
Eco-Active Learning: Sports Pedagogy and Environmental
Education Synergy
Arzikulov Dilshod Ne'matovich
Uzbek State University of Physical Culture and Sport, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Environmental Education, Opportunities, Modern Coach, Responsible Consumption, Sports Pedagogical
Activity.
Abstract: According to various sources, there exists a meaningful connection between environmental education and
sports pedagogical activities. Environmental education has the potential to enrich the awareness, knowledge,
skills, and values of individuals engaged in sports-pedagogical pursuits, fostering a positive attitude towards
the natural environment. Simultaneously, sports-pedagogical activities offer opportunities for environmental
education by exposing participants to diverse natural settings, involving them in outdoor experiences, and
nurturing an appreciation for the beauty and diversity of nature. Both environmental education and sports
pedagogical endeavours can actively contribute to the objectives of environmental sustainability by promoting
healthy lifestyles, responsible consumption, social justice, and cultivating ecological citizenship.
1 INTRODUCTION
Specialists exhibit particular abilities closely tied to
their performance in specific activities. These
abilities enable them to execute actions or employ
specific strategies. A specialist's capabilities are
intrinsic to their personality, professional
background, life experiences, and the knowledge,
skills, and abilities acquired over time. In the realm of
sports and pedagogy, scholars view these activities as
intricate, multifaceted processes marked by extreme,
emotional, and effective athlete training. The diverse
nature of sports necessitates varying approaches,
although common features exist in the sports
pedagogical activities of trainer-teachers across
different disciplines.
Analysing relevant scientific literature reveals
that contemporary sports and pedagogical activities
are intricate processes involving extreme, emotional
athlete training and strong psychophysiological
pressures for optimal results. Each sports discipline
possesses unique characteristics, influencing the
diverse action plans employed by trainer-teachers.
While differences exist among sports, common
features persist in sports pedagogical activities, as
recognized by scholars in the field. This
acknowledgment underscores the multifaceted nature
of sports training and coaching.
Trainer-teachers engaged in sports and
pedagogical activities exhibit abilities linked to their
personality, professional experiences, and
accumulated knowledge. Scholars emphasize the
complexity of these processes, marked by emotional
and effective athlete training. While each sport has its
distinct characteristics, shared elements define sports-
pedagogical activities across disciplines.
Understanding these common features aids in
comprehending the nuanced yet interconnected
nature of trainer-teachers' roles in different sports.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
To understand the complexities of sports and
pedagogical activities, our research employs an
empirical analysis approach. We aim to delve beyond
superficial perceptions by identifying socio-
psychological conditions vital for effective
development. Through this methodology, we intend
to reveal the essence of the trainee teacher's role,
going beyond mere organizational aspects. By
scrutinizing social experiences in physical education
settings, we aim to unravel underlying factors shaping
sports and pedagogical skills.
Data Collection Method: Our data collection
method entails a comprehensive examination of
1176
Ne’matovich, A.
Eco-Active Learning: Sports Pedagogy and Environmental Education Synergy.
DOI: 10.5220/0012956200003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1176-1180
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
socio-psychological factors influencing sports and
pedagogical skills development. We employ surveys,
interviews, and observations to gather diverse
perspectives from trainers, athletes, and educational
institutions. By engaging with various stakeholders,
we aim to capture nuanced insights into the
multifaceted nature of sports and pedagogy.
Data Interpretation Technique: Utilizing a
qualitative approach, we analyze collected data to
determine the factor structure underlying sports and
pedagogical activities. Through thematic analysis and
pattern recognition, we seek to uncover recurrent
themes and emerging patterns within our data set. By
triangulating multiple data sources, we aim to offer a
holistic interpretation of the state of sports and
pedagogical skills development and elucidate the
factors driving this process.
3 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The study focuses on the comprehensive assessment
of content and structural aspects of sports and
pedagogical skills, employing factor analysis and
exploring various methods to evaluate the
development of these skills with a particular emphasis
on socio-psychological factors. Through an initial
expert evaluation, a systematic categorization of
factors influencing sports pedagogical skills
development was established.
Ten socio-psychological factors contributing to
the advancement of sports and pedagogical activities
were identified based on expert assessments.
