
An Ecological Perspective on Healthy Nutrition as a Component of
Health Attitude
Marietta Karamyan
National University of Uzbekistan, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Health, Biopsychosocial Model, Ecological Model, Environment, Environmental Conditions, Health Attitude,
Cognitive and Emotional Components of Health Attitude, Health Behaviour, Healthy Nutrition, Health Locus
of Control, Self-Efficacy, Self-Regulation, Constructive Self-Assertiveness, Psychological Well-Being.
Abstract: The aim of the present paper is to analyse an ecological perspective of health attitude in personality on the
example of healthy nutrition. The significance of biopsychosocial and ecological approaches for
comprehensive understanding of health and health attitude is emphasized. These approaches holistically
explain health and health attitude as a result of complex interaction of biological, psychological and social
factors at multiple levels and as an integral part of individual’s physical, natural, social and cultural
environment. The component structure of health attitude is briefly described in the frames of V. Myasishev’s
theory of attitudes. The relationship of health attitude and psychosocial characteristics in personality on the
example of healthy nutrition is discussed. The research findings are considered in the course of general idea
that the relationships between psychosocial characteristics and healthy nutrition as component of health
attitude are complex. It is shown that high indicators of internal health locus of control, self-efficacy, self-
regulation, constructive self-assertiveness, psychological well-being correlate to healthy nutrition in adults
and teenagers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Health as a value has one of the important positions
in the individual and social hierarchy of values. Even
though there are more than hundred definitions of
‘health’ and ‘illness’ in the modern literature, the
definition given by World Health Organization
(WHO) in 1948 is still among popular: ‘health is a
state of complete physical, mental and social well-
being, and not merely the absence of disease or
infirmity’ - Babicz-Zielińsk, E (2006) - Barzegari, A,
& et. al. (2012) - Bennet, P., & et. al. (1997) -
Berezovskaya, R.A, & et. al. (2006). This definition
underlines that health has not only biological
peculiarities, but psychosocial, that health status is
dependent on biological, psychological and social
determinants. One of the main contributing factors for
health state is attitude towards health in personality.
The present paper addresses the following
objectives: 1) to give a general overview on
biopsychosocial and ecological understanding of
health as fundamentals for analysis of attitude
towards health; 2) to discuss research data on the
relationship of health attitude and psychosocial
characteristics in personality on the example of
healthy nutrition.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Component encompasses person’s feelings, emotions
and emotional resources related to his/her health
status. Behavioural component is defined by presence
or absence of actions directed to support of one’s own
health or coping with illness conditions.
The modern understanding of health attitude is
based on biopsychosocial model of health and illness
and ecological paradigm towards health. The
mentioned above WHO's definition of health is one
of the examples of this model. The biomedical model
of health and illness has been the dominant model for
several centuries. Although this model has proven to
be very effective in treating disease, it is limited
because it disregards the fact that health and illness
are the outcomes of an interaction of social,
psychological and biological factors.
The biopsychosocial model holistically explains
health as a result of complex interaction of biological,
Karamyan, M.
An Ecological Perspective on Healthy Nutrition as a Component of Health Attitude.
DOI: 10.5220/0012956100003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1171-1175
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
1171

psychological and social factors at multiple levels. It
shows ecological-systemic understanding of health.
In modern publications, scientists prove the need to
consider health as a dynamic system. The use of the
concept of ‘dynamics’ emphasizes that the influence
of biological, psychological, interpersonal and
contextual factors on human health is not strictly
fixed. For example, it is possible to investigate the
mechanisms of influence of a teenager's peer group
and his/her close friendships on the development of
healthy habits.
According to the ecological paradigm of health a
human being is understood as an integral part of
his/her physical, natural, social and cultural
environment. There are several key characteristics of
health in ecological approach: 1) health is
multidimensional phenomenon; 2) health is seen via
dynamic balance and interaction of an individual with
environment, which are holistic and integrated; 3)
health is both a process of active adaptation of
individual to changing conditions of environment and
its result; 4) health is related to spiritual and
emotional individual well-being as well with cultural
lifestyles.
