
Exploring Determinants of Organizational Engagement in Supply
Chain Management an Integrated Approach: A Comprehensive
Literature Review
Bhavana Mathur
1
, Deepak Gupta
1
and Sonal Malhotra
2
1
Mechanical Engineering, Anand International College of Engineering/ Rajasthan Technical University, India
2
Department of CSE, Graphic Era Hill University, Dehradun, Uttarakhand-248007, India
Keywords: Performance Management, Integrated SCM, Supply Chain Management, Quality, Quality Management.
Abstract: The focus of this research is to explore the determinants that facilitate or inhibit organizations from engaging
in supply chain management initiatives. And indeed, the literature includes an abundance of studies dealing
with that. For the purpose of this study, a literate review delineates the main internal and external categories
of factors influencing SCM practices. They are organizational behavior, a framework of control, customer-
acquisition dynamics, competitive intensity, and societal expectations. Withal, there has been little research
on the role of suppliers, which can act as facilitators in areas where SCM integration could improve firm
performance. Cost constraints and a perceived lack of legitimacy are intended to be internal obstacles, whereas
regulatory constraints, lack of supplier uptake, and context-dependent conditions are external scope
limitations . Due to such differentiation, this research takes an exploratory approach and uses previous
literature and researchers’ insights in addition to interviews because the issues in the supply chain are
disciplinary and integrated. Encouragingly, across the organizations, supply chain management is seemed to
be more influenced by external rather than internal drivers. It is again concluded from the research that health
systems need to work more efficiently and effectively to met these growth targets. Therefore, it is necessary
to look for innovative solutions and appropriate modern ways to ensure that the changing needs for health
care and health systems are met.
1 INTRODUCTION
Side flicker the ever-growing demands of customers,
on the other – the imperatives of the company’s
growth and profitability. This image makes it possible
to reveal the dual nature of the SCM. It constitutes a
business process: encompassing all tasks involved in
regulating the movement of products, services, and
information from suppliers’ suppliers to customers’
customers. The supply chain is depicted as a rope,
highlighting tangible outcomes: revenue growth,
asset optimization, and cost management.
Therefore, as the degree of coordination between
departments affects a company’s success directly or
indirectly also its SCM will be influenced. When
SCM is effective, an organization will flourish, and
the service delivery system will be superior.
However, when organizational changes are made to
SCM processes, the instability that follows makes
functioning across departments chaotic. Eventually,
this turns into an existential threat to the company
(Thomas 2015). SCM is the failure of pinpointing the
sectors needing transformation, and that makes the
development of a supply chain transformation plan
critical. The word “supply chain” was developed in
the early 1980s to characterize a company’s various
actions to obtain and handle supplies. SCM is a
system of organizations, operations, and business
operations that facilitate products and services in
various sectors by providing and maximizing profits
in an enterprise. Each business will operate in various
industries or within a comprehensive supply chain
system, and each has a distinct purpose (Datta 2011).
There are three basic steps in SCM which a company
needs to decide before implementing it.
1) Suppliers (who supplies the raw product/
material)
2) Manufacturer (who assemble or arrange or
manufacture the raw material and passed it to next
step)
1710
Mathur, B., Gupta, D. and Malhotra, S.
Exploring Determinants of Organizational Engagement in Supply Chain Management an Integrated Approach: A Comprehensive Literature Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0013405600003882
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 2nd Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies (PAMIR-2 2023), pages 1710-1716
ISBN: 978-989-758-723-8
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
3) Customers ( the end use of the product)
These steps may change as per of type of company
or sector in which supply chain needs to apply.
There are so many sectors today where SCM
functions logically.