Subsequently, these factors were ranked according to
their significance, providing insights into their
respective roles in the study's research objectives. The
study employed a method of organizing expert
relationships to analyse socio-psychological
conditions crucial for sports and pedagogical skills
development.
Using a 5-point scale, the study assessed the
importance of these factors, with rankings ranging
from 1st to 10th indicating strong to weak
importance. The empirical data, presented in Table 1,
delves into the order of development of sports-
pedagogical skills.
Factors influencing the abilities of trainer-
educators in the realm of sports education were then
outlined. Notably, master classes emerged as the top-
ranked factor, with their organization garnering the
highest importance. Trainers and educators
emphasized the pivotal role of master classes in
enhancing sports pedagogical skills. The leading role
was attributed to expert organizers with profound
knowledge in the field, showcasing well-rounded
skills in both pedagogical and socio-pedagogical
aspects. Additionally, the factor of "Creating a
pedagogical support environment for sports teachers"
held the second rank, underscoring the significance
organizations place on the socio-psychological milieu
within the community for efficient work.
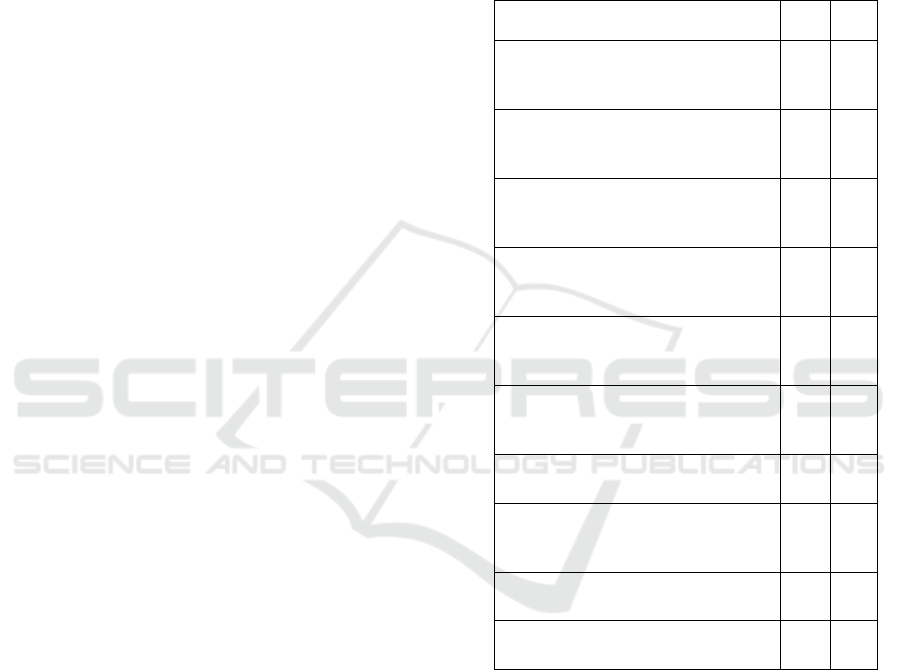
Table 1: Socio-Psychological Dimensions Shaping Sports
Pedagogical Skill Development
Factors Mean Rank
Organization of scientific and
practical conferences dedicated to
sports and
p
edagogical activities
4.29 5
Organization of master classes on the
development of sports and
p
edagogical activities;
1.19 1
Organizing meetings with teachers
with high experience in sports and
p
edagogical activities
2.92 4
Organization of competitions for the
development of sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
7.11 10
Preparation of guidelines for the
independent development of sports
and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
2.35 3
Formation of traditions in universities
on the development of sports and
p
edagogical skills
5.61 7
Ensuring civic and personal maturity
in the s
p
orts teache
r
6.08 8
Creating an environment of
pedagogical support for sports
educators
1.36 2
Formation of emotional maturity in
s
p
orts-
p
eda
g
o
g
ue
6.63 9
Enhancing the social maturity of
sports educators
4.56 6
The importance of fostering a healthy socio-
psychological environment within a sports education
team is highlighted as crucial for the development of
sports and pedagogical skills. It is emphasized that a
supportive team atmosphere plays a significant role in
assisting sports educators, emphasizing the need for
mutual support and a conflict-free professional
environment.
