
Hybrid Quanvolutional Echo State Network for Time Series Prediction
Rebh Soltani
1 a
, Emna Benmohamed
2 b
and Hela Ltifi
3 c
1
Research Groups in Intelligent Machines, University of Sfax, National Engineering School of Sfax (ENIS),
BP 1173, Sfax, 3038, Tunisia
2
Department of Cyber Security, College of Engineering and Information Technology, Onaizah Colleges,
P.O. Box 5371, Onaizah, K.S.A.
3
Computer Science and Mathematics Department, Faculty of Sciences and Technology of Sidi Bouzid,
University of Kairouan, Tunisia
fi
Keywords:
Echo State Network, Quantum Computing, Reservoir Computing, Quanvolution Filter.
Abstract:
Quantum Machine Learning (QML) combines quantum physics with machine learning techniques to enhance
algorithm performance. By leveraging the unique properties of quantum computing, such as superposition and
entanglement, QML aims to solve complex problems beyond the capabilities of classical computing. In this
study, we developed a hybrid model, the quantum convolutional Echo State Network, which incorporates QML
principles into the Reservoir Computing framework. Evaluating its performance on benchmark time-series
datasets, we observed improved results in terms of mean square error (MSE) and reduced time complexity
compared to the classical Echo State Network (ESN). These findings highlight the potential of QML to advance
time-series prediction and underscore the benefits of merging quantum and machine learning approaches.
1 INTRODUCTION
QML is the fusion of machine learning and quantum
computing (Biamonte et al., 2017). The objective of
QML is to harness the computational advantages of-
fered by quantum computers, which can process data
at exponentially faster rates than classical comput-
ers. By leveraging quantum systems, algorithms are
developed to facilitate the continual improvement of
computer programs over time. QML capitalizes on
the inherent efficiency of quantum computers to ad-
dress machine learning problems. Notably, the uti-
lization of superposition quantum states enables the
simultaneous analysis of multiple states, leading to
substantial speedups. A key research focus lies in
the design of networks known as quantum neural net-
works (Altaisky et al., 2014), where every element,
including individual neurons and training algorithms,
operates on a quantum computer.
In the 1990s, the field of quantum neural network
research began to emerge, as evidenced by early pub-
lications (Fern
´
andez P
´
erez et al., 2022). However, in
comparison to other areas of quantum machine learn-
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5644-2049
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3934-3962
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3953-1135
ing discussed previously, neural networks in the quan-
tum realm have not yet attained the same level of
scientific maturity. This lack of progress can be at-
tributed to the inherent non-linearity of neural net-
work components conflicting with the linear nature
of quantum physics (Schuld et al., 2015). To over-
come this challenge, researchers have explored the
application of a quantum mechanical framework to
simulate the activation function of perceptrons. This
approach involves incorporating specialized measure-
ments and proposing non-linear quantum operators.
Notably, Schuld (Schuld et al., 2015) has described a
direct implementation of the activation function using
the quantum phase estimation approach and a circuit-
based model of quantum computation. These ad-
vancements offer promising avenues for bridging the
gap between neural networks and quantum mechan-
ics, thus unlocking new possibilities for quantum-
inspired machine learning paradigms (Chen et al.,
2022). Defining quantum neural networks remains a
topic of ongoing debate and lacks a consensus, de-
spite recent efforts to construct neural network ver-
sions that rely solely on principles from quantum me-
chanics. The primary obstacle in developing a quan-
tum artificial neural network stems from the linear na-
ture of quantum physics, whereas artificial neural net-
works necessitate non-linearity (Schuld et al., 2015)
40
Soltani, R., Benmohamed, E. and Ltifi, H.
Hybrid Quanvolutional Echo State Network for Time Series Prediction.
DOI: 10.5220/0012271600003636
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2024) - Volume 2, pages 40-46
ISBN: 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.
(Cao et al., 2017) (Zhao et al., 2019). Consequently,
many research papers have encountered challenges
in reproducing essential features of traditional neu-
ral networks, contributing to the absence of successful
replications in this regard.
