
E-Commerce Adoption in Developing Markets: SME Perspectives
Amit Mishra
1
, Shashi Kant Gupta
2
, Prabhdeep Singh
3
and Orooj Siddiqui
4
1
University of Lucknow, India
2
Eudoxia Research University, U.S.A.
3
Shri Ramswaroop Memorial University, India
4
Integral University, India
Keywords: E-Commerce, Readiness, Awareness, Barriers, Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMEs).
Abstract: E-commerce may enhance communications among manufacturers, retailers, customers, and even
policymakers. However for a number of causes, the usage of e-commerce by small and medium-sized
businesses (SMEs) in the process of countries is still constrained. This research seeks to establish the variables
that affect how SMEs in Ho Chi Minh City employ the E-commerce model. Next, numerous policy
implications are offered for Ho Chi Minh City Businesses to encourage e-commerce. The research included
data from 302 Ho Chi Minh City Firms. In order to analyze data, statistical methods such as correlation test,
the Cronbach's Alpha reliability scale, as well as the linear regression model along with exploratory factors
(EFA) was utilised. Results indicate adoption of e-commerce is boosted by the enterprise's preparedness,
understanding of the advantages of online shopping, and promoting regulations.
1 INTRODUCTION
The integration of electronics, telecommunications,
and the internet into manufacturing and commerce
represents a monumental paradigm shift in global
economic dynamics. E-commerce has emerged as a
focal point in various academic disciplines, including
economics, management, technology, marketing, and
finance (Rajagopal et al., 2022). Its significance
extends to both developed and developing nations,
providing numerous opportunities for economic
advancement. However, challenges persist that can
inhibit the full exploitation of e-commerce benefits,
particularly in developing nations. These challenges
include underdeveloped monetary and financial
infrastructure and legal frameworks characterized by
outdated laws and inadequate regulations (Pandey et
al., 2021).
Consequently, many developing nations struggle to
fully exploit the benefits of e-commerce, which can
impede their economic growth potential. Despite
these obstacles, e-commerce offers innovative
avenues for enhancing competitiveness and
organizational development, fostering consumer
engagement, and expanding market reach (Alrumiah
et al., 2021). These advantages are particularly
relevant in regions like Ho Chi Minh City, where
there is a notable lack of literature on the factors
influencing e-commerce adoption.
Small and mid-size enterprises (SMEs), which
typically lack extensive resources, stand to gain
significantly from engaging with e-commerce.
However, the limited research on this topic creates a
gap in understanding how these businesses can
effectively leverage e-commerce to their advantage
(Lv et al., 2020). Addressing this gap is crucial for
identifying opportunities and formulating effective
policy interventions aimed at enhancing SMEs'
engagement with e-commerce.
The essay proposes specific policy changes tailored
to bolster SMEs' adoption of e-commerce,
recognizing the pivotal role they play in the economic
landscape of Ho Chi Minh City and beyond. By
examining the unique challenges and opportunities
faced by SMEs in this region, the research aims to
provide a comprehensive framework for supporting
their integration into the e-commerce ecosystem
(Tolstoy et al., 2022).
This exploration is essential not only for fostering
local economic growth but also for contributing to the
broader understanding of e-commerce's impact on
small businesses in developing regions. By
addressing the infrastructural and regulatory
challenges and promoting targeted policy
Mishra, A., Gupta, S., Singh, P. and Siddiqui, O.
E-Commerce Adoption in Developing Markets: SME Perspectives.
DOI: 10.5220/0012988200003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1613-1616
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
1613
interventions, the potential for e-commerce to drive
economic development and enhance the
competitiveness of SMEs in Ho Chi Minh City can be
significantly improved. This approach highlights the
transformative potential of e-commerce and
underscores the need for ongoing research and policy
support to realize its full benefits.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Table 1: Exploring SME E-commerce Adoption: Global Perspectives and Insights.
Author Findings
Wanzu, et al., 2019 E-commerce usage affects SMEs' growth in Uganda. A structured, self-administered questionnaire
was used to surve
y
172 U
g
andan SME owners/mana
g
ers in Kam
p
ala.
