
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation
Milo Roucairol
1, a
, J
´
er
ˆ
ome Arjonilla
1, b
, Abdallah Saffidine
2 c
and Tristan Cazenave
1 d
1
Paris Dauphine University - PSL, Paris, France
2
University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia
fi
Keywords:
Monte Carlo Search, Coalition Structure Generation, Algorithm, Agents, Combinatorial, Optimization.
Abstract:
This paper explores Monte-Carlo Search algorithms applied to Multiagent Systems (MAS), specifically fo-
cusing on the problem of Coalition Structure Generation (CSG). CSG is a NP-Hard problem consisting in
partitioning agents into coalitions to optimize collective performance. Our study makes three contributions:
(i) a novel action space representation tailored for CSG, (ii) a comprehensive comparative analysis of multiple
algorithms, and the introduction of Lazy NMCS, (iii) a cutting-edge method that surpasses previous bench-
marks. By outlining efficient coalition formation strategies, our findings offer insights for advancing MAS
research and practical applications.
1 INTRODUCTION
Multiagent Systems (MAS) is a vast field of study
where multiple entities have different preferences,
goals, or beliefs (Shoham and Leyton-Brown, 2008).
One of the main goals of MAS research is to plan and
coordinate agents in order to improve global perfor-
mance or to complete task goals that are difficult or
impossible for an individual agent.
Among the different fields of study in MAS, our
work focuses on the partitioning of the agents into
mutually disjoint coalitions (Rahwan et al., 2015).
Partitioning agents into a coalition structure’s goal
can be stability (i.e., where no agent has an interest in
changing coalition) (Cechl
´
arov
´
a et al., 2001) or opti-
mality (i.e., maximizing the total performance / social
welfare) (Aziz and de Keijzer, 2011). Here we decide
to focus on maximizing the sum of the performances
of all the coalitions in the coalition structure, which
is also called Coalition Structure Generation (CSG)
(Rahwan et al., 2015).
Out of the existing methods used on the resolu-
tion of the CSG problem, some of them are trying
to resolve optimally such as dynamic programming
(Yun Yeh, 1986) or integer partition-based search
(Rahwan et al., 2009). Nevertheless finding the best
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7794-5614
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0082-1939
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9805-8291
d
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4669-9374
These authors contributed equally to this work.
coalition structure, especially with many agents, will
be costly since the problem is NP-complete. There-
fore, methods have been introduced to produce coali-
tion structures with better values on large number
of agents at the cost of a loss in theoretical guaran-
tees. Genetic algorithms (Sen and Dutta, 2000) and
GRASP (Mauro et al., 2010) algorithms fall into this
category.
In this paper we compare multiple Monte Carlo
search algorithms, including the state of the art one
on the CSG problem: CSG-UCT (Wu and Ramchurn,
2020). Monte Carlo search algorithms are the state of
the art in many applications and have recently been
combined with reinforcement algorithms, beating hu-
man professional players in multiple games such as
Go, Chess, and Shogi (Silver et al., 2017; Silver et al.,
2018).
Monte Carlo search algorithms are used on coali-
tion problems in two resources. One in (Wu and Ram-
churn, 2020) which uses a modified version of Upper
Confidence bounds applied to Trees (UCT) (Browne
et al., 2012) with a greedy playout. Another one is
presented in (Pr
¨
antare et al., 2021), where different
Monte Carlo Search algorithms are outperformed by
the Random Hill Climbing (RHC) algorithm in the
Simultaneous Coalition Structure Generation and As-
signment (SCSGA) (Pr
¨
antare and Heintz, 2020) prob-
lem. It is stated that the SCSGA problem is an exten-
sion of the CSG problem with the inclusion of an as-
signment problem and that the RHC should perform
well on the CSG problem (theorem 1 of (Pr
¨
antare and
58
Roucairol, M., Arjonilla, J., Saffidine, A. and Cazenave, T.
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation.
DOI: 10.5220/0012302300003636
Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)
In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence (ICAART 2024) - Volume 2, pages 58-67
ISBN: 978-989-758-680-4; ISSN: 2184-433X
Proceedings Copyright © 2024 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda.

Heintz, 2020)).
In this paper, we extend the research on Monte
Carlo algorithms for the CSG problem by using
other Monte Carlo based algorithms, either already
present in the CSG literature (RHC, CSG-UCT),
or new to the problem but well known (NMCS,
UCT) or completely new (LNMCS). Algorithms
based on NMCS showed great result in puzzles
and optimization problems, particularly in multiple
applications such as Single Player General Game
Playing (M
´
ehat and Cazenave, 2010), Cooperative
Pathfinding (Bouzy, 2014), Software testing (Pould-
ing and Feldt, 2014), heuristic Model-Checking
(Poulding and Feldt, 2015), Games (Cazenave et al.,
2016), RNA Inverse Folding problem (Portela, 2018;
Cazenave and Fournier, 2020), Graph Coloring
(Cazenave et al., 2020) and refutation of spectral
graph theory conjectures (Roucairol and Cazenave,
2022).
We contribute to the CSG problem in three ways:
(i) We provide a new representation of the action
space of the CSG problem, which can improve the
performance under given conditions. (ii) We use it for
the first time and compare the performance of multi-
ple algorithms on the CSG problem. (iii) We intro-
duce a new algorithm, the Lazy NMCS, which solves
past problems of NMCS and outperforms the previ-
ous state of the art (at least) on the main benchmarks
of the problem.
The paper is structured as follows: the second
section presents notations for CSG problems, section
three presents the various representations used, sec-
tion four presents the different algorithms, section five
presents our results on multiple benchmarks, and the
last section summarizes our work and outlines future
work.
2 CSG MODEL
The modelization of the action space is a key factor
for the performances. One of the first model pro-
posed was (Sandholm et al., 1999) which represents
the coalition with levels, where at level i, each node
is a coalition structure composed of i coalitions. This
model is explained more precisely in Subsection 2.1.
Other models are available such as in (Rahwan
et al., 2007b), where coalition structures are re-
grouped by multiset of positive integers whose sum
is equal to A . This representation has been used for
integer partition graph (Rahwan et al., 2009).
In Subsection 2.2, we introduce a new model that
allows us to reduce the number of actions at each node
and to enhance the performance under certain condi-
tions.