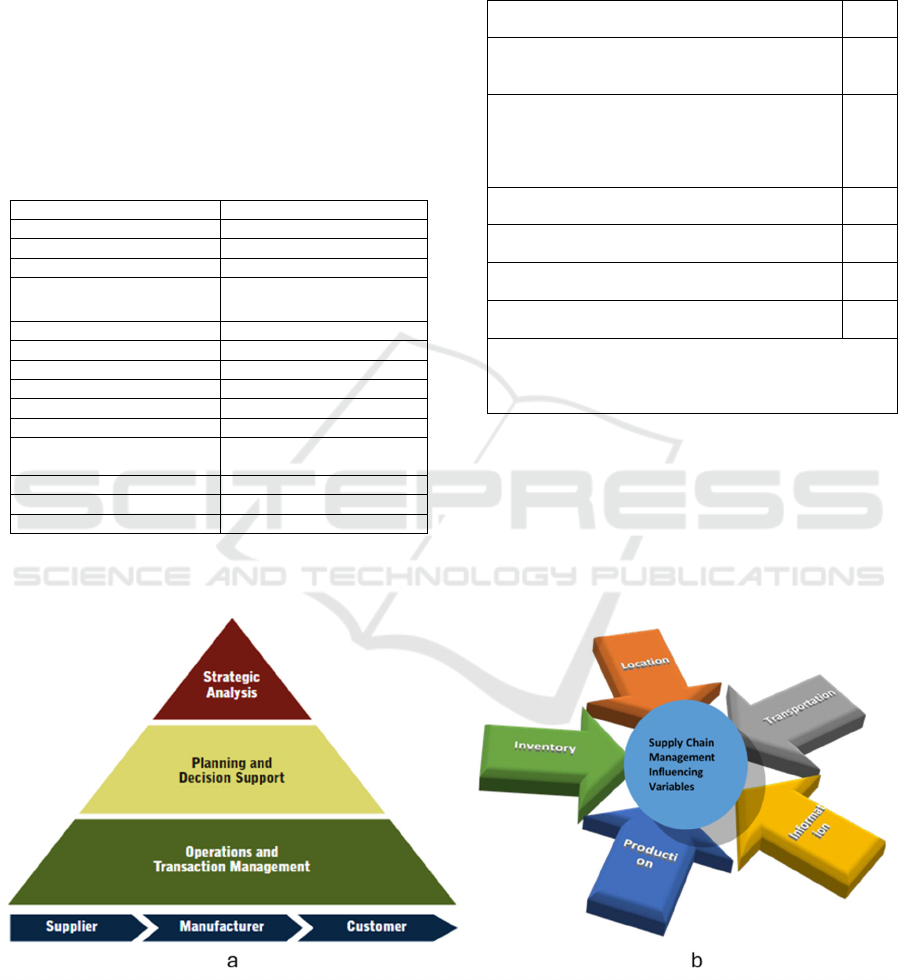
Supply Chain Influencing Factors: Even for the
industry SCM is the best tool for providing better
service to the customers and enhancing the profit for
itself, SCM is standing over some pillars. These
pillars always influences to the SCM. Profitable SCM
and poor SCM all are the reflection of these pillars.
Table 1: List of sectors where SCM is in functioning today.
Secto
r
SCM applies in terms of as
Communication information transfe
r
Manufacturing secto
r
Material handling
Field Marketing Transportation
Online marketing Transportation
Online services Transportation
Production Material handling
Logistics Transportation and services
Banking Services
Education Services
Health care secto
r
Services
Wall-Marts and
Malls/shopping complexes
Product handling and
services
Traffic syste
m
transportation
Railways Transportation and services
Metro Train Transportation and services
So the effecting “SCM is nothing but the managing
balance over these pillars in a best of best way”
(Figure1a & b, and Figure 2).
Table 2: Supply Chain implementation year to year.
The earliest form of supply chain was likely the
b
arter system.
1904
The origins of outsourcing can be traced back to
instances such as Charles S. Rolls acting as a selling
agent for cars manufactured by F. Henry Royce.
1960-
1975
The foundational understanding of Supply Chain
Management (SCM) emerged during its initial phase,
characterized by an inventory 'push' era that
emphasized the physical distribution of finished
goods.
1975-
1990
Businesses started transitioning from an inventory
push model to a customer pull approach.
1980
Wal-Mart pioneered the introduction of the concept
of cross-docking.
1985
The internet revolutionized business distribution
systems.
1996
The concept of e-commerce redefined the business
landscape.
1998
Since 1998, Supply Chain (SC) involvement has expanded
into numerous sectors including services, production, material
handling, healthcare, logistics & distribution, and various
other integrated fields.
Figure 1: a. SCM Steps, b. SCM influencing factor.
