. D. (2019). Dual Job
Holding and the Gig Economy: Allocation of Effort
across Primary and Gig Jobs. Southern Economic
Journal, 85(4), 1217–1242.
Friedman, G. (2014). Workers without employers: shadow
corporations and the rise of the gig economy. Review
of Keynesian Economics, 2(2), 171–188.
Koutsimpogiorgos, N., Slageren, J., Herrmann, Andrea M.,
& Frenken, K. (2020). Conceptualising the Gig
Economy and Its Regulatory Problems. Policy &
Internet, 12(4).
Langley, P., & Leyshon, A. (2017). Platform capitalism:
The intermediation and capitalisation of digital
economic circulation. Finance and Society, 3(1), 11–
31.
Vyas, N. (2020). “Gender inequality- now available on
digital platform”: an interplay between gender equality
and the gig economy in the European Union. European
Labour Law Journal, 12(1).
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
660