2.1 Model A: Simple Coalition Merging
The initial state is the singleton coalition (a CS com-
posed of the A singleton coalitions), and the avail-
able moves consist in the CS CS 1 2 two by
two merging of coalitions among the coalition struc-
ture CS. Thus, this action space is a directed graph
where each node represents a coalition structure. The
graph representing the action space is therefore com-
posed of levels, where each level corresponds to the
number of coalitions in each coalition structure i.e.,
in the level i, each node is composed of i coalitions.
The graph naturally ends up with the structure made
of one coalition encompassing all agents, called the
grand coalition.
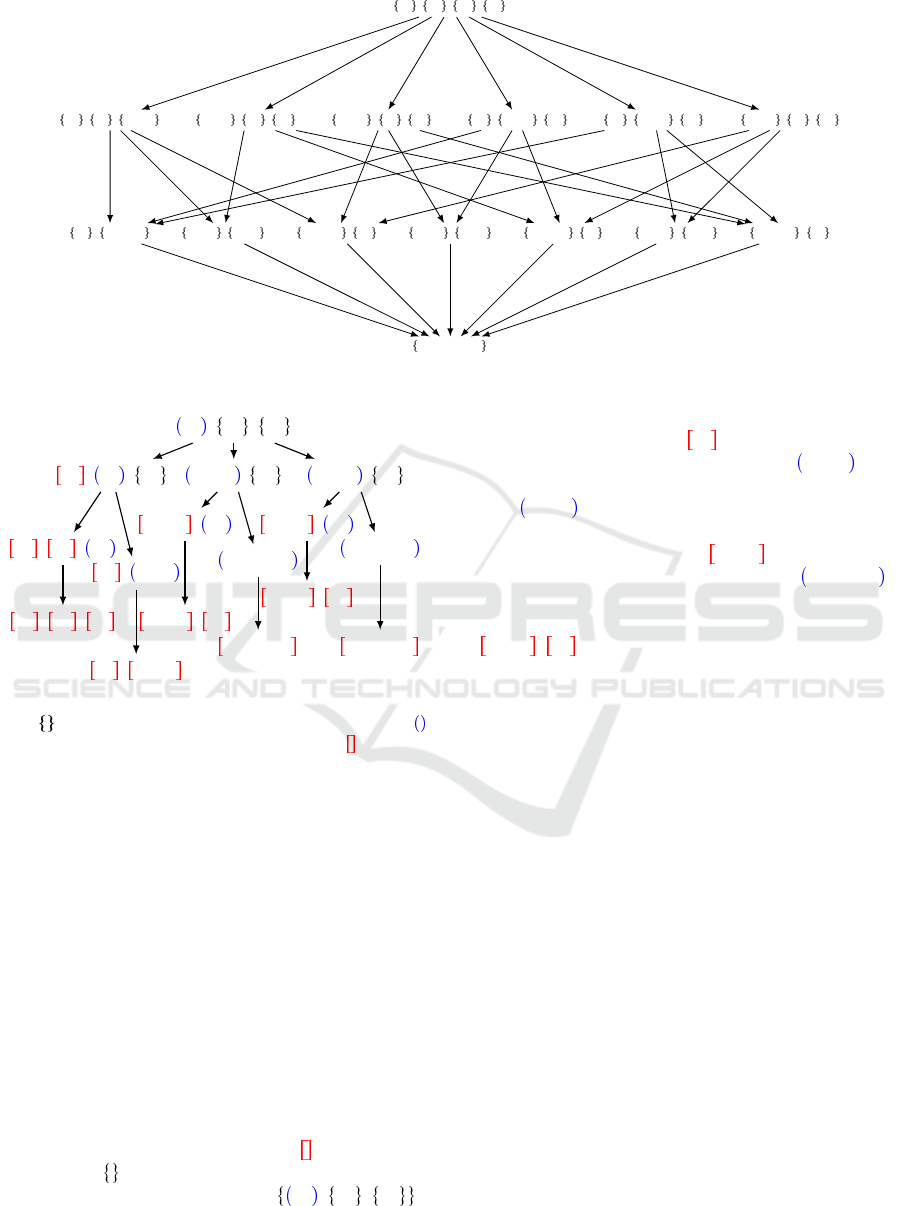
For an example of the CS graph with 4 agents see
figure 1. In this model, the action space and the search
space increase greatly with each new agent. For each
node (coalition structure CS), there are
CS CS 1
2
possible actions, and the closer we are from the start-
ing node, the more actions are possible with the first
one having CS A . To reduce the size of the ac-
tion space (4950 available moves from the singleton
coalition structure with 100 agents), we introduce a
new representation.
2.2 Model B : Locked Merge
In model A, all sequences of actions (playouts) lead to
the grand coalition. In Monte Carlo Search algorithm,
the playout usually returns the value of the last state
of the playout, but in model A it will return the grand
coalition value each time. To alleviate this problem
it is possible to modify the playout algorithm to keep
in memory the best state encountered yet and return
it at the end of the playout, this is the method used
with CSG-UCT (Wu and Ramchurn, 2020), however,
computing the score after each move can be costly. As
stated before, the action space for larger CS in model
A can get large enough for it to be problematic (4950
moves for 100 coalitions).
Our aim with this new model is (i) to reduce the
number of available moves, especially from the first
and largest coalition structure (singleton), and (ii) to
avoid the costly computation of each state’s score of
a playout that model A requires.
We propose a new model representation where we
get a tree of the state space of depth A , with CS
moves possible at each node-state and with CS A
moves for the starting node.
The new model is defined as follows: The starting
node is the coalition structure of all singleton coali-
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation
59
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
, a
4
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
, a
4
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
, a
4
a
1
, a
3
, a
2
, a
4
a
1
, a
2
, a
4
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
, a
4
a
1
, a
4
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
a
3
a
4
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
4
a
1
a
3
a
4
, a
2
a
1
, a
3
, a
2
a
4
a
1
a
2
a
4
, a
3
a
1
, a
4
, a
2
a
3
a
1
a
2
a
3
, a
4
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
, a
4
Figure 1: Model A: an example with four agents.
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
3
, a
2
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
3
, a
2
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
a
1
, a
3
, a
2
a
1
, a
2
, a
3
Figure 2: Model B: an example with three agents. We de-
note when the coalition is not locked and not active,
when the coalition is not locked and active, and when the
coalition is locked.
tions as with model A, without any coalition locked
(a coalition that cannot be merged and will be present
as is in the final state). At any time, only one coali-
tion is active. Two types of moves can be applied to
the coalition structure: (i) locking the active coalition
and selecting another coalition as the active coalition
or (ii) merging another coalition with the active coali-
tion (it remains the active coalition).
