
CRM Strategies in Commercial Banks: Fostering Long-Term
Customer Relationships
Ajatashatru Samal
1
, N. Manasa
2
, Priya Vinod
2
and Hemalata Radhakrishna
3
1
Visvesvaraya Technological University, India
2
Christ University, India
3
Reva University, Bengaluru, India
Keywords: Data Privacy, Long Term Relationship, Retention, Acquires Quick Service.
Abstract: The research paper investigates the impact of socio-economic characteristics on Customer Relationship
Management (CRM) practices within private banks, highlighting CRM's role as a customer-centric, holistic
approach. In the context of economic uncertainties, rapid technological advancements, swift market dynamics,
and intensifying competition, CRM technologies are critical for coordinating sales, marketing, and support
services. The study reveals significant variability in socio-economic factors across different bank branches,
with these factors correlatively influencing customer accounts. Notably, elements such as customer
satisfaction, robust privacy policies, and prompt service are pivotal in fostering enhanced relationships
between private banks and their clientele. The analysis confirms that effective CRM not only safeguards data
privacy but also strengthens customer relationships and proactively anticipates customer needs, thereby
underpinning the strategic importance of CRM in retaining loyalty and driving bank revenues.
1 INTRODUCTION
The idea of CRM in private banks has attracted the
attention of academicians, experts and bankers in the
financial area. The organizations have extensively
recognized that customers are profitable now-a-days.
CRM develops life time customers. It allows
developing customer base. It manages all aspects of
customer interaction in a manner that enables banks
to maximize profitability from every customers.
CRM is a business model that aligns product and
sales strategic with needs of customers and
preferences (Sampath et al. 2014). CRM has been
viewed as a process aimed at collecting customer
data, find profiles of customers and use the customer
knowledge in specific marketing activities (Anu
Putney et al. 2013). Indian private banks are facing a
dual challenge of building customer base and
performance maintenance. CRM helps to build
customer base through IT and helps in the building of
long term relationship and sustainability. CRM can be
viewed as a process geared towards increasing the
value of a customer order life time (Farress P. 2001).
Banks need to focus for creating added value and
establishing forever relationship with customer. For
the last two decades there is a significant changes in
the banking industries for business process like
mobile banking, ATMC, cost reduction in transaction
and delivering better service for managing the
supplier- CRM is continuously the important critical
issue in the banking sector (Ndubisi et al. 2007)
customers have also started demanding more and
more, more knowledgeable, aware of alternatives and
capable of negotiating with different service
providers (Heinonen 2014).
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Dr S Sudhakar, Dr Thomas Michael, Mrs V
Santhiya(2023) focus that Customer relationship
management establish a long term relationship with
customers by analysing the need and wants for their
immediate services which is the essential components
of banking CRM . He also focus through the process
of CRM helps the customer complaint resolution in
banks with a timely and effective manner . As a result
it solved the immediate issues of customer complaints
in a fast way and retain customer loyalty.
Dr G Manoj, Dr Leena Jenefa(2022) refers CRM
maintain a long relationship with the process and
722
Samal, A., Manasa, N., Vinod, P. and Radhakrishna, H.
CRM Strategies in Commercial Banks: Fostering Long-Term Customer Relationships.
DOI: 10.5220/0012914600003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 722-726
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
enhance the banking instrument and services in
current scenario of present situation.
K.P Anjana(2021) indicates the vital role of CRM
practises in the present environment which influence
the better functioning in the banking sector. core
benefits in banking business process and customers
by using better tools and techniques in the banking
sectors.
The authors suggested that Indian banking need to
focus new services and develop new marketing
strategy for the betterment of banking sectors.
3 STUDY OBJECTIVE
• To understand the socio-economic feature of
respondents.
• To understand CRM as a customer-centric
approach.
• To examine the CRM practices in private
banks.
• To identify the factors influencing long-term
relationships between private banks and
customers.
4 PROBLEM STATEMENT
Customer switching to others banks and effective
retention and attraction of customers can be
effectively managed by CRM strategies. On account
of severe competition among banks CRM came into
existence with much focus on customers. Consumer
attraction and retention has become a complex
impressing factors banks here introduced different
strategies to retain the existing customers or attract
new customers. The strategies followed by different
private banks speak about the significance of CRM in
banks. CRM is a approach for management that gives
the firm to get, attract and retain the customer
profitability through the process of CRM. The CRM
achievement depends upon the needs and desires of
the customers and by integrating them by using
organizing strategy, people technology and business
process.
