
Development of Ecological Imagination in the Process of Teaching
Text Structure
Klarakhon Mavlonova
a
Tashkent State University of Uzbek Language and Literature named after Alisher Navoi, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Text, Text Structure, Lexical-Grammatical Tools, Laws of Logic, Communication, Text Error, Ecology,
Environmental Education, Psychology of Environmentally Responsible Behaviour, Environmental Education.
Abstract: This article describes the structure of the text, the importance of learning the rules for it, the types of text
errors in the text (essays), the content of education on the study of text structure in 6th grade native language
lessons; examples of rules and exercises are given; the issues of directing students’ linguistic knowledge of
text structure to the development of speaking skills related to text writing, texts, methods of providing
environmental education to students by working on dialogues.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today in the native language classes of general
secondary schools’ special attention is paid to the
development and implementation of the content,
tools, methods and techniques of teaching related to
text linguistics, which serve to form the speech and
linguistic competencies of students in text structure
and attention began to be focused on - Abramova S.V.
(2007) - N.S. Valgin (2003) - Sadykhova, S (2010) -
Antonova E.S. (2007) - N. Bekniyazova (2012). For
the teaching of the native language of Uzbekistan,
research work is being carried out on the system of
rules and exercises, questions and assignments on the
structural features of the text for grades 5-9 -
Mavlonova K. (2021) - Mavlonova K (2021) - N.S.
Valgin (2003) - Galperin I.R (1974). Teaching text
structure is one of the most important learning
objectives in developing students’ connected speech.
It is important to develop students’ oral and written
speaking skills by teaching them the features of the
functional-semantic structure of the whole text and
the laws of text creation.
2 MANUSCRIPT PREPARATION
The rules of text creation are partially (elementally)
started in the primary grades, and from the 5th grade
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4954-9996
onwards, they are implemented through continuous,
coherent and gradual learning. Continuity is ensured
by gradually improving and complicating the rules of
text structure from class to class. Based on this
principle, the rules of text structure in 7th grade
Native Language lessons are established. The
following cases are taken into account:
Review some of the rules covered in grades
5-6.
Theoretical knowledge covered in grades 5-
6 will be expanded and deepened in grade 7
and classifications will be more detailed.
new information.
The first group of rules is not repeated in the 7th
grade at the beginning of the school year but is simply
repeated and memorized. Even then, it is not the rules
themselves that are taken, but the steps taken to
restore action.
The second group of rules introduces new aspects
of linguistic concepts learned in grades 5-6.
In Grade 7, the Native Language textbook takes
the opportunity to better understand some of the
concepts, that is, to expand students' knowledge
through new aspects of concepts. It is also planned to
teach new rules in order to get acquainted with a more
detailed classification of linguistic phenomena. For
example, in grades 5–6, sentences and parts of text
are studied using personal and visual pronouns, while
in grade 7, students use other types of pronouns for
this purpose.
Mavlonova, K.
Development of Ecological Imagination in the Process of Teaching Text Structure.
DOI: 10.5220/0012952400003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1075-1079
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
1075
The rules of the third group include modal words,
punctuation (colon, dots, etc.). The content of the text
structure rules for Grade 7 will be further clarified
based on the current “Native Language” textbooks
and the requirements set for Grade 7 in the national
curriculum.
The interactive method has a good effect in the
process of working in more groups: passion for the
success of the group leads to activity in the content of
teaching each other so that all the members of the
group can prepare in the same way, it leads to
important mental and physiological states such as
joint decision-making and joint response. Below we
will focus on the recommended interactive methods
for classes:
Table 1: Interactive methods for different grades.
Grade 5 "Let's choose a title", "Wrong sentence", "Is there a limit to the sentence?"