Awe, et al., 2021 A research study wishes to explore the motivations of young Gambian business owners to use e-
commerce technolo
gy
and their
p
ers
p
ectives on its advanta
g
es.
Rabayah, et al., 2022 SME e-commerce application model development efforts are mentioned. The study reviews
empirical data showing how firms' preparation influences SMEs' IT adoption.
Nather et al., 2020 The study focuses on e-commerce usage and attitudes among six manufacturing SMEs in Wenzhou,
Zhe
j
ian
g
P
r
ovince, China, a re
g
ion economicall
y
develo
p
ed for SMEs.
Wongsunopparat, et
al., 2021
Investigated factors affecting live streaming e-commerce client buying behaviour. The study
examines one purchase decision and six independent factors, including platform loyalty,
engagement, pricing, product individualization, and the live streamer's public image.
3 HYPOTHESIS DEVELOPMENT
H1: Enterprise readiness improves E-commerce apps.
H2: E-commerce awareness improves business E-
commerce applications.
H3: E-commerce obstacles hurt corporate
applications.
H4: Supporting policies boost business e-commerce
applications.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A comprehensive investigation into the adoption of e-
commerce among small and medium-sized
enterprises (SMEs) in Ho Chi Minh City incorporates
both qualitative and quantitative methodologies. In
the qualitative approach, the research model's
variables including Enterprise Readiness (ER),
Awareness of E-commerce Benefits (BE), E-
commerce Application Hurdles (BA), Support
Policies (PO), and E-commerce Application
Performance (AP) were refined through a
collaborative discussion involving seven e-commerce
specialists. This qualitative phase allowed for a
nuanced understanding of the key factors influencing
e-commerce adoption within the SME sector.
Subsequently, the quantitative method involved
the practical sampling of 302 businesses in Ho Chi
Minh City. Businesses were selected from compiled
lists and contacted directly via email to participate in
the study by completing a questionnaire. The
collected data were then subjected to analysis using
the SPSS 20 tool, enabling researchers to derive
statistical insights into the patterns of e-commerce
adoption, the challenges faced by SMEs, and the
effectiveness of existing support policies. This
combined qualitative-quantitative approach provides
a holistic perspective on the dynamics of e-commerce
utilization among SMEs in Ho Chi Minh City,
facilitating informed policy recommendations and
strategic interventions to foster greater uptake in the
sector.
5 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
The reliability of a scale, as assessed by Cronbach's
Alpha coefficient, is crucial in research to ensure
consistency and accuracy of measurements. In this
study, the Cronbach's Alpha coefficients ranged from
0.830 to 0.929, with the highest value attributed to the
influencing element for policy and the lowest to
Internet applications. These coefficients indicate high
internal consistency, with values above 0.8
considered satisfactory. Moreover, individual
components such as enterprise preparation,
applications obstacles to e-commerce, and
comprehending the benefits of e-commerce
demonstrated robust reliability with coefficients of
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1614
0.914, 0.904, and 0.888, respectively. The overall
correlation exceeding 0.3 further confirms the
adequacy of the variables included in the analysis.
Furthermore, the study assures the reliability of
the exploratory factor analysis (EFA) with a total of
20 variables, 17 independent and 3 dependent, all
meeting the requisite criteria. This comprehensive
analysis provides a solid foundation for
understanding the factors influencing policy, e-
commerce applications, and associated challenges,
thus offering valuable insights for decision-makers
and researchers in the field.
Table 2: Cronbach’s Alpha analysis results.
Factor Cronbach’s
alpha
Variable
Enterprise readiness 0.907 5
E-commerce app hurdles 0.915 6
Support policies 0.931 4
A
wareness of E-commerce benefits 0.929 5
E-commerce application 0.898 5
All 17 independent factors examined in the
exploratory factor analysis (EFA) met the
requirements for reliability as evidenced by
Cronbach's Alpha analysis. Bartlett's test, with a
significant level of 0.000, indicated satisfactory
results, validating the factor structure. Furthermore,
the Total Variance Explained, exceeding 50% at
79.837%, underscores the adequacy of the factors in
explaining the data variability. Factor correlation
analysis, as presented in Table 1, revealed the nature
of relationships between variables. Notably, the E-
commerce application demonstrated positive
correlations with ER and BE, while exhibiting a
negative correlation with BA, all within acceptable
significance levels below 5%. Consequently, these
findings support the use of a linear regression
approach to establish connections between variables,
indicating a promising avenue for further analysis and
interpretation of the data.
