
Improving Pseudo-Labelling and Enhancing Robustness for
Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization
Adnan Khan
a
, Mai A. Shaaban
b
and Muhammad Haris Khan
c
Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence, Abu Dhabi, U.A.E.
Keywords:
Visual Recognition, Domain Generalization, Semi-Supervised Learning, Transfer Learning.
Abstract:
Beyond attaining domain generalization (DG), visual recognition models should also be data-efficient dur-
ing learning by leveraging limited labels. We study the problem of Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization
(SSDG) which is crucial for real-world applications like automated healthcare. SSDG requires learning a
cross-domain generalizable model when the given training data is only partially labelled. Empirical investi-
gations reveal that the DG methods tend to underperform in SSDG settings, likely because they are unable
to exploit the unlabelled data. Semi-supervised learning (SSL) shows improved but still inferior results com-
pared to fully-supervised learning. A key challenge, faced by the best performing SSL-based SSDG methods,
is selecting accurate pseudo-labels under multiple domain shifts and reducing overfitting to source domains
under limited labels. In this work, we propose new SSDG approach, which utilizes a novel uncertainty-guided
pseudo-labelling with model averaging (UPLM). Our uncertainty-guided pseudo-labelling (UPL) uses model
uncertainty to improve pseudo-labelling selection, addressing poor model calibration under multi-source unla-
belled data. The UPL technique, enhanced by our novel model averaging (MA) strategy, mitigates overfitting
to source domains with limited labels. Extensive experiments on key representative DG datasets suggest that
our method demonstrates effectiveness against existing methods. Our code and chosen labelled data seeds are
available on GitHub: https://github.com/Adnan-Khan7/UPLM.
1 INTRODUCTION
Domain shift (Tzeng et al., 2015) (Hoffman et al.,
2017) is an important challenge for several computer
vision tasks e.g., object recognition (Krizhevsky et al.,
2017). Among others, domain generalization (DG)
has emerged as a relatively practical paradigm for
handling domain shifts and it has received increas-
ing attention in the recent past (Li et al., 2017) (Zhou
et al., 2021b) (Khan et al., 2021). The goal is to
train a model from the data available from multiple
source domains that can generalize well to an un-
seen target domain. We have seen several DG ap-
proaches (Huang et al., 2020) (Wang et al., 2020) that
have displayed promising performance across vari-
ous benchmarks (Li et al., 2017) (Venkateswara et al.,
2017). However, the performance of many DG meth-
ods is sensitive to the availability of sufficiently anno-
tated quality data from available source domains. As
such, this requirement is difficult to meet in several
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0583-9863
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1454-6090
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9746-276X
real-world applications of these models e.g., health-
care, autonomous driving and satellite imagery (Khan
et al., 2022b). Besides attaining generalization, it is
desirable for the learning algorithms to be efficient in
their use of data. This means that the model can be
trained using a minimal amount of labelled data to
reduce development costs. This concept is closely re-
lated to semi-supervised learning (SSL) (Grandvalet
and Bengio, 2004) (Tarvainen and Valpola, 2017)
which seeks to make use of large amounts of unla-
belled data along with a limited amount of labelled
data for model training. To this end, this paper studies
the relatively unexplored problem of semi-supervised
domain generalization (SSDG). It aims to tackle both
the challenges of model generalization as well as
data-efficiency within a unified framework. Both DG
and SSDG share the common goal of training models
capable of performing well on unseen target domain
using only source domain data for training. How-
ever, DG is based on the assumption that all data from
source domains is fully labelled, while SSDG oper-
ates under the SSL setting, where only few images
within each source domain have labels and large num-
Khan, A., Shaaban, M. and Khan, M.
Improving Pseudo-Labelling and Enhancing Robustness for Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization.
DOI: 10.5220/0012269400003660
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 19th International Joint Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP 2024) - Volume 2: VISAPP, pages
293-300
ISBN: 978-989-758-679-8; ISSN: 2184-4321
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
293

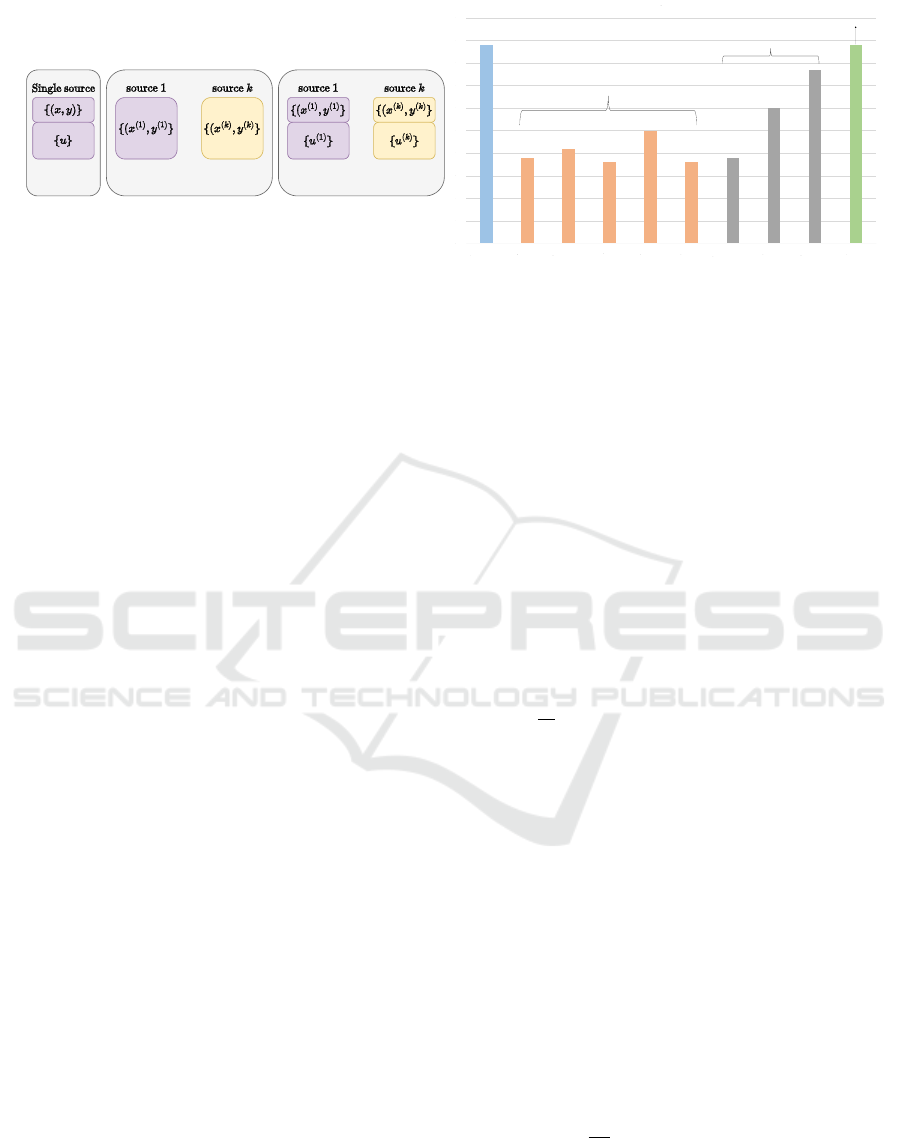
ber of images are unlabelled. Figure 1 shows the vi-
sual comparison among the settings of three related
paradigms.