Grade 6 "Specific Order", "Replace with Pronoun", "Bottom Up"
Grade 7 "Compare - Differentiate", "Silent conversation", "From simple to complex"
Grade 8 "Thinking and evidence", "Enriching the text", "I am a reporter"
Grade 9 “Editing and Analysis”, “From Part to Whole”
We will recommend one of the methods of activating
ecological concepts through language education to
students below:
2.1 Assignment
Read the text of the given dialogue. Make up suitable
questions for the answers given by the interviewer,
fill in the text and write.
– What is the weather?
– A mixture of various gases and substances
necessary for human, animal and plant life.
– …?
– Of course, there is air in the water.
– …?
– That's right, there is air in the soil too. Earthworms
also get air from underground.
– …?
– Plants breathe air through their leaves.
– …?
– There is more oxygen in the air in forests, pastures
and mountain slopes.
– …?
– The more plants there are on Earth, the more oxygen
there is in the air.
Through this task, it is aimed to form students' ability
to create a dialogue and develop their ability to
understand the environment. If they are required to
work with punctuation marks related to the text of the
dialogue through the first task, they should create
sentences corresponding to the content of the
sentences given in the second task. It is advisable for
students to work with their classmates.
In the 6th grade, it is required to inform students
that, in addition to the main topic, sub-topics, i.e.,
plan items, are reflected within this topic in the
sequence indicated by the order number. To show
what the main topic is about, that sub-topics are
within this main topic, that each topic (main, sub-
topic) should talk (write) about something is the
content of education. It is said in which way sub-
topics are compatible with the main topic. These can
be illustrated in the diagram below.
Figure 1: Sequential representation of main and sub-topics.
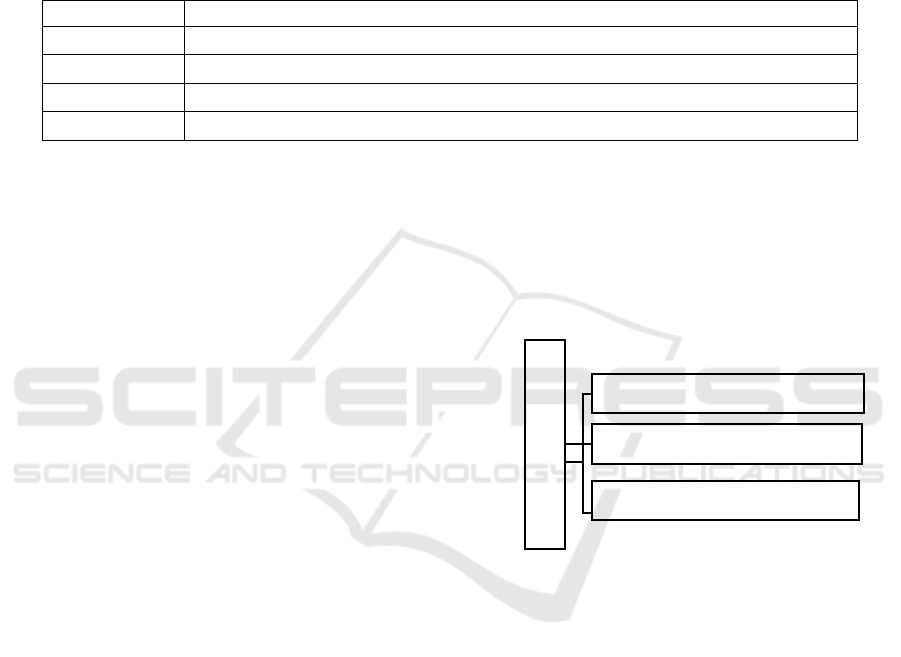
There are such topics, each of which reflects more
than 10 sub-topics, and sub-topics can be branched in
turn, as described above:
Main topic
sub-topic
sub-topic
sub-topic