Thus any CS has exactly as many moves avail-
able as non-locked coalitions with model B, and each
move played reduces the total of non-locked coali-
tions in the CS by 1. Once all coalitions are locked
there is no more action available and it is then possi-
ble to compute the value of the coalition structure.
An example is provided in Figure 2 with three
agents. Locked coalitions are noted and unlocked
coalition as . As said previously, the first node is
the CS of all singleton coalitions ( a
1
, a
2
, a
3
),
with none of them being locked. From this node-state,
there are three actions/moves possible, the first one is
to lock the first coalition ( a
1
), the second action is
to merge the first and second coalition ( a
1
, a
2
) and
the last action is to merge the first and third coali-
tion ( a
1
, a
3
). If we chose the second action, we
now have two actions available. The first action is
to lock the current coalition ( a
1
, a
2
) and the second
one is to merge the remaining coalitions ( a
1
, a
2
, a
3
).
If we decide to lock the coalition, we are left with one
non-locked coalition and the last action is to lock it
( a
1
, a
2
, a
3
).
It should be noted that it is possible to modify
model B to make all terminal states return different
structures by not merging the coalitions that were re-
jected by the current active coalition until the current
active coalition is locked. This results in an unbal-
anced tree. We did not explore this version of the
model due to poor preliminary results.
3 ALGORITHMS
In this section, we present the algorithms we tried
on the CSG problem: (i) Upper Confidence bound
applied to Trees (UCT) (Browne et al., 2012) (ii)
CSG-UCT (Wu and Ramchurn, 2020) (iii) Random
Hill Climbing (RHC) (Pr
¨
antare and Heintz, 2020)
(iv) Nested Monted Carlo Search (NMCS) (Cazenave,
2009) (v) Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search (LN-
MCS).
In the subsequent pseudo-codes, we use the fol-
lowing notations:
c-st denotes the current state,
n-st denotes the next state,
b-score denotes the best score,
M
state
denotes the legal actions possible in state,
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
60

σ denotes the sequence kept in memory,
σ denotes the best sequence,
b denotes the number of times we can repeat the
playout algorithm.
play state, move is a function returning the next
state when move is applied on state,
l denotes the current level in NMCS and LNMCS,
list i.. denotes the part of list from the i-th ele-
ment to the end.
3.1 Monte Carlo Tree Search and UCT
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) (Browne et al.,
2012) is a popular category of tree search algorithms,
notably used in recent and world-leading research
projects such as Alphazero (Silver et al., 2017), Al-
phafold (Jumper et al., 2021) or Astrazeneca’s tool
for retrosynthesis AiZynthFinder (Genheden et al.,
2020). MCTS consists of four steps: (i) selection —
select nodes by going down the tree according to the
exploitation policy until an unexplored node or a fi-
nal state is hit (ii) expansion — unless the node is
a terminal state, add it to the explored tree (iii) sim-
ulation — estimate the child node by using an ex-
ploration strategy (playout) (iv) backpropagation —
backpropagate the result obtained from the playout
through the nodes chosen during the selection phase.
3.1.1 Selection
Most of the time, the selection phase is done by ban-
dit algorithms. Bandit algorithms are a class of al-
gorithms used when one needs to choose between K
actions. To do so, bandit algorithms must balance be-
tween the exploitation of the current best action and
the exploration of other actions that are currently sub-
optimal.
The formula for UCT is as follow:
UCT
child
¯
X
child
C
ln n
n
child
The child node selected from a current node is the
one that maximizes UCT
child
.
¯
X
child
is the average re-
ward of the child, C is a constant parameter, n
child
the
number of times the child node has been visited and n
the number of times the current node has been visited.
3.1.2 Simulation
In this paper, we are using two types of playouts: (i)
random playout or (ii) greedy playout. Random play-
outs select uniformly a child node, greedy playouts
select the child node with the best value (a node is a
coalition structure).
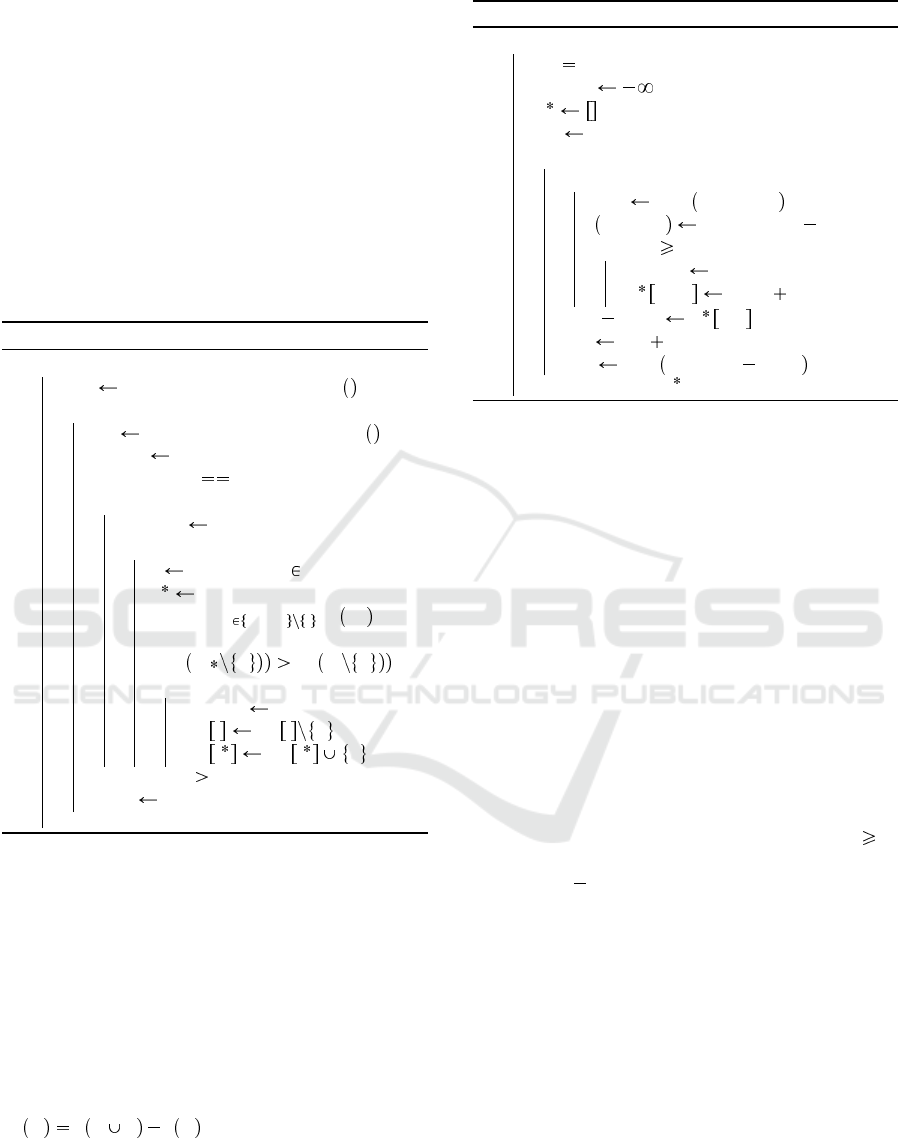
Algorithm 1: Playout algorithm.
