
Learner-Centric Approaches: The Effectiveness of the Seven-I
Framework
Monika Suri and Vishwas Madhavrao Deokar
Auro University, Surat, India
Keywords: Higher Education, Futuristic Pedagogy, Learner Growth, Development, Teaching Management.
Abstract: This research paper presents a case study analysis of the impact of the Seven-I Learner Centric Framework
on teaching management and communication processes in higher education. The framework is designed to
provide a futuristic and effective pedagogical approach that caters to the needs of learners in the field of
management and communication. The study examines the implementation of the Seven-I Framework in a
higher education institution, focusing on its influence on learner growth, development, teaching management,
and student-teacher communication. Qualitative research methods, including interviews and observations,
were utilized to collect data. The findings highlight the transformative effects of the framework in enhancing
teaching practices, facilitating effective communication between students and teachers, and fostering learner
development. This research contributes to the existing literature by providing insights into the practical
application and outcomes of the Seven-I Learner-Centric Framework in the context of management and
communication education within higher education.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the past few years, there has been an increasing
emphasis on learner-centric approaches within higher
education. This shift moves away from the
conventional teacher-centered model and instead
prioritizes placing the learner at the heart of the
educational experience. The objective of learner-
centric education is to empower students by actively
engaging them in the learning process, fostering
critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and self-
directed learning. Consequently, educational
institutions have been actively exploring different
frameworks and models to facilitate and improve
learner-centric practices.
The field of higher education is constantly
evolving, necessitating the exploration and
implementation of pedagogical tools that align with
the needs and interests of modern learners. Both
domestic and international higher education
institutions recognize the significance of making
education meaningful and future-oriented to succeed.
Alongside a holistic educational approach, vibrant
campuses, technologically advanced SMART
classes, digitally adept faculty, and the inclusion of
industry and community engagement are
prerequisites for impactful teaching and learning
methodologies.
One such framework that has gained attention is
the Seven-I Learner-Centric Framework. This
framework is designed to provide a comprehensive
approach to learner-centric education by addressing
seven key dimensions: individualization, inquiry-
based learning, and integration of technology,
interaction, and collaboration, interdisciplinary
learning, intrinsic motivation, and assessment for
learning. By integrating these dimensions, the Seven-
I Learner Centric Framework.
The significance of the Seven-I Learner Centric
Framework lies in its potential to offer educators a
structured approach for designing and delivering
learner-centric instruction. This framework ensures
that teaching methods and communication strategies
align with the principles of active student engagement
and individualized learning. By implementing the
Seven-I Learner Centric Framework, educators can
cultivate a positive and supportive learning
environment that promotes student motivation,
creativity, and critical thinking skills.
Suri, M. and Deokar, V.
Learner-Centric Approaches: The Effectiveness of the Seven-I Framework.
DOI: 10.5220/0012914500003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 717-721
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
717

2 RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
This research aims to investigate the impact of the
Seven-I Learner Centric Framework on teaching
management and communication process-learning in
higher education. The study will employ a case study
approach, focusing on a specific higher education
institution that has implemented the framework. The
research objectives include:
• To examine how the Seven-I Learner
Centric Framework is implemented in
the selected institution.
• To assess the effects of the framework
on teaching management practices,
including instructional design, delivery,
and assessment methods.
• To evaluate the impact of the framework
on communication processes between
educators and students.
• To identify the challenges and
opportunities encountered during the
implementation of the framework.
3 RESEARCH QUESTIONS
I. How is the Seven-I Learner Centric
Framework implemented in the selected
higher education institution?
II. What are the effects of the framework on
teaching management practices,
including instructional design, delivery,
and assessment methods?
III. How does the framework influence
communication processes between
educators and students?
IV. What are the challenges and
opportunities encountered during the
implementation of the Seven-I Learner-
Centric Framework?
V. What recommendations can be made for
the effective implementation of the
framework in higher education settings?
4 CASE STUDY CONTEXT
The case study institution selected for this research
paper represents a higher education institution known
for its distinctive educational practices. This section
provides a detailed description of the institution,
highlighting its unique characteristics and approaches
to education. Additionally, it explores the institution's
implementation of the Seven-I Learner-Centric
Framework, elaborating on how the framework has
been integrated into its teaching and learning
processes. Furthermore, this section delves into the
challenges and opportunities faced during the
implementation of the framework, fostering a
comprehensive understanding of the institution's
journey toward learner-centric education.
By addressing these research objectives, this
study aims to contribute to the existing knowledge on
learner-centric education and offer practical insights
to educators and institutions seeking to implement the
Seven-I Learner-Centric Framework to enhance
teaching management and communication processes
in higher education.