Table 3: Correlation analysis result.
Enterpris
e
readiness
A
warenes
s
of E-
commerce
b
enefits
E-
commerce
applicatio
n
b
arriers
Support
policies
E-
commerce
applicatio
n
Pearson
c
orrelatio
n
0.354** 0.671** -0.237** 0.200** 1
Sig.
(2-tailed)
1.001 1.001 1.001 1.001
N 304 304 304 304 304
The regression analysis indicates that the parameters
ER, BE, and PO positively influence AP, while BA
has an adverse effect on AP. The R2 value of 0.586
suggests that the model accounts for 58.6% of the
variance in e-commerce usage. In other words, ER,
BA, BE, and PO collectively explain 58.6% of the
variation observed in the use of e-commerce. This
underscores the significance of these factors in
understanding and predicting patterns of e-commerce
adoption and usage.
Table 4: Regression model results.
Model Unstandardized
coefficients
Standardized
coefficients
t Sig.
B Std.Error Beta
1 (Constant) -0.781 0.325
-2.446 0.016
E-
commerce
application
b
arriers
-0.224 0.047 -0.204 -5.847 0
Enterprise
readiness
0.253 0.038 0.279 7.942 0
Support
p
olicies
0.245 0.043 0.234 5.607 0
E-
commerce
advantages
0.467 0.037 0.515 13.187 0
The standardized regression coefficients reveal the
impact of various components on the dependent
variable, AP. Beginning with BE, its positive beta
value of 0.514 indicates a significant positive
influence on AP. For every unit increase in BE, AP
rises by 0.389 units, underscoring their positive
relationship. Similarly, ER demonstrates a positive
impact on AP, with a beta value of 0.278. A one-unit
increase in ER corresponds to a 0.278 unit
improvement in AP, further highlighting their
constructive association. Conversely, BA exhibits a
negative impact on AP, with a beta value of 0.203,
implying that AP decreases by 0.203 units for every
unit increase in BA. Lastly, the relationship between
AP and PO is also positive, as indicated by a beta
value of 0.236. With each unit increase in PO, AP
improves by 0.236 units, reinforcing their favourable
correlation. Overall, these findings underscore the
varying influences of different components on AP,
highlighting both positive and negative associations.
E-Commerce Adoption in Developing Markets: SME Perspectives
1615
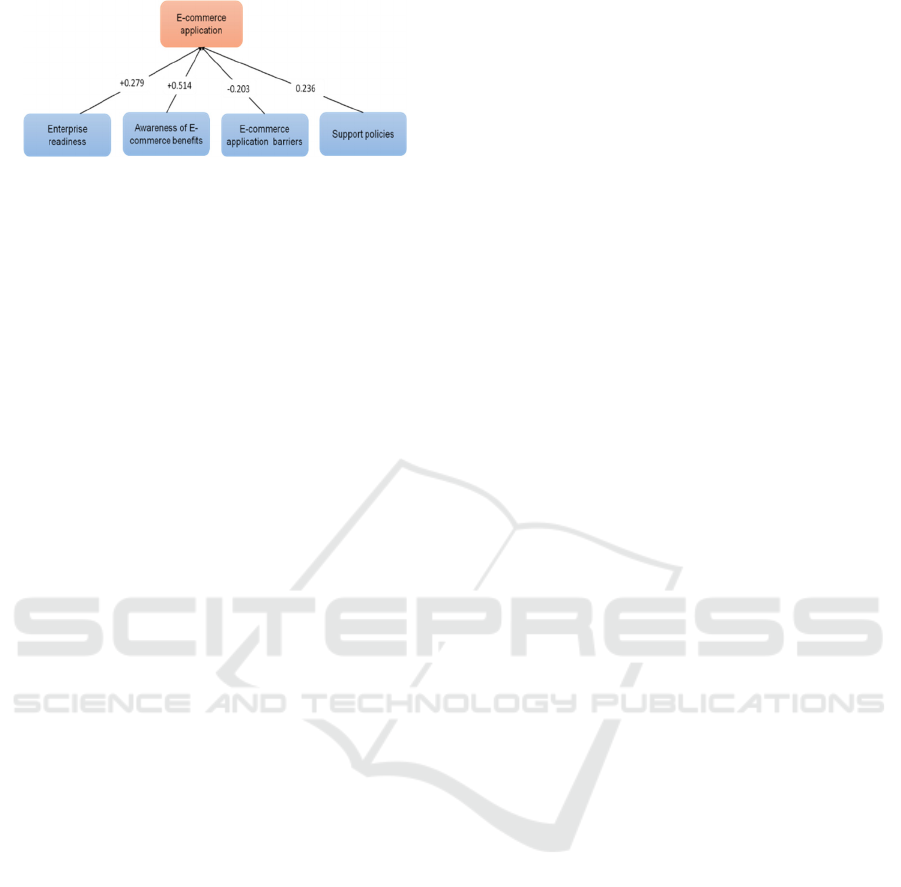
Figure 1: Research model results.
6 CONCLUSION
In Ho Chi Minh City, the adoption of e-commerce by
small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is crucial
for enhancing customer retention and facilitating
growth. This study aims to identify the factors
influencing the utilization of e-commerce among
companies in the region. Employing a qualitative
