
Sustainable Path Forward for the Green Economy in South Korea
Mehri Kh. Vokhidova, Ulugbek I. Narov, Shakxnoza E. Abdullayeva,
Farida M. Bukharova and Norhayati Rafida Abdul Rahim
Tashkent State University of Oriental Studies, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
Keywords: South Korea, Green Economy, Sustainability, Government Policy, Renewable Energy, Green Finance,
Sustainable Urban Planning, Equity, International Collaboration, Environmental Stewardship.
Abstract: South Korea's pursuit of a green economy is an exemplary case study in the global shift toward sustainability.
This article, "The Green Economy in South Korea: A Sustainable Path Forward," delves into the multifaceted
journey of South Korea as it endeavours to harmonize robust economic growth with responsible
environmental stewardship. The analysis traverses’ diverse dimensions, including government policies and
frameworks, renewable energy initiatives, green finance and investments, sustainable urban planning,
considerations of equity, and international collaborations. Government policies, notably the "Green New
Deal," underscore South Korea's commitment to sustainable development, with investments in renewable
energy, green infrastructure, and job creation. The expansion of renewable energy sources, led by private
sector giants, is pivotal in reducing fossil fuel dependency. Green finance instruments such as green bonds
mobilize capital for eco-friendly projects, aligning financial markets with environmental goals. Integrating
technology and sustainable practices in urban planning reflects South Korea's commitment to reducing carbon
footprints. However, the journey is challenging, notably balancing economic growth with environmental
preservation and ensuring equitable distribution of green benefits. South Korea's active participation in global
environmental agreements, particularly the Paris Agreement, solidifies its commitment to tackling climate
change worldwide.
1 INTRODUCTION
South Korea has emerged as a dynamic player
committed to pioneering sustainability in the heart of
Asia. Fueled by innovation, ambitious policies, and a
dedication to reducing its ecological footprint, Korea
is swiftly transforming its economic landscape into a
vibrant green oasis. This transformation, commonly
called the "green economy," embodies a multifaceted
approach to sustainable development encompassing
renewable energy, eco-friendly technologies, and a
renewed focus on preserving natural resources.
As nations worldwide grapple with the urgent
need to address climate change, Korea's journey
toward a green economy is an inspiring case study.
This article will explore the critical facets of Korea's
green evolution, from its renewable energy initiatives
to its commitment to electric vehicles, green finance,
and beyond. Join us on a journey through the vibrant
tapestry of Korea's environmental endeavours as we
delve into the innovations, challenges, and global
implications of this dynamic shift toward
sustainability.
South Korea has emerged as a beacon of hope and
innovation in a world grappling with the urgent
challenges of climate change and environmental
degradation. This East Asian powerhouse,
historically known for its rapid industrialization and
technological prowess, is turning its formidable
strengths toward a new and pressing goal: building a
green economy.
The concept of a green economy is rooted in
achieving economic growth while safeguarding the
environment and promoting social equity. South
Korea, a nation with a rich tapestry of culture and a
dynamic economy, is on a transformative journey to
harmonize economic development with ecological
responsibility.
Over the past few decades, South Korea has
undergone a remarkable evolution. It has transitioned
from a resource-intensive, pollution-prone economy
to one that champions clean energy, sustainable
1402
Vokhidova, M., Narov, U., Abdullayeva, S., Bukharova, F. and Rahim, N.
Sustainable Path Forward for the Green Economy in South Korea.
DOI: 10.5220/0012969000003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1402-1407
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

practices, and innovation. This shift is not just a
response to global environmental imperatives but is
also driven by a recognition that sustainability is
intrinsically tied to economic resilience and societal
well-being.
This article delves into the various aspects of South
Korea's green economy, aiming to understand the
many facets of this transformation. It investigates the
primary catalysts propelling this change, which
include governmental policies, private sector
innovations, and the evolving attitudes of the Korean
population. South Korea is actively progressing
towards a more sustainable future through endeavors
such as renewable energy projects, green finance
strategies, sustainable urban development, and the
adoption of advanced technologies.
As we navigate South Korea's green journey, we
also highlight its challenges, including balancing
economic growth with environmental preservation,
addressing social inequalities, and ensuring the
transition to a green economy benefits all citizens.
Moreover, we reflect on South Korea's role on the
global stage, as it actively participates in international
efforts to combat climate change and shares its green
expertise with the world.