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1076
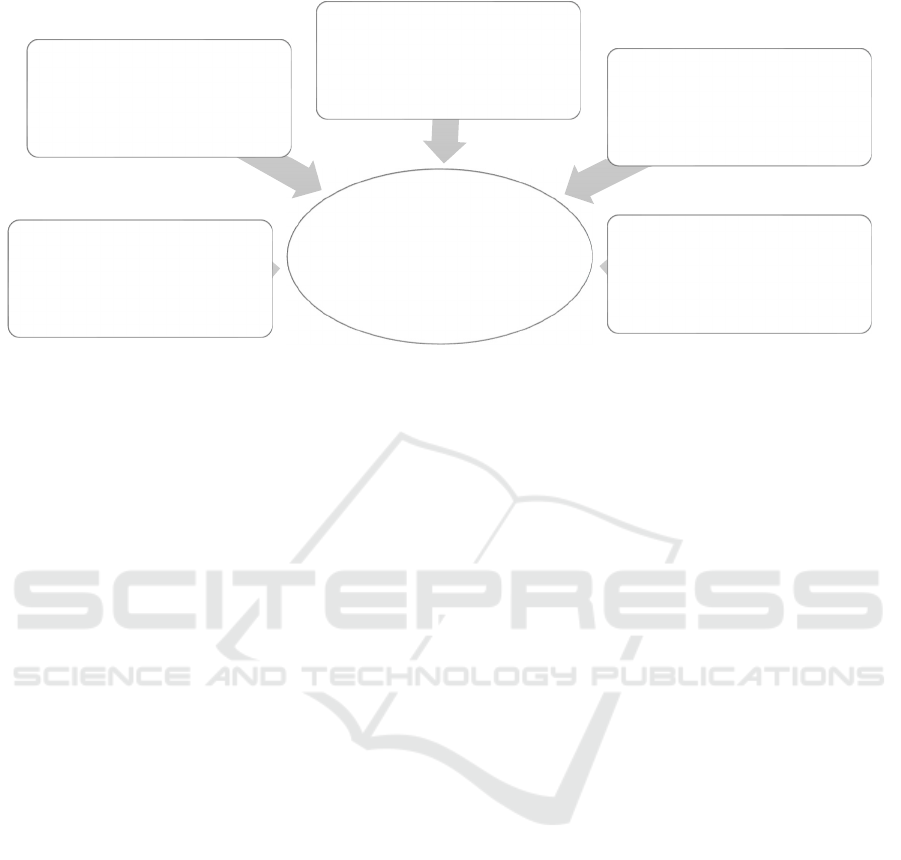
Figure 2: Branches of sub-topics.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Rules are an important part of teaching text structure
to students. Y.S. Antonova explains the difference
between the teacher's explanation and the following
knowledge: that is, it is a material for future
knowledge or skills. The success of the educational
process depends on the formation of students' skills in
the transformation of information received into
knowledge". In other words, it is not the knowledge
(the rule that forms the basis of knowledge) that a
teacher gives information about the structure of the
text. Knowledge, according to analysis, is almost in
the form of a strict judgment.
Y.S. Antonova's views on grammar and pragmatics
can be summarized as follows: In methodological
science, the text is interpreted in two ways: 1)
grammatically; 2) pragmatically. While grammar
teaches the concepts of text structure, pragmatics
teaches the use of textual language phenomena in
speech. In native language classes, grammar is used
as a tool for learning, and pragmatics is used to apply
knowledge to skills and competencies through
exercises.
Problems of teaching writing in the native language,
as well as in Uzbek (state) language lessons
T.Ziyodova, M.Rikhsieva, N.I.Bekniyazova,
R.A.Yuldashev and M.M. Rikhsieva researched,
created monographs, methodical manuals. Recent
achievements in linguistics are mentioned in these
works, components specific to the syntactic integrity
of the text (paragraph) are separated, typical text
errors in students' written creative works are
classified and explained, attempts are made to reveal
the reasons, based on what to teach recommendations
are outlined. These recommendations, as noted by
Y.S. Antonova, are information provided to students.
I.R. Galperin noted that the type of this document,
which consists of a number of separate units,
expressed in the form of a written document,
combined by different types of lexical and
grammatical connections, is literary processed
according to the genre and has a certain modal
character and pragmatic direction. 'kidladi.