CRM in banks in banks must maintain good
relationship with customers. This makes the banks to
take up branch expansion all over the country.
Further, maintenance customers loyalty and trust is
utmost important in addition to providing different
products and services.
Customer will never switch to other banks if they
are fully satisfied with quality of service.
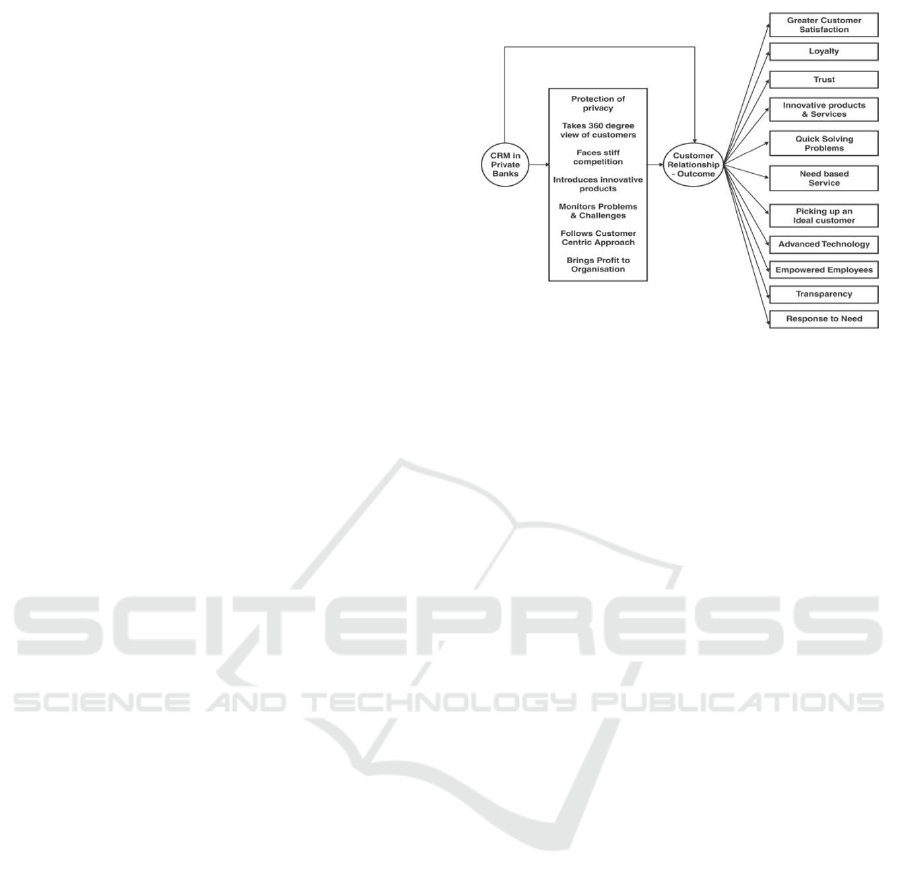
Figure 1: Conceptual Model of the Study.
5 HYPOTHESES
• H
0
: The socio-economic characteristics are
not impacting on the study.
• H
1
: The socio economic characteristics are
impacting the study.
• H
2
: Private commercial banks do not
practice CRM.
• H
3
: There is no customer centric approach in
private banks.
• H
4
: There exist significant variation in the
customer centric approach followed by
banks.
6 LIMITATIONS
• The study is restricted only to Yelahanka
Sub-district and covered only the private
banks.
• The study considers only 200 respondents.
7 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The current study adopts a customer-centric approach
to explore Customer Relationship Management
(CRM) practices within the banking sector. Drawing
inspiration from academic contributions in the field,
the research aims to identify factors influencing long-
term relationships between banks and their customers
and to analyse CRM strategies through the lens of
customer-centricity. The research was conducted
within the naturalistic settings of bank premises in the
CRM Strategies in Commercial Banks: Fostering Long-Term Customer Relationships
723

Yelahanka subdistrict of Bengaluru Urban district,
capturing insights from customers either before or
after their banking transactions. This method ensures
that the data reflects genuine customer experiences
and attitudes towards the CRM practices of their
respective banks.