Exploring Determinants of Organizational Engagement in Supply Chain Management an Integrated Approach: A Comprehensive Literature
Review
1711
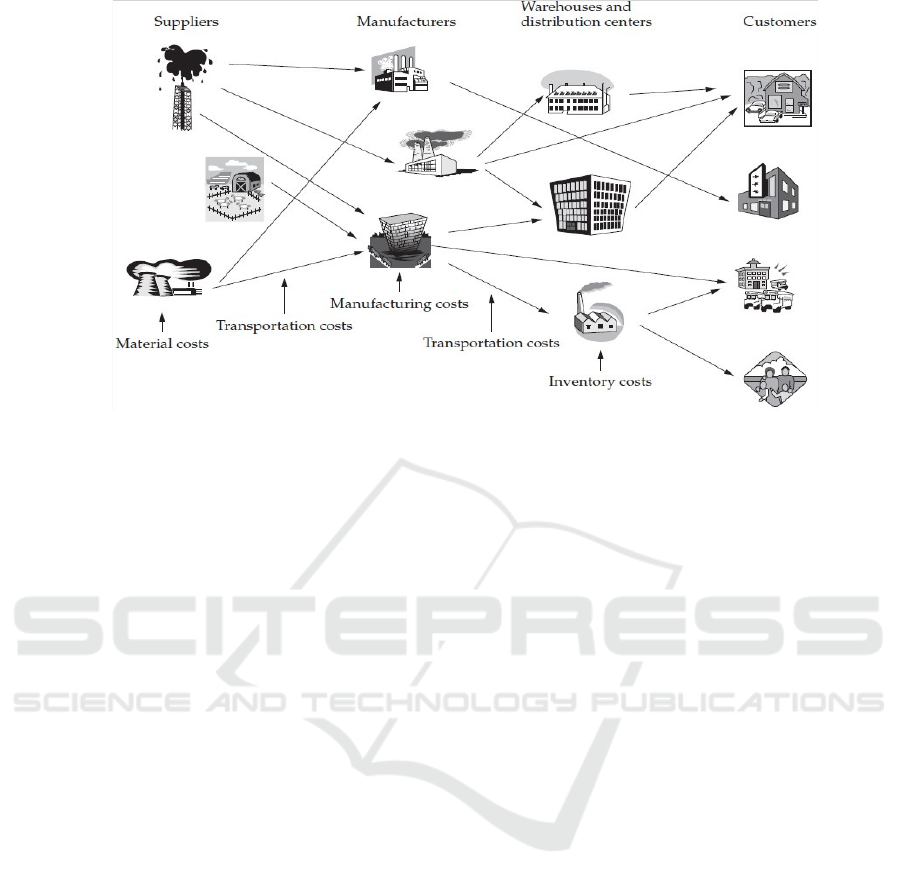
Figure 2: The hierarchical network of SCM.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
SCM has evolved directly or indirectly in qualitative
performance of industry over the last 20-25 years.
Studies over the past researchers have investigated
the relationships qualitative performance with supply
chain management. Therefore an integrating
approach of SCM upon the different sector apart of
the manufacturing fields has been useful and famous
over the researcher’s perspectives and that’s why
integrated SCM will be important for future
competitiveness (Shah 2023).
In the literature researchers found a number of
fields where SCM has been involved a part of the
common fields like manufacturing, information and
material handling etc. So many integrated approaches
are using by the researchers in various fields. Accept
these, there are many review papers which also has
been reviewed by the author during the research. The
scope of supply chain performance measurement
studies includes a variety of models, methods, and
frameworks. There are models such as Supply Chain
Partnership , Supply Chain Integration , Supply Chain
Interaction, Supplier Relations and Selection , Supply
Chain Information , and Quality Improvement (Joshi
2022).
Supply chain quality management is described as
all partner organizations in the supply channel
formally coordinating and integrating business
processes. The primary goal is to measure, analyze,
and continuously enhance product reliability,
serviceability, and customer satisfaction at the
intermediate stages and final consumption stages.
Quality-SCM is integral to academic research and
industrial practice, and a conceptual framework for
Quality-SCM will enhance quality initiatives in the
field of SCM. Standardization, through norm
adherence (for example, to ISO 9001:2000) to
establish management systems, has a significant role
in identifying critical supply chain processes and
Drivers (Robinson 2005). TQM and supply chain
management systems have a lot in common because
of a common goal of satisfying customers. Effective
quality management in the supply chain can be
defined through three central dimensions: supplier
selection, supplier, and supplier development, and
supplier integration. The Quality and Technology
framework highlights the relationship between
supply quality, supplier quality, and buyer quality.