Apparently, the characteristics of the text are
reflected in this definition, that is, the text has the
following aspects:
a logical whole;
informative nature;
structural formation;
integrity in meaning;
intellectual completeness
The difference between a text and a sentence syntax
is that the sentences are lexically and grammatically
connected, logically connected, and have their own
peculiarities in formation. Organizational aspects of
the text include concepts such as paragraphs, titles,
parts of the text, the internal structure of the text, the
laws of interdependence of sentences, the role of
lexical and grammatical devices. With this in mind,
Y.S. Antonova states the following: when analyzing
textbooks from this point of view, exercises based on
certain words and phrases become useless. Some
derived language units make it difficult to determine
lexical and grammatical meanings”.
In the hierarchy of levels of knowledge, pragmatics
ranks higher than linguistics. Language exists as a
system, and pragmatics learns how to use this system.
"PinGeneral
classification
of penguins"
"Nutrition
Source"
"History of origin"
"Common type"
"Life style"
"Unique feature"
Development of Ecological Imagination in the Process of Teaching Text Structure
1077

The essence of a linguistic approach to the analysis of
oral works is to determine whether the text depends
on the purpose of the author, because the effect of the
pragmatic instruction of the speaker or writer extends
(applies) to the whole idea. Accordingly, the analysis
of textbooks from this point of view shows the
ineffectiveness of exercises based on individual
words and phrases.
From the cause of classify text errors and their causes,
the essence of communicative and activity-based
approach, cognitive approach in the scientific article
of T.N. Sokolniskaya, methodical manual of R.
Yuldashev and M. Rikhsieva we set ourselves the
goal of developing rules and exercises for text
structure for grades 5-9, based on their age
characteristics, level of knowledge, and interest in
mastering the culture of speech.
T.N. Sokolniskaya suggests the following
classification of text errors based on the criteria for
evaluating essays:
Text errors, that is, errors that violate the
integrity and consistency of the meaning of
the statement.
Errors in breaking text into paragraphs.
Errors that disrupt the verbal connection of
sentences and content in the text.
Mistakes in the organizational aspects of the essay are
not reflected here.
In the methodical manual of R.Yuldashev and
M.Rikhsieva "Textual errors in essays, methods of
their correction" textual errors are classified in terms
of technical design, content and compositional
structure of the written work as follows:
organizational and technical text errors in
essays;
semantic-logical text errors;
text errors in lexical-grammatical
connection of sentences (including
punctuation marks);
textual errors in parts of the text due to the
compositional structure of its type.
We know that the laws of logic are the sequence of
ideas, the logical completeness of which is expressed
in the placement of units of text in a certain way. The
laws of logic apply in the essay (text). “The laws of
logic, which are specific to clear and reasonable
thinking, apply to all disciplines: authenticity,
contradiction, exception, and sufficient fundamental
law. These laws are the basis of right thinking”.
Textbook Errors and Methods for Correcting Essays
states that “Textual errors are the result of a lack of
practical knowledge of language phenomena that are
not specifically studied in native language classes.
These mistakes are not three or four, but many. This
prevents the written essays (created texts) from
meeting the standard requirements”. As one of the
practical solutions to this scientific-methodological
problem, the rules related to the organizational and
technical aspects of the text (text structure) and
exercises to strengthen them were developed and put
into practice for students. This handbook introduces
Grade 5 students to the following skills: delimiting
sentences in a text; text subject; text title; pieces of
text; plan the text (essay); paragraph; add
classification to the text; placement of poetic verses
in the text; insert narrations, hadiths, proverbs and
sayings, wise sayings into the text in the form of
quotations; to ensure consistency of sentences in parts
of the text.
It is well known that text research and analysis is the
most important educational process for creating a text
in a communicative context. In this process, it is
necessary to approach the issue both practically and
theoretically, so that students know the specifics of
the structure of the text, as well as be able to create an
independent text.