The study encompasses a sample of 200
customers from diverse backgrounds, ranging from
agriculture to homemaking, residing in the Yelahanka
subdistrict. To ensure a comprehensive
understanding, four bustling localities were chosen:
Yelahanka Old Town, Hunusamaranahalli,
Yelahanka New Town, and the broader Bengaluru
area. The banks involved in the study included major
players like ICICI, HDFC, Axis, Indusind, and Citi
Bank. Participants were selected using a convenience
sampling technique, which involved approaching
customers at different branches of these banks,
ensuring each bank had equal representation of 40
participants.
Data collection was conducted through a
structured questionnaire, designed as the primary
research instrument. This questionnaire employed a
bipolar Likert 5-point scale to measure the intensity
of customer opinions regarding various aspects of
CRM practices. The choice of a bipolar scale
facilitated the capture of a spectrum of customer
attitudes, from strongly agree to strongly disagree,
thus enabling a nuanced analysis of customer
satisfaction and engagement. Additionally, the study
utilised secondary data sources, including academic
books, e-journals, and relevant websites, to enrich the
analysis and contextualise the findings within
existing literature.
Data analysis was carried out using robust
statistical tools such as the chi-squared test and
contingency coefficient, aimed at assessing the
relationships and dependencies between the variables
under study. The Garrett Ranking method was also
utilised to prioritise the factors as per their influence
on customer satisfaction and loyalty. The findings
were systematically presented, with a focus on the
socio-economic characteristics of the respondents,
such as gender, marital status, age, education,
occupation, monthly income, account types, and the
duration of their relationship with the banks. This
comprehensive methodological approach ensured a
thorough exploration of CRM practices, offering
valuable insights into how banks can enhance their
customer relationships in a competitive sector.
8 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
In examining the influence of socio-economic factors
on the study of Customer Relationship Management
(CRM) practices within private commercial banks, a
rigorous analysis has been conducted, as evidenced
by the findings presented in Table I. This analysis
categorises the respondents based on various socio-
economic characteristics, including gender, marital
status, age, education, occupation, and monthly
income, as well as their tenure with the bank and
whether they hold accounts with different financial
institutions. The chi-square (χ²) test was utilised to
determine the statistical significance of the
differences observed in these categories. It is
noteworthy that except for two categories—namely,
the presence of multiple bank accounts and the
duration of the relationship with the bank—
significant and substantial relationships have been
identified across all other demographics,
demonstrating a high degree of variance.
The implications of these findings are profound,
suggesting that socio-economic parameters indeed
play a pivotal role in the application and efficacy of
CRM practices. For instance, the significant
differences observed across age groups and
educational levels indicate that CRM strategies may
need to be tailored to meet the specific needs and
preferences of distinct demographic cohorts.
Similarly, variations in occupation and income levels
may influence customers' expectations and their
perceptions of value, which are critical components
in establishing and maintaining long-term customer
relationships. This supports the alternative hypothesis
(H₁) that socio-economic characteristics do impact
CRM studies, thus challenging the null hypothesis
(H₀) which posited that these factors do not influence
CRM.
Ultimately, the research underscores the necessity
for banks to adopt a customer-centric approach that
recognises and addresses the diverse backgrounds
and needs of their clientele. This approach not only
enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty but also
positions the banks to better manage their customer
relationships in a dynamic and competitive
environment. These insights are particularly valuable
for formulating strategic decisions and refining CRM
practices that are inclusive and effective, thereby
fostering enduring customer relationships that
contribute to sustained business success.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
724

Table 1: Factors Impacting CRM as a Customer Centric
Approach.
Factors impacting CRM as a
customer centric approach
SA
A
SDA
RT
RT2
Establishes and maintains
strong relationship
14
6
4
24
576
CRM understand all customers
and better the understand
stronger will be relationship
8
2
1
11
121
CRM understands customer
base and hence renders better
service
7
3
2
12
144
Stabilised customer
satisfaction leads to strong
implement in the business
6
3
1
10
100
CRM understands customer
interactions
15
2
1
18
324
CRM prefer to schedule tasks
and set up reminders which
leads to better business
8
4
2
14
196
CRM strategies helps to retain
the existing customer and
thereby enhances better
performance
20
6
4
30
900
CRM anticipates needs to
customers
16
4
2
22
484
CRM protects data privacy
26
10
5
41
1681
CRM ensures faster
communication
10
5
3
18
324
Total
130
45
25
200
4750
The study in question utilises the customer
relationship management (CRM) framework to
investigate its efficacy as a customer-centric
approach within private commercial banks. The data
outlined in Table II focuses on various factors that
purportedly enhance CRM's role as a customer-
centric tool. These factors range from establishing
robust customer relationships to ensuring the
protection of customer data privacy. The responses
collected were categorised under strongly agree (SA),
agree (A), and strongly disagree (SDA), alongside
their respective totals (RT) and the square of these
totals (RT2). It is evident from the higher scores
associated with certain factors—particularly the
protection of data privacy—that there is a strong
inclination towards acknowledging CRM’s pivotal
role in fostering a customer-centric environment. The
statistical method employed here, Kendall’s
coefficient of concordance, helps in quantifying the
consensus among the variables studied.