South Korea's story of forging a green economy is
an inspiring case study for nations worldwide. It
underscores the possibility of redefining economic
success, where prosperity coexists with a thriving
environment and social harmony. Join us in exploring
South Korea's path towards a sustainable future,
where innovation meets conservation and where a
green economy shapes tomorrow's world.
2 THE MAIN RESULTS AND
FINDINGS
The concept of a green economy has gained
significant attention globally as societies grapple with
the pressing need to balance economic growth with
environmental sustainability. South Korea, known for
its rapid industrialization and technological prowess,
has emerged as a noteworthy case study - Dayton L.
(2020). The literature provides a comprehensive
overview of critical studies and research papers that
shed light on South Korea's transition towards a green
economy, spanning its policy framework, renewable
energy initiatives, green finance, urban planning, and
sustainability challenges.
A cornerstone of South Korea's transition to a
green economy is its government's commitment to
policy and regulatory frameworks that incentivize
sustainability. Research by Lee and Kim (2018)
underscores the significance of the South Korean
government's "Green New Deal" policy, which
includes investments in renewable energy, green
infrastructure, and green jobs. Their study highlights
how these policies are integral to the country's efforts
to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote
sustainable growth (Lee, S et al., 2018).
Promoting renewable energy sources has been
pivotal to South Korea's green economy agenda.
Scholars like Park and Hong (2020) examine the
country's rapid expansion of solar and wind energy,
emphasizing the government's ambitious targets and
the involvement of private sector actors such as
Hyundai and Samsung in the renewable energy
sector. Such initiatives reflect South Korea's
commitment to reducing its dependence on fossil
fuels and transitioning to a low-carbon economy
(Park H. et al., 2020).
South Korea has also made significant strides in
the realm of green finance. Lee and Kim (2019) delve
into the emergence of green bonds and sustainable
investment funds in the country, illustrating how
these financial instruments mobilize capital for eco-
friendly projects. The study emphasizes the
importance of aligning financial markets with
environmental objectives and fostering green
innovation (Lee H. et al., 2019).
Urbanization is a prominent feature of South
Korea's landscape, and as such, sustainable urban
planning plays a vital role in the country's green
economy narrative. Research by Choi and Kim
(2021) explores South Korea's innovative city
initiatives, focusing on integrating technology,
energy efficiency, and eco-friendly infrastructure in
urban development. The study underscores how these
efforts contribute to reducing carbon footprints in
urban areas and enhancing overall liveability - Choi,
Y., & et. al. (2021).
Despite its remarkable progress, South Korea
faces challenges in its green economy journey. Kim
and Lee (2019) discuss the need for balancing
economic growth with environmental preservation,
drawing attention to concerns over environmental
justice and social inequalities. Their research
highlights the importance of ensuring that the benefits
of green initiatives are equitably distributed among
the population - Kim, E., & et. al. (2019).
South Korea's role in international environmental
agreements and collaborations is another critical
aspect of its green economy efforts. Scholars like Han
(2020) examine South Korea's commitments under
the Paris Agreement and active participation in global
climate negotiations. It underscores the nation's
Sustainable Path Forward for the Green Economy in South Korea
1403

global commitment to addressing climate change -
Han J. (2020).
The literature reviewed here collectively
highlights South Korea's remarkable journey towards
a green economy. It underscores the pivotal role of
government policies, renewable energy, green
finance, sustainable urban planning, and the
imperative of addressing sustainability challenges
and equity concerns. South Korea's story serves as a
valuable case study for countries striving to achieve
economic growth within environmental
sustainability, offering lessons and insights that
resonate globally.
A qualitative approach was employed, which
involved conducting in-depth interviews, case
studies, and analysing content from secondary
sources. These secondary sources encompassed prior
literature, government publications, and industrial
reports. An in-depth interview was performed, which
involved experts in government officials,
environmentalists, economists, and business leaders.
The interviews provided qualitative insights into the
challenges and opportunities associated with South
Korea's green economy.
A comprehensive examination of the existing
body of literature was conducted concerning South
Korea's green economy, encompassing academic
papers, government reports, and pertinent articles.
This review provided a thorough understanding of the
historical background of the subject and highlighted
fundamental research discoveries.
The government publications include official
documents that provide valuable statistics and policy
information about South Korea's green initiatives
from the Ministry of Environment, the Ministry of
Trade, Industry, and Energy, and the Korea Energy
Agency. The industrial reports were included to
understand the current state of green industries in
South Korea in terms of reports from industry
associations, market research firms, and
environmental organizations. Besides, an analysis of
policy examined South Korea's green policies and
initiatives, including the Green New Deal and carbon
pricing mechanisms. The study also examined the
policy documents, legislative changes, and their
impact on the country's transition to a green economy.