Quality relationships between suppliers and buyers
can be captured in the terminology and are defined in
two stages. The first stage is supply chain quantity, a
collection of buyer-specific qualities, and the second
stage is supply chain technology, a reflection of
supply quality (Mahdiraji 2012).
A quality management QM model recommended by
Kaynak and Hartley emphasizes internal and external
integration to drive quality performance (Kaynak
2008). The quality performance stems from studies
that highlight initiatives to focus on improving and
controlling the supply chain. Integrated SCM systems
led to attempts to improve the quality of all processes
in the supply chain. These initiatives resulted in cost
reductions, better use of resources, and increased
process performance. Proposed conceptual models
for measuring quality of service in the supply chain
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1712
identified areas of future research on the selected
domains of service quality. They also played a vital
role in other organizational components. The
performance measurement systems help direct
actions and enable the implementation of strategies
that drive the quality of the organization. In
measuring and relying on performance measurement,
the data is commonly utilized in public reporting,
provider incentive programs, and quality
improvement initiatives. Efficiency of performance
depends on how prepared the organization’s culture
is across its life cycle. Performance measurement
systems are balanced and dynamic systems that aid
decision-making processes by collecting, processing,
and analysing data, focusing on efficiency and
effectiveness (Kaynak 2008).
The next approach to be considered as dynamicity.
Dynamicity is related to the adaptability and
capability of changes in the established system. It
means that the system can be changed and adjusted
with time and in response to changes in the internal
and external environment. The first two perspectives
ensure that the measurement system can change and
met the current needs and the challenging market
conditions. The supply chain in the healthcare sector
is an inherently complicated system due to its direct
influence on patient care. Poor SC performance is a
significant source of avoidable cost for healthcare
delivery facilities and could account for a
considerable portion of their operating expenditure.
Other problems associated with SC in the health
sector include communication failure, patient
accidents, long waiting times, and inadequate
integration. Therefore, integration between
businesses units and facilities is essential to providing
high-quality patient outcomes. The data quality is
another significant problem in the health sector. The
lack of data quality reduces the potential of SC data
to address the system’s problems, as to ensure that
better data quality, SC management must follow
quality-related procedures (Burgess 2023, Emir
2024).
3 GAPS IN LITERATURE
Reviewed current researches in SCM, Integrated
SCM, and performance management and identified
some themes which are actually variables of SC. The
variables under consideration encompass customer
focus, quality practices, supplier relations, leadership,
HR practices, business results, and aspects related to
safety, transportation, healthcare, and artificial
intelligence. Even after the literature review of many
research papers author made a survey also on SCM.
Several industries (Dell, Amazon, Saras Dairy, Amul
Dairy, Local manufacturers & suppliers) directly and
indirectly are involved in that survey. Survey initiated
with direct meeting to the departmental head and
workers and their customers of respective
organization as well as at some stage telephonic
survey has also been conducted. Likert scale of 1 to 5
marking is used for rating the SCM performance in
the respective organizations and the service received
by the customers of respective organization (Table 3).
Table 3: Some important organizations which are involved
in survey.
Name of
Organization
ICICI Bank
LOCAL
SUPPLIERS
INFOSYS Axis Bank LOCAL
MANUFACTURES
HCL Info
systems
DELL BOSCH
Wipro GENPACT Apollo Hospital
Life Insurance
Corporation of
India
AMUL DAIRY APEX HOSPITAL
HDFC Bank SARAS DAIRY FORTIS
HOSPITAL
EHCC
HOSPITAL
MAHATMA
GANDHI
MEDICAL
COLLEGE
SWAI MAN
SINGH
HOSPITAL
Organizations on table can be clustered in the five
groups as per of their service provided to the
customers for representing the responses of the
customers. Total score from all the responses is
counted separately for the services provided with
respective questions.
Total Score =[rating 1x no. of customers who rate it
as 1] + [rating 2x no. of customers who rate it as 2]
+[rating 3x no. of customers who rate it as 3] +[rating
4x no. of customers who rate it as 4] +[rating 5x no.
of customers who rate it as 5].