Function Playout(state):
b-score ;
σ ;
c-st state;
σ ;
while c-st is not terminal do
if greedy then
move Greedy M
c-st
;
else move Random M
c-st
;
c-st play c-st, move ;
σ. push move ;
if b-score c-st.score or
classicPlayout then
b-score c-st.score;
σ σ;
return b-score, σ ;
In Algorithm 1, we present the pseudo-code of
the playouts used in the multiple algorithms presented
later in the paper. If classicPlayout is true, the algo-
rithm returns the terminal value and not the best it
encountered on its path (suitable for model B).
3.1.3 Backpropagation
Once a value is obtained from the simulation step, all
nodes selected during the selection step (a path going
down the CS tree) see their total number of visits in-
creased by 1, and their average reward updated with
the value from the simulation.
3.2 CSG UCT
CSG-UCT is introduced in (Wu and Ramchurn,
2020) and designed for model A (Subsection 2.1).
CSG-UCT differs from UCT in three ways: (i) in
the selection phase, the average value of X
child
is
replaced with the maximum value observed (ii) the
value backpropagated is the maximum value between
the value backpropagated and the current value saved.
(iii) The playouts are greedy, thus CSG-UCT cannot
work for model B.
Greedy playouts do not select the next state uni-
formly like random playouts, instead, they select
the state (merge the two coalitions C
1
and C
2
) that
will improve the coalition structure value the most:
argmax
C
1
,C
2
CS
v C
1
C
2
v C
1
v C
2
.
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation
61
3.3 Random Hill Climbing
Random Hill Climbing (RHC) is defined in (Pr
¨
antare
and Heintz, 2020). In this work, they compare a basic
version of MCTS against RHC and obtain better re-
sults with RHC. The authors compare the algorithms
over the Simultaneous Coalition Structure Generation
and Assignment (SCSGA) problem, which is an ex-
tension of CSG with an assignment problem. They
claim that an algorithm that can provide good results
on an instance of the SCSGA problem can also pro-
vide good results on a CSG instance, so we decided
to compare RHC against the other algorithms.
Algorithm 2: RHC algorithm.
Function RHC(b):
b-st RandomCoalitionStructure ;
while b not exhausted do
CS RandomCoalitionStructure ;
succes true;
while succes true and b not
exhausted do
success f alse;
for a in a
k
1
, . . . , a
k
n
do
i l such that a C
l
;
i
argmax
j 1,...,m i
∆
a
C
j
;
if
∆
a
C
i
a ∆
a
C
i
a
then
success true;
CS i CS i a ;
CS i CS i a ;
if b-st.score CS.score then
b-st CS ;
return b-st
RHC uses neither of the models (A or B). In-
stead, RHC starts from a randomly generated CS and
for each agent checks if swapping with any coali-
tion would increase the value of the CS, if so the
agent swaps coalitions with the one providing the
largest marginal contribution. If none of the agents
swapped to another coalition, the value is returned as
a potential optimal CS, and RHC is restarted from
another random CS until the budget b is exhausted.
The pseudo-code of RHC is available in Algorithm 2,
and has been modified to match the CSG formalism.
∆
a
C v C a v C is the marginal contribution
of agent a to the coalition C.
Algorithm 3: NMCS algorithm.
Function nmcs(c-st, l):
if l 0 then return Playout(c-st) ;
b-score ;
σ ;
ply 0;
while c-st is not terminal do
foreach move in M
c-st
do
n-st play c-st, move ;
score, σ nmcs ( n-st, l 1 );
if score b-score then
b-score score;
σ ply.. move σ;
next move σ ply ;
ply ply 1;
c-st play c-st, next move ;
return b-score, σ
3.4 NMCS
Nested Monte Carlo Search (NMCS) (Cazenave,
2009) is a Monte Carlo Search algorithm that recur-
sively calls a lower level of NMCS on each child state
of the current state. This lower level of NMCS allows
the algorithm to decide which move to choose next.
The lowest level of NMCS being a random playout.
The main improvement of NMCS is the memoriza-
tion of the best sequence at each recursion level.
NMCS is available in Algorithm 3 and in all our
experiments with NMCS we used a level l of 3.
3.5 LNMCS
The Lazy NMCS inherits its main features from the
NMCS, but solves an obstacle encountered for the
CSG problem. Calling a higher level NMCS (l 3)
yields better results. However, the cost of calling a
lower level l 1 NMCS on each of the resulting states
of the available actions can be prohibitive and some
of these actions produce subtrees doomed to produce
underwhelming results.
Therefore, we propose a new algorithm based on
NMCS named Lazy NMCS (LNMCS). LNMCS was
first proposed as a prototype and applied to the HP-
model for protein folding (Roucairol and Cazenave,
2023), this new version corrects some flaws of the
prototype such as the separation between evaluation
and pruning. LNMCS works the same as NMCS with
the following exceptions (i) before expanding a state,
we compute the mean of each available action by
launching b playouts (ii) we update a dynamic thresh-
old relative to the depth of the current state (iii) we
compare the score of each child to the threshold, if
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
62

the score is below the threshold, the node is pruned.
The pseudocode of LNMCS is available in Algo-
rithm 4 and you can find each part of this process
marked in the pseudocode.