5 LITERATURE REVIEW
Allen, Kern, Vella-Brodrick, et al. 2018 conducted a
systematic review that identified ten key themes
influencing various factors such as personal
characteristics. This research provides valuable
insights into the factors shaping students' sense of
belonging, informing the development of policies,
pedagogical strategies, and teacher training programs
for supportive school environments.
Bali 2014 conducted a pedagogical assessment of
Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs). The
findings revealed variations in MOOC
implementation, with some courses demonstrating
effective pedagogy fostering higher-order thinking
skills, while others fell short. Through analysis and
relevant literature reviews, the author identified
noteworthy pedagogical practices and areas for
improvement within MOOCs. This assessment
underscores the importance of effective learning
outcomes in MOOCs.
Yigitcanlar, T., Corchado, J. M., Mehmood, R.,
Li, R. Y. M., Mossberger, K., & Desouza, K. 2021
explore the use of digital technologies by higher
education institutions to address urbanization
challenges. They specifically examine a
comprehensive literature review and analysis, the
authors present a conceptual framework emphasizing
the need to balance costs, benefits, risks, and impacts.
The insights gained have practical implications for
achieving responsible outcomes in urban settings.
Reeve, J. 2006 highlights the varying levels of
student engagement in classroom learning, influenced
by the supportive quality of the classroom climate.
Teachers can foster autonomy-supportive motivation
by nurturing students' inner resources. The article
discusses autonomy-supportive behaviors and
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
718

statements of teachers, emphasizing enhancing
autonomy support, balancing autonomy support and
structure, and the importance of autonomy-supportive
motivation in teacher-student relationships.
Khan et al. 2021 had the objective of creating and
validating questionnaires through cognitive
interviews. This process led to modifications,
ultimately yielding curriculum viability inhibitor
questionnaires that are both valid and reliable. These
questionnaires can be utilized by medical schools to
identify inhibitors and enhance curriculum standards.
Ivan Sipos 1980 explores the challenges posed by
the rapid growth of higher education and emphasizes
the role of educational technology as a solution.
Educational technology enables higher education
institutions to enhance access, offer a broader range
of subjects, manage resources effectively, and
improve overall teaching and learning experiences.
Vlachopoulos and Makri 2019 concentrate on
distance education and the instructional design
approach required for educational transformation.
The study analyzes different factors and develops
instructions for creating effective online courses, with
an emphasis on well-structured, interactive, and
dynamic approaches.
6 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
Seven-I Learner Centric Framework on teaching
management and communication processes in higher
education. This objective will be achieved through a
case study approach, focusing on a specific higher
education institution that has implemented the
framework. The study aims to examine the
implementation of the framework, assess its effects
on teaching management practices, evaluate its
impact on communication processes between
educators and students, identify challenges and
opportunities during implementation, and provide
recommendations for effective implementation in
higher education settings.
6.1 Research Design
This study adopts a descriptive and exploratory
research design to investigate the influence of the
Seven-I Learner Centric Framework on teaching
management and communication processes within
higher education. The aim is to provide valuable
insights and practical recommendations for the
effective implementation of the framework.
6.2 Case Study Selection
The case study institution was chosen based on its
successful implementation of the Seven-I Learner
Centric Framework, showcasing a strong dedication
to learner-centric education and notable practices in
teaching management and communication processes.
6.3 Data Collection Methods
Given the absence of direct participant interaction,
this research does not involve interviews, surveys, or
observations. Instead, data were collected through an
extensive examination of existing literature, reports,
institutional documents, and pertinent materials
relating to the case study institution's adoption of the
framework. This secondary data collection approach
facilitated a comprehensive comprehension of the
framework's impact on teaching management and
communication processes.
6.4 Data Analysis Techniques
The collected data underwent rigorous analysis using
a qualitative content analysis approach. This method
allowed for the examination and interpretation of
information obtained from the literature review,
reports, and institutional documents. Through
systematic analysis, key themes, patterns, and
insights relevant to the influence of the Seven-I
Learner Centric Framework on teaching management
and communication processes in higher education
were identified and synthesized.
The comprehensive analysis of existing literature and
institutional materials ensures a robust understanding
of the case study institution's implementation of the
framework and its effects on teaching management
and communication processes.
The Seven-I Learner Centric Framework, which has
been self-conceptualized. This framework serves as a
defining symbol of an effective teaching and learning
environment that can be seamlessly integrated into
both online and offline educational approaches.