The following is a list of the best ways to determine
the theoretical knowledge and practical skills of text
structure in 6th grade Native Language lessons.
Lexical-grammatical connection between
sentences in the text:
o rhyming connections of
sentences in the text;
o the connection of sentences with
conjunctions.
Text types and their parts.
Expressing the thesis in the essay (text).
General structure of the text.
The subject of parts of the text.
Use of nicknames in text types
(document, letter, message, message,
image, narration, travel).
Inconsistencies in the content of some
sentences in the essay (text).
Consistency, logic, semantic accuracy of
the statement in the essay (matm).
Use the word in its proper place in the
text.
Some sentences and paragraphs in the
essay are connected in the sense of place
and time.
4 CONCLUSION
The above recommended content for 6th grade is
based on the current content of Native Language
education, analysis of foreign literature and written
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1078

works of students, and further improvement,
enrichment, new theoretical rule as well as practical
exercises. In the context of grammatical literacy, to
increase the student's vocabulary, to feel and
comprehend the subtleties, differences and
similarities of words, to pronounce and write
correctly, to connect words, to compose a text from
sentences , find and correct logical and grammatical
errors in connections, logical errors in the text,
correctly understand the opinion of others, express a
thought in different ways, perform a series of logical
operations, such as restoring the continuation of a
broken thought, correctly assess the speech situation
and focuses on developing and developing skills to
use language opportunities appropriately.
Exploring the types of sentences, the
interrelationships of sentences at the level of text
creation, while acquiring knowledge and skills in text
structure, creates a solid foundation for students to
pursue specific goals and effectively master the native
language. After all, linguistic phenomena act mainly
through connected speech and show their real
communicative nature.
REFERENCES
Abramova S.V. Aspects of educational and research work
of high school students in the Russian language //
Ryash. – 2007. No. 2. – P. 25–31.
Antonova E.S. Where to look for resources to update the
school methodology? / Russian language at school. –
2007. No. 6. – P. 10–14.
N. Bekniyazova, Methods of teaching students to create text
in primary school lessons in the native language (on the
example of schools with Uzbek and Karakalpak
languages of instruction): Monograph. Tashkent:
Science and Technology, 2012.
N.S. Valgin. Text theory. Moscow, Logos. 2003.
Galperin I.R. On the concept of "text" // Questions of
linguistics. 1974. No. 6.
T.U. Ziyodova, Text creation technology. Monograph. -
Tashkent: Fan, 2008.
Yuldashev, R.A., Rikhsieva, M.M. Text errors in essays,
methods of their correction. - Tashkent: Science and
Technology, 2019.
Mavlonova K., Yuldashev R., Khakimova N. Rules of text
structure. Textbook. – Tashkent: Nodirabegim, 2021.
86 p.
Mavlonova K. The content of education on the rules of
writing. Issues of Uzbek applied linguistics and
linguodidactics. Republican scientific-practical
conference. 2021. – P. 310–313.
Rikhsieva M. Methods of teaching students to write in the
Uzbek language classes of schools with Russian as the
language of instruction. Doctor of Pedagogical
Sciences. ... diss. – Tashkent, 2009.
Sadykhova, S. Compositional and semantic structure of the
syntactic whole. Baku: Nurlan, 2010.
Sokolnitskaya T.N. Text errors and their classification. /
Zhurn. Russian language at school. 2007. No. 7. – P.
13–18.
Yusupova Sh.J. Scientific and methodological bases of
developing students' thinking in modern Uzbek literary
language lessons (on the example of academic
lyceums). Doctor of Pedagogical Sciences... auto
referat of dissertation. – Tashkent, 2005.
Mavlonova K. Methodology of teaching text structure in
native language classes. Monograph. – Tashkent:
Anorbooks, 2023. 256 p.
Development of Ecological Imagination in the Process of Teaching Text Structure
1079