We draw attention to the fact that despite sev-
eral studies on quantum neural networks (Gupta and
Zia, 2001), (Purushothaman and Karayiannis, 1997)
, (Bharti et al., 2022), and (Panella and Martinelli,
2011), no attempt has been made to explicitly model
non-linearity on amplitudes, suggesting that no really
effective quantum neural network has yet been pre-
sented. The Echo State Network (ESN) is a funda-
mental Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) model with
a sparse reservoir and a straightforward linear output
(Jaeger, 2002). It has found applications in various
domains, including human activity recognition, clin-
ical applications, distributed, embeddable and fed-
erated learning, and distributed intelligence applica-
tions (Sun et al., 2022) (Soltani et al., 2023). How-
ever, the ESN suffers from several fundamental chal-
lenges (Soltani et al., 2022). For instance, since the
reservoir is randomly created prior to training, deter-
mining the hyperparameters of the dynamic reservoir
typically involves experimentation (Liu et al., 2020).
The analysis of reservoir hyperparameters is a com-
plex task, and the initial connection and weight struc-
ture are unlikely to be in an optimal state. Conse-
quently, creating a highly efficient reservoir that is
specifically tailored to certain tasks becomes chal-
lenging. To tackle these challenges, various tech-
niques have been proposed to address these issues.
One technique introduced a deterministic reservoir
topology that outperformed the standard ESN (Rodan
and Tino, 2010). In an alternative approach, a highly-
clustered ESN with a scale-free network structure was
utilized (Deng and Zhang, 2006). In pattern recogni-
tion, leak integral neurons were employed to improve
performance compared to conventional ESNs, utiliz-
ing filter neurons, delay variables, and readout (Jaeger
et al., 2007). These methods offered various opti-
mizations to the ESN model. The primary objective of
this study is to assess the viability and potential bene-
fits of utilizing a quantum echo state network. Our fo-
cus lies in integrating the dynamic reservoirs of ESNs
with quantum computing to enhance the overall per-
formance of the network and unlock unprecedented
levels of efficiency. By leveraging the unique proper-
ties of quantum computing, we aim to explore novel
avenues for improving the capabilities of echo state
networks and achieving remarkable enhancements in
their performance.
In this study, we delve into the realm of Quanvo-
lutional Neural Networks (QNNs), a novel class of
models. QNNs leverage certain strengths of quan-
tum computation to enhance the capabilities of ESNs.
A pivotal contribution of QNNs is the introduc-
tion of quantum convolutional (quanvolutional) lay-
ers, which augment the conventional ESN architec-
ture. These quanvolutional layers operate in a man-
ner akin to classical convolutional layers, generating
