
Critical Factors in E-Commerce Adoption by Construction SMEs
Mahesh Singh
1
, Manoj Kumar Rao
2
, Manoj B Pandey
3
and Abdul Ahad
4
1
Swiss Business School, Al Tareeqah Management Studies, U.A.E.
2
J. D. College of Engineering and Management, India
3
Jhulelal Institute of Technology, India
4
Central India College of Business Management and Studies, India
Keywords: E-Commerce, Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs), Electronic Technology (ET), Cronbach Alpha,
Impediments.
Abstract: Electronic technologies (ET) have changed the corporate environment and its competitiveness. It has also
made many companies pay attention to e-commerce approaches, and some have been able to benefit from
them. To compete with large organisations and gain market share, small and medium-sized businesses (SMEs)
must embrace ET. Hence, it's essential to investigate these companies' e-commerce challenges. This study
examined the challenges SMEs encounter while using E-commerce. Descriptive survey and correlational
data collection approaches are utilized to give practical implications. At Bushehr, Iran's commercial hub, a
questionnaire was provided to gather managers' and subject-matter specialists' opinions. Cronbach's alpha
was used to determine the content validity and reliability of the questionnaire. The data was analysed using
smart PLS and structural equation modelling with a partial least square approach. The results showed that
organisational, technical, and environmental barriers to technology affect the two initial variables in the
technology acceptance model.
1 INTRODUCTION
E-commerce describes the exchange of goods and
services by companies and their customers using
electronic networks such as the internet and the
World Wide Web. As more company owners use e-
commerce in their businesses, the usage of the web
for commercial contracts has been regarded as a
crucial development (Raharja et al. 2019). SMEs are
critical to social transformation, economic status and
well-being, economic development, and technology.
They also serve as a significant employer (Carnevale
et al. 2020). Small e-commerce businesses are
beginning to see how e-commerce might assist global
growth, but they may still be limited by a lack of
resources, regional biases, where customers value
locally created goods, and a lack of technical
proficiency (Pandey et al. 2022). To enhance and
succeed in business competitiveness and sales
revenue, e-commerce in the business sector must
flourish. E-commerce will be used to show off how
easy it is to engage, how expenses can be reduced,
and how quickly payments can be processed, all of
which improve business and marketing processes
(Rajagopal et al. 2022). When it comes to adopting
commerce, SMEs businesses move far more slowly
than their larger counterparts in industrialised nations.
Iran, one of the developing nations, is preparing to
adopt e - commerce and largely uses it as a marketing
device. Although there may be a situation where
SMEs businesses in Iran would benefit from using e-
commerce, these businesses currently tend to use it
less frequently than the national average, rely more
on internet connections and enterprise software, and
only to a limited extent on strategic and operational
e-commerce. These investing in small- and medium-
sized businesses are not as substantial or appropriate.
Despite the fact that SMEs businesses may benefit
greatly from e-commerce, there are still a number of
barriers preventing its broad adoption and use. The
initial and most crucial stage in preparing for success
in the technology and e-commerce industries is to
determine what the obstacles are to adopting e-
commerce (Tolstoy et al. 2022). Organizations should
be aware of these challenges in order to develop and
enacted proper e-commerce strategy. The factors that
influence, obstruct, and complicate the use of
communication systems should be taken into account
by small and medium-sized businesses. The research
Singh, M., Rao, M., Pandey, M. and Ahad, A.
Critical Factors in E-Commerce Adoption by Construction SMEs.