I. Kickbusch shows that ecological model is
comprehensive because it is concerned with the
whole individual in its environment. It considers all
range of health determinants, takes into account
cultural and personal meanings of health, aims to
understand emotional and behavioural sides of health.
This model allows to discuss primary health care,
disease prevention and health promotion. For
example, the ecological approach to health promotion
includes both the need to conserve natural resources
and to respond to the environmental factors (e.g.,
urbanization, technology) changing people’s lives. In
other words, the ecological understanding of health
underlines the individual’s position at the centre of
complex interaction of social, cultural and physical
environment.
The biopsychosocial and ecological models frame
the social psychological theories of health attitude,
health behaviour and their studies, health promotion
programs and design for behaviour change
interventions. According to these models health
attitude is determined by various sets of factors such
as socio-demographic (sex, age, education and social
status), socio-economic and legislative (e.g.
socioeconomic status, laws restricting the
advertisement of alcohol), socio-cultural (e.g. dietary
culture), socio-medical (e.g. health care provision,
access to health care), psychosocial (e.g. social
support, motivational factors).
In a broader context it is shown that the
psychosocial impacts associated with environmental
conditions. For example, the research by Crighton et
al (2003) was devoted to the impact of environmental
conditions on health in Karakalpakstan. It was found
that residents of three Karalpak districts (Kungrad,
Shumanay, Muynak) were more likely to report
environmental concern if they had trouble keeping
employment, perceived their health as fair or poor,
were involved in more local activities; and the
respondents were less likely to have environmental
concerns if they had more close relatives and friends.
This study indicated the positive relationship between
psychosocial impacts and negative environmental
perceptions (i.e. environmental awareness, perceived
health impacts).
The research on gender factors is another good
example of ecological understanding of health
attitude and health behaviour. The idea that the
differences between men and women in their health
outcomes are the consequences of behaviours had
been raised in the mid-1970s. Many studies
demonstrate strong evidence that fewer health-
promoting practices and greater risk taking among
men contribute to their increased risk of serious
chronic disease, injury and death. They show that
women are more likely than men to engage in a
variety of health-enhancing practices and to have
healthier lifestyle patterns. Men, in contrast, are more
likely than women to engage in health-impairing
behaviour. Men are also less likely than women to
engage in a variety of preventive and self-care
techniques and the failure to do so is a major
contributor to men’s shorter lives and increased
health risks.
It is shown that beliefs about manhood are
associated with increased risk for health. Men who
adopt stereotypic beliefs about masculinity have
greater health risks than their peers with less
traditional beliefs. More prominent masculine
features in individuals are associated with better self-
assessed health status for both women and men.
Psychosocial factors also play an important role in
understanding person’s healthy nutrition in the
frames of the ecological paradigm. The literature
review shows that the considerable body of studies on
the psychosocial correlates of healthy nutrition can be
divided into several research directions:
▪ the first research direction focuses on knowledge
of what constitutes a healthy diet, i.e. on beliefs about
nutrition and food;
▪ the second research direction primarily
investigates an influence of psychological factors on
food choice;
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1172
▪ the third research direction pays attention to
possible relationship of eating habits and
psychosocial mediators such as social and family
influence, age, gender;
▪ the fourth research direction attempts to find
associations between eating and dietary habits and
self-attitudes, including self-esteem, ‘self-silencing’,
self-regulation;
▪ the fifth research direction analyses how
different motivational and emotional characteristics
such as perceived behavioural control, locus of
control, self-efficacy may possibly influence person’s
eating behaviours and dietary habits.
Based on the mentioned above the article presents
some empirical data on the relationship between
psychosocial factors (health locus of control, self-
efficacy, self-regulation, psychological well-being)
and nutrition.