The case studies in this context showcase various
aspects of South Korea's green economy endeavours,
encompassing projects, corporate initiatives, and
policy implementations. These specific case studies
were selected to offer tangible instances of successful
green undertakings and the obstacles faced. To
provide a broader perspective on South Korea's green
economy initiatives, we also conducted a
comparative analysis with other countries that have
embarked on similar transitions. The comparison
highlights South Korea's distinct approach and
exemplifies best practices in pursuing a green
economy. In projecting the future of South Korea's
green economy, we used a combination of expert
opinions, trend analysis, and policy trajectory
assessments. This section provides insights into the
potential challenges and opportunities for South
Korea in its pursuit of sustainability.
South Korea has been actively implementing
green policies and initiatives to transition toward a
more sustainable and environmentally responsible
economy. These policies address pressing
environmental challenges, reduce greenhouse gas
emissions, promote renewable energy, and foster
green innovation. Here are some vital green policies
and initiatives in South Korea.
Green New Deal: The Green New Deal is a
comprehensive national strategy launched in 2020 to
stimulate economic growth while addressing climate
change and the environment. It includes plans to
invest in green infrastructure, create green jobs, and
achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. The South Korean
government responded. The New Deal plans to invest
approximately $144 billion to create 1,901,000 jobs
by 2025. The plan focuses on the Digital New Deal
and Green New Deal and includes comprehensive
policy support to strengthen employment and social
safety nets. The Green New Deal focuses on
renewable energy, green infrastructure, and the
industrial sector. Its clean vehicle subsidy program
offers subsidies of up to $17 million for people
buying electric vehicles in 2021 and up to $33.5
million for hydrogen fuel cell electric vehicles. In
December 2020, South Korea submitted its NDC and
carbon neutral strategy 2050 to the UNFCCC. The
latter includes Korea's long-term plan to achieve
carbon neutrality by 2050.
Carbon Pricing: A national ETS system was
introduced in 2015, covering 74% of domestic
emissions from energy, transport, aviation,
construction, and waste management industries. The
carbon price remains relatively low at $21.57 per
tonne of CO2, about a quarter of Europe's. Only 10%
of the allocated carbon credits were auctioned
between 2021 and 2025, and the rest will be
transferred to companies for free.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1404
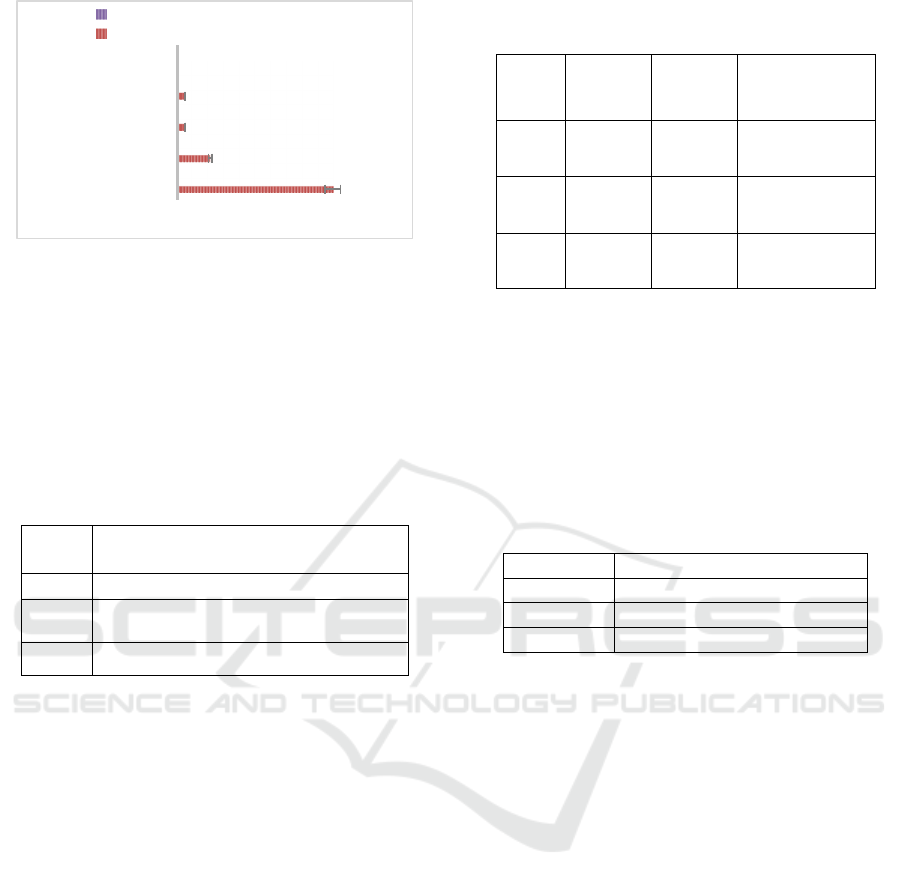
Figure 1: Carbon-Di-Oxide Emissions in 2021.