We note that, the DG methods, which cannot uti-
lize unlabelled data, tend to show degraded perfor-
mance upon reducing the quantity of labelled data
(Zhou et al., 2021a). On the other hand, the SSL
methods e.g, FixMatch (Sohn et al., 2020) display
relatively better performance than the DG methods
under limited labels setting, still their performance is
noticeably inferior to the fully labelled setting. SSL
methods lose performance in SSDG setting due to dif-
ferences in data distributions between various source
domains and the limited amount of labelled data avail-
able, which are unique challenges to SSDG problem.
We propose a systematic approach, namely
Uncertainty-Guided Pseudo-Labelling with Model
Averaging (UPLM) to tackle the challenges in SSDG.
First, we develop an uncertainity-guided pseudo-
labelling (UPL) technique to overcome the problem
of noisy pseudo-labels (PLs), typically produced by
confidence-based methods (Sohn et al., 2020) under
domain shift. We leverage model’s predictive uncer-
tainty to develop a pseudo-label selection criterion
that provides accurate PLs by mitigating the impact of
miscalibrated predictions, especially for out-domain
data. Second, we propose a novel model averaging
(MA) technique which overcomes the effect of over-
fitting to limited labels in source domains to achieve
cross-domain generalization at the inference stage.
Through empirical results we show the intuition and
motivation behind our two components. Our sug-
gested approach demonstrates its effectiveness in ad-
dressing the SSDG problem when compared to other
SSDG and SSL methods, as evidenced by thorough
experimentation on four demanding DG datasets.
2 RELATED WORK
Domain Generalization. (Vapnik, 1999) is rec-
ognized as pioneering work in Domain Generaliza-
tion (DG), introducing Empirical Risk Minimiza-
tion (ERM) to minimize the sum of squared errors
across diverse source domains. It led to various
approaches for extracting domain-invariant features,
such as (Muandet et al., 2013) employing maximum
mean discrepancy (MMD), (Ghifary et al., 2015)
introducing a multi-task autoencoder, and (YANG
and Gao, 2013) using canonical correlation analysis
(CCA). Meta-learning frameworks, like those in (Shu
et al., 2021), have also been employed for domain
generalization to simulate training domain shifts. For
semantic alignment, domain generalization such as
(Kim et al., 2021) and (Dou et al., 2019), leverage
self-supervised contrastive formulations (Khan et al.,
2022a). The idea of improving diversity in source do-
mains is shown to be effective for DG (Khan et al.,
2021). (Volpi et al., 2018) applied a wasserstein con-
straint in semantic space and (Shankar et al., 2018)
introduced Crossgrad training as a DG method to
enhance DG. The aforementioned DG methods as-
sume supervised settings with fully labeled source
domain data for training. However, there is limited
research on enhancing DG performance in scenarios
with scarce labeled data. This work addresses the
SSDG problem, unifying data efficiency and model
generalization, and proposes a principled approach to
tackle relevant SSDG challenges.
Uncertainty Estimation in DNNs. Quantifying un-
certainty in deep nerual networks (DNNs) has re-
mained an important research direction (Kendall and
Cipolla, 2016). These methods proposed to quan-
tify the uncertainty associated with the predictions
made by DNNs. For instance, (Gal and Ghahra-
mani, 2016) presented dropout training in DNNs as
approximate Bayesian inference to model uncertainty.
(Kendall and Gal, 2017) developed a Bayesian DNNs
framework that combines input-dependent aleatoric
uncertainty with epistemic uncertainty. The work of
(Lakshminarayanan et al., 2017) proposed alternative
to Bayesian DNNs, which includes ensembles and
adversarial training, for estimating predictive uncer-
tainty on out-of-distribution examples. (Smith and
Gal, 2018) investigated measures of uncertainty fo-
cusing on mutual information and proposed an im-
provement in uncertainty estimation using probabilis-
tic model ensembles. In this work, we leverage model
uncertainty from Monte-Carlo (MC) dropout tech-
nique (Gal and Ghahramani, 2016) which is used to
develop a pseudo-label selection criterion under mul-
tiple domain shifts in the SSDG problem.
Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization. The
problem setting in DG assumes fully-supervised set-
tings i.e., the source domains data is completely
labelled. In many real-world deployment scenar-
ios, however, this is a strict requirement, as it is
costly and some times infeasible to acquire suffi-
ciently labelled data. To address this limitation, a
more practical and widely applicable setting is semi-
supervised domain generalization (SSDG), which
combines model generalization and data efficiency
into a single paradigm. For instance, (Lin et al.,
2021) introduced a cyclic learning framework to en-
hance model generalization by promoting a positive
feedback between the pseudo-labelling and general-
ization phases. The authors in (Zhou et al., 2021a)
proposed StyleMatch as an effective approach that ex-
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
294
35
40
45
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
Full Labels
Vanilla
CrossGrad
RSC
EISNet
DDAIG
MeanTeacher
EntMin
FixMatch
UPLM
PACS (5 labels per class)
DG Methods
Ours
SSL Methods
SSL DG
...