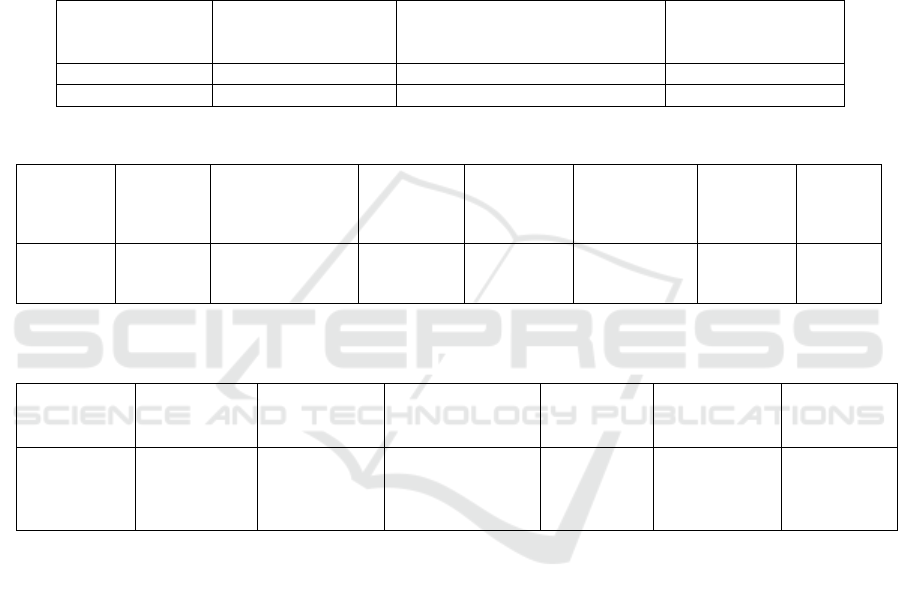
Table 1. Means and Standard Deviations in Groups with External and Internal Locus of Control (N=122, adults)
Components of
Health Behaviour
Participants with
External Locus of
Control (N=53)
Participants with Internal Locus of
Control (N=69)
Student’s test, p<0.05
M SD M
Nutrition 1.16 1.10 1.84
Table 2: Bivariate Correlations of Healthy Nutrition, Self-Efficacy and Indicators of Self-Regulation (N=200, teenagers)
Variables Self-
Efficacy
Constructive Self-
Assertiveness
Self-
Regulation:
Planning
Self-
Regulation:
Modelling
Self-
Regulation:
Programming
Self-
Regulation
: Results'
Evaluation
Nutrition
Correlation
Coefficient
s
.306** .215** .142* .182** .127 .144* .206**
p<0.05 (*), p<0.01 ()**
Table 3. Bivariate Correlations of Healthy Nutrition and Personality’s Psychological Well-Being (N=122, adults)
Variables Positive
Relations
Autonomy Environmental
Mastery
Self-
acceptance
General
Psychological
Well-Being
Nutrition
Bivariate
Correlations
with
Nutrition
.248** .128 .266** .238** .188*
Note: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01
3 METHODOLOGY
The participants (adults’ sample of 122 females and
males, teenagers’ sample of 200 girls and boys) were
asked to indicate how well the specific health actions
described his/her typical behaviour and to answer
psychological questionnaires. Also, they were asked
to define the notion of ‘healthy life style’ which
allowed to conduct a content analysis of social
representations of respondents.
Health practices in the sphere of nutrition were
studied with the help of list of items which compose
healthy nutrition (e.g. ‘Eat sensibly’, ‘Avoid eating
fast food’, ‘Have a balanced diet’). Motivational
characteristics of adults were evaluated using
Multidimensional Health Locus of Control (by
Wallston et al, 1978), Self-Efficacy Scale
(R.Schwarzer, M. Jerusalem), psychological well-
being – The Ryff Scale of Psychological Well-Being.
Motivational features of teenagers were studied using
Self-Efficacy Scale (R.Schwarzer, M. Jerusalem),
Self-Regulation Style Questionnaire
(V.I.Morosanova), Self-assertion Scale for
Teenagers.
Data analysis was performed by the SPSS 23.0
software. Descriptive, inferential statistics
(Independent Samples Student’s Test or Mann-
Whitney Test depending on normality of distribution)
and correlation analysis (Spearman's Rank
Correlation Coefficient) were used.
