
Green Ambition: Personal Journeys Toward Environmentally Aware
Success and Motivation
Khalilova Nargiza and Alimardonov Zoxid
Public Security University of The Republic of Uzbekistan, Karshi, Uzbekistan
Keywords: Personality, Eco-friendly, Activity, Environmental Education, Reflexivity.
Abstract: The article thoroughly examines the pivotal role played by motivation for success in environmental
conservation in fostering individual reflexivity. It explores the characteristics of the resultant effect and
discusses the psychological mechanisms underlying its emergence. Employing a psychological examination
tool, the study methodically determines how the development of motivation for success influences reflexive
processes. In doing so, it sheds light on the nuanced interplay between motivational factors and the age-related
progression of reflexivity in individuals. The research underscores the intricate connections between success
motivation and cognitive processes, emphasizing their impact on environmental protection efforts. By
highlighting these dynamics, the article contributes valuable insights into the psychological dimensions of
motivation, offering a nuanced understanding of its significance in the broader context of environmental
stewardship and personal development.
1 INTRODUCTION
The role of motivation is crucial in achieving success
in human activities. Indeed, reflexive processes play
a unique role in the success and accomplishment of
human activity. It is through these processes that the
expected benefits of the activity are realized, and the
speed of activity and action increases. It should be
noted that a high level of motivation in people leads
to an increase in negative qualities, stress, and
excitement, resulting in ineffective outcomes.
Research on the motivation for success in psychology,
as well as the level of aspiration, has been conducted
by various scholars, including M.Sh. Magomed-
Eminov, G.V. Kornilov, I.M. Taley, and others.
Motivation to succeed is the desire to achieve high
results in successful activities. According to the
specific definition of motivation by the German
psychologist H. Heckhausen, the motivation for
success "can lead to a person's high potential or
failure in various areas of activity". It also highlights
the specifics of achieving motivation. The idea of
achieving something involves two possibilities: to
succeed or to endure failure. In highly motivated
people, more emphasis is placed on success. It is
important to note that success is manifested when
opportunities for improvement are offered. Therefore,
tasks should be of medium complexity. In addition,
achieving motivation is always focused on a clear end
result, a goal. To achieve this, it is necessary to
constantly reconsider the goals. Highly motivated
individuals revisit their previous stalled work and
bring them to completion.
T.O. Gordiva emphasizes that the work done to
achieve motivation is important in motivating success.
The activity carried out to achieve motivation is an
activity in which the world of other people's
relationships changes with itself in the process of
achieving the goal. Such activity is stimulated by the
desire to achieve basic human needs, to do something
fast and well in development and progress, and to
strive for progress (Gordiva, 2006).
The achievement motivation in psychology has been
studied in-depth by M.Sh. Magomed-Eminov. It
defines the motivation for success as a functional
system of integral affective and cognitive processes
that govern the process of its realization.
Achievement motivation can specify specific
components that perform certain functions in the
process of regulating activities.
It is also understood that success, as a stable
description of a person, is first highlighted by G.
Murray, and the desire to do something quickly and
well and to achieve a certain level in any job. Scholars
such as D. McClelland and H. Heckhausen have
Nargiza, K. and Zoxid, A.
Green Ambition: Personal Journeys Toward Environmentally Aware Success and Motivation.
DOI: 10.5220/0012989400003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1645-1648
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
1645

identified two independent motivational directions in
the process of applying this motive: the desire to
succeed and the desire to avoid failure. In this case,
the motive for success is determined by a person's
desire to increase their level of ability (Gordiva, T. O.,
2006).
According to H. Heckhausen, the motive for success
is emphasized as an attempt to maintain and expand
the highest level of potential when the criteria of
human success are applied. The results of such
activities can lead to success or failure. The
motivation to succeed is focused on a specific end
result, i.e., to succeed or not to fail. To be successful,
goals need to be constantly reconsidered.