Exploring Determinants of Organizational Engagement in Supply Chain Management an Integrated Approach: A Comprehensive Literature
Review
1713
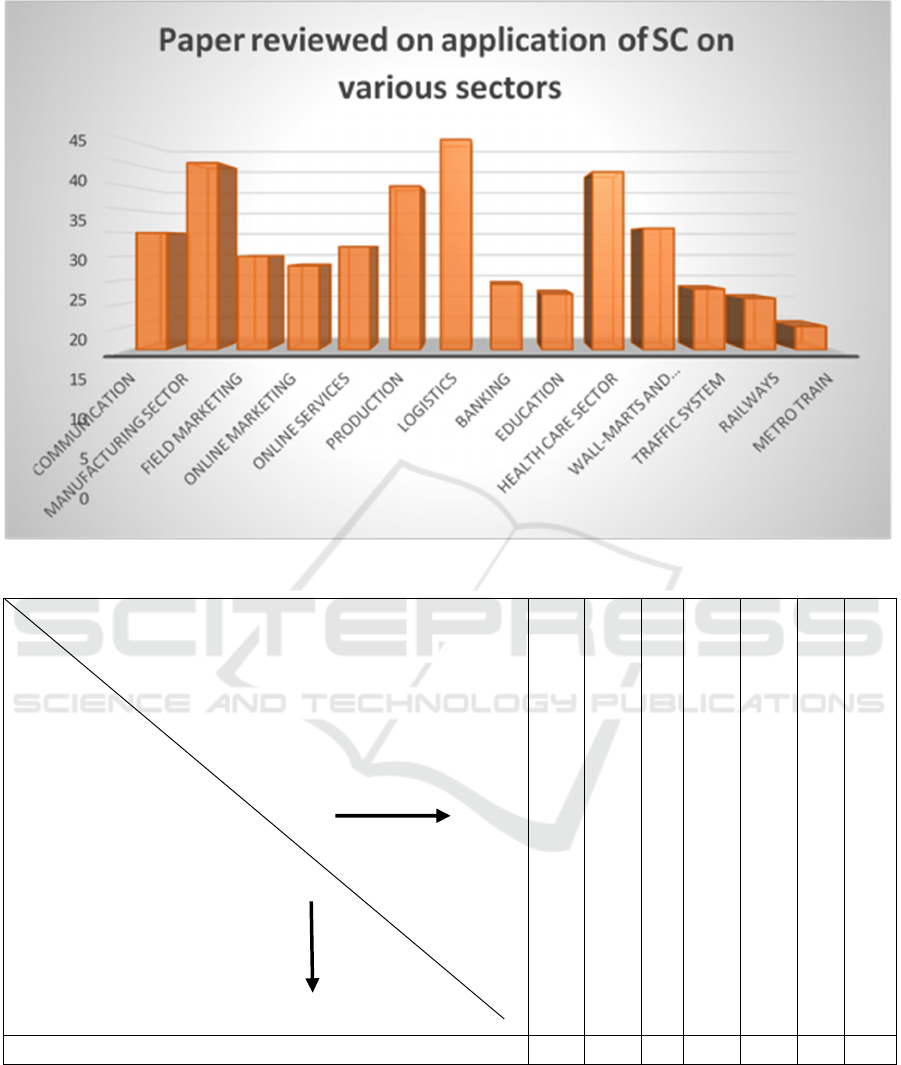
Figure 3. Sector view segregation of SC reviewed papers.
Question Asked for rating performance or
serviceability
Groups of services provided to the customers
Need to improve serviceability with proper and simple
arrangements
No need any improvement in serviceability
External Factors are responsible for poor serviceability
Internal Factors are responsible for poor serviceability
Working stress is responsible for poor serviceability
Money is responsible for poor serviceability.
Total Score
Online marketing 78 50 25 22 10 35 220
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1714
Figure 4: Paper reviewed on SCM according to facility (Pie Chart).
Figure 5. Serviceability Questionnaire.