An Ecological Perspective on Healthy Nutrition as a Component of Health Attitude
1173

4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Cognitive component of health attitude
The idea of importance of healthy nutrition for health
state is reflected in people’s social representations of
‘healthy life style’. In other words, cognitive
component of health attitude encompasses people’s
understanding of their health and life style. The
content-analysis of adult’s and teenagers’
(Karamyan, M. 2018) social representations was
conducted in the frames of final year research
projects. It was found that ‘nutrition’ takes the third
place among actions which adults (16,3%) and
teenagers (12%) consider to be health practices.
‘Healthy food’, ‘right nutrition’, ‘useful food’, ‘eat
what it is useful for you’, ‘fresh products’, ‘diet’,
‘regular eating’, ‘you are what you eat’ are the
examples of answers related to healthy nutrition. The
results of these studies show that adults and teenagers
relate healthy life style with healthy nutrition
including choice and intake of safe food, appropriate
eating behaviour and dietary habits.
Behavioural component of health attitude and
motivational correlates
Healthy nutrition as health-related behaviour can be
governed by specific characteristics of human being
motivational sphere such as locus of control and self-
efficacy.
The locus of control concept could be defined as
person’s belief that he/she has control over their
health, including healthy nutrition. It was shown that
people with internal health locus of control more
likely find information on health, follow healthy diet
and physical activity. Self-efficacy is seen as sense
which concerned with perceived capabilities to
produce effects and personal influence. It has been
found that self-confident people more often that non-
confident ones perform health practices, e.g. people
with high self-efficacy were less likely to relapse to
their previous unhealthy diet.
These data are confirmed by correlational analysis
which revealed statistically significant positive
correlation between healthy nutrition and internality
(rs=0.259, p<0.01) and self-efficacy (rs=0.226,
p<0.05). It allows to conclude that individual’s belief
in his/her own capacities and disposition to rely on
oneself determines high behavioural activity in the
sphere of healthy nutrition and physical activity.
Table 2 shows statistically significant positive
correlations between healthy nutrition scale and self-
efficacy (rs=0.306, p<0.01), constructive self-
assertiveness (rs=0.215, p<0.01), self-regulation
(rs=0.142, p<0.05), planning (rs=0.182, p<0.01),
programming (rs=0.144, p<0.05), results’ evaluation
(rs=0.206, p<0.01) in the teenagers sample. In other
words, those teenagers who are characterized by high
self-efficacy, flexible and adequate reactions to
environment, independence, conscious and realistic
planning of activity, are more confident in their
choice of healthy nutrition and performance of
healthy eating.
Behavioural component of health attitude and
psychological well-being. Psychological well-being
is multidimensional concept consisting of person’s
self-acceptance, skills to establish quality ties to
others, sense of autonomy, ability to manage complex
environments to suit personal values, to develop as a
person. It has been explored that success of weight
loss program and improvement of nutrition
behaviours are related to the development of
psychological well-being in individuals with the help
of Kripalu yoga.
The results of correlational analysis between health
behaviour components and indicators of
psychological well-being are given in Table 3. The
analysis of the relationship between total healthy
nutrition score and psychological well-being
dimensions showed that there are positive
correlations of adequate nutritional practices and
general indicator of psychological well-being
(rs=0.188, p<0.05), positive relations with others
(rs=0.248, p<0.01), environmental mastery
(rs=0.266, p<0.01), self-acceptance (rs=0.238,
p<0.01).
Although these correlations are not strong, they may
reflect the specific dynamics in the personal response
to healthy nutrition as behaviour. They demonstrate
that there is a variety in explanation of relationship
between psychological well-being and healthy
nutrition. For instance, person’s high level of life
satisfaction, his/her positive affective emotions
explain his/her activity in relation to choose and
following to healthy nutrition. If people are
characterized by warm, satisfying, trusting relations
with others, are concerned about their welfare and are
capable of strong empathy and intimacy, then they
have enough power to follow healthy life style in
general and healthy nutrition in particular. Also if one
possesses a positive attitude toward his/herself, feels
positive about past life and acknowledges different
parts of his/her life and personality, then he/she is
more successful in performing healthy nutrition.