DOI: 10.5220/0012914700003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 727-730
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
727
paper's goal is to examine several sorts of
impediments that SMEs in developing countries face
while adopting e-commerce.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The study's newly discovered structural and static
obstacles are examined in the research. They are
separated into four themes: expanded entrepreneurial
traits of owner-managers, organization, ecology, and
technology. The article establishes a new conceptual
framework and provides a comprehensive overview
of topics related to contextual barriers for the next
years (Nazir et al. 2020). In the study, specific
analytical methods will be used to assess obstacles to
e-commerce platforms in developing nations. The
current economic examination offers an exhaustive
analysis of the obstacles preventing people from
using e-commerce networks (Yadav et al. 2022). The
study discovered that e-commerce ethics, information
quality, client trust, user interface value, and client
satisfaction were the primary factors influencing e-
consumer devotion. To improve client loyalty,
businesses are recommended to use e-commerce (Al-
Tit et al. 2020). The study examines corporate
strategy from the perspective of economic procedures
and examines the methodology of e-commerce
platform empowerment on SME export growth (Fan,
et al., 2023). The study utilizes structural equation
modelling to investigate when various e-commerce
levels impact a wide variety of competitive edges.
(Hu et al. 2019).
3 RESEARCH HYPOTHESIS
Based on the Technological Acceptance Model, this
research aims to clarify the obstacles to SMEs
adopting e-commerce. The theoretical and empirical
literature on the subject was studied, together with the
findings of earlier studies, to establish the study
hypothesis. These hypotheses were then tested by
acquiring primary data using instruments for data
collection.
H1: The perceived ease of use of E-commerce is
significantly influenced by the organizational
impediments to development.
H2: The perceived utility of E-commerce is
significantly impacted by organization impediments
to development.
H3: The perceived usability of E-commerce is
significantly impacted by technical constraints.
H4: The perceived value of E-commerce is
significantly impacted by its technical limitations.
H5: E-commerce environment restrictions
significantly affect how easy it is to use, according to
users.
H6: E-commerce environment obstacles have a
significant impact on how helpful it is considered to
be.
H7: Perceived utility of E-commerce is
significantly and positively influenced by the
perceived ease of usage.
H8: The attitude towards using E-commerce is
positively and significantly impacted by how easy it is
seen to be to use.
H9: The attitude towards using e-commerce is
positively and significantly impacted by how
beneficial it is seen to be.
H10: A considerable and advantageous influence
on intention to use is provided by views regarding the
usage of e-commerce.
H11: The degree to which someone intends to
engage in e-commerce affects that usage significantly
and positively.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
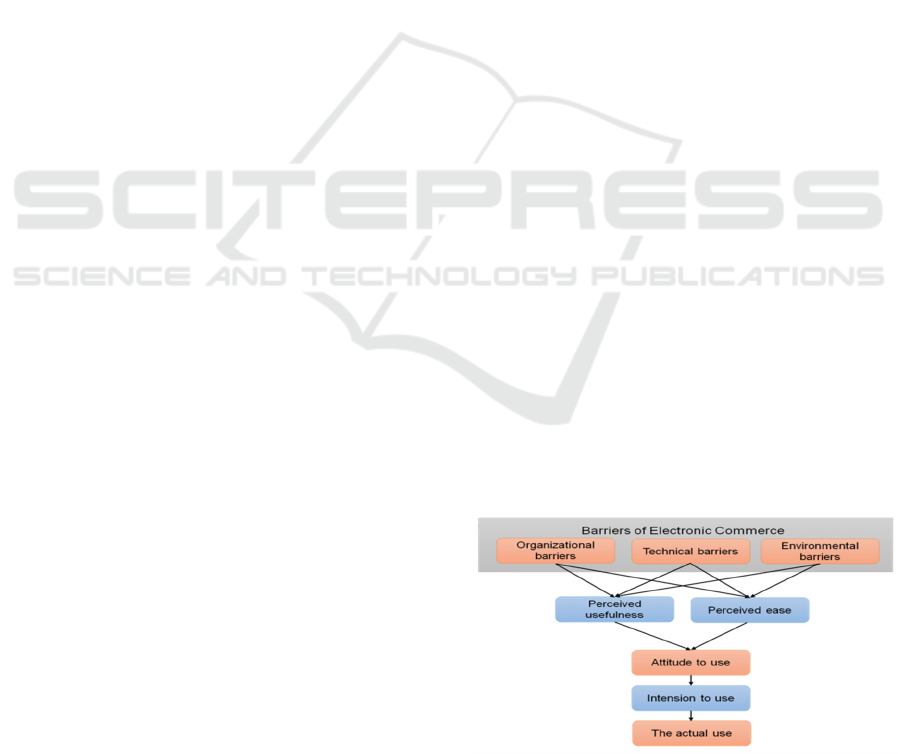
Research Model: The research model (Figure 1) was
produced by Davis using technological development
and usage as well as the results of the preceding
investigations mentioned above. The perception of
the utility of technologies is influenced by outside
variables, according to Davis' model of technological
acceptance.