According to G. Murray, the need to succeed is
characterized by the following concepts: the
performance of difficult tasks, management,
regulation, organization of the relationship of
individuals and ideas of physical objects; complete
tasks as quickly and independently as possible;
overcoming obstacles and achieving high results;
development, competition, and superiority;
demonstration of talents and strengthening self-
esteem.
Accordingly, M. Sh. Magomed-Eminov defines the
integration of motivation for success as a functional
system of affective and cognitive processes. In the
process of motivational management of activity,
special components can be distinguished that perform
certain functions: relevance motivation (desire to act
and initiative), selection motivation (process of
selection of goals and corresponding activities),
implementation motivation (regulation of action and
control over the implementation of desire), post-
realization motivation (processes aimed at stopping
movement or changing one action to another).
One of the mechanisms for achieving success
motivation is the assessment of the emotional-
motivational significance of the situation, which
stems from the assessment of the situation and the
overall competence to achieve success. The intensity
of the motivational tradition varies depending on the
magnitude of the two parameters, such as the motive
for success and the avoidance of failure (Vilyunas, V.
K., 2006).
There are relatively different views on the
relationship between striving for success and
avoiding failure. In particular, D. Atkinson
emphasizes that the motives for success are
proportional poles; if a person is focused on success,
he is not afraid of failure, and vice versa. In other
studies, if the desire to succeed is clearly expressed,
it is believed that failure does not lead to strong fear
if it is associated with some serious consequences.
There is evidence that there can be a positive
relationship between striving for success and
avoiding failure. Therefore, the desire to strive for
success or to avoid failure is inseparable. They can
also be at both high and low levels of both aspirations
(Ilyin, 2000).
The motivation to avoid failure is to try to avoid
failure in any situation, especially when its results are
accepted and evaluated by other people (Davletshin,
1997).
It is known that research on the motivation of human
activity and the results of research in this area show
that the success of human activity, when faced with
three factors, increases the attractiveness and interest
in solving these tasks. People who fail do such work
with very little interest, sometimes losing interest.
Individuals who initially tried to succeed often
achieve good results after failing. But with failure at
first, individuals, on the contrary, achieve high results
after success. The activity of a person with a high
motivation to achieve a goal is more productive than
that of a person with a motivation to avoid failure.
In addition, there are certain differences between
the personal successes and failures of individuals who
succeed and those who do not. Individuals who strive
for success believe that their success depends on
personal factors, i.e., effort, perseverance, ability, and
that unsuccessful things usually happen in random
situations. People who avoid failure associate their
success with external factors, particularly luck, the
difficulty or ease of a given task. If the activity fails,
they analyze their options. In addition, subjects with
a very strong motivation to avoid failure often fail to
properly assess their potential, become frustrated by
failure, and lose confidence in themselves. Success-
oriented subjects usually act differently; they value
their opportunities and abilities appropriately and are
not confused by failure (Kuraev et. al., 2000).
2 ANALYSIS
In general, motivation for success is understood as a
force that can lead to success based on certain human
actions. This particular direction, intensity, and
determination are manifested in the activity.
Motivation to avoid failure is a mechanism designed
to avoid various mistakes and failures, and the person
who fails tries not to make mistakes again, sometimes
trying to change their failures completely or partially.