In addition to past notation, we are using r as the
ratio to the threshold a state will be pruned, e is the
number of possible moves we will focus on in case
there are too many moves, and, as in NMCS, l is the
nesting level. tr is a list of tuples containing the mean
value and the number of experiments made to con-
tribute to that value in order to compute the mean eas-
ily. trmax keeps in memory the best evaluation for
each level of depth. randomSample M
state
, e ran-
domly selects e actions from the moves from state if
there is too many available actions.
See Figure 3 for a graphic description of LNMCS,
subtrees are sampled and the underperforming ones
are pruned.
5
3
6
2
2
18
21
18
20
19 19
21
22
19
21
...
...
...
...
...
...
level n
level n-1
Figure 3: Level n LNMCS pruning a search subtree and
launching n-1 LNMCS on surviving search subtrees.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Experimental Setup
To refer to our models-algorithms combinations, we
use the following notations:
C
A
: model A CSG-UCT, C 1
L
A
: model A LNMCS, r 0, b 2, l 5, e 10
N
A
: model A NMCS, l 3
U
A
: model A UCT, C 1
L
B
: model B LNMCS, r 0, b 2, l 5, e 10
F
B
: (Full action space) model B LNMCS, r 0.9,
b 2, l 5, e 100
N
B
: model B NMCS, l 3
U
B
: model B UCT, C 1
L
G
: model A LNMCS with greedy playouts, r
0, b 1, l 5, e 10
N
G
: model A NMCS with greedy playouts, l 3
R: RHC
To compare these algorithms, we launched 100 in-
stances of the CSG problem with 100 agents with a
time budget of 100 seconds on four benchmarks.
Algorithm 4: LNMCS algorithm.
tr ;
trmax ;
Function lnmcs(c-st, l, b, r, e):
if l 0 then return Playout(c-st) ;
b-score ;
σ ;
ply 0;
while c-st is not terminal do
budget moves
randomSample M
c-state
, e
candidates ;
d c-st.nbplay;
/* d: number of moves played
from initial state */
foreach move in budget moves do
n-st play c-st, move ;
ev 0.0;
/* (i) */
for in 0..b do
plsc, plsq
Playout(n-st);
if score b-score then
b-score plsc;
σ ply.. move plsq;
ev ev plsc;
n n 1;
candidates. push ev, move ;
/* (ii) */
if tr.length d 1 then
tr. push val : 0.0, n : 0 ;
trmax. push ev ;
tr d .val
tr d .val tr d .n ev
tr d .n 1
;
tr d .n tr d .n 1 ;
if trmax d
ev
n
then
trmax d
ev
n
;
/* (iii) */
foreach can in candidates do
nl l 1;
if can 0
tr d r trmax d tr d
then nl 0 ;
score, σ
lnmcs(play(c-st, can[1]), nl, p);
if score b-score then
b-score score;
σ ply.. can 1 σ;
next-move σ ply ;
ply ply 1;
c-st play c-st, next-move
return b-score, σ ;
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation
63
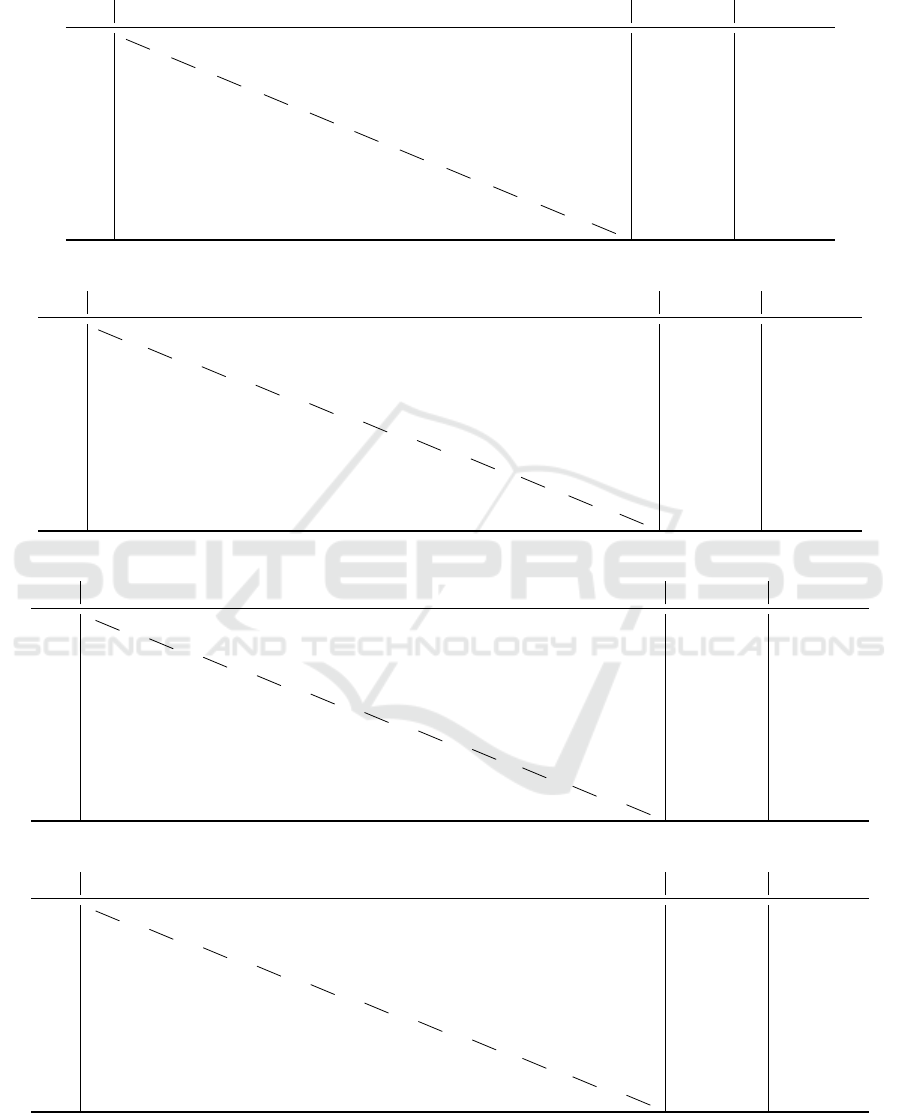
Table 1: The uncurated data, number of times the algorithm from a line beats the algorithm from a column over 100 experi-
ments.