The results of these studies demonstrate that there are
different psychosocial factors contributing to
person’s healthy nutrition including choice of safe
food, its intake, eating and dietary habits. These data
show that according to ecological paradigm the
modification of behaviour related to healthy nutrition
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1174

assumes not changing only social, political, economic
conditions but also careful consideration of
individual’s role in producing and performing the
health practices. However, this article does not claim
that one or other of the generalisations made are more
right. The most important point is to look not only at
the statistical significance of results but also at their
practical significance..
5 CONCLUSIONS
There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that
ecological understanding of health attitude and the
healthy nutrition as its part gives many practical
applications for effective development of health care,
health education and health promotion. It is especially
significant because one’s nutrition play a key role in
prevention of food- and life style-related diseases and
improvement of his/her health.
What people eat and how much and how often are
behavioural processes, which lead researchers and
health promotion specialists to consideration of
psychosocial factors as determinants of food choice,
its intake and nutritional habits.
The effective promotion of healthy nutrition among
people is only possible with development of their own
responsibility for health, life style and environment.
In other words, an ecological perspective allows to
consider an individual and his/her psychosocial
peculiarities (including health locus of control, self-
efficacy, self-regulation, constructive self-
assertiveness, psychological well-being) in the
environmental and cultural context..
REFERENCES
Babicz-Zielińsk, E. (2006) Role of Psychological Factors in
Food Choice – a Review. Polish Journal of Food and
Nutrition Sciences, Vol. 15/56, No 4, 379–384.
Barzegari, A., Ebrahimi, M., Azizi, M., Ranjbar K. (2012)
A Study of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitudes and Food
Habits of College Students. World Applied Sciences
Journal, Vol. 15 (7): 1012-1017.
Bennet, P., Murphy, S. (1997) Psychology and Health
Promotion. In: Bunton, R., Macdonald, G. (Eds.)
Health Promotion. Disciplines, diversity, and
developments. London and New York: Open
University Press, pp.31-51.
Berezovskaya, R.A., Nikiforov, G.S. (2006) Attitude
towards Health. In: Health Psychology G.S. Nikiforov
(Ed.). St.Petersburg.: Piter, pp.275-292.
Braun, T.D., Park, C.L., Conboy, L.A. (2012)
Psychological Well-Being, Health Behaviors, and
Weight Loss among Participants in a Residential,
Kripalu Yoga-Based Weight Loss Program.
International Journal of Yoga Therapy, 22, 9-22.
Conner, M. (2013) Health Cognitions, Affect and Health
Behaviours. European Health Psychologist, Vol.15.
No.2. Pp.33-39.
Conner, M., Norman, P. (2017) Health Behavior: Current
Issues and Challenges. Psychology&Health. Vol. 32.
No.8. P.895-906.
Courtenay, W. (2000) Behavioral Factors Associated with
Disease, Injury, and Death among Men: Evidence and
Implications for Prevention. Journal of Men’s Studies,
9 (1), 81-142.
Courtenay, W., Mccreary, D., Merighi, J. (2002) Gender
and Ethnic Differences in Health Beliefs and
Behaviours. Journal of Health Psychology, 7 (3), 219-
231.
Crighton, E., Elliott S., Meer. J. et al (2003) Impacts of an
Environmental Disaster on Psychosocial Health and
Well-being in Karakalpakstan. Social Science and
Medicine. 56. 551-567.
Wallston, K. A., Strudler Wallston, B., & DeVellis, R.
(1978). Development of the multidimensional health
locus of control (MHLC) scales. Health education
monographs, 6(1), 160-170.
Karamyan, M. (2018). HEALTH EDUCATION: A
SOCIAL PSYCHOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVE.
European Journal of Research and Reflection in
Educational Sciences Vol, 6(1)..
An Ecological Perspective on Healthy Nutrition as a Component of Health Attitude
1175