approach, the research involved group discussions
among E-commerce specialists to refine criteria and
develop a questionnaire. Subsequently, a
combination of quantitative techniques such as linear
equation modelling, Cronbach's Alpha test, and EFA
tests were employed to analyse the gathered data and
categorize questions.
Several challenges impede the widespread
adoption of e-commerce among SMEs, including
reliance on traditional methods of buying and selling,
limited human resources, high investment costs, lack
of expertise, and inconsistent business strategies.
Nonetheless, certain factors support the integration of
e-commerce. Financial, technological,
infrastructural, and human resources all play crucial
roles in preparing a firm for e-commerce
implementation.
To overcome barriers and capitalize on
opportunities, it is imperative for employers and
employees to engage in training sessions focused on
e-commerce programmes. These sessions are
essential for equipping individuals with the necessary
knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of
the e-commerce landscape effectively.
REFERENCES
Ariansyah, K., Sirait, E.R.E., Nugroho, B.A., &
Suryanegara, M. (2021). Drivers of and barriers to e-
commerce adoption in Indonesia: Individuals’
perspectives and the implications. Telecommunications
Policy, 45(8), 102219.
Taher, G. (2021). E-commerce: advantages and limitations.
International Journal of Academic Research in
Accounting Finance and Management Sciences, 11(1),
153-165.
Rajagopal, N.K., Qureshi, N.I., Durga, S., Ramirez Asis,
E.H., Huerta Soto, R.M., Gupta, S.K., & Deepak, S.
(2022). Future of business culture: an artificial
intelligence-driven digital framework for organization
decision-making process. Complexity, 2022.
Pandey, A.K., Singh, R.K., Jayesh, G.S., Khare, N., &
Gupta, S.K. (2022). Examining the Role of Enterprise
Resource Planning (ERP) in Improving Business
Operations in Companies. ECS Transactions, 107(1),
2681.
Tolstoy, D., Nordman, E.R., & Vu, U. (2022). The indirect
effect of online marketing capabilities on the
international performance of e-commerce SMEs.
International Business Review, 31(3), 101946.
Rabayah, K.S., Maree, M., & Alhashmi, S.M. (2022).
Cultural factors that influence the adoption of e-
commerce: A Palestinian case study. Information
Development, 38(4), 623-640.
Wongsunopparat, S., & Deng, B. (2021). Factors
influencing purchase decision of Chinese consumer
under live streaming e-commerce model. Journal of
Small Business and Entrepreneurship, 9(2), 1-15.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1616