The third-ranked factor involves the preparation
of guidelines for independent development in sports
and pedagogical activities. Sports educators
acknowledge the necessity of guidelines for skill
development, emphasizing that methodological
instructions do not spontaneously emerge. The
Eco-Active Learning: Sports Pedagogy and Environmental Education Synergy
1177
creation of these guidelines requires an experienced
specialist with both pedagogical and professional
expertise, coupled with a research-oriented mindset.
The importance of an independent and inquisitive
approach by teachers in utilizing methodological
guidelines is underscored.
Organizing meetings with highly experienced
teachers in sports and pedagogical activities is ranked
fourth. Such meetings offer benefits such as receiving
advice and guidance from experienced colleagues,
motivation, emotional uplift, and a focus on
enhancing operational efficiency.
Surprisingly, the social, emotional, civic, and
personal maturity of sports educators is given limited
importance, possibly stemming from the perception
that high maturity in professional training may
inherently contribute to personal growth.
In Table 2, expert assessments of teachers' skills
necessary for sports pedagogy activities are
presented, showcasing a unique arrangement of
factors contributing to skill formation.
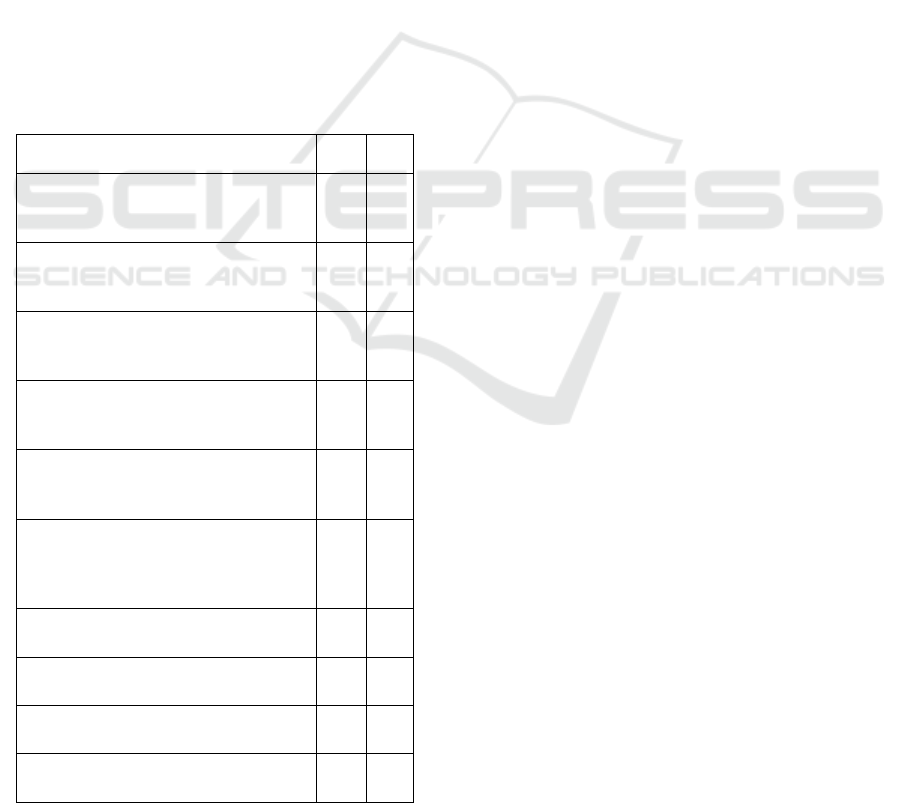
Table 2: Impacts of Social Factors on Sports Pedagogy:
Teacher Skill Development
Factors Mean Rank
Organization of scientific and practical
conferences dedicated to sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
1.16 1
Organization of master classes on the
development of sports and pedagogical
activities
3.00 5
Organizing meetings with teachers with
high experience in sports and
p
edagogical activities
8.40 10
Organization of competitions for the
development of sports and pedagogical
activities
3.50 6
Preparation of guidelines for the
independent development of sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
5.25 8
Formation of traditions in higher
education institutions for the
development of sports and pedagogical
skills
1.23 2
Ensuring civic and personal maturity in
the sports teache
r
2.50 4
Creating an environment of pedagogical
su
pp
ort for s
p
orts educators
4.20 7
Formation of emotional maturity in
s
p
orts-
p
eda
g
o
g
ue
7.00 9
Enhancing the social maturity of sports
educators
1.75 3
The primary criterion identified by teachers as the
most significant factor is the "Organization of
scientific and practical conferences dedicated to
sports and pedagogical activities". Scientific
conferences address current issues in the field,
providing valuable insights into both theoretical and
practical aspects along with recommendations for
potential solutions. This underscores the deliberate
choice of teachers to engage in scientific-practical
conferences for the advancement of their sports-
pedagogical skills.