C
A
L
A
N
A
U
A
L
B
F
B
N
B
U
B
L
G
N
G
R total wins Copeland
C
A
36 53 82 6 24 97 74 13 39 100 524 538.5
L
A
63 60 83 22 45 97 81 39 65 100 655 661.5
N
A
46 38 67 16 30 97 73 24 39 100 530 537.5
U
A
18 16 32 3 14 89 46 9 16 100 343 347.5
L
B
94 76 83 95 77 99 94 74 92 100 884 892
F
B
74 53 66 83 16 97 84 43 64 100 680 690
N
B
3 3 3 11 1 3 8 1 1 100 134 134
U
B
24 15 24 48 4 12 92 8 24 100 351 361.5
L
G
81 60 75 91 26 55 99 90 77 100 754 767
N
G
48 35 61 84 8 33 99 75 16 100 559 570.5
R 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
(a) Uniform benchmark with 100 agents.
C
A
L
A
N
A
U
A
L
B
F
B
N
B
U
B
L
G
N
G
R total wins Copeland
C
A
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 36 94 100 930 930
L
A
0 40 100 100 100 100 100 0 0 9 549 549
N
A
0 60 99 99 99 99 100 0 0 27 583 583
U
A
0 0 1 86 38 100 100 0 0 0 225 325
L
B
0 0 1 14 1 99 100 0 0 0 215 215
F
B
0 0 1 62 99 100 100 0 0 0 362 362
N
B
0 0 1 0 1 0 100 0 0 0 102 102
U
B
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
L
G
64 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 94 100 958 958
N
G
6 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 6 100 812 812
R 0 91 73 100 100 100 100 100 0 0 664 664
(b) Gaussian benchmark with 100 agents.
C
A
L
A
N
A
U
A
L
B
F
B
N
B
U
B
L
G
N
G
R total wins Copeland
C
A
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0 73 100 873 873
L
A
0 84 100 97 93 100 100 0 0 3 577 577
N
A
0 16 92 39 31 48 94 0 0 4 324 324
U
A
0 0 8 0 0 0 45 0 0 0 53 53
L
B
0 3 61 100 39 82 100 0 0 1 386 386
F
B
0 7 69 100 61 94 100 0 0 2 433 433
N
B
0 0 52 100 18 6 100 0 0 1 277 277
U
B
0 0 6 55 0 0 0 0 0 0 61 61
L
G
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 1000 1000
N
G
27 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0 100 827 827
R 0 97 96 100 99 98 99 100 0 0 689 689
(c) Agent based benchmark with 100 agents.
C
A
L
A
N
A
U
A
L
B
F
B
N
B
U
B
L
G
N
G
R total wins Copeland
C
A
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0 85 100 885 885
L
A
0 79 100 98 87 100 100 0 0 2 566 566
N
A
0 21 95 37 33 43 94 0 0 2 325 325
U
A
0 0 5 0 0 0 53 0 0 0 58 58
L
B
0 2 63 100 33 91 100 0 0 0 389 389
F
B
0 13 67 100 67 94 100 0 0 1 442 442
N
B
0 0 57 100 8 6 100 0 0 1 272 272
U
B
0 0 6 47 0 0 0 0 0 0 53 53
L
G
100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 1000 1000
N
G
15 100 100 100 100 100 100 100 0 100 815 815
R 0 98 98 100 100 99 100 100 0 0 695 695
(d) NDCS benchmark with 100 agents.
For example, L
B
beats N
A
83 times out of 100 with 1 ex-aequo on the uniform benchmark, and F
B
beats U
A
62
times out of 100 with no ex-aequo on the gaussian benchmark.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
64

As the CS values of an instance of the problem
are randomly initialized, we decide to compare the
result by measuring the number of times an algorithm
is better than another on each of the 100 instances.
The average performances and the standard devi-
ation are vulnerable to differences among the 100 dif-
ferent synthetic problem instances we used i.e., when
the standard deviation does not go below 0.5 on the
gaussian benchmark, it is in part due to the optimal
structure score having a standard deviation of about
0.5 over the 100 instances.
We chose to compare our algorithms on four coali-
tion value distributions/benchmarks from the litera-
ture:
• Uniform first used in (Larson and Sandholm,
1999) i.e., v C U 0, C .
• Normal or Gaussian first used in (Rahwan et al.,
2007a) i.e., v C N 10 C , 0.1 , σ 0.1 being
the standard deviation.
• Agent based first used in (Rahwan et al., 2021)
i.e., v C
a C
U 0, p
a
where p
a
U 0, 1 is
the power of an agent and is fixed on start..
• NDCS first used in (Rahwan et al., 2009) i.e.,
v C N C , C , σ C being the stan-
dard deviation.
The experiments were made with Rust 1.59, on
an Intel Core i7-11850H 2.50GHz using a single core
(but parallel processing is very accessible). We use a
random generator with a set seed as our value func-
tion, and the values of each coalition are only pro-
duced once on demand by the random generator and
then stored in a hashmap for later use. The raw results
are available in Table 1.
4.2 Raw Results
As observed in Table 1, on the uniform benchmark,
the LNMCS with model B significantly outperforms
all of the other algorithms, with the greedy LNMCS
coming in second place. Surprisingly, CSG-UCT did
not perform very well and was only able to outper-
form UCTs and NMCS. On the Gaussian, NDCS,
and agent-based benchmarks, the difference is even
greater with the greedy LNMCS, being close to 100
wins each time against each of the other algorithms.
By calculating confidence intervals, we can assert
with a confidence of 95% that one method is superior
to another only if that method wins at least 60 times
out of 100, and with a confidence of 99% if it wins
at least 63 times. LNMCS outperforms other meth-
ods significantly. The only duel that would leave any
doubts about the performances of the LNMCS is the
one between the greedy LNMCS and CSG-UCT on
the Gaussian benchmark. We decided to run 100 ad-
ditional experiments (seeds 100 to 199), and obtained
62 wins for the greedy LNMCS and 38 for CSG-UCT.
These experiments give a 0.99% certitude that the A
LNMCS is at least slightly superior to the A CSG-
UCT on the Gaussian benchmark. We think this per-
formance can be explained by the fixed variance of
the Gaussian coalition value function and does not fa-
vor larger coalitions. Since UCT explores from the
root every time it is advantaged at finding small but
high-value coalitions.
In the next sections, we analyze the performances
of each algorithm relative to the others and explain
these results.