Banking 100 10 10 25 60 8 213
Health care / hospitals 120 8 37 15 22 65
267
Information sharing 85 10 35 35 15 10 190
Material / product Transportations 95 8 48 20 35 47 253
Total Score
478
86 155 117 142 165 1143
Based on the available literature and survey
results, I would like to propose the future research
direction in supply chain quality management. Much
of the supply chain’s aspects, such as performance,
coordination, integration, communication,
leadership, and best practices , have been studied in
many industries. However, what has not been given
is the serviceability quality of a supply chain in the
context of the healthcare industry. One may notice
that, while studying product quality, most research
PAPER REVIEWED ON SCM ACCORDING
TO FACILITY
Logistics information
12% transfer
21%
Services
Material
handling 14%
Transportation
and services 17%
Transportation 12
%
Exploring Determinants of Organizational Engagement in Supply Chain Management an Integrated Approach: A Comprehensive Literature
Review
1715

has been conducted on improving performance and
time to patient in the healthcare supply chain. The
existing supply chains such as the one in hospitals and
pharmacies do not serve the customers well; that is,
the patients and, hence, need supply quality
improvement. This is because imported supply
change management practices, perhaps implemented
as an integrated approach, can help increase this
performance
4 CONCLUSIONS
Supply Chain Management is a set of integrated
processes that enables the transformation of raw
materials into valuable products and their distribution
to customers via a systematic channel. SCM
comprises a network of facilities and distribution
mechanisms, such as the process of procurement,
change of structure from materials, and circulation of
the complete product. The growth of the healthcare
industry in India is significant, driven by the high
population growth, significant government outlay on
health, and raising per capita income. The growth rate
of the industry creates the necessity to tackle such
challenges as an ability to keep up with increasingly
more demands of customers, an ability to adapt to the
market’s demands for pharmaceuticals and medical
devices, as stated by other researchers and
policymakers. There is little doubt that a more
efficient system’s performance is a necessity for
economies to hit growth targets. As such, modern
approach and innovative solutions are a must to meet
the increased demands of the system and tackle its
evolving challenges. The purpose of this study is to
present the SCM’s concept, its critical components,
and the relationships among them with an
organizational performance.
REFERENCES
A. Thomas, M. Krishnamoorthy, G. Singh, J.
Venkateswaran, Coordination in a multiple producers–
distributor supply chain and the value of information,
Int. J. Prod. Econ. 167 (2015) 63–73. https://doi.
org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2015.05.020.
P.P. Datta, M.G. Christopher, Information sharing and
coordination mechanisms for managing uncertainty in
supply chains: a simulation study, Int. J. Prod. Res. 49
(2011) 765–803. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207540
903460216.
N. Singh, V. Mittal, V. Rawat, P. Malik, A. Rana, Research
Trends in Supply Chain Management: A Machine
Learning Perspective, 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CISES58720.2023.10183623.
J.K. Shah, M. Sharma, S. Joshi, Digital Supply Chain
Management: A Comprehensive Review Using Cluster
Analysis, with Future Directions and Open Challenges,
Int. J. Supply Oper. Manag. 10 (2023) 337–364.
https://doi.org/10.22034/ijsom.2023.109914.2739.
S. Joshi, M. Sharma, Impact of sustainable Supply Chain
Management on the Performance of SMEs amidst
COVID-19 Pandemic: An Indian Perspective, Int. J.
Logist. Econ. Glob. 9 (2022) 248–276.
https://doi.org/10.1504/IJLEG.2022.10044917.
C. Robinson, M. Malhotra, Defining the concept of supply
chain quality management and its relevance to
academic and industrial practice, Int. J. Prod. Econ. 96
(2005) 315–337.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2004.06.055.
H. Mahdiraji, M. Arabzadeh, R. Ghaffari, Supply chain
quality management, Manag. Sci. Lett. 2 (2012) 2463–
2472. https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2012.07.020.
H. Kaynak, J. Hartley, A Replication and Extension of
Quality Management Into the Supply Chain, J. Oper.
Manag. - J OPER Manag. 26 (2008) 468–489.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jom.2007.06.002.
P.R. Burgess, F.T. Sunmola, S. Wertheim-Heck, A review
of supply chain quality management practices in
sustainable food networks, Heliyon. 9 (2023) e21179.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e
21179.
S. Emir, N. Sulistyowati, The effect of supply chain
management and total quality management on
operational performance through competitive
advantage, Int. J. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. (2147- 4478). 13
(2024) 27–37.
https://doi.org/10.20525/ijrbs.v13i1.3087.
PAMIR-2 2023 - The Second Pamir Transboundary Conference for Sustainable Societies- | PAMIR
1716
