
Agile Workforce: Embracing Digital Evolution
Namita Nath
1
, Thiruma Valavan A
2
, Rohit Kumar Rana
3
and Aastha Bhatia
4
1
Teerthanker Mahaveer University, Uttar Pradesh, India
2
Indian Institute of Banking & Finance, Maharashtra, India
3
Hyundai E&C, India
4
Impart Self Service, Delhi, India
Keywords: E-Training, Digital Transformation, Technology, Agility, Resilience.
Abstract: This investigation explores the evolving landscape of labour in the digital era and the imperative for
businesses to adapt their models to remain competitive. The primary objective is to assess the efficacy of E-
training in cultivating employee agility and resilience amidst technological shifts. Employing a survey
methodology, a sample of 802 managers from both public and private sector enterprises in India was examined.
The findings underscore the critical role of providing workers with access to transformative technologies,
particularly digitalization, to enhance their nimbleness and productivity. In an era characterized by rapid
digital advancements, organisations must invest in E-training initiatives to equip their workforce with the
skills necessary to navigate the evolving technological landscape. This study contributes valuable insights
into the importance of leveraging digital tools and training strategies to foster employee adaptability,
ultimately enhancing organisational competitiveness in the digital age.
1 INTRODUCTION
Despite significant advancements in understanding
how individuals adopt new technology, there has
been limited integration of this knowledge into
contemporary thinking, particularly concerning
employee-related aspects that can influence digital
transformation. Existing models predominantly focus
on technology processes and strategies, often
neglecting other crucial factors that impact the
successful adoption and utilization of new
technologies within organizations. This oversight can
lead to gaps in fully understanding the holistic effects
of technology adoption, particularly how it impacts
employees' day-to-day experiences and overall job
satisfaction. Until recently, there has been a scarcity
of frameworks addressing the impact of technology
on employee and work-related outcomes (Trenerry et
al., 2021). This gap highlights the need for more
comprehensive approaches that consider both
technological and human elements in digital
transformation initiatives. Recent developments have
seen the emergence of worker-centric frameworks
designed to assess and enhance Industry 4.0
environments. These frameworks draw inspiration
from earlier models of work-related wellness,
integrating research on technology adoption with
indicators of work-related well-being, such as job
satisfaction and work engagement (Kaasinen et al.,
2018).
By acknowledging that workers' initial perceptions
of new technologies are shaped by factors at
individual, organizational, and environmental levels,
these frameworks provide a more nuanced
understanding of the adoption process. This holistic
approach ensures that both individual and
organizational well-being are considered, facilitating
a smoother transition to digitally transformed
workplaces. The integration of these elements helps
create a more supportive environment where
employees feel valued and engaged, ultimately
contributing to the success of digital transformation
efforts. As businesses navigate digital transformations,
prioritizing employee happiness becomes increasingly
imperative. Workplace resilience and adaptability,
although not extensively studied in connection to
digital transformation, are likely to significantly
impact the outcomes of this process for both
individuals and organizations (Mangalaraj et al.,
2023). Resilient and adaptable employees are better
equipped to handle the challenges and uncertainties
associated with technological changes, leading to
Nath, N., A., T., Rana, R. and Bhatia, A.
Agile Workforce: Embracing Digital Evolution.
DOI: 10.5220/0012988600003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1627-1631
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
1627
more positive outcomes in terms of job satisfaction,
engagement, and overall productivity.
Therefore, it is crucial for organizations to
develop strategies that foster these qualities among
their workforce. By doing so, they can not only
enhance the effectiveness of their digital
transformation initiatives but also promote a healthier,
more supportive work environment that benefits both
employees and the organization as a whole.