feature maps through localized modifications of in-
put data. In contrast, quantum circuit-based quan-
volutional filters reshape specific subsets of data spa-
tially to extract features from the input. We propose
that leveraging features produced by random quanvo-
lutional circuits can enhance the accuracy of machine
learning models employed for time series forecasting.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 pro-
vides a comprehensive description of the ESN model.
In Section 3, we delve into the suggested Approach,
which combines quantum theory with the ESN, of-
fering a detailed exploration of the proposed model.
Section 4 is dedicated to the performance analysis and
presentation of experimental results. Finally, Section
5 concludes the article by summarizing the key find-
ings and conclusions.
2 ECHO STATE NETWORK
Echo state networks (Soltani et al., 2023) are a type
of RNNs which has the ability to extract the time
correlation of time series data(Bouazizi et al., 2022)
(Bouazizi et al., 2023). For this reason, they are fre-
quently employed to tackle time series forecasting
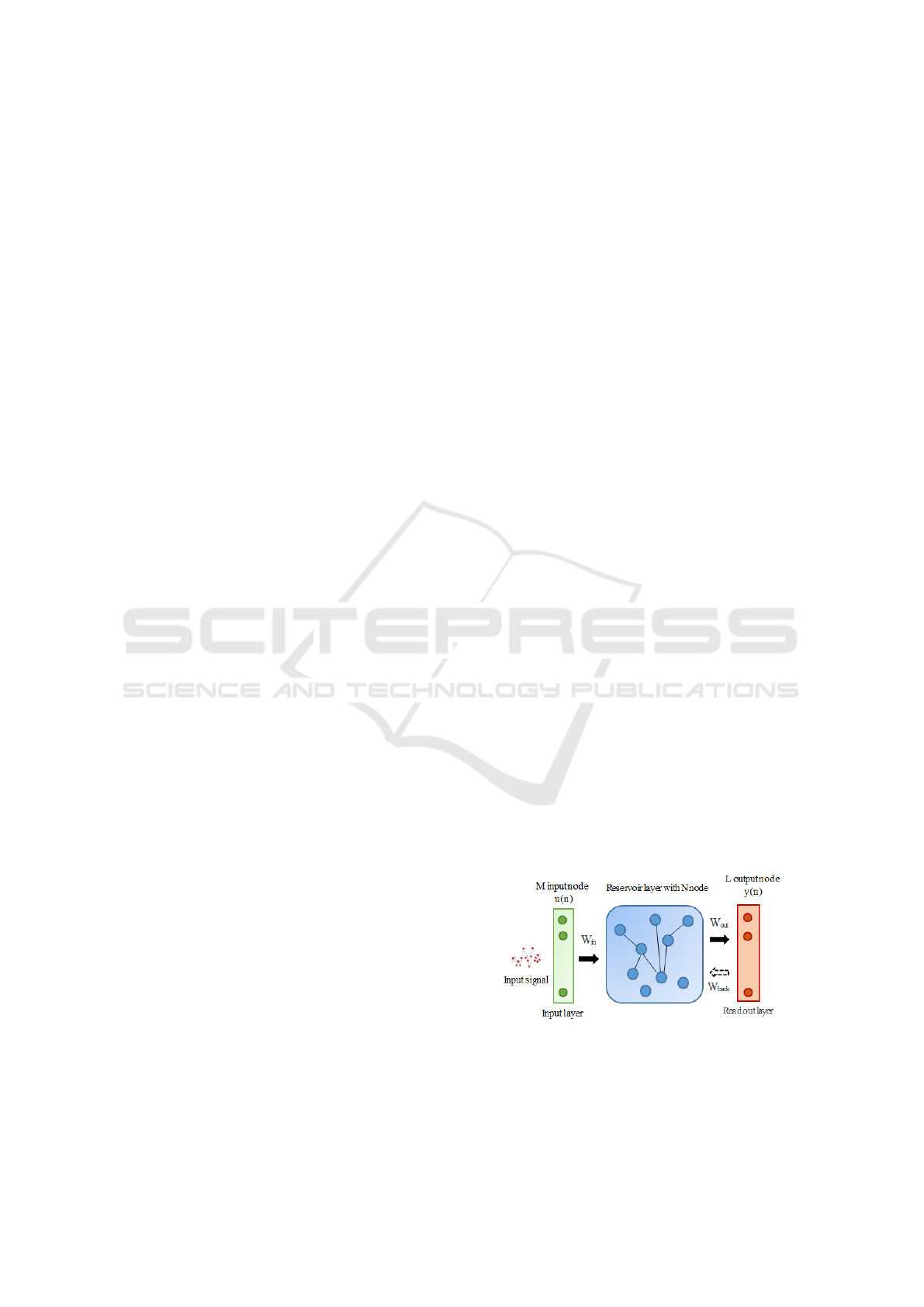
tasks. As demonstrated in Fig. 1, ESN model uses
a reservoir whose state and dynamics play the role of
memory of past experiences, and from which we wish
to extract the relevant information through the readout
layer. Since just the weights in the readout layer may
be trained, the training time is kept to a minimum.
Considering that the network includes M input units,
Figure 1: The structure of ESN.
N internal compute nodes (i.e. reservoir layer neu-
rons), and L output units (as shown in Fig. 1). The
Hybrid Quanvolutional Echo State Network for Time Series Prediction
41

ESN can be modelled by :
x(n + 1) = f (W x(n) +W
in
u(n + 1) +W
back
y(n)) (1)
y(n + 1) = W
out
f
out
(x(n + 1), u(n + 1), y(n)) (2)
The internal state of ESN neurons is updating, as il-
lustrated in equations (1) and (2). The hidden layer
activation function is f. f is often a nonlinear function
such as tanh or sigmoid. The reservoir’s internal up-
dating state is denoted by x(n), while the output of the
linear function f
out
is denoted by y(n). W
in
represents
the input weights from the input to the reservoir layer.
The internal weights inside the reservoir are called W.
W
out
is the output weights from the reserve pool to
the readout layer and is the only one that needs to be
trained.W
back
is the backward weights from the read-
out to the reservoir layer.
3 HYBRID QUANTUM ESN
This section first covers the basic concepts of quan-
tum mechanics. The model is then proposed, fol-
lowed by a full explanation.
3.1 Quantum
(Qubit): Conventional information is represented by
one or more bits. A bit can take the values 0, 1 or true,
false. A qubit can take on values of both |0⟩ and |1⟩
said in quantum superposition (Gupta and Zia, 2001).