South Korea recorded 602.6 Mt and 626.8 Mt of CO2
emissions in 2021. South Korea's greenhouse gas
reduction targets indicate a clear commitment to
mitigating climate change. The table shows the
progressive nature of these targets, which align with
international agreements like the Paris Agreement.
Table 1. Targets of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reduction
(2020-2030)
Yea
r
Target (Percentage Reduction from 2017
levels)
2020 24%
2025 37%
2030 50%
Renewable Energy Promotion: The government
has set ambitious targets for renewable energy
development, focusing on solar and wind power.
Incentives, subsidies, and feed-in tariffs have been
provided to accelerate the growth of renewable
energy capacity. Table 2 demonstrates the rapid
growth of renewable energy capacity in South Korea,
with solar and wind energy playing significant roles.
The total renewable energy capacity doubled between
2015 and 2020, showcasing the country's
commitment to clean energy. According to the Green
Plan, by 2034, the total production capacity of
renewable energy will increase to 40 per cent of the
country's energy balance. As of January 2021, it will
be only 15%. Currently, the LNG makes up the most
significant part of South Korea's energy balance
structure: coal - 27.1% of the total volume, and
nuclear energy - 19.2% of energy production. 2030,
according to plans, the share of nuclear energy in the
total ratio will be reduced to 11.7%, and then by 2034
to 9.9%.
Table 2. Renewable Energy Capacity Growth in South
Korea
Year
Solar
Capacity
(
MW
)
Wind
Capacity
(
MW
)
Total Renewable
Capacity (MW)
2015 2,500 235 5,100
2017 7,000 702 11,500
2020 14,200 1,645 26,400
Green Finance: The government has been actively
promoting green finance, including issuing green
bonds and developing green financial products. It
encourages investments in sustainable projects and
businesses. South Korea has witnessed a substantial
increase in green bond issuance, indicating growing
interest in sustainable investments. Table 3
underscores the significant rise in green finance and
its contribution to funding eco-friendly projects.
Table 3. South Korea's Green Bond Issuance (USD million)
Yea
r
Green Bond Issuance
2016 300
2018 900
2020 2,200
South Korea's green bond market became the second
largest in Asia in 2021 (after China). However, the
country focuses more on social bonds and is among
the top 5 issuers in the world. Last year, the Korean
market issued $66 billion worth of ESG bonds - 71
per cent of which were social. ESG funding totalled
$140 billion at the end of 2020. Also, ESG investment
flows into the country have increased eightfold since
2017. Green bonds are typically fixed-income
instruments designed to raise money for
environmental and climate projects. In 2023, the
Ministry of Environment supported issuers of
qualified bonds by providing interest expenses of up
to 300 million won ($226,586) per year.
Air Quality Improvement: South Korea has
implemented measures to combat air pollution,
including stricter vehicle emission standards,
introducing city low-emission zones, and incentives
for clean transportation.
Plastic Waste Reduction: South Korea has
implemented policies to reduce single-use plastic
consumption and promote recycling to address the
issue of plastic waste. It includes a ban on plastic bags
in major supermarkets and convenience stores.
Biodiversity Conservation: The government has
taken steps to protect biodiversity and natural
12 466.3
0
2 648.80
626.8
602.6
33.2
8.7
1.9
12.13
2.2
4.4
-5000.00 0.00 5000.0010000.0015000.00
China
India
Korea
Indonesia
Hongkong
CO2emissionspercapita,CO2t
CO2emissions,MTCO2
Sustainable Path Forward for the Green Economy in South Korea
1405
ecosystems. It includes the creation of protected areas
and initiatives to restore damaged ecosystems.
Green Technology and Innovation: South Korea
invests in research and development of green
technologies, including eco-friendly materials,
energy-efficient technologies, and sustainable
agriculture practices.