Action towards success is determined by the
predominance of motivation in a person to avoid
failure. Thus, the motivation to succeed is positive
and contributes to a person’s personal development.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1646
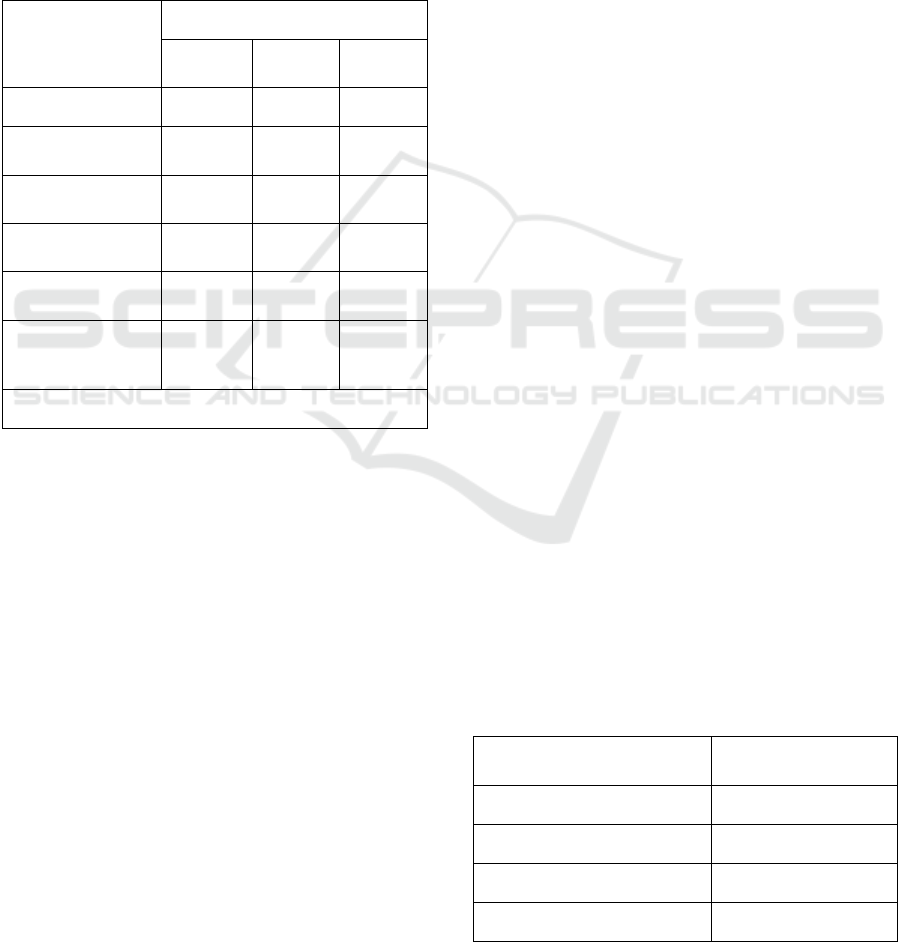
Based on the above, we considered it important to
examine the relationship between the development of
reflexivity in an individual and the motivation to
succeed. To this end, a group of subjects conducted a
survey "Motivation to succeed and avoid failure"
(A.A. Rean) "Determining the level of reflexivity"
(VV Ponamaryov) and "Determining priority
strategies for reflexivity" developed by A.A. Rean
(author's development) were conducted, and
empirical data were collected.
Table 1: Mapping Personality and Success Motivation:
Correlational Insights.
Directions of
reflexivity
Motivation to strive for success
Teenagers Level 1
students
Level 3
students
Self-direction 0,05 -0,07 0,12
Orientation to other
p
eo
p
le
8 -0,03 0,09
Orientation to past
activities
0,02 0,07 0,18*
Focus on current
activities
0,10 0,09 0,08
Focus on future
activities
-0,02 0,02 0,04
Collaborate and
communicate with
others
0,02 -8 0,17*
Note: ** r≤0,05
According to the results presented in the table, the
development of self-awareness in adolescents at this
age depends on their influence on the area of
motivation. When a person does not fully realize their
potential, the process of striving for success also
manifests itself in a state of misunderstanding.
Empirical studies have shown that even in a group
of Level 1 students, there is no significant association
between reflexive orientations and motivation to
strive for success. It is known that Phase 1 is
characterized by the beginning of a new type of
activity, as well as the fact that most of the tasks are
not sufficiently understood, the implementation of
which is superficial in the organization and
management of educational activities. At the same
time, it is not uncommon for students to be ahead of
their peers in unfamiliar environments during this
period, preferring to be first in the team.