This is in contrast to analog circuits which take values
between 0 and 1. The algebraic part of qubits is better
understood using Dirac notation. The |0⟩ states and
|1⟩ states are algebraically equivalent to the 0 and 1
of a classical bit. The phenomena of quantum super-
position is represented by the linear combinations of
both |0⟩ and |1⟩. As a result, various potential states
emerge:
|Ψ⟩ = α|0⟩ + β|1⟩ (3)
where α and β are complex values that make up a unit
norm vector:
∥α∥
2
+ ∥β∥
2
= 1 (4)
The coefficients α and β reflect the probability ampli-
tude or for making shorter amplitude in a quantitative
sense. The probability of measuring |0⟩ is given by
the squared norm, while the probability of measuring
|1⟩ is given by the squared norm.The squared norm of
an amplitude reflects a probability (Biamonte et al.,
2017), hence ∥α∥
2
+ ∥β∥
2
= 1.
4 HYBRID QUANVOLUTIONAL
ESN MODEL
The idea behind this approach is that the quanvolution
filter can extract more relevant features from the input
data, which can improve the performance of the ESN.
Additionally, the quanvolution filter allows including
quantum mechanical properties, such as superposition
and entanglement, which could enhance the represen-
tational power of the ESN. Fig 2 presents in details
our proposed method.
1) The input data is transformed into a quantum
state, which is a mathematical representation of the
data in the quantum mechanical system (equation 3).
This can be done using techniques such as quantum
state encoding, which maps classical data to a quan-
tum state.
i
t
= e(u(t)) = e
iu(t)
= cos(u(t))+isin(u(t)) (5)
where u(t) is the input data at time t. 2) The quantum
state is then passed through a quantum random circuit
that applies a random sequence of quantum gates to
the qubit.
O
t
= g(i
t
) (6)
3) Next, the output of the random quantum circuit is
passed through a measurement gate.
Z
t
= d(O
t
) =< O
t
> (7)
4) The output of the quanvolutional filter is a new in-
put that contains the relevant features extracted from
the input data. The new input is then used in the re-
current part of the ESN. the following equation can
describe the state dynamic of our model:
x(n + 1) = f (W x(n) +W
in
Z
t
+W
back
y(n)) (8)
5) The output of the ESN is then generated.
y(n + 1) = W
out
f
out
(x(n + 1), u(n + 1), y(n)) (9)
By incorporating the quanvolution filter and its asso-
ciated quantum computations, this approach aims to
extract relevant features from the input data and inte-
grate them into the ESN framework, potentially lead-
ing to improved performance in time series forecast-
ing tasks.
5 EXPERIMENTATIONS AND
RESULTS
5.1 Experimental Environment
The experiments conducted in this research employed
the PennyLane quantum machine learning library.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
42
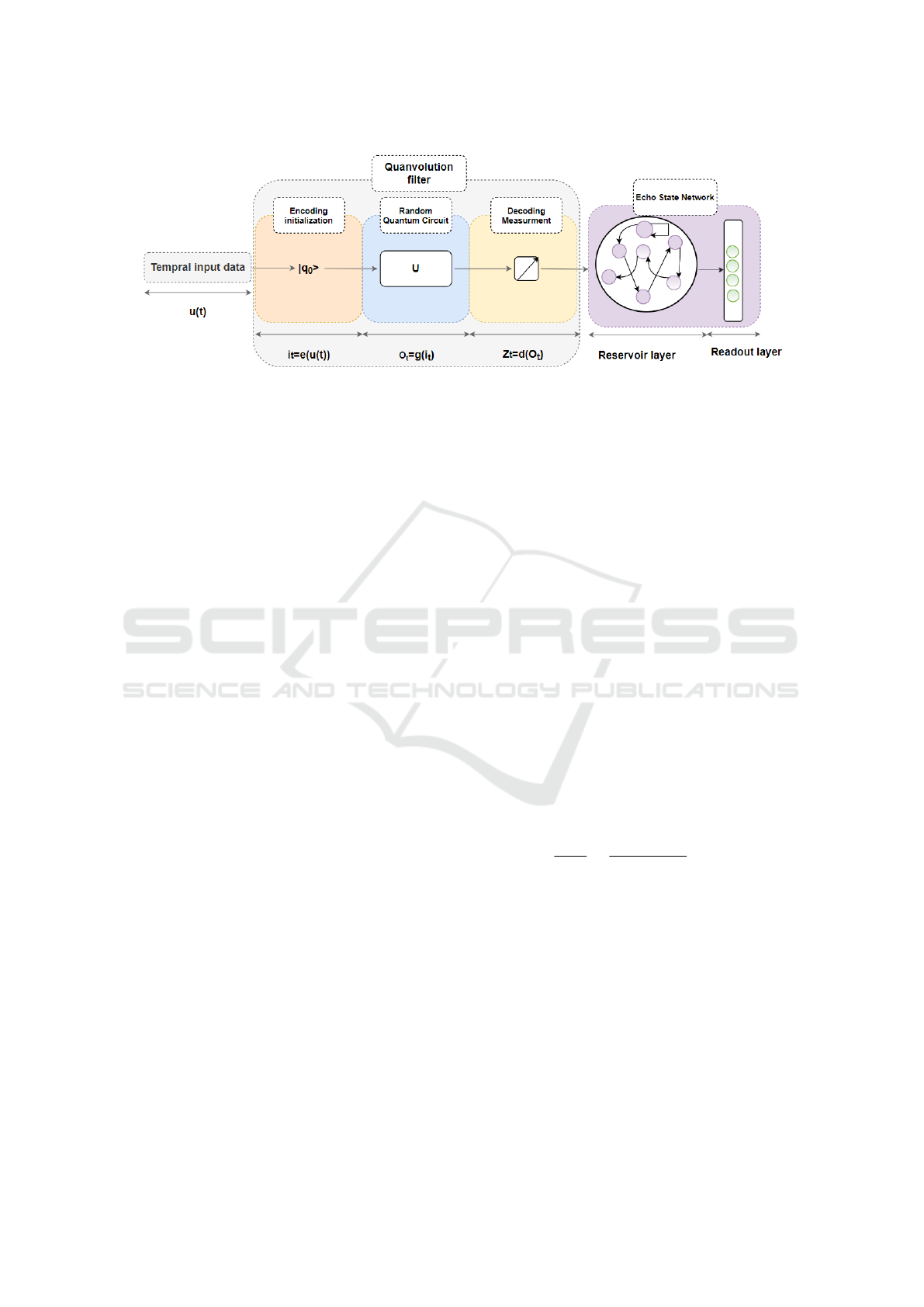
Figure 2: Hybrid Quanvolutional Echo State Network.