4.2.1 Playout Choice
MCTS/UCT generally uses a random playout, how-
ever, the CSG-UCT algorithm uses a strictly greedy
playout. The authors of CSG-UCT (Wu and Ram-
churn, 2020) did not compare the impact of using a
different playout. We propose to look into the effects
of the playout type, both for UCT and for the other
algorithms.
By looking at the results from the uniform bench-
mark in Table 1 (a), we can observe that C
A
out-
performs U
A
(CSG-UCT is comparable to UCT with
greedy playouts) with 82 wins, L
G
performs better
than L
A
with 60 wins and N
G
performs better than N
A
with 61 wins.
On the Gaussian, NDCS, and agent-based bench-
marks, the results show that the performance of the
greedy is further enhanced, to such an extent that the
greedy playout does not lose a single time against a
random playout.
While the greedy playouts seem more effective,
retrieving the values of all the possible child CS (up
to 4950 with model A) can be costly and slows down
the playouts. It is the most resource-consuming part
of all of these algorithms.
4.2.2 Model Choice
Model B (random playouts only) provides superior re-
sults on the uniform benchmark with the LNMCS, be-
ing able to outperform the LNMCS on model A with
greedy playouts and with random playouts. However,
it provides far inferior results on the other benchmark.
We think it’s due to the other benchmarks favoring
trying as many coalitions as possible, which model
B can not do since it only returns the terminal CS. It
however proves the interest of trying new representa-
tions of the problem.
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation
65

4.2.3 Algorithm Family Choice
With regard to the choice of the type of algorithm,
the nested family is overall preferable to the MCTS
family on the CSG problem, especially with LN-
MCS which dominates in every benchmark. From the
MCTS family, we observe overall great performances
with the CGT-UCT except on the uniform benchmark.
Precisely, we observe the following dominance or-
ders:
Uniform: L
B
L
G
F
B
L
A
C
A
others
Gaussian: L
G
C
A
N
G
R N
A
others
Agent-based: L
G
C
A
N
G
R L
A
others
NDCS: L
G
C
A
N
G
R L
A
others
4.2.4 Discussion: The Benchmark Problem
As you can see in Table 1 (b, c, d), and in the pre-
vious observations, most random playout based al-
gorithms perform poorly compared to their greedy
playout-based versions on the Gaussian, agent-based,
and NDCS benchmarks. We can notice that this is not
the case for Sandholm’s initial uniform benchmark.
To understand why, we computed the optimal
coalitions for instances of the problem with 15 agents
using an exact algorithm, and then compared the
CSG-UCT to a BEAM search with a width of 10.
On such small instances of the problem, the BEAM
search returned the optimal value, slightly higher or
equal to the value returned by CSG-UCT.
We tried various other benchmarks such as Sand-
holm’s second uniform benchmark, where the value
of a coalition is sampled uniformly between 0 and 1
regardless of its size (Sandholm et al., 1999). It turns
out that every benchmark other than Sandholm’s first
uniform greatly favors greedy playouts and gives sim-
ilar results to the Gaussian benchmark. It is the main
reason why we decided to experiment on only 3 of the
benchmarks introduced by Rahwan.
Alternatively, the RHC algorithm which consists
of a greedy playout stopping at the first local max-
imum and starting from a randomly initialized state
outperforms the random playouts-based state of the
art machine learning algorithms on the agent-based,
NDCS, and Gaussian distributions. For these distribu-
tions, a single greedy playout is much better than al-
gorithms using random playouts. That result leads us
to question the interest of these distribution, and oth-
ers introduced by Rahwan, as their introduction was
never justified in the first place and their number is
getting out of hand.
As shown in Table 1, replacing LNMCS random
playouts with greedy playouts is enough to outper-
form the current state-of-the-art algorithms.
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this paper, we proposed to analyze Nested Monte
Carlo based algorithms for the CSG problem. We
present a new algorithm called Lazy Nested Monte
Carlo Search which answers some of NMCS’s short-
comings. In addition, we present a new model repre-
sentation of CSG which allows us to strongly reduce
the number of actions at the beginning of the search.
Our new algorithm is able to outperform the pre-
vious state-of-the-art algorithms on all of the main
coalition value distributions we experienced upon.
We also proposed a new modelization of the search
tree that provides better results over the initial uni-
form distribution.
In future works, we may aim at:
(i) Finding real-life coalition value distributions to
compare algorithms on real problems. In this work,
we have been assuming that coalition values are not
affected by other coalitions. In many realistic set-
tings, such as in the Partition Function Games (PFG)
formalism (Thrall and Lucas, 1963), this property is
not satisfied. Another task will be to extend our work
to probabilistic CSG (Schwind et al., 2021).
(ii) Proposing a new coalition value distribution
that is resistant to the greedy playouts approach to fur-
ther the CSG problem.
You can access our implementation
as well as the result files containing the
value improvements and their timestamps at
https://github.com/RoucairolMilo/coalition.
REFERENCES
Aziz, H. and de Keijzer, B. (2011). Complexity of coalition
structure generation.
Bouzy, B. (2014). Monte-Carlo Fork Search for Coopera-
tive Path-Finding. In Cazenave, T., Winands, M. H.,
and Iida, H., editors, Computer Games, pages 1–15,
Cham. Springer International Publishing.
Browne, C. B., Powley, E., Whitehouse, D., Lucas, S. M.,
Cowling, P. I., Rohlfshagen, P., Tavener, S., Perez, D.,
Samothrakis, S., and Colton, S. (2012). A Survey of
Monte Carlo Tree Search Methods. IEEE Trans. Com-
put. Intell. AI Games, 4(1):1–43.
Cazenave, T. (2009). Nested Monte-Carlo Search. In
Boutilier, C., editor, IJCAI, pages 456–461.
Cazenave, T. and Fournier, T. (2020). Monte Carlo inverse
folding. In Monte Carlo Search at IJCAI.
Cazenave, T., Negrevergne, B., and Sikora, F. (2020).
Monte Carlo graph coloring. In Monte Carlo Search
at IJCAI.
ICAART 2024 - 16th International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
66

Cazenave, T., Saffidine, A., Schofield, M. J., and
Thielscher, M. (2016). Nested monte carlo search for
two-player games. In AAAI, pages 687–693.