The framework consists of seven key dimensions:
1. Informative.
2. Interesting.
3. Impactful.
4. Innovative.
5. Integral.
6. Interactive.
7. Industry-ready.
By incorporating these dimensions, the framework
provides a comprehensive learner-centric approach
that fosters an inclusive and engaging learning
Learner-Centric Approaches: The Effectiveness of the Seven-I Framework
719
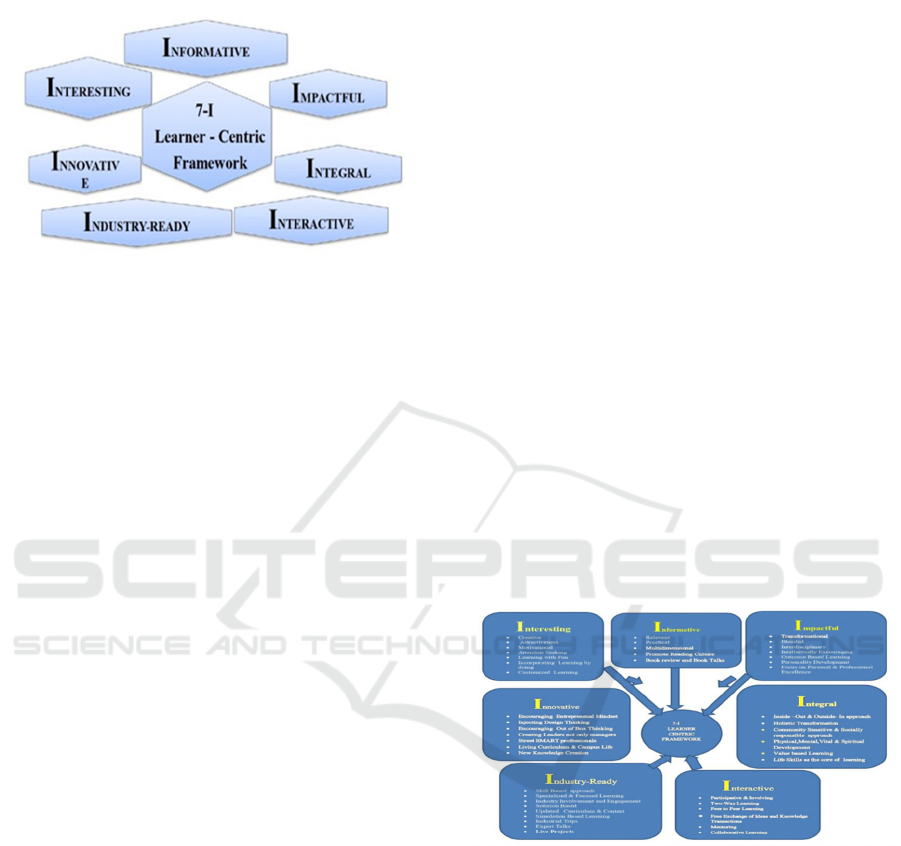
environment, supporting the growth and development
of students.
Figure 1: Visualization of the Seven-I Learner-Centric
Framework.
Informative: The effectiveness of teaching lies in its
alignment with the defined learning objectives of
specific modules. It should embrace a practical
approach that integrates real-life scenarios from
business, industry, and everyday life. Nurturing
multidimensional knowledge equips learners with the
necessary skills to consciously make informed
decisions. To foster informative learning experiences,
practices such as encouraging reading habits through
book reviews and discouraging superficial
understanding should be employed.
Interesting: Modern learners seek engaging and
enjoyable learning experiences. Employing
pedagogies that incorporate experiential learning can
capture their attention and motivation using various
edutainment tools.
Impactful: It is essential to measure the impact of the
effectiveness of teaching-learning along with various
techniques. Outcome-based learning and visible
personality development validate the efficacy of
teaching methodologies.
Innovative: Innovative teaching practices foster an
entrepreneurial mindset, encourage design thinking,
and nurture out-of-the-box thinking. Establishing
incubators on university campuses facilitates the
growth of start-ups and entrepreneurship, cultivating
leaders who shape the future of higher education. The
demand for street-smart professionals with fresh
perspectives is increasing, as they reshape the
landscape of businesses and industries. Living
curricula and campuses play a vital role in promoting
innovative teaching and learning methodologies,
complemented by the development of SMART
infrastructure.
Integral: Integral development encompasses
behavioural, cognitive, and attitudinal
transformations in learners. An integral approach to
education encompasses learners' physical, mental,
vital, and spiritual aspects, preparing them for
lifelong learning beyond specific scenarios or
professions. Integrating learners' competencies, skills,
personalities, and lifestyles in ways that align with the
interests of the industry and community fosters social
responsibility and moral accountability.
Interactive: Interactions with Digital classrooms
have transformed the dynamics between learners and
teachers, making teaching more participatory and
collaborative. Mentorship and peer-to-peer learning
enhance knowledge accessibility and facilitate
collaborative learning experiences.
Industry-Ready: Active industry involvement in the
teaching-learning process plays a pivotal role in
enhancing learners' employability and fostering their
economic independence. Effective teaching
methodologies prioritize specialized and skills-based
learning as key objectives. By incorporating
simulation-based learning, industry visits, and expert
talks, learners acquire practical skills and develop
problem-solving abilities that are directly applicable
to real-world contexts. This active engagement with
the industry enriches the learning experience,
promotes experiential learning, and inculcates core
values and ethics in learners, thereby equipping them
with a competitive edge.