The code utilized a local qubit simulator designated
as ”default.qubit” in PennyLane, enabling quantum
computations on a single qubit. This setup allowed
for executing gate-model instructions with flexibility
in gate width, circuit depth, and fidelity. The experi-
ments intentionally omitted the incorporation of noise
models to assess the effectiveness of the ideal univer-
sal quantum computational model compared to clas-
sical computational models. Future experimentation
could involve investigating the impact of noise or uti-
lizing alternative quantum hardware or simulators.
To construct the quantum filter in this implemen-
tation, a single qubit is considered. The size of the in-
put for the quanvolutional filters determines the num-
ber of qubits required for the circuit. In this particular
case, a 1-by-1 quanvolutional filter is employed, re-
sulting in a circuit with 1 qubit (n = 1).
Random 1-qubit gates are generated for the quan-
volutional filter, selected from the gate set [X(θ),
Y(θ), Z(θ), U(θ), P, T, H]. The value of θ represents
a randomly determined rotational parameter, and the
target qubit for each gate is also selected randomly.
We applied the first training-test split to all
datasets. We further deduced a divide into train-
ing (75 %) and validation (25 %) for model selec-
tion. Bayesian Optimization was used to tweak the
hyper-parameter values on the validation set. We in-
vestigated the following configurations in our stud-
ies using Hybrid quanvolutional ESN: the number of
units [5, 500] in the reservoir layer, input scaling
[0.01, 1.5], and spectral radius [0.01, 1.5] for the most
part. We employed a single dense layer trained using
adam optimizer as the output readout, with a learn-
ing rate of 1e-5 , for the Mackey-Glass (MG) dataset
(Mackey and Glass, 1977), the model was trained for
100 epochs. Similarly, for the NARMA-10 dataset,
the model underwent 50 epochs of training. Follow-
ing model selection, we trained our models using the
chosen hyper-parametrameter on the whole training
set, evaluated their performance on the test set. We
carried out the same trials with ESN for compari-
son. In both instances, we used the same model se-
lection and performance evaluation procedure, look-
ing at the identical values for the training algorithm’s
hyper-parameters and the number of recurrent units.
The model’s performance was assessed by mea-
suring the mean square error and computation time
on the test set. The experiments were conducted in a
Python environment, utilizing a computer equipped
with an i5 CPU and 8.0 GB RAM. The results of
the quanvolutional filter applied to ESN method were
evaluated on the Mackey-Glass (Zhao et al., 2019)
and NARMA-10 (Connor et al., 1991) datasets which
are a classic example of a chaotic system and is often
used as a benchmark for testing the performance of
numerical methods for solving differential equations.