SSDG
...
Figure 1: (Left) Visual comparison of SSL, DG, and SSDG setting. (right) Performance comparison of three paradigms.
tends FixMatch with stochastic modeling and multi-
view consistency learning to achieve significant im-
provements in SSDG problem. (Yao et al., 2022) pro-
posed confidence-aware cross pseudo supervision al-
gorithm that utilizes Fourier transformation and im-
age augmentation to enhance the quality of PLs for
SSDG medical image segmentation. (Qi et al., 2022)
proposed MultiMatch, a SSDG method that extends
FixMatch to the multi-task learning framework, uti-
lizing the theory of multi-domain learning to produce
high-quality PLs.
3 PROPOSED FRAMEWORK
The problem of semi-supervised domain generaliza-
tion (SSDG) has two distinct challenges: (1) how to
obtain accurate pseudo-labels under multiple domain
shifts, and (2) reduce overfitting to source domains
under limited labels. To this end, we present a prin-
cipled approach to SSDG namely uncertainty-guided
pseudo-labelling (Section 3.1) with model averaging
(Section 3.2) to counter the two challenges in SSDG.
Problem Settings. We first define few notations and
then present the formal definition of SSDG. Formally,
X and Y denote the input and label spaces, respec-
tively. A domain is a combination of the (joint) prob-
ability distributions for X and Y , denoted by P(X,Y ),
over the corresponding spaces X and Y . We use
P(X) and P(Y ) to show the marginal distributions
of X and Y , respectively. Our focus in this study is
on distribution shifts only in P(X ), while P(Y ) re-
mains constant. This means that all domains share
the same label space. Similar to DG, in SSDG, we
are provided with K distinct but related source do-
mains D = {D}
K
k=1
, where D
k
denotes the distribu-
tion over the input space X for domain k, and K is the
total number of source domains. From each source
domain D
k
, we are provided with a labelled set com-
prising of input-label pairs D
L
k
= {(x
k
,y
k
)} and an un-
labelled set D
U
k
= {u
k
}. Note that, |D
U
k
| ≫ |D
L
k
|. We
also assume the existence of a set of target domains
T typically set to 1. The objective in SSDG is to
leverage the labelled set D
L
k
from the source domains,
along with the unlabelled data D
U
k
, to learn a mapping
F
θ
: D
L
k
∪ D
U
k
→ Y that can provide accurate predic-
tions on data from an unseen target domain T .
Semi-Supervised DG Pipeline. We instantiate our
proposed method in FixMatch, which is an SSL
method and performs better than all DG methods
in SSDG settings (Figure 1). It combines consis-
tency regularization (Sajjadi et al., 2016) and pseudo-
labelling (PL) (Xie et al., 2020) techniques to achieve
state-of-the-art results on several SSL benchmarks.
The algorithm consists of two standard cross en-
tropy losses, the supervised loss L
s
, and an unla-
belled loss L
u
. The supervised loss is calculated as:
L
s
= −
1
|S|
∑
j∈S
y
j
log( ˆy
j
), where S = D
S
k=1:K
is the
aggregation of labelled set from all K source domains.
y
j
and ˆy
j
is the ground truth and the predicted proba-
bility for j
th
labelled example, respectively.
Two augmented versions of the an unlabelled ex-
ample u are generated i.e., weak and strong aug-
mentations (DeVries and Taylor, 2017) denoted by
u
′
and u
′′
, respectively. Let q
u
′
and q
u
′′
be the pre-
dicted probability distributions for u
′
and u
′′
, respec-
tively. For a weakly augmented unlabelled exam-
ple u
′
, the pseudo-label ˜y
u
′
is generated if g
u
′
is 1,
where g
u
′
is a binary variable and obtained as follows:
g
u
′
= 1 [max(q
u
′
) ≥ τ], τ is a scalar hyperparameter
denoting the confidence threshold. The cross entropy
(CE) loss is used at the model output for a strongly
augmented version u
′′
, which introduces the form of
consistency regularization to reduce the discrepancy
between u
′
and u
′′
. The unsupervised loss L
u
be-
comes: L
u
=
1
|U|
∑
u∈U
1 [max (q
u
′
) ≥ τ]CE( ˜y
u
′
,q
u
′′
),
where U = D
U
k=1:K
is the aggregated unlabelled set
from all K source domains. The overall loss then
becomes: L
f inal
= L
s
+ λL
u
, where λ is the weight
given to the unsupervised loss. The presence of un-
Improving Pseudo-Labelling and Enhancing Robustness for Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization
295

labelled data in different source domains, manifest-
ing different shifts, pose a challenge to confidence-
based selection of PLs leading to generation of noisy
PLs. Due to various domain shifts, the model is more
prone to generating a high confidence for an incor-
rect prediction, which will then translate into a noisy
pseudo-label. To this end, we leverage model’s pre-
dictive uncertainty to develop pseudo-label selection
criterion which allows countering the poor calibration
of model, leading to the selection of accurate PLs.
3.1 Uncertainty-Guided
Pseudo-Labelling (UPL)
We describe our uncertainty-guided pseudo-labelling
(UPL) mechanism to address the challenge of noisy
PLs when the unlabelled data could be from different
(source) domains. We first quantify the model’s pre-
dictive uncertainty and then leverage it to construct a
uncertainty-guided pseudo-label selection criterion.
Uncertainty Quantification. We choose to use
the Monte-Carlo (MC) dropout method to quantify
model’s predictive output uncertainty V
u
′
for an un-
labelled example u
′
. It requires the addition of a sin-
gle dropout layer (D) that is incorporated between
the feature extractor network and the classifier. The
MC dropout technique requires N Monte-Carlo for-
ward passes for an unlabelled example u
′
through the
model. This produces a distribution of probability
outputs denoted as c
u
′
∈ R
N ×C
where C is the number
of classes. Now, we obtain the uncertainty V
u
′
∈ R
C
by computing the variance along the first dimension
of c
u
′
. Finally, the V
u
′
is transformed using tanh
function, to obtain a measure of model certainty κ
u
′
:
κ
u
′
= (1 − tanh(V
u
′
)).