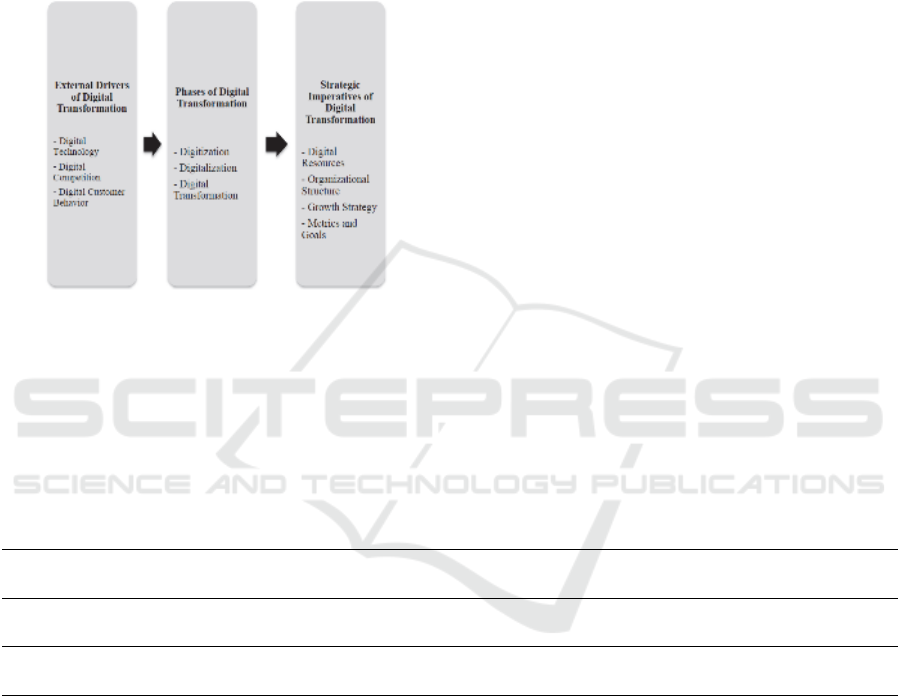
Figure 1: Flow of digital transformation (Verhoef et al.,
2021).
As technological advancements continue to
accelerate, the demand for qualified workers faces a
corresponding challenge. Companies and
governments alike are grappling with the imperative
to reskill and upskill their workforces. Key attributes
such as critical thinking, analytical prowess, problem-
solving skills, self-management, flexibility, and
resilience are increasingly coveted by employers
(Ghosh et al., 2021). Projections for the future labour
market suggest a widening gap in essential skills,
posing a significant concern for businesses
worldwide (World Economic Forum, 2020).
This study centres on the efficacy of online
training courses designed to enhance workers'
adaptability and resilience in the face of rapidly
evolving technology. It seeks to evaluate the
effectiveness of online training methodologies in
equipping employees with the necessary skills and
knowledge to navigate swiftly changing
technological landscapes. By delving into pertinent
literature, this research aims to inform the
development of tailored e-training programmes that
foster employees' adaptability and resilience in the
digital age, addressing a critical need in contemporary
workforce development strategies.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Table 1: E-HRM Practices: Enhancing Efficiency and Performance.
Author Findings
Kumar & Kumar
(2021)
E-training at a hydroelectric plant in Himachal Pradesh improved employee behaviours and resilience,
p
roving adaptable and cost-effective for modern companies.
Al-Shorman et
al.
(
2021
)
Factors like PEU, CIS, PUS, and TEC significantly influence people's decisions to use e-training, as
evidenced b
y
a surve
y
of
p
rivate universit
y
em
p
lo
y
ees.
Milon et al.
(
2022
)
Bangladesh's private sector could benefit from adopting e-HRM practices like e-communication, e-
trainin
g
, and e-recruitment, identified throu
g
h a surve
y
amon
g
HR
p
rofessionals.
Oyoru (2023) E-recruitment positively impacts employee performance in Nigerian banks, enhancing service delivery
and HR management efficiency, according to a study on e-HRM practices.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A multi-stage random sampling approach was
employed to select a representative sample of
managers from both public and private sector
enterprises in India, spanning lower, medium, and top
management tiers. A total of 1000 questionnaires
were distributed, evenly split between online and
offline modes, resulting in 802 returned
questionnaires and an impressive response rate of
80.2%. The OCTAPACE profile tool was utilized to
construct a learning agility instrument, influenced by
the prevailing organizational culture. E-training
technology was leveraged to assess outcomes post-
measurement of individual and organizational
performance. The refinement of all measurement
tools was undertaken with the input of experienced
practitioners from diverse backgrounds across both
public and private sector domains.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1628
In summary, the study meticulously selected its
sample, leveraging a robust sampling methodology,
and utilized a blend of online and offline distribution
channels to achieve a commendable response rate. By
incorporating established instruments and refining
them in collaboration with seasoned practitioners, the
study aimed to comprehensively gauge learning
agility and its relationship with organizational culture
and performance outcomes.
4 RESULTS AND ANALYSIS
Data samples were collected from workers of both
genders, with 78.02% being male and 22.08% female,
spanning across different age groups and levels of
experience.