5.2 Mackey-Glass Time Series
Prediction
For the prediction of chaotic series, the Mackey-
Glass’ chaotic series is a widely used test (Fig. 2).
The following is MG’s mathematical model:
dx(t)
dt
=
ax(t − τ)y
1 + x
n
(t − τ)
+ bx(t) (10)
The key parameters are set as a=0.2, b=-0.1, τ=17,
n=10. The results obtained on the Mackey-Glass
datasets are presented in Table 1, Table 2, Figure 3
and Figure 4.
Quanvolutional ESN model is computationally
more efficient and faster in processing the data com-
pared to the ESN model.
Based on the provided results on Table 1 Fig 3
and 4, the Hybrid Quanvolutional ESN model out-
performed the ESN model in terms of both predic-
tive accuracy and computational efficiency. The Hy-
brid Quanvolutional ESN model achieved a lower
MSE, indicating better predictive performance on
Hybrid Quanvolutional Echo State Network for Time Series Prediction
43
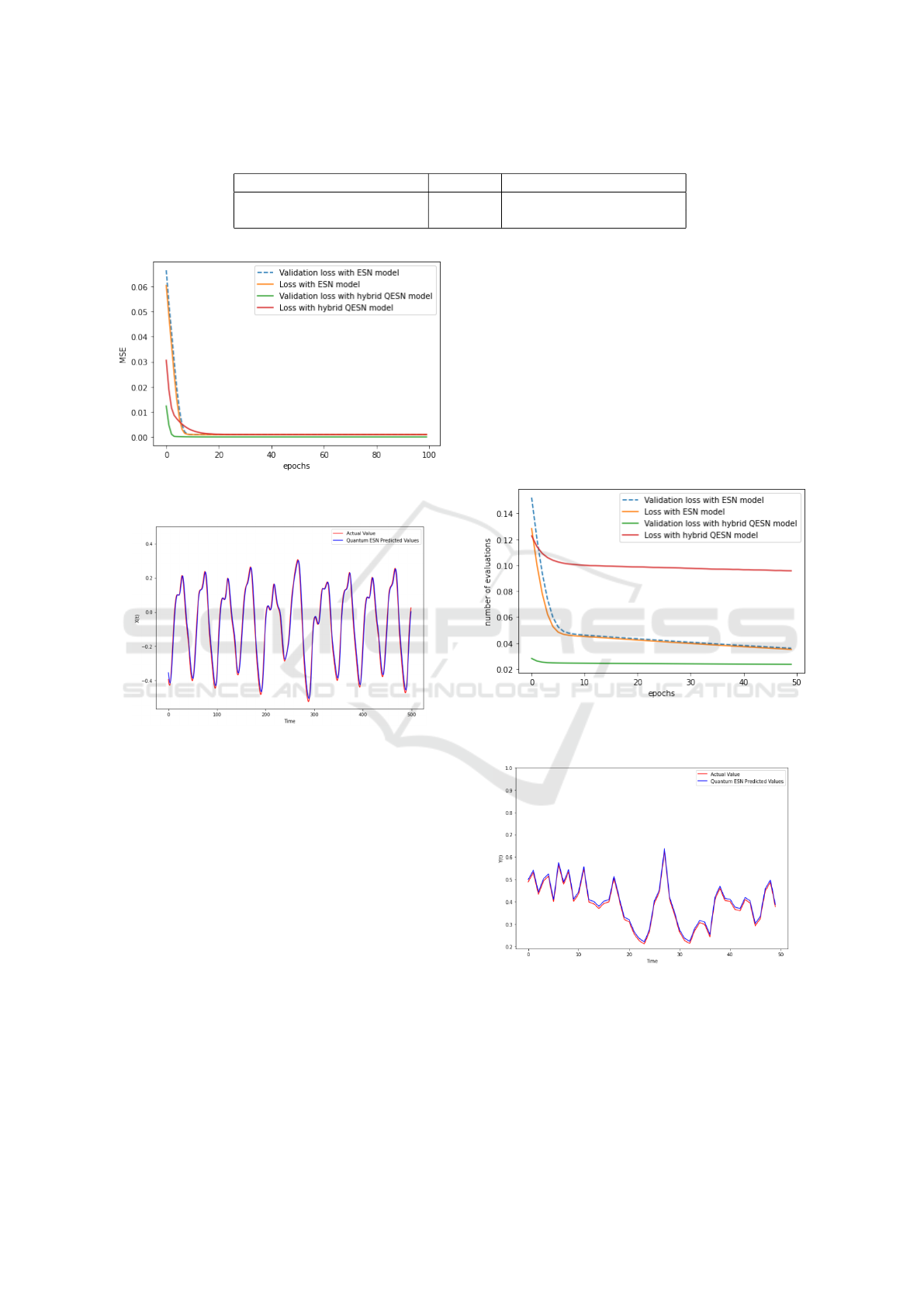
Table 1: Results on Mackey-Glass dataset.