Uncertainty Constraint in PL Selection. In SSDG,
due to domain shifts, for an unlabelled input, a model
can yield high confidence for an incorrect predic-
tion. This happens because the model is typically
poorly calibrated for out-domain predictions. So a
confidence-based PL selection criterion is prone to
generating noisy PLs. To implicitly mitigate the im-
pact of poor calibration of the model under various
domain shifts, motivated by (Rizve et al., ), we de-
velop a pseudo-label selection criterion that uses both
the predictive confidence and predictive uncertainty
of a model. Specifically, for an unlabelled weakly
augmented example u
′
, given the confidence of the
predicted class label as: max(q
u
′
) and the correspond-
ing certainty as κ
u
′
(argmax(q
u
′
)). The max (q
u
′
)
should be greater than the confidence threshold τ
and at the same time the κ
u
′
(argmax(q
u
′
)) should be
greater than the certainty threshold η as:
g
u
′
= 1 [max (q
u
′
) ≥ τ]1 [κ
u
′
(argmax(q
u
′
)) ≥ η] (1)
In Figure 2, we plot the relationship between the
model output uncertainty and its Expected Calibra-
tion Error (ECE) (see also Appendix A). It shows that
in all cases when the uncertainty of selected PLs in-
creases, the ECE increases and vice versa. Therefore,
choosing PLs that are both certain and confident will
likely lead to better PL accuracy via counteracting the
negative effects of poor calibration.
3.2 Model Averaging (MA)
In the training stage, the model may overfit to the
limited labelled (or pseudo-labelled) data and even-
tually perform poorly on unseen target domain data.
This problem exacerbates when we introduce hard
constraints on PLs selection. Consequently the ro-
bustness of a model against domains shifts gets af-
fected and could lead to convergence at poor opti-
mum. To address this, we propose a simple yet ef-
fective model averaging (MA) technique at the infer-
ence stage. Specifically, we take the weighted average
of the model parameters obtained from the best per-
forming model on on held-out validation set (θ
best
),
the model checkpoint from last epoch (θ
last
), and
the exponential moving average model (θ
ema
). The
predictions of the three models are averaged using
the combined state dictionary, which is created by
taking the average of the corresponding weights of
the three models denoted by θ
avg
given as: θ
avg
=
α · θ
best
+ β · θ
last
+ γ · θ
ema
where α, β, and γ are the
weights assigned to each model. We set α, β, and γ
to 1/3 each, indicating that we give equal importance
to each model. θ
avg
is then used to make predictions
on the test data. By using θ
avg
model, we reduce the
reliance on a single model and its parameters, which
leads to better generalization at inference stage.
4 EXPERIMENTS
Datasets. We evaluate on four distinct DG datasets:
PACS (Li et al., 2017) (9,991 images, 7 classes,
four domains), OfficeHome (Venkateswara et al.,
2017) (15,588 images, 65 classes, four domains), Ter-
raIncognita (Beery et al., 2018) (24,778 images, 10
classes, four domains), and VLCS (Fang et al., 2013)
(10,729 images, 5 classes, four domains).
Training and Implementation Details. We follow
the evaluation protocol of (Gulrajani and Lopez-Paz,
2020). For model selection we use the training do-
main validation protocol. We partition the data from
each training domain in 90% training and 10% valida-
tion subsets and use only 10 labels per class from each
source domain. The model that maximizes the ac-
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
296
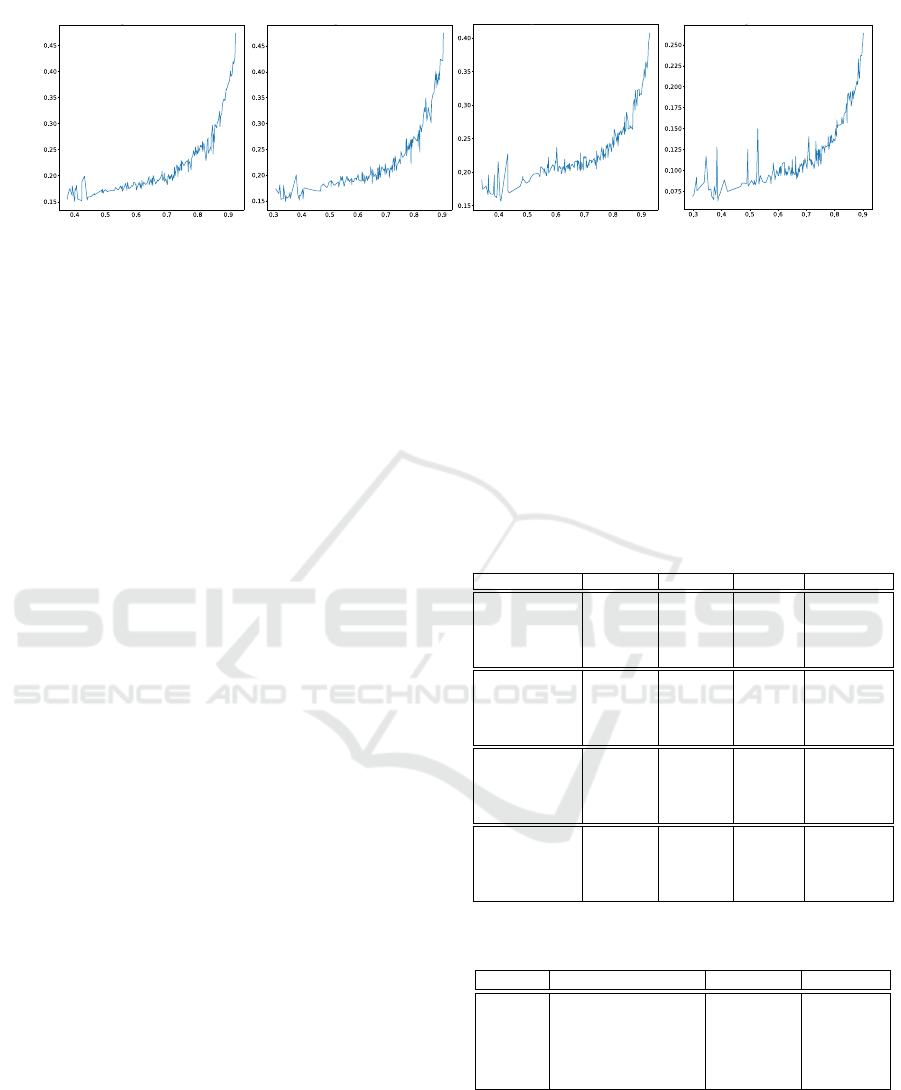
Photo Art
Cartoon Sketch
Uncertainty
Uncertainty Uncertainty
Uncertainty
ECE
Figure 2: Uncertainty of selected PLs vs Expected Calibration Error (ECE).
curacy on validation set is considered the best model
which is then evaluated on the target domain to report
classification (top-1) accuracy. All experiments use
an NVIDIA Quadro RTX 6000 GPU with 24GB ded-
icated memory. We use ResNet-50 (He et al., 2016a)
model as a backbone with a batch size B of 24 for la-
belled data and µ×B for unlabelled data where µ = 5.