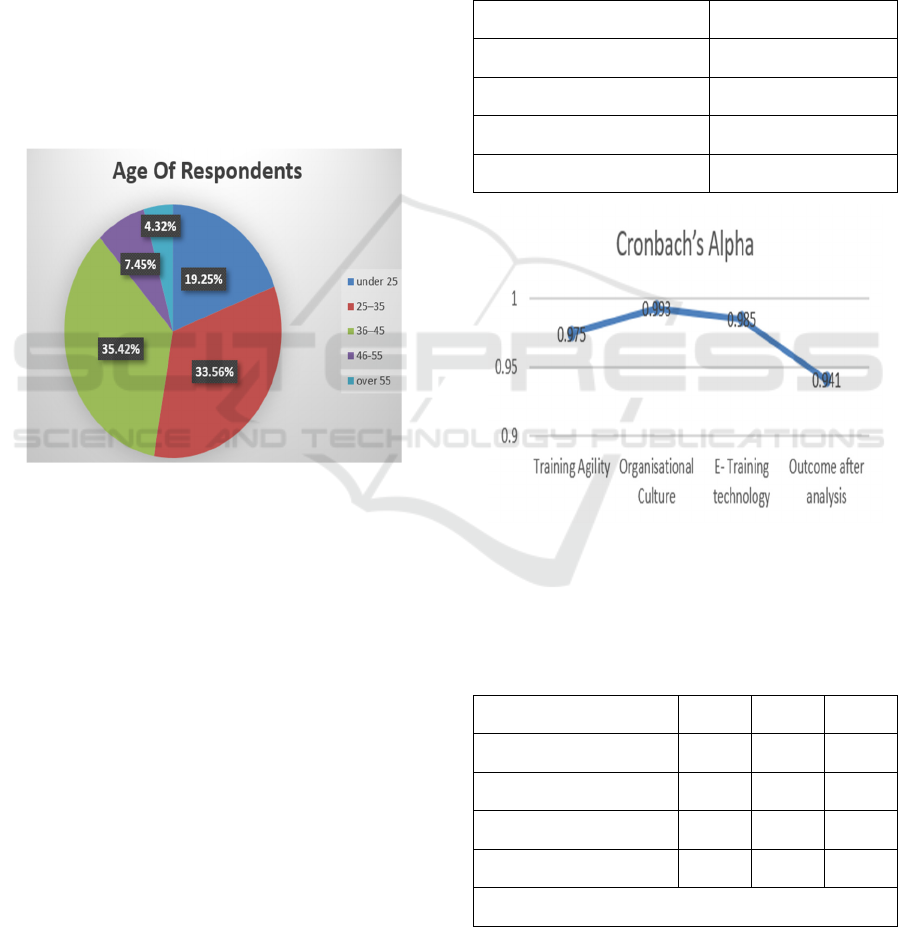
Figure 2: Age of Respondents.
The survey encompassed a diverse range of
respondents, reflecting varying levels of experience
within the workforce. Among the participants, those
with less than two years of experience constituted
17.30%, while those with two to five years made up
19.99%. The distribution continued with cohorts
spanning from six to thirty-plus years, indicating a
balanced representation across career stages. A total
of 96 items were evaluated, categorised into four key
domains: training agility, organisational culture, e-
training technology, and outcome. Each item was
assessed using a Likert-type scale, ranging from 1 to
5, capturing nuanced perceptions across the spectrum
of workplace dynamics.
Drawing upon the OCTAPACE framework by
Ghosh et al. (2021), the survey delved into
dimensions such as staff empathy, support for
innovation, and technological readiness. With 24
items clustered within eight dimensions, the tool
provided a comprehensive lens to gauge
organisational culture. Sample items, such as 'Policies
Facilitate Employee Learning Development' and
'Encouragement for Innovation', exemplify the
nuanced aspects explored. The scale's range, from
'very unhappy' to 'extremely satisfied', facilitated a
nuanced understanding of respondents' attitudes
towards workplace dynamics, offering insights
crucial for organisational development and
improvement initiatives.
Table 2: Cronbach’s Alphas.
Constructs Cronbach’s Alpha
Training Agility 0.975
Organisational Culture 0.993
E- Training technology 0.985
Outcome after analysis 0.941
Figure 3: Cronbach’s Alpha.
The table below illustrates the correlation among the
variables.
Table 3: Correlations among Variables.
Variables 1 2 3
Training Agility 1
Organisational Culture
0.634∗∗
1
E - Training Technology
0.567∗∗ 0.729∗∗ 0.578∗∗
Outcome
0.565∗∗ 0.656∗∗
1
∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.
Agile Workforce: Embracing Digital Evolution
1629

Figure 4: Correlation among variables.
In the dynamic landscape of business, adaptability is
paramount for managers to navigate swiftly changing
environments. A recent investigation delved into the
correlation between learning agility and outcomes,
highlighting its critical role in successful performance.
The study also explored the interplay between culture
and online learning as a mediator between learning
agility and results. The conclusions underscored the
significance of learning agility in accurately
predicting outcomes. Managers with a propensity for
agile learning can effectively steer their companies
towards success by optimizing resources, innovating
new processes, and delivering high-quality products
and services.