Model MSE Time Complexity (second)
ESN 9.96e-05 116.74
Hybrid Quanvolutional ESN 5.05e-05 106.58
Figure 3: Evolution of training and validation loss during
train with MG dataset.
Figure 4: Real output and predicted output generated by
hybrid Qanvolutional ESN on MG dataset.
the Mackey-Glass dataset. Additionally, the Hybrid
Quanvolutional ESN model demonstrated a faster
processing time, making it more efficient in handling
the dataset.
The results show that the quantum convolutional
filter applied to ESN method achieved a better perfor-
mance in terms of MSE and time complexity on both
datasets, compared to the classical ESN. This indi-
cates that the quantum convolutional filter can extract
more relevant features from the input data, which can
improve the performance of the ESN. In summary, the
proposed method shows a promising performance on
time series prediction problems, and it is worth to fur-
ther investigate this approach on other datasets and
problems.
5.3 NARMA-10 Time Series Prediction
one of the most popular tasks, known as NARMA-10
for NARMA defined in (Connor et al., 1991), which
entails modeling the following order 10 systems:
y(t + 1) = c
1
y(t) + c
2
y(t)
∑
k−1
i=0
y(t − i) + c
3
x(t − (k − 1))x(t) + c
4
(11)
The important variables are set to k=10, c1=0.3,
c2=0.05, c3, and c4=0.1. The results obtained on the
NARMA-10 datasets are presented in Table 1, Table
2, Figure 3 and Figure 4.
Figure 5: Evolution of training and validation loss during
train with NARMA-10 dataset.
Figure 6: Real output and predicted output generated by
hybrid Qanvolutional ESN on NARMA-dataset.
Based on the provided results on Table 3, Fig 5
and 6, the Hybrid Quanvolutional ESN model outper-
forms the ESN model in terms of both predictive ac-
curacy and computational efficiency on the NARMA-
10 dataset. The Hybrid Quanvolutional ESN model
achieved a lower MSE, indicating superior predic-
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
44

Table 2: Results on Narma-10 dataset.
Model MSE Time Complexity (second)
ESN 0.04 677.48
Hybrid Quanvolutional ESN 0.02 479.52
tive performance. Additionally, the Hybrid Quanvo-
lutional ESN model demonstrated a faster processing
time, making it more efficient in handling the dataset.
In conclusion, the Hybrid Quanvolutional ESN model
shows superiority over the ESN model for both MG
and NARMA-10 datasets. It achieves better predic-
tive accuracy and is more computationally efficient.
These results suggest that the Hybrid Quanvolutional
ESN model could be a favorable choice for modeling
and predicting time series. However, it is important to
note that further analysis and experimentation may be
necessary to confirm these findings and explore the
models’ generalizability to other datasets or scenar-
ios.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this research, we suggested a new method for
time-series prediction using quanvolution filter ap-
plied to ESN. On the Mackey-Glass and NARMA
datasets, we assessed the method’s performance and
contrasted the outcomes with those obtained using
traditional ESN. The results shown that, when com-
pared to the traditional ESN, the suggested technique
outperformed it in terms of MSE and time complex-
ity on both datasets. This suggests that by extracting
more relevant features from the input data, the quan-
tum convolutional filter may enhance the effective-
ness of the ESN. It is crucial to note that the findings
are still in the research stage and that more studies are
required to prove the method’s efficacy across a range
of issues and datasets.
REFERENCES
Altaisky, M. V., Kaputkina, N. E., and Krylov, V.
(2014). Quantum neural networks: Current status and
prospects for development. Physics of Particles and
Nuclei, 45:1013–1032.
Bharti, K., Cervera-Lierta, A., Kyaw, T. H., Haug, T.,
Alperin-Lea, S., Anand, A., Degroote, M., Heimonen,
H., Kottmann, J. S., Menke, T., et al. (2022). Noisy
intermediate-scale quantum algorithms. Reviews of
Modern Physics, 94(1):015004.