We use the SGD (Robbins and Monro, 1951) opti-
mizer and train model for 20 epochs (512 iterations
each). The learning rate is set to 0.03 with nesterov
momentum (Nesterov, 1983). We do grid search in
the range {0.2,0.9} using the validation set for the hy-
perparameter η in UPL method. The optimal η values
are 0.2, 0.5, 0.5 and 0.7 for PACS, TerraIncognita, Of-
ficeHome and VLCS respectively. We report accuracy
for target domains and their average, where a model
is trained on source domains and evaluated on an (un-
seen) target domain. Each accuracy on the target do-
main is an average over three different trials with dif-
ferent labelled examples. Appendix B shows the abla-
tion on different hyperparameters including the num-
ber of MC forward passes N , certainty threshold κ
and the parameter µ which governs the proportion of
unlabelled data within each training batch.
4.1 Results
We investigate the impact of each proposed compo-
nent for all four datasets. Table 1 presents a com-
parison of test accuracies achieved by four different
methods: FixMatch (baseline), uncertainty-guided PL
approach (UPL), model averaging (MA), and our fi-
nal model (UPLM) across different target domains
of four benchmark datasets. The average test ac-
curacy across all target domains is also shown for
each dataset. The results demonstrate that the UPLM
method achieves the highest test accuracy in three
out of four datasets, with an average test accuracy of
78.94% for PACS, 50.61% for OfficeHome, 62.72%
for VLCS, and 30.19% for TerraIncognita. On Of-
ficeHome the constraint of uncertainty limits the num-
ber of PLs, and hence relatively less improvement is
seen in UPLM as compared to MA. For instance, the
class to training examples ratio for VLCS and Office-
Home is 1:2146 and 1:238 respectively. Enforcing
an uncertainty constraint on this small set of exam-
ples reduces their number even further, making the
ResNet-50 model more prone to overfitting. Over-
all, the UPLM method outperforms in the most tar-
get domains across all datasets, indicating that the
uncertainty-guided PL approach with model averag-
ing leads to improved performance in SSDG.
Table 1: Comparison of FixMatch, UPL, MA, and UPLM.
Target FixMatch UPL MA UPLM (Ours)
PACS
Photo 82.67
±4.73
89.76
±3.12
90.40
±1.24
88.09
±1.92
Art 70.79
±0.88
72.75
±5.50
76.53
±1.08
76.84
±1.02
Cartoon 70.39
±3.21
66.87
±3.46
75.78
±1.54
74.05
±5.25
Sketch 70.19
±5.00
74.63
±3.98
71.43
±3.60
76.79
±3.38
Average 73.51
±2.19
76.35
±3.41
78.54
±1.44
78.94
±1.49
OfficeHome
Art 38.64
±3.14
39.37
±5.09
43.52
±0.82
42.47
±0.66
Clipart 39.28
±4.05
41.69
±3.32
41.76
±0.90
40.58
±1.94
Product 58.73
±1.48
58.10
±2.36
59.41
±0.62
58.00
±1.15
Real World 56.88
±2.22
60.87
±0.65
63.91
±0.98
61.37
±1.47
Average 48.38
±0.51
50.00
±0.50
52.15
±0.59
50.61
±1.23
VLCS
Caltech101 43.37
±32.44
74.08
±12.60
36.42
±1.10
85.68
±3.65
LabelMe 52.78
±1.91
59.23
±6.71
51.49
±0.72
61.09
±4.98
SUN09 49.88
±1.61
42.96
±6.19
62.60
±3.90
50.41
±5.93
VOC2007 27.26
±1.98
41.02
±12.00
41.87
±4.70
53.68
±7.61
Average 43.32
±9.13
54.33
±5.14
48.10
±1.81
62.72
±3.66
Terra
Location 38 15.00
±13.52
22.14
±7.50
28.59
±7.10
32.32
±18.06
Location 43 14.07
±2.46
14.07
±1.55
17.88
±7.10
25.82
±5.94
Location 46 19.04
±3.18
21.15
±4.51
21.77
±3.18
24.22
±3.59
Location 100 22.14
±16.59
25.23
±1.99
40.97
±4.81
38.38
±9.65
Average 17.56
±2.24
20.07
±2.92
27.30
±3.38
30.19
±4.78
Table 2: Comparison of FixMatch, StyleMatch and UPLM
on labelled seed examples from (Zhou et al., 2021a).
Target Baseline (FixMatch) StyleMatch UPLM
Photo 89.18
±0.30
78.20
±11.30
91.82
±1.15
Art 73.85
±3.77
78.10
±1.31
79.05
±1.74
Cartoon 74.73
±3.72
82.02
±1.11
78.37
±2.08
Sketch 74.74
±5.65
78.60
±1.87
79.06
±0.52
Avg. 78.12
±1.35
76.60
±2.77
82.02
±1.11
Furthermore, we conducted a thorough compar-
ative analysis, using the labelled seed examples of
StyleMatch (Zhou et al., 2021a) (Table 2). Consider-
ing factors like unavailable source code ((Yuan et al.,
2022)) and relatively large batch sizes(StyleMatch)
the comparison of SSDG methods becomes difficult.