Following closely, the second key indicator
emphasizes the "Formation of traditions in
educational institutions for the development of sports
and pedagogical skills". Educational institutions
establish traditions to foster the growth of
pedagogical skills. These traditions may manifest in
the "teacher-student" dynamic within the institution,
faculty, or department. Experienced teachers often
contribute by offering guidance through model
lessons, creating a vital framework for the cultivation
of qualities essential to sports pedagogy.
The third and fourth indicators, as ranked by
teachers, focus on "Ensuring civic and personal
maturity in sports teachers" and "Increasing the social
maturity of sports teachers." These factors are
deemed crucial for honing sports and pedagogical
skills. The argument posits that the development of
skills integral to sports education is linked to the
formation of personality traits with socio-
psychological significance. Individuals with
emotional and social maturity can effectively regulate
themselves both personally and professionally,
allowing for an independent approach in shaping the
necessary skills.
In the realm of skills required for sports
pedagogy, issues such as "Ensuring civic and
personal maturity in sports pedagogy" and
"Arranging meetings with teachers with high
experience in sports and pedagogical activities" hold
the 9th and 10th positions. While these factors are
acknowledged, they are somewhat undervalued in
comparison to others.
A third group of experts involved in the research
comprises education managers, whose assessments
are presented in Table 3, providing additional insights
into the problem at hand.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1178
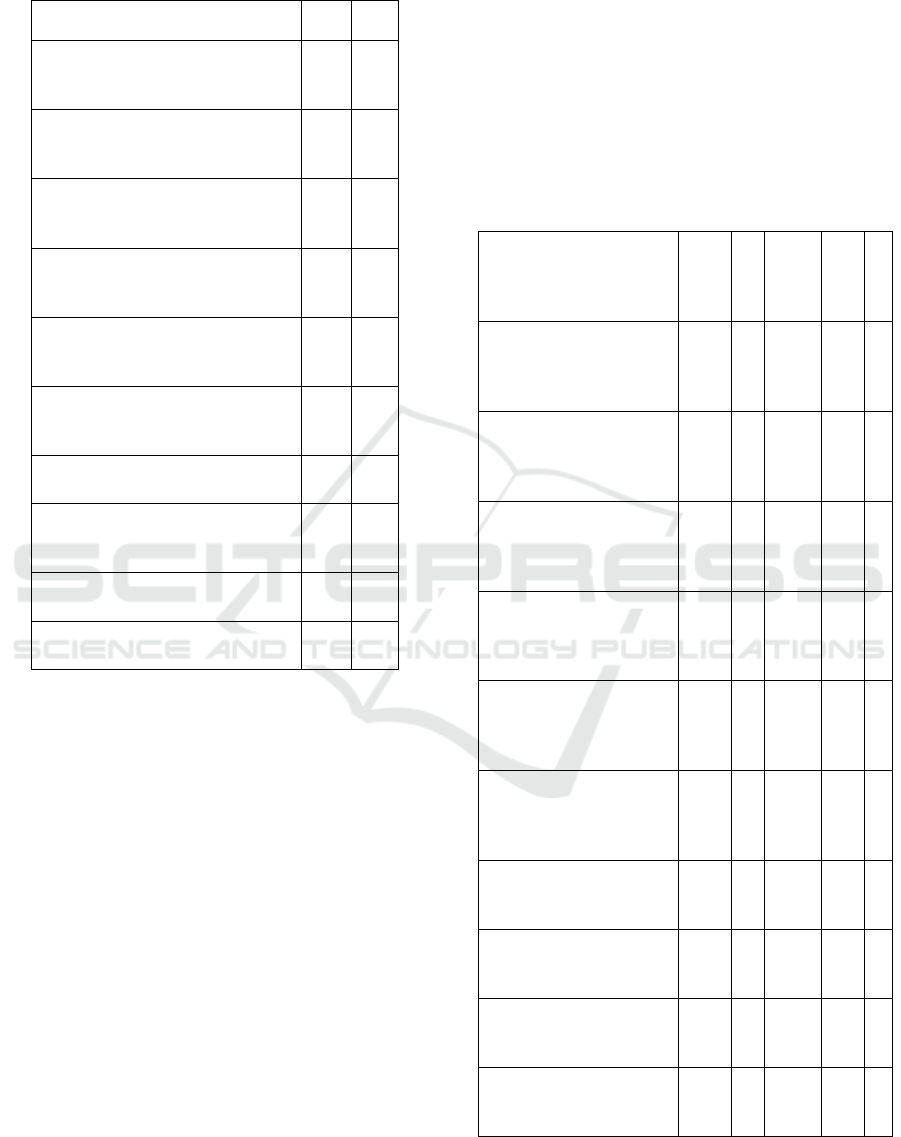
Table 3: Impact of Socio-Psychological Elements on Sports
and Pedagogical Skills
Factors Mean Rank
Organization of scientific and
practical conferences dedicated to
s
p
orts and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
4.59 6
Organizing meetings with teachers
with high experience in sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
3.26 4
Organization of master classes on
the development of sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities;
3.20 3
Organization of competitions for
the development of sports and
p
edagogical skills
1.57 2
Preparation of guidelines for the
independent development of sports
and pedagogical activities
1.16 1
The educational institution has a