Figure 2: The 'Seven-I' Learner Centric Teaching-Learning
Self-Conceptualized Framework.
7 CONCLUSION
This study sheds light on the key findings regarding
the integration of the Seven-I Learner-Centric
framework offers significant benefits. It establishes a
transformative mentor-mentee relationship and
strengthens the connections among all stakeholders
within higher education systems. The integration of
blended learning practices, incorporating both online
and offline modalities, is crucial. It provides insights
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
720

into the effective implementation of the Seven-I
Learner Centric Framework and its impact on
teaching management and communication processes
in higher education. The framework offers a
comprehensive approach to learner-centric education,
creating an inclusive and engaging learning
environment that promotes student growth and
development.
Based on the findings, several recommendations can
be made for further research and practical
implementation of the Seven-I Learner-Centric
Framework. The long-term effects of the framework
on student outcomes and exploring additional
dimensions that can enhance learner engagement and
success has scope and it is also essential for futuristic
research. Practical implementation should involve
faculty training and development programs, as well
as continuous monitoring and evaluation to ensure the
framework's effectiveness.
By embracing this collaborative journey and
implementing the Seven-I Learner Centric
Framework, higher education institutions can
enhance their value proposition and gain a
competitive edge globally. This integration fosters an
integrated approach to learning, aligning with the
evolving needs and demands of learners in India and
beyond. Institutions must identify and adopt best
practices from blended learning, providing a
teaching-learning experience that is not only
memorable but also sustainable in the long run.
Thus, The Integration of the Seven-I Learner Centric
Framework holds great promise for higher education
institutions, offering a transformative approach to
teaching and learning. The Seven-I Framework is also
helpful and effective for a relationship between
Online-Offline mode. By implementing this
framework and incorporating the recommendations
mentioned, institutions can create a learner-centric
environment that prepares students for success in a
rapidly changing educational landscape.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
We extend our sincere appreciation to Honourable
Prof. (Dr.) Parimal Vyas, Vice Chancellor of Auro
University, Chief Operating Officer Mr. Suresh
Mathur, Chief Finance Officer Mr. Nayan Banker,
Registrar Prof. Amreesh Misra, Controller of the
Examinations Mrs. Prerana Dahiwade, Head of
AICEC Prof. Sandeep Sharma, as well as all the
Heads of Departments and Faculty members of Auro
University for their valuable inspiration and
unwavering support throughout the course of this
research endeavor.
REFERENCES
Allen, K., Kern, M. L., Vella-Brodrick, D., & et al. (2018).
What schools need to know about fostering school
belonging: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology
Review, 30(1), 1–34.
Bali, M. (2014). MOOC pedagogy: Gleaning good practice
from existing MOOCs. MERLOT Journal of Online
Learning and Teaching, 10(1), 44–56.
Yigitcanlar, T., Corchado, J. M., Mehmood, R., Li, R. Y.
M., Mossberger, K., & Desouza, K. (2021).
Responsible urban innovation with local government
artificial intelligence (AI): A conceptual framework
and research agenda. Journal of Open Innovation:
Technology, Market, and Complexity, 7(1), 71.
Reeve, J. (2006). Teachers as facilitators: What autonomy-
supportive teachers do and why their students benefit.
The Elementary School Journal, 106(3), 225–236.
Khan, R. A., Spruijt, A., Mahboob, U., Al Eraky, M., & Van
Merrienboer, J. J. G. (2021). Development and
validation of teacher and student questionnaires
measuring inhibitors of curriculum viability. BMC
Medical Education, 21(1).
Vlachopoulos, D., & Makri, A. (2019). Online
communication and interaction in distance higher
education: A framework study of good practice.
International Review of Education, 65(4), 605–632.
Evans, C., Kandiko Howson, C., Forsythe, A., & Edwards,
C. (2020). What constitutes high-quality higher
education pedagogical research? Assessment &
Evaluation in Higher Education, 46(4), 525–546.
Fittipaldi, D. (2020). Managing the dynamics of group
projects in higher education: Best practices suggested
by empirical research. Universal Journal of Educational
Research, 8(5), 1778–1796.
Tweheyo, G., & Mugarura, A. (2021). Strategic response to
crises: A case study of universities in Uganda during
COVID-19. International Journal of Social Science and
Economic Research, 6(4), 1250-1271.
Thomas, K., & Melanie, E. (2021). Computer-assisted
instruction tools: A model to guide users in low- and
middle-income countries. International Journal of
Education and Development using Information and
Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 17(1), 82-99.
Learner-Centric Approaches: The Effectiveness of the Seven-I Framework
721