Improving Pseudo-Labelling and Enhancing Robustness for Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization
297
We optimized our model by adjusting the batch size
to 24 and using the ResNet-50 backbone instead of
ResNet-18 (He et al., 2016b). These modifications
were essential for enhancing both performance and
computational efficiency. Notably, in comparison
with StyleMatch, our method demonstrated superior
performance, particularly in the photo domain, using
our randomly chosen seeds (available on our GitHub
project page) providing a practical and accessible al-
ternative to the examples employed by StyleMatch.
4.2 Ablation Study and Analysis
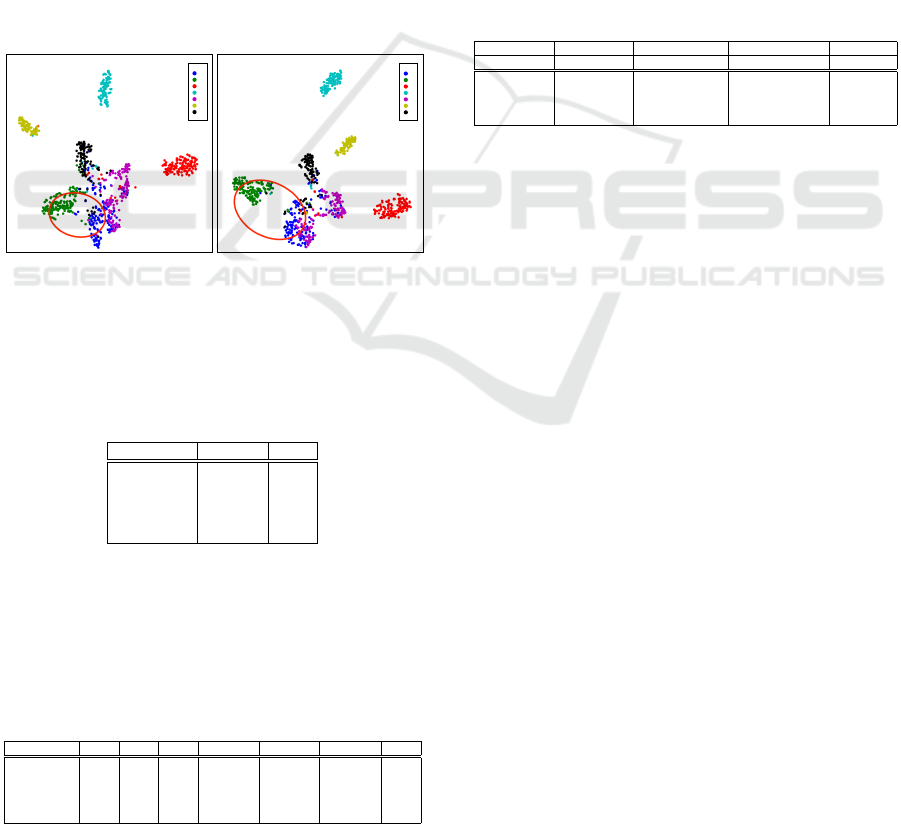
t-SNE Plots For Class-Wise Features. Figure 3
plots class-wise feature representations obtained us-
ing t-SNE for both the FixMatch and UPLM. Our ap-
proach facilitates the learning of more discriminative
features, resulting in more tightly clustered features
within the same class while maintaining greater dis-
tance between features belonging to different classes.
t-SNE Visualization (FixMatch) t-SNE Visualization (UPLM-Ours)
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
1
0
2
3
4
5
6
Figure 3: Class-wise feature visualization using t-SNE.
Pseudo-Labelling Accuracy UPL vs FixMatch. We
compare the accuracy of PLs on the target domains of
the PACS dataset (Table 3). Results indicate that UPL
generates more accurate PLs compared to FixMatch.
Table 3: Comparison of Pseudo-Labelling accuracy (%).
Target FixMatch UPL
PLs Acc.
Photo 87.09 88.05
Art 78.80 95.93
Cartoon 83.93 89.52
Sketch 91.55 95.30
Average 85.34 92.20
Performance of Individual Components of MA.
Table 4 compares the results of six different variants
of the model, with each variant utilizing a different
strategy for combining the model’s parameters during
training. Combining all three models (θ
avg
), as per
our proposal, provides the best performance. Perfor-
Table 4: Our proposed θ
avg
outperforms other variants.
Target θ
last
θ
best
θ
ema
θ
(last+ema)
θ
(last+best)
θ
(best+ema)
θ
avg
MA (PACS)
Photo 87.64 87.72 82.67 89.90 89.30 89.08 90.40
Art 72.98 73.93 70.79 78.24 73.11 72.38 76.53
Cartoon 73.93 69.16 70.39 75.43 75.90 73.08 75.78
Sketch 68.72 72.23 70.19 65.48 75.31 68.90 71.43
Average 75.82 75.76 73.51 77.26 78.41 75.86 78.54
mance Under Various Domain Shifts. We report the
performance in various domain shifts in Table 5, e.g.,
changes in backgrounds, corruptions, textures, and
styles. For instance, background shifts only affect the
background of an image and not the foreground ob-
ject’s pixel, texture, and structure (Zhang et al., 2022).
On the other hand, style shifts involve variations in
texture, and object parts across different concepts.
To evaluate this, we categorize four DG datasets i.e.,
PACS, VLCS, OfficeHome, and TerraIncognita based
on their exhibited shift(s) into the four categories and
report results. UPLM outperforms all other methods
in all domain shifts, except for a slight advantage of
MA in style. The OfficeHome dataset has a limited
number of examples per class, leading to potential
overfitting due to uncertainty constraints. However,
our MA approach demonstrates strong performance
by effectively mitigating mis-calibrated PLs.
Table 5: Accuracy (%) for different types of domain shifts.
Texture Shifts Corruption Shifts Background Shifts Style Shifts
Methods PACS Terra VLCS, Terra OH, PACS
FixMatch 73.51 17.56 30.44 60.94
UPL 76.35 20.07 37.20 63.17
MA 78.54 27.30 37.70 65.34
UPLM (Ours) 78.94 30.19 46.46 64.78
5 CONCLUSION
We presented a new SSDG approach (UPLM) fea-
turing uncertainty-guided pseudo-labelling and model
averaging mechanisms. The proposed approach lever-
ages the model’s predictive uncertainty to develop a
pseudo-labelling selection criterion that mitigates the
impact of poor model calibration under multi-source
unlabelled data. The model averaging technique re-
duces overfitting to source domains in the presence
of limited labels and domain shifts. Results on sev-
eral challenging DG datasets suggest that our method
provides notable gains over the baseline. We believe
that our work will encourage the development of more
data-efficient visual recognition models that are also
generalizable across different domains.