Looking at the experimental results, there is a
significant correlation between reflexive orientations
and motivation to succeed in a group of 3rd-year
students. This is explained by the fact that they have
a real understanding of the requirements of the
activity, can imagine the result in real life, as well as
the essence and content of educational activities.
Especially during this period, it is noted that the
student has an increased desire to pass without
knowing it, an increased tendency to achieve results
through the knowledge that is understood for them.
Experiments have shown that reflection on past
activity has a significant correlation with motivation
to strive for success (r = 0.18; r≤0.05). The student's
quest for success is inextricably linked to his or her
past activities. Because a person who strives for
success first and foremost tries not to repeat the
mistakes and shortcomings he has made in the past.
This, in turn, helps to analyse the activities done in
the past and draw the necessary conclusions.
It is known that a person's desire to work, the
achievement of effective results in it is largely
determined by the organization of activities in
collaboration with others and the ability to establish
effective communication. In this sense, the success of
any activity process is largely determined by an
understanding of the purpose and content of the
collaborative activity.
Based on the results of the experiment, it is
observed that the reflection of cooperation and
communication with others has a significant
correlation with the motivation to strive for success (r
= 0.17; r≤0.05). Indeed, the process of human activity
does not take place in solitude, in which the need for
constant support from others is felt as a priority. It
should be noted that the success of any person in the
activity depends on the personal example and
behaviour of others. Indeed, human activity is always
characterized by a collective character. Because
human activity is always necessitated by needs.
Therefore, a significant correlation is noted between
these two events.
Based on the data obtained during our research,
we were able to determine the characteristics of the
relationship between the areas of reflexivity and
motivation to strive for success among the subjects.
Table 2: Motivation's Link to Success: A Reflexivity
Perspective.
Directions of reflexivity Motivation to strive for
success
Self-direction 0,02
Orientation to other people 0,04
Orientation to past activities 0,11**
Focus on current activities 0,12**
Green Ambition: Personal Journeys Toward Environmentally Aware Success and Motivation
1647

Focus on future activities 0,03
Collaborate and communicate
with others
0,03
Note: ** r≤0.01
According to the results presented in the table, a
positive correlation between reflection on past
activities and motivation to succeed is evident (r =
0.11; p≤0.01). The analysis of empirical data reveals
a strong desire to act towards the result by
understanding the goal.
In examining the empirical data, it is found that
reflection on current activity is significantly related to
the motivation to strive for success (r = 0.12; p≤0.01).
It should be noted that, due to the involvement of our
youth in education and labor, their main goal today is
to achieve high results through success.
While the motivation to strive for success in the early
stages of a person’s development may not be obvious,
it can be observed that the development of reflexive
processes is necessitated by behaviors that are not
understood.
3 CONCLUSION
Based on the above, the following conclusions are
appropriate:
Motivation for success in the development
of reflexivity in the person is a key
component.
The person must develop such reflexive
qualities as self-management, self-
awareness, and self-control in advance, so as
not to face failure and misfortune in their
activities.
Different age-related aspects of the
development of motivation to succeed in the
individual are apparent. In particular, it can
be seen that in the early stages of personality
development, although this is not clearly
expressed, the later stages develop with age.
REFERENCES
Vilyunas, V. K. (2006). Psychology of development
motivation. SPb: Speech.
Gordiva, T. O. (2006). Psychology of achievement
motivation (tex). G. O. Gordieva. M: Meaning
Publishing center "Academy".
Davletshin, M. G. (1997). Psychologydan qiskacha isohli
lugat. T.
Ilyin, E. P. (2000). Motivation and motives. St. Petersburg:
St. Petersburg.
Kuraev, G. A., & Pozharskaya, E. N. (2002). Human
psychology: a course of lectures. Rostav n/D.
Magomed-Eminov, M. Sh. (1987). Achievement
motivation: structure and mechanisms. Abstract of
Candidate of Psychology. M.
Hekhauzen, H. (2001). Psychology of achievement
motivation. St. Petersburg: Speech.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1648