Table 4 Investment in Smart City Initiatives
Yea
r
Investment (USD billion)
2017 3.5
2019 6.2
2021 10.1
Investment in innovative city initiatives in South
Korea has steadily increased, demonstrating the
country's focus on sustainable urban planning and the
integration of technology to improve energy
efficiency and liveability in urban areas. The Korean
government has prioritized smart city pilot projects in
Sejong and Busan.
Table 5. Investment in Sustainable Urban Planning (2017-
2021)
Year
Investment in Smart City Initiatives (USD
b
illion
)
2017 3.5
2018 `4.2
2019 5.8
2020 7.5
2021 10.1
Investment in innovative city initiatives in South
Korea has steadily increased, reflecting the country's
commitment to sustainable urban planning,
technology integration, and enhancing the quality of
life in urban areas. The green policies and initiatives
underscore South Korea's commitment to a more
sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
While challenges remain, including reducing fossil
fuel dependency and achieving carbon neutrality,
these policies demonstrate the nation's dedication to
balancing economic growth with environmental
responsibility and contributing to global
sustainability efforts.
Based on the above findings, this article suggests
that there should be continuous research and
development in renewable energy and green
technologies. As technological advancements are at
the heart of the green economy, supporting R&D can
ensure Korea stays at the forefront of eco-
innovations. There should be programs to educate the
public about the importance of the green economy, its
benefits, and the individual's role is vital. It may foster
a culture of sustainability and motivate consumers to
make environmentally friendly choices.
In addition to that, small and medium-sized
enterprises (SMEs) play a crucial role in any
economy. The government should offer incentives
and support to green SMEs, thus allowing them to
thrive and contribute more effectively to the green
economy. While Korea has made substantial
progress, collaborating with other nations can further
its reach and effectiveness. Sharing best practices,
technologies, and policy strategies can benefit all
parties. While green technologies and techniques are
ever-evolving, Korea should regularly review and
update its policies and strategies to ensure alignment
with the latest developments.
To ensure the seamless operation of a green
economy, it is essential to have the required
infrastructure, including renewable energy grids and
efficient transportation systems. Investing in green
infrastructure has the potential to stimulate economic
growth and generate employment opportunities.
Korea has the opportunity to implement policies and
incentives that encourage the adoption of
environmentally friendly products and services,
thereby increasing demand and demonstrating the
advantages of transitioning to greener production
practices for businesses. Implementing ongoing
training programs for professionals across different
sectors can also ensure they possess the requisite
skills and knowledge to make meaningful
contributions to the green economy.
3 CONCLUSION
The green economy in Korea stands as a testament to
the country's dedication to sustainable development
and environmental conservation. Over the years,
Korea has taken significant strides in pivoting from
an industrial, growth-driven economic model to one
that prioritizes sustainability, ecological balance, and
social inclusivity. The country's efforts, from the
Green New Deal to its focus on renewable energy and
eco-friendly technologies, reflect a commitment to a
future combining economic prosperity and
environmental responsibility. In conclusion, while
Korea has made commendable strides in pursuing a
green economy, there is always room for
improvement. By adopting these recommendations,
the country can ensure a more sustainable,
prosperous, and eco-friendly future.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1406

REFERENCES
Dayton, L. (2020). How South Korea made itself a global
innovation leader. Nature, 581, S54-S56. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-01466-7
Lee, S., & Kim, J. (2018). South Korea's Green New Deal:
Policy Innovation for Addressing Climate Change and
Economic Crisis. Sustainability, 10(8), 2751
Park, H., & Hong, J. (2020). Solar and Wind Energy
Expansion in South Korea: Policy Drivers and Market
Dynamics. Energy Policy, 141, 111465
Lee, H., & Kim, H. (2019). Green Finance Initiatives in
South Korea: A Review of Progress and Prospects.
Sustainability, 11(20), 5616
Choi, Y., & Kim, S. (2021). Smart City Initiatives in South
Korea: Towards Sustainable Urban Development.
Sustainability, 13(1), 22
Kim, E., & Lee, S. (2019). Balancing Economic Growth
and Environmental Sustainability in South Korea:
Challenges and Strategies. Sustainability, 11(21), 6115
Han, J. (2020). South Korea's Role in the Paris Agreement:
Commitments and Collaborations. Climate Policy,
20(7), 863-877
Sustainable Path Forward for the Green Economy in South Korea
1407