REFERENCES
Beery, S., Van Horn, G., and Perona, P. (2018). Recognition
in terra incognita. In Proceedings of the European
conference on computer vision (ECCV), pages 456–
473.
DeVries, T. and Taylor, G. W. (2017). Improved regular-
ization of convolutional neural networks with cutout.
arXiv preprint arXiv:1708.04552.
Dou, Q., Coelho de Castro, D., Kamnitsas, K., and Glocker,
B. (2019). Domain generalization via model-agnostic
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
298

learning of semantic features. Advances in Neural In-
formation Processing Systems, 32.
Fang, C., Xu, Y., and Rockmore, D. N. (2013). Unbiased
metric learning: On the utilization of multiple datasets
and web images for softening bias. In Proceedings of
the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vi-
sion, pages 1657–1664.
Gal, Y. and Ghahramani, Z. (2016). Dropout as a bayesian
approximation: Representing model uncertainty in
deep learning. In international conference on machine
learning, pages 1050–1059. PMLR.
Ghifary, M., Kleijn, W. B., Zhang, M., and Balduzzi, D.
(2015). Domain generalization for object recognition
with multi-task autoencoders. In Proceedings of the
IEEE international conference on computer vision,
pages 2551–2559.
Grandvalet, Y. and Bengio, Y. (2004). Semi-supervised
learning by entropy minimization. Advances in neural
information processing systems, 17.
Gulrajani, I. and Lopez-Paz, D. (2020). In search
of lost domain generalization. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2007.01434.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016a). Deep resid-
ual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of
the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 770–778.
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., and Sun, J. (2016b). Deep resid-
ual learning for image recognition. In CVPR, pages
770–778.
Hoffman, J., Tzeng, E., Darrell, T., and Saenko, K. (2017).
Simultaneous deep transfer across domains and tasks.
Domain Adaptation in Computer Vision Applications,
pages 173–187.
Huang, Z., Wang, H., Xing, E. P., and Huang, D. (2020).
Self-challenging improves cross-domain generaliza-
tion.
Kendall, A. and Cipolla, R. (2016). Modelling uncertainty
in deep learning for camera relocalization. In 2016
IEEE international conference on Robotics and Au-
tomation (ICRA), pages 4762–4769. IEEE.
Kendall, A. and Gal, Y. (2017). What uncertainties do we
need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision?
Advances in neural information processing systems,
30.
Khan, A., AlBarri, S., and Manzoor, M. A. (2022a). Con-
trastive self-supervised learning: a survey on different
architectures. In 2022 2nd International Conference
on Artificial Intelligence (ICAI), pages 1–6. IEEE.
Khan, A., Khattak, M. U., and Dawoud, K. (2022b). Ob-
ject detection in aerial images : A case study on per-
formance improvement. In 2022 International Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence of Things (ICAIoT),
pages 1–9.
Khan, M. H., Zaidi, T., Khan, S., and Khan, F. S. (2021).
Mode-guided feature augmentation for domain gener-
alization. In Proc. Brit. Mach. Vis. Conf.
Kim, D., Yoo, Y., Park, S., Kim, J., and Lee, J. (2021). Self-
reg: Self-supervised contrastive regularization for do-
main generalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
International Conference on Computer Vision, pages
9619–9628.
Krizhevsky, A., Sutskever, I., and Hinton, G. E. (2017). Im-
agenet classification with deep convolutional neural
networks. Communications of the ACM, 60(6):84–90.
Lakshminarayanan, B., Pritzel, A., and Blundell, C. (2017).
Simple and scalable predictive uncertainty estimation
using deep ensembles. Advances in neural informa-
tion processing systems, 30.
Li, D., Yang, Y., Song, Y.-Z., and Hospedales, T. M. (2017).
Deeper, broader and artier domain generalization. In
Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on
computer vision, pages 5542–5550.
Lin, L., Xie, H., Yang, Z., Sun, Z., Liu, W., Yu, Y., Chen,
W., Yang, S., and Xie, D. (2021). Semi-supervised
domain generalization in real world: New benchmark
and strong baseline. arXiv preprint arXiv:2111.10221.
Muandet, K., Balduzzi, D., and Sch
¨
olkopf, B. (2013). Do-
main generalization via invariant feature representa-
tion. In International conference on machine learning,
pages 10–18. PMLR.
Nesterov, Y. E. (1983). A method of solving a con-
vex programming problem with convergence rate
o\bigl(kˆ2\bigr). In Doklady Akademii Nauk, volume
269, pages 543–547. Russian Academy of Sciences.
Qi, L., Yang, H., Shi, Y., and Geng, X. (2022). Multimatch:
Multi-task learning for semi-supervised domain gen-
eralization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.05853.
Rizve, M. N., Duarte, K., Rawat, Y. S., and Shah, M.
In defense of pseudo-labeling: An uncertainty-aware
pseudo-label selection framework for semi-supervised
learning. In International Conference on Learning
Representations.
Robbins, H. and Monro, S. (1951). A stochastic approxi-
mation method. The annals of mathematical statistics,
pages 400–407.
Sajjadi, M., Javanmardi, M., and Tasdizen, T. (2016). Reg-
ularization with stochastic transformations and pertur-
bations for deep semi-supervised learning. Advances
in neural information processing systems, 29.
Shankar, S., Piratla, V., Chakrabarti, S., Chaudhuri, S.,
Jyothi, P., and Sarawagi, S. (2018). Generalizing
across domains via cross-gradient training. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1804.10745.
Shu, Y., Cao, Z., Wang, C., Wang, J., and Long, M. (2021).
Open domain generalization with domain-augmented
meta-learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Con-
ference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,
pages 9624–9633.
Smith, L. and Gal, Y. (2018). Understanding measures of
uncertainty for adversarial example detection. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1803.08533.