Furthermore, the study revealed that managers
with robust learning capacities are more adept at
meeting official performance standards and fulfilling
assigned duties and responsibilities. This aligns with
previous research findings and emphasizes the pivotal
role of learning agility in managerial effectiveness.
Moreover, the investigation identified culture as a
moderator in the relationship between learning agility
and performance, highlighting the importance of
fostering an OCTAPACE culture within
organisations.
In essence, the study recommends nurturing a
culture grounded in openness, trust, pro-action,
autonomy, authenticity, collaboration, confrontation,
and experimentation. Such a culture not only
enhances performance but also facilitates the
manifestation of learning agility in achieving
organisational goals. Additionally, the utilization of
e-training technology emerged as a key mediator
between learning agility and outcomes. The findings
suggest that e-training enhances learning agility and
effectiveness by providing access to diverse online
resources tailored to individual educational needs.
Moreover, individuals proficient in learning
exhibit superior performance when adequately
supported through e-training technologies. This
underscores the potential of e-training to enhance
employee expertise and provide up-to-date
knowledge for efficient job performance. The study's
implications may prompt businesses to integrate e-
training technologies, thereby fostering continuous
employee education and facilitating goal attainment.
Ultimately, the significance of e-learning in the
workplace is underscored, as it not only promotes
ongoing learning but also contributes to enhanced job
performance and organisational success.
5 CONCLUSION
The investigation's findings highlight the positive
impact of online learning technologies on the
performance of agile learners. Consequently,
businesses are shifting their focus towards crafting
strategies that leverage e-training technology.
Employers have a responsibility to ensure easy access
to e-learning platforms and the requisite tools for their
staff. Meeting basic training needs and tailoring
instruction to individual employees' requirements are
also imperative. Managers play a crucial role in
encouraging learners to acquire new skills to adeptly
engage with advancing technology. By facilitating
opportunities for staff to learn and experiment with
newly acquired ideas, managers effectively harness
the potential of e-training technology. Those who
stand to benefit the most from this approach are
workers who exhibit flexibility in their learning
methods.
In essence, the investigation underscores the
pivotal role of e-training technology in enhancing
performance outcomes. This prompts businesses to
adopt a proactive stance towards integrating such
tools into their developmental strategies. Ensuring
accessibility to e-learning resources becomes a
fundamental aspect of employers' obligations,
alongside meeting diverse training needs and
fostering a culture of continuous learning. Through
proactive guidance and support, managers can
empower employees to embrace evolving
technologies effectively. By embracing e-training
solutions, organisations pave the way for flexible
learners and workers to thrive in an increasingly
dynamic digital landscape.
REFERENCES
Trenerry, B., Chng, S., Wang, Y., Suhaila, Z. S., Lim, S. S.,
Lu, H. Y., & Oh, P. H. (2021). Preparing workplaces
for digital transformation: An integrative review and
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1630

framework of multi-level factors. Frontiers in
psychology, 822.
Mangalaraj, G., Nerur, S., & Dwivedi, R. (2023). Digital
transformation for agility and resilience: An
exploratory study. Journal of Computer Information
Systems, 63(1), 11-23.
Verhoef, P. C., Broekhuizen, T., Bart, Y., Bhattacharya, A.,
Dong, J. Q., Fabian, N., & Haenlein, M. (2021). Digital
transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and
research agenda. Journal of business research, 122,
889-901.
Kumar, A. D., & Kumar, S. (2021). Building Employee
Resilience through e-Training: A Case study of
National Hydroelectric Power Corporation's Unit.
Turkish Online Journal of Qualitative Inquiry, 12(5).
Al-Shorman, H., Alshawabkeh, R., Aldaihani, F.,
Aityassine, F., Mohammad, A., & Al-Hawary, S.
(2021). Drivers of E-training Intention to Use in the
private universities in Jordan. International Journal of
Data and Network Science, 5(4), 831-836.
Milon, M., Alam, M. A., & Pias, M. H. (2022). Exploring
the Key Practices of E-HRM in Place of Traditional
HRM: A Study on Private Industry of Bangladesh.
Journal of Human Resource and Sustainability Studies,
10(3), 403-417.
Ghosh, S., Muduli, A., & Pingle, S. (2021). Role of e-
learning technology and culture on learning agility: An
empirical evidence. Human Systems Management,
40(2), 235-248.
Oyoru, R. A. (2023). Effect of E-HRM Practices on
Organizational Performance: A Study of the Banking
Industry in Nigeria. Journal of Public Administration,
Policy and Governance Research, 1(1), 84-97.
Agile Workforce: Embracing Digital Evolution
1631