Biamonte, J., Wittek, P., Pancotti, N., Rebentrost, P., Wiebe,
N., and Lloyd, S. (2017). Quantum machine learning.
Nature, 549(7671):195–202.
Bouazizi, S., Benmohamed, E., and Ltifi, H. (2022). Sa-
k2pc: Optimizing k2pc with simulated annealing for
bayesian structure learning. In International Confer-
ence on Hybrid Intelligent Systems, pages 762–775.
Springer.
Bouazizi, S., Benmohamed, E., and Ltifi, H. (2023). A
novel approach of esn reservoir structure learning for
improved predictive performance. In 2023 IEEE Sym-
posium on Computers and Communications (ISCC),
pages 232–237. IEEE.
Cao, Y., Guerreschi, G. G., and Aspuru-Guzik, A. (2017).
Quantum neuron: an elementary building block for
machine learning on quantum computers. arXiv
preprint arXiv:1711.11240.
Chen, S. Y.-C., Wei, T.-C., Zhang, C., Yu, H., and Yoo, S.
(2022). Quantum convolutional neural networks for
high energy physics data analysis. Physical Review
Research, 4(1):013231.
Connor, J., Atlas, L., and Martin, D. (1991). Recurrent net-
works and narma modeling. Advances in neural infor-
mation processing systems, 4.
Deng, Z. and Zhang, Y. (2006). Complex systems modeling
using scale-free highly-clustered echo state network.
In The 2006 IEEE international joint conference on
neural network proceedings, pages 3128–3135. IEEE.
Fern
´
andez P
´
erez, I., Prieta, F. d. l., Rodr
´
ıguez-Gonz
´
alez, S.,
Corchado, J. M., and Prieto, J. (2022). Quantum ai:
Achievements and challenges in the interplay of quan-
tum computing and artificial intelligence. In Inter-
national Symposium on Ambient Intelligence, pages
155–166. Springer.
Gupta, S. and Zia, R. (2001). Quantum neural networks.
Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 63(3):355–
383.
Jaeger, H. (2002). Adaptive nonlinear system identification
with echo state networks. Advances in neural infor-
mation processing systems, 15.
Jaeger, H., Luko
ˇ
sevi
ˇ
cius, M., Popovici, D., and Siewert, U.
(2007). Optimization and applications of echo state
networks with leaky-integrator neurons. Neural net-
works, 20(3):335–352.
Liu, J., Sun, T., Luo, Y., Yang, S., Cao, Y., and Zhai, J.
(2020). An echo state network architecture based on
quantum logic gate and its optimization. Neurocom-
puting, 371:100–107.
Mackey, M. C. and Glass, L. (1977). Oscillation and
chaos in physiological control systems. Science,
197(4300):287–289.
Panella, M. and Martinelli, G. (2011). Neural networks with
quantum architecture and quantum learning. Inter-
national Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications,
39(1):61–77.
Purushothaman, G. and Karayiannis, N. B. (1997). Quan-
tum neural networks (qnns): inherently fuzzy feedfor-
Hybrid Quanvolutional Echo State Network for Time Series Prediction
45

ward neural networks. IEEE Transactions on neural
networks, 8(3):679–693.
Rodan, A. and Tino, P. (2010). Minimum complexity echo
state network. IEEE transactions on neural networks,
22(1):131–144.
Schuld, M., Sinayskiy, I., and Petruccione, F. (2015). An
introduction to quantum machine learning. Contem-
porary Physics, 56(2):172–185.
Soltani, R., Benmohamed, E., and Ltifi, H. (2022). Opti-
mized echo state network based on pso and gradient
descent for choatic time series prediction. In 2022
IEEE 34th International Conference on Tools with Ar-
tificial Intelligence (ICTAI), pages 747–754. IEEE.
Soltani, R., Benmohamed, E., and Ltifi, H. (2023). Echo
state network optimization: A systematic literature re-
view. Neural Processing Letters, pages 1–35.
Sun, C., Song, M., Cai, D., Zhang, B., Hong, S., and Li, H.
(2022). A systematic review of echo state networks
from design to application. IEEE Transactions on Ar-
tificial Intelligence.
Zhao, J., Zhang, Y.-H., Shao, C.-P., Wu, Y.-C., Guo, G.-
C., and Guo, G.-P. (2019). Building quantum neural
networks based on a swap test. Physical Review A,
100(1):012334.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
46