Sohn, K., Berthelot, D., Carlini, N., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H.,
Raffel, C. A., Cubuk, E. D., Kurakin, A., and Li, C.-L.
(2020). Fixmatch: Simplifying semi-supervised learn-
ing with consistency and confidence. Advances in neu-
ral information processing systems, 33:596–608.
Tarvainen, A. and Valpola, H. (2017). Mean teachers are
better role models: Weight-averaged consistency tar-
gets improve semi-supervised deep learning results.
Improving Pseudo-Labelling and Enhancing Robustness for Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization
299

Advances in neural information processing systems,
30.
Tzeng, E., Hoffman, J., Darrell, T., and Saenko, K. (2015).
Simultaneous deep transfer across domains and tasks.
In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference
on computer vision, pages 4068–4076.
Vapnik, V. (1999). The nature of statistical learning theory.
Springer science & business media.
Venkateswara, H., Eusebio, J., Chakraborty, S., and Pan-
chanathan, S. (2017). Deep hashing network for
unsupervised domain adaptation. In Proceedings of
the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern
recognition, pages 5018–5027.
Volpi, R., Namkoong, H., Sener, O., Duchi, J. C., Murino,
V., and Savarese, S. (2018). Generalizing to unseen
domains via adversarial data augmentation. Advances
in neural information processing systems, 31.
Wang, S., Yu, L., Li, C., Fu, C.-W., and Heng, P.-A. (2020).
Learning from extrinsic and intrinsic supervisions for
domain generalization.
Xie, Q., Luong, M.-T., Hovy, E., and Le, Q. V. (2020).
Self-training with noisy student improves imagenet
classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF con-
ference on computer vision and pattern recognition,
pages 10687–10698.
YANG, P. Y. and Gao, W. (2013). Multi-view discriminant
transfer learning.
Yao, H., Hu, X., and Li, X. (2022). Enhancing pseudo
label quality for semi-supervised domain-generalized
medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of
the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol-
ume 36, pages 3099–3107.
Yuan, J., Ma, X., Chen, D., Kuang, K., Wu, F., and Lin,
L. (2022). Label-efficient domain generalization via
collaborative exploration and generalization. In Pro-
ceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference
on Multimedia, pages 2361–2370.
Zhang, C., Zhang, M., Zhang, S., Jin, D., Zhou, Q., Cai, Z.,
Zhao, H., Liu, X., and Liu, Z. (2022). Delving deep
into the generalization of vision transformers under
distribution shifts. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recogni-
tion, pages 7277–7286.
Zhou, K., Loy, C. C., and Liu, Z. (2021a). Semi-supervised
domain generalization with stochastic stylematch.
arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.00592.
Zhou, K., Yang, Y., Qiao, Y., and Xiang, T. (2021b). Do-
main generalization with mixstyle. arXiv preprint
arXiv:2104.02008.
APPENDIX
A Uncertainty κ vs ECE Plot
For each training iteration, we first calculate the mean
of uncertainty (V ) for all input examples in a batch
across class dimension to obtain the overall uncer-
tainty for each example. Also, we compute the cor-
responding ECE score for this batch. Next, after each
epoch, we compute mean of overall uncertainty (for
each example) over all examples seen and also com-
pute the mean over ECE. Each epoch yields a pair of
mean uncertainty and corresponding mean ECE over
all examples. We then sort the mean uncertainty val-
ues in ascending order to build x-axis and the corre-
sponding mean (ECE) to plot y-axis.
B Analysis of Hyperparameters
Table 6: Ablation of κ in range [0.2, 0.8].
Target 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
PACS
Photo 87.07 86.11 86.77 78.32 84.79 70.42 65.09
Art 75.73 71.58 68.70 69.73 68.02 57.13 60.40
Cartoon 68.09 66.3 65.02 61.56 63.14 59.68 59.90
Sketch 79.38 72.13 73.12 59.96 71.21 46.17 66.45
Average 77.57 74.03 73.40 67.39 71.79 58.35 62.96
OfficeHome
Art 42.89 37.99 42.69 43.22 38.90 42.89 40.34
Clipart 40.92 42.15 37.55 42.50 39.31 36.70 41.05
Product 57.92 58.95 56.25 58.71 56.32 57.02 57.02
Real World 63.76 59.44 60.80 62.98 61.65 58.30 59.93
Average 51.37 49.63 49.32 51.85 49.05 48.73 49.59
VLCS
Caltech101 29.40 57.03 50.46 85.72 80.71 87.42 80.42
LabelMe 54.14 53.77 55.76 60.69 54.18 64.72 60.47
SUN09 65.42 60.02 56.79 52.16 51.22 43.57 49.18
VOC2007 33.56 48.13 35.55 36.58 38.00 51.18 39.19
Average 45.63 54.74 49.64 58.79 56.03 61.72 57.32
Terra
Location 38 22.09 12.26 4.18 39.54 44.48 11.54 33.57
Location 43 10.96 22.80 15.19 25.84 16.73 20.10 12.95
Location 46 23.97 19.46 23.98 20.57 16.66 22.49 22.11
Location 100 39.72 48.20 32.40 37.63 41.95 30.65 32.38
Average 24.19 25.68 18.94 30.90 29.96 21.20 25.25
B.1 Computational Cost of MC Forward Passes
We use N = 10 Monte Carlo (MC) forward passes in
all experiments, with negligible computational over-
head. The per-iteration execution times in millisec-
onds for different values of N (1, 5, 10, 20, 40, 80,
160) are 134.6, 135.1, 135.6, 137.5, 138.5, 141.7,
146.6, respectively.
B.2 Accuracy with Changing the Amount of
Unlabelled Data µ
The average accuracies on PACS for µ = [1 − 6] are
65.25, 71.90, 75.47, 73.7, 78.94, 78.22, respectively.
µ = 5 performs best overall, which is used throughout
in all our experiments. Note that, µ values beyond 6
are not possible due to computational constraints.
B.3 Effect of Certainty Threshold
We present an ablation study concerning the selection
of the certainty threshold κ = 0.2 (indicating the least
certainty) to κ = 0.8 (indicating the highest certainty),
as detailed in Table 6.
VISAPP 2024 - 19th International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
300