Cechl
´
arov
´
a, K., Romero-Medina, A., et al. (2001). Stability
in coalition formation games. International Journal of
Game Theory, 29(4):487–494.
Genheden, S., Thakkar, A., Chadimov
´
a, V., Reymond, J.-L.,
Engkvist, O., and Bjerrum, E. (2020). AiZynthFinder:
a fast, robust and flexible open-source software for
retrosynthetic planning. Journal of Cheminformatics,
12(1):70.
Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A., Green, T., Figurnov,
M., Ronneberger, O., Tunyasuvunakool, K., Bates, R.,
ˇ
Z
´
ıdek, A., Potapenko, A., Bridgland, A., Meyer, C.,
Kohl, S. A. A., Ballard, A. J., Cowie, A., Romera-
Paredes, B., Nikolov, S., Jain, R., Adler, J., Back, T.,
Petersen, S., Reiman, D., Clancy, E., Zielinski, M.,
Steinegger, M., Pacholska, M., Berghammer, T., Bo-
denstein, S., Silver, D., Vinyals, O., Senior, A. W.,
Kavukcuoglu, K., Kohli, P., and Hassabis, D. (2021).
Highly accurate protein structure prediction with Al-
phaFold. Nature, 596(7873):583–589.
Larson, K. S. and Sandholm, T. W. (1999). Anytime coali-
tion structure generation: an average case study. In
Proceedings of the third annual conference on Au-
tonomous Agents, pages 40–47.
Mauro, N. D., Basile, T., Ferilli, S., and Esposito, F. (2010).
Coalition structure generation with grasp. In Interna-
tional Conference on Artificial Intelligence: Method-
ology, Systems, and Applications, pages 111–120.
Springer.
M
´
ehat, J. and Cazenave, T. (2010). Combining UCT and
Nested Monte Carlo Search for single-player general
game playing. IEEE Transactions on Computational
Intelligence and AI in Games, 2(4):271–277.
Portela, F. (2018). An unexpectedly effective Monte
Carlo technique for the RNA inverse folding problem.
BioRxiv, page 345587.
Poulding, S. M. and Feldt, R. (2014). Generating structured
test data with specific properties using nested Monte-
Carlo search. In GECCO, pages 1279–1286.
Poulding, S. M. and Feldt, R. (2015). Heuristic model
checking using a Monte-Carlo tree search algorithm.
In GECCO, pages 1359–1366.
Pr
¨
antare, F., Appelgren, H., and Heintz, F. (2021). Anytime
heuristic and monte carlo methods for large-scale si-
multaneous coalition structure generation and assign-
ment. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Ar-
tificial Intelligence, volume 35, pages 11317–11324.
Pr
¨
antare, F. and Heintz, F. (2020). An anytime algorithm
for optimal simultaneous coalition structure genera-
tion and assignment. Autonomous Agents and Multi-
Agent Systems, 34(1):1–31.
Rahwan, T., Michalak, T., and Jennings, N. (2021). A hy-
brid algorithm for coalition structure generation. Pro-
ceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelli-
gence, 26(1):1443–1449.
Rahwan, T., Michalak, T. P., Wooldridge, M., and Jennings,
N. R. (2015). Coalition structure generation: A sur-
vey. Artificial Intelligence, 229:139–174.
Rahwan, T., Ramchurn, S. D., Dang, V. D., Giovannucci,
A., and Jennings, N. R. (2007a). Anytime optimal
coalition structure generation. In AAAI, volume 7,
pages 1184–1190.
Rahwan, T., Ramchurn, S. D., Dang, V. D., and Jennings,
N. R. (2007b). Near-optimal anytime coalition struc-
ture generation. In IJCAI, volume 7, pages 2365–
2371.
Rahwan, T., Ramchurn, S. D., Jennings, N. R., and Giovan-
nucci, A. (2009). An anytime algorithm for optimal
coalition structure generation. Journal of artificial in-
telligence research, 34:521–567.
Roucairol, M. and Cazenave, T. (2022). Refutation of spec-
tral graph theory conjectures with monte carlo search.
In COCOON 2022.
Roucairol, M. and Cazenave, T. (2023). Solving the
hydrophobic-polar model with nested monte carlo
search. In International Conference on Computational
Collective Intelligence, pages 619–631. Springer.
Sandholm, T., Larson, K., Andersson, M., Shehory, O., and
Tohm
´
e, F. (1999). Coalition structure generation with
worst case guarantees. Artificial intelligence, 111(1-
2):209–238.
Schwind, N., Okimoto, T., Inoue, K., Hirayama, K.,
Lagniez, J.-M., and Marquis, P. (2021). On the
computation of probabilistic coalition structures. Au-
tonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 35(1):1–
38.
Sen, S. and Dutta, P. S. (2000). Searching for optimal coali-
tion structures. In Proceedings Fourth International
Conference on MultiAgent Systems, pages 287–292.
IEEE.
Shoham, Y. and Leyton-Brown, K. (2008). Multiagent sys-
tems: Algorithmic, game-theoretic, and logical foun-
dations. Cambridge University Press.
Silver, D., Hubert, T., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou, I., Lai,
M., Guez, A., Lanctot, M., Sifre, L., Kumaran, D.,
Graepel, T., Lillicrap, T., Simonyan, K., and Hass-
abis, D. (2018). A general reinforcement learning
algorithm that masters chess, shogi, and Go through
self-play. Science, 362(6419):1140–1144.
Silver, D., Hubert, T., Schrittwieser, J., Antonoglou, I., Lai,
M., Guez, A., Lanctot, M., Sifre, L., Kumaran, D.,
Graepel, T., Lillicrap, T. P., Simonyan, K., and Hass-
abis, D. (2017). Mastering Chess and Shogi by Self-
Play with a General Reinforcement Learning Algo-
rithm. ArXiv, abs/1712.01815.
Thrall, R. M. and Lucas, W. F. (1963). N-person games
in partition function form. Naval Research Logistics
Quarterly, 10:281–298.
Wu, F. and Ramchurn, S. D. (2020). Monte-carlo tree search
for scalable coalition formation. In Proceedings of the
29th International Joint Conference on Artificial In-
telligence (IJCAI), pages 407–413, Yokohama, Japan.
Yun Yeh, D. (1986). A dynamic programming approach to
the complete set partitioning problem. BIT Numerical
Mathematics, 26(4):467–474.
Lazy Nested Monte Carlo Search for Coalition Structure Generation
67