tradition of developing sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical skills
8.13 10
Ensuring civic and personal
maturity in the sports teache
r
7.25 9
Creating an environment of
pedagogical support for sports
educators
7.07 8
Formation of emotional maturity in
sports-
p
edagogue
3.46 5
Enhancing the social maturity of
s
p
orts educators
6.16 7
Education managers have provided evaluation
indicators for the development of sports and
pedagogical skills, emphasizing the importance of
various factors. The first rank focuses on the
preparation of guidelines for independent
development in sports and pedagogy, followed by the
organization of competitions (2nd rank), master
classes (3rd rank), and meetings with experienced
teachers (4th rank). Some of these factors have been
considered by experts of the previous category.
The alignment of education managers' feedback
with the nature of the educational process suggests a
connection to methodical instructions, pedagogical
master classes, and interactions with experienced
teachers. Notably, the 8th rank pertains to the
"Formation of the environment of pedagogical
support of the sports teacher," the 9th rank to
"Ensuring civic and personal maturity in the sports
teacher," and the 10th rank to "Educational institution
has a tradition of developing sports and pedagogical
skills." The organizational and methodological
factors play a significant role in shaping sports-
pedagogical skills.
Upon a separate analysis of expert attitudes, a
comprehensive overview of factors influencing sports
pedagogical skill development emerges.
Summarizing the performance of all expert categories
provides a holistic description. The generalized result
categorizes these factors into three levels for a more
nuanced understanding (see Table 4).
Table 4: Influence of Social Psychology on Skill
Development in Sports Education.
Factors Train
er-
pedag
o
g
ue
Te
ac
her
Educa
tion
Mana
g
e
r
Mea
n
R
an
k
Organization of scientific
and practical conferences
dedicated to sports and
p
edagogical activities
4.29 1.1
6
3.46 3.34 3
Organization of master
classes on the
development of sports and
p
edagogical activities
2.92 3 3.26 2.48 1
Organizing meetings with
teachers with high
experience in sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical activities
1.19 8.4 3.2 4.84 7
Organization of
competitions for the
development of sports and
p
eda
g
o
g
ical skills
7.11 3.5 7.25 4.06 4
Preparation of guidelines
for the independent
development of sports and
p
edagogical activities
2.35 11.