The organization, technological, and ecological
constraints that had been previously discovered in the
research were taken into consideration as outside
variables in this study. With the collection of relevant
data, this study aims to evaluate theoretical
frameworks and research hypotheses.
Figure 1: External Impediments and the Technology
Adoption Model.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
728

To select the necessary sample from the general
population and since it was difficult to contact
individuals, convenience sampling was used in the
study. The information was gathered using a survey.
Directors and experts from companies in
Bushehr(Iran), an economic hub, participated in the
research. Around 86 firms are situated in the
industrial city of Bushehr, and these companies
employ more than 280 directors and experts,
according to information gleaned from Bushehr
county organizations. Cochran's estimate of a
constrained population, with a 95% probability value
and a variation of 5%, indicated that the research
sample was greater than 162. In this study, the survey
approach was used since it was not feasible to
produce a complete list of the population from which
to pull the necessary percentages in additional to the
difficult-to-find individuals.
The study is organized into three sections,
demography, questions on the main survey variables,
and an explanation. 58 questions were created by
combining questionnaires with the survey's topic to
assess the six primary survey factors. The research
uses complete five-item variability measurement
items. Data about the questionnaire's design process
is provided in Table 1. Some 163 surveys were finally
gathered after 165 surveys were physically handed to
service users. 157 questionnaires were used for
analysis after 6 surveys were eliminated because
participants had not correctly completed them. The
most used technique for evaluating questionnaire
reliability, Cronbach's alpha value, was employed to
test the questionnaire's dependability. The total
response rate to the survey was 84%, and Cronbach's
alpha values for each component were all higher than
0.7. This is a sign that the accuracy of the survey is at
an acceptable level. The outcomes of the
questionnaire's reliabilities are shown in Table1.
Table 1: Research factors, item-extracting resources, and
data-collecting technology accuracy consequences.
Variable Number of
questions
Cronbach’s alpha
coefficients
Technological
obstacles
10 0.715
Environmental
b
arriers
18 0.796
Perceived
usefulness
12 0.903
Organizational
b
arriers
5 0.763
Attitude 3 0.749
Perceived ease of
use
4 0.862
Actual use 3 0.737
Intention to use 3 0.861
Total questionnaire 58 0.845
5 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
Demographic Characteristics of Respondents:
Descriptive statistical analysis was employed to
examine demographic characteristics while assessing
study results. Table 2 details the demographic survey
factors that were examined using 157 questions.
According to Table 2, the majority of participants
were men (63.2%), while the majority of participants
were young adults (20–30 years old) (50.10%),
specialists (80.5%) with the greatest levels of
education, and the steel sector (27.5%) accounted for
the majority of the businesses in Bushehr's industrial
estate.
Table 2: Demographic Details of the Responders.