The analysis confirms a significant alignment
among the variables impacting CRM’s effectiveness
in centring customer needs. This is underlined by the
rejection of the null hypothesis (H0), which posited
no significant variance in customer approaches
amongst different banks. The results compellingly
advocate for a customer-centric orientation in CRM
practices, with high priority given to data privacy and
customer retention strategies. By confirming the
alternate hypothesis (H1), the study substantiates the
considerable relationship between CRM strategies
and a customer-centric approach. Thus, it is
justifiable to assert that CRM, when effectively
implemented, is intrinsically geared towards
enhancing customer relationships and satisfaction,
thereby solidifying its standing as a fundamentally
customer-centric approach.
9 DISCUSSION
This paper is to focus how far the socio-economic
factors impress the study on CRM practices, factors
shape the long term relationship, and to know about
customer centric approach followed by private
commercial banks. The different experts opinions
were considered in order to give the present work an
appropriate context. The present study followed
research design. A open end organized questionnaire
was administered as schedule after considering delay,
non-response, incompleteness and raising Covid-19.
Internet was referred to arrive at the private banks and
their branches in Yelahanka sub district. Further, the
study revealed about long term factors like customer
satisfaction, developed policy and quick service are
impressing long term policy between bank and
customer. Finally the study also asserts that CRM, a
customer centric holistic approach. The factors decide
customer centric approach includes CRM protects
data piracy, retention of existing customers and
establishing and maintaining strong relationship.
Depending upon the views stated by the Yelahanka
sub-district respondents of Bengaluru Urban district,
it was found that the socio economic characteristics
are impacting the study. The execute CRM followed
by the banks helps to survive in the competitive
situation, and variable impresses long term
relationship indicates banks can follow and consider
variables impacts relationship.
10 CONCLUSION
The main focus of this paper is to examine whether
demographic profile impacts in CRM or not. The
CRM Strategies in Commercial Banks: Fostering Long-Term Customer Relationships
725

study also probed about CRM practices in banks.
Factors influencing long term relationship, CRM – a
customer centric holistic approach. The result of the
study reveals that demographic profile of the
respondent’s significant and high relationship
between the characters and CRM except account of
different bank branches. Further, the study reveals
ranked CRM practices which include prioritizing
security of funds, transparency in banking services
and providing.
greater value for money. The factors as per the
study which influences long term relationship
includes customer satisfaction, developed private
policy and quick service. The study also asserts that
factors like CRM protect data privacy, retention of
existing customers and maintenance of strong
relations. Bank should use the existing favorable
socio economic factors and other issues which are
highlighted in the present study.
REFERENCES
Sudhakar, S., et al. (2023). An empirical analysis of factors
influencing customer relationship management
practices pursued by select private sector banks in
Tamil Nadu. European Chemical Bulletin, 12(4), 8280-
8291.
Manoj, G., & Jenefa, L. (2022). CRM practices and its
effects on public and private sector banks across
Chennai. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business
and Government, 20(4), 1848-1863.
Anjana, K. P. (2021). A study on the impact of customer
relationship management of South Indian Bank in
Bangalore City. International Journal of Research in
Engineering, Science and Management, 4(11), 64-68.
Putney, A. M. M. (2013). A study on the role of customer
relationship management in the Indian banking sector.
International Journal of Management and Business
Studies, 3(2), 88-89.
Sampath, L., & Narender. (2014). CRM practices in
banking sector. Global Journal of Commerce and
Management Perspective, 3(5), 141-145.
Pal, S. (2018). A study on CRM practices in banking sector.
Multidisciplinary International Journal, 2(2), 70-79.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
726