5
1.16 2.92 2
Formation of traditions in
educational institutions on
the development of
sports-
p
edagogical skills
5.61 1.2
3
8.13 4.99 8
Ensuring civic and
personal maturity in the
sports teache
r
6.08 5.2
5
4.59 5.27 9
Creating an environment
of pedagogical support for
s
p
orts educators
1.36 4.2 7.07 4.2 6
Formation of emotional
maturity in sports-
p
eda
g
o
g
ue
6.63 7 1.57 5.69 10
Enhancing the social
maturity of sports
educators
4.56 1.7
5
6.16 4.15 5
Eco-Active Learning: Sports Pedagogy and Environmental Education Synergy
1179

The performance evaluation for the development of
sports-pedagogical skills is structured into three
ranks. The first rank comprises the top three
positions, the second rank includes places 4 to 7, and
the third rank combines factors 8 to 10. Noteworthy
contributors to sports-pedagogical skill development,
as identified by experts, include "Organization of
master classes on the development of sports and
pedagogical activities," "Preparation of guidelines for
independent development," and "Organization of
scientific and practical conferences."
Empirical findings underscore the significance of
organizing master classes for sports and pedagogical
skill development. Some experts prioritize this factor
at the forefront of the rank order. Master classes
conducted by industry leaders offer practical insights,
serving as a valuable program for sports educators.
In the overall assessment, the "Preparation of
guidelines for independent development" secures the
second rank. Methodical instructions are considered
crucial tools for sports pedagogues, enabling them to
organize activities based on these guidelines.
Taking the third position is the factor
"Organization of scientific and practical conferences
dedicated to sports and pedagogical activities."
Experts emphasize the importance of such
conferences in presenting theoretical and practical
solutions, fostering collaboration among experts, and
constantly enriching data.
On the second tier of importance, factors like
"Organization of competitions," "Increasing social
maturity of sports teachers," "Creating a pedagogical
support environment," and "Organization of meetings
with experienced teachers" are highlighted.
Competitions are seen as a means to identify
ambitious educators while enhancing social maturity
involves collaborative sharing of experiences. The
creation of a supportive pedagogical environment
depends on the socio-psychological atmosphere of
the educational institution. Meetings with
experienced teachers serve as motivational tools,
providing methodological advice and fostering a
positive professional attitude.
The tertiary factors also play a role in stimulating
specialists' professional activity. Empirical evidence
supports the importance of socio-psychological
factors in sports-pedagogical skill development, but
challenges and barriers exist in the process.
Difficulties in certain activities have led to the
identification of socio-psychological barriers
hindering sports and pedagogical skill development.
4 CONCLUSION
In summary, it is crucial to highlight the significance
of empirically analyzing socio-psychological factors
for fostering the growth of sports and pedagogical
skills in the training of prospective coaches and
educators. This becomes particularly relevant due to
the continual expansion of the roles within modern
sports and pedagogical activities. During this ongoing
process, the emphasis should not only be on imparting
professional and specialized knowledge acquired
through education but also on cultivating specific
competencies and pedagogical skills. Primarily, the
focus should be on activating sports pedagogical
skills, thereby tapping into unexplored resources to
establish a robust foundation for independent
development in the realm of sports and education.
REFERENCES
Zavalishina, D. N. (2001). Ways to identify a person with a
profession. In D. N. Zavalishina (Ed.), Psychology of
the subject of professional activity (pp. 104-128).
Yaroslavl: Teacher and time.
Aksenov, A. A. (2010). Actual prospects for improving the
training of specialists in sports and pedagogical
activities. Sports Pedagogy, (5), 54-67.
Vnukov, U. K. (2002). Integral individuality of a person in
sports activities. Science in Olympic Sports, (1), 88-98.
Kondratev, I. B. (2012). Sports and pedagogical
innovations in coaching. Sports Psychology, (4), 125-
133.
Bagadirova, S. K. (2016). Actual directions of research in
sports psychology. In Perspective directions in the field
of physical culture, sports and tourism: Proceedings of
the VI All-Russian scientific and practical conference
with international participation (pp. 35-39).
Morgan, U. (2006). Philosophy of sports: historical and
conceptual review and assessment of its future. Logos,
3 (54), 147-159.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1180