Demographics
component
Levels Frequency Proportion
of
fre
q
uenc
y
Gender Male 97 63.2
Female 55 37.8
Education Diploma 7 4.5
Undergraduate 124 80.5
Associate 16 10.5
Graduate and
highe
r
15 8.7
Age Over 50 years 17 3.9
41 to 50 years 19 13.2
30 to 40 years 61 39.3
20 to 30 years 74 50.1
Type of
enterprise
activity
Chemical
b
usiness
28 18.3
Mining sector 23 15
Metal industry 44 27.5
Service
industries
18 10.7
Critical Factors in E-Commerce Adoption by Construction SMEs
729

Industrial
electricit
y
15 8
Food industry 25 16.4
Fish processing
industr
y
14 9.5
Test of Research Model: Structural equation
modelling and smart PLS technology were used to
assess the conceptual model and research
assumptions. The structural equation modelling test
results reveal a considerable strong connection
between components of the various levels of the study
constructs. The t statistics is used in this method to
evaluate all structure and measuring variables. In
accordance with this analysis, unit material and route
coefficients are substantial at a 95% level of certainty
if the value of the t statistic for ways is more than 1.96,
and they are not if the values of the t statistic is less
than 96.1 for ways. The route coefficient and factor
loading are significant at a 99% probability value in
this scenario if the value of the t-statistic is larger than
2.58. By extracting data from the structural equation
framework, we could verify the major research
hypotheses since the overall research model fitness is
excellent and supported. With a confidence level
between 90% and 99%, we may conclude that factors
significantly affect the perceived utility and
simplicity of use factors based on the findings from
the relevant correlations and normal statistical
significance. Also, based on the established
coefficients between the variables of Intention and
actual usage, we should conclude that, with 99%
certainty, overall influence of both the Involved in the
decision making just on real use factor is satisfactory
and substantial.
6 CONCLUSION
The study made an attempt to account for the
difficulties and obstacles that SME adoption of e-
commerce in Bushehr, an economic hub, faced.
Analysis of the theoretical literature and literature
evaluation in this area led to the development of a
recommended methodology for the hypotheses and
investigation. According to the paper's findings, there
are a variety of hypotheses. It was discovered that
there was a growing interest in managing digital
marketing and e-commerce had an impact on how
competitively SME operations performed. The
implementation of e-commerce has significant
obstacles, as this research has shown. The study
aimed to find out more about how SMEs adopted and
used e-business technologies.
REFERENCES
Raharja, S.U.J., Kostini, N., Muhyi, H.A., & Rivani,
(2019). Utilisation analysis and increasing strategy: e-
commerce use of SMEs in Bandung, Indonesia.
International Journal of Trade and Global Markets,
12(3-4), 287-299.
Carnevale, J.B., & Hatak, I. (2020). Employee adjustment
and well-being in the era of COVID-19. Journal of
Business Research, 116, 183-187.
Pandey, A.K., Singh, R.K., Jayesh, G.S., Khare, N., &
Gupta, S.K. (2022). Examining the Role of Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP) in Improving Business
Operations in Companies. ECS Transactions, 107(1),
2681.
Nazir, M.A., & Roomi, M.A. (2020). Barriers to Adopting
Electronic Commerce for Small and Medium-sized
Enterprises in Emerging Economies. EMAJ: Emerging
Markets Journal, 10(2), 43-55.
Yadav, H., Soni, U., Gupta, S., & Kumar, G. (2022).
Evaluation of Barriers in the Adoption of E-Commerce
Technology in SMEs: A Fuzzy DEMATEL Approach.
Journal of Electronic Commerce in Organizations
(JECO), 20(1), 1-18.
Al-Tit, A.A. (2020). E-commerce drivers and barriers and
their impact on e-customer loyalty in small and
medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Verslas: teorija ir
praktika, 21(1), 146-157.
Fan, Z., Wang, Y., & Ying, Z. (2023). Empowerment of
Cross-Border E-Commerce Platforms for Small and
Medium-Sized Enterprises: Evidence from China.
Journal of Business-to-Business Marketing, pp., 1-12.
Hu, X., Ocloo, C.E., Akaba, S., & Worwui-Brown, D.
(2019). Effects of business-to-business e-commerce on
the competitive advantage of small and medium-sized
manufacturing enterprises.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
730
