
Deep Q-Networks for Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware Classification
Antonio Maci
a
, Giuseppe Urbano
b
and Antonio Coscia
c
Cybersecurity Laboratory, BV TECH S.p.A., Milan, Italy
Keywords:
Malware, Application Programming Interface, Imbalanced Data Classification, Deep Reinforcement Learning.
Abstract:
Nowadays, defending against malware-induced computer infections represents a key concern for both individ-
uals and companies. Malware detection relies on analyzing the static or dynamic features of a file to determine
whether it is malicious or not. In the case of dynamic analysis, the sample behavior is examined by performing
a thorough inspection, such as tracking the sequence of functions, also called Application Programming Inter-
faces (APIs), executed for malicious purposes. Current machine learning paradigms, such as Deep Learning
(DL), can be exploited to develop a classifier capable of recognizing different categories of malicious software
for each API flow. However, some malware families are less numerous than others, leading to an imbalanced
multi-class classification problem. This paper compares Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) algorithms that
combine Reinforcement Learning (RL) with DL models to deal with class imbalance for API-based malware
classification. Our investigation involves multiple configurations of Deep Q-Networks (DQNs) with a proper
formulation of the Markov Decision Process that supports cost-sensitive learning to reduce bias due to ma-
jority class dominance. Among the algorithms compared, the dueling DQN showed promising macro F1 and
area under the ROC curve scores in three test scenarios using a popular benchmark API call dataset.
1 INTRODUCTION
Despite the development of sophisticated defense and
protection methods, malware remains the most rel-
evant cyber threat because it is the main cause of
computer network infections. Malware analysis is
generally divided into static and dynamic categories,
which can be leveraged to combat malware prolifera-
tion (Aboaoja et al., 2022). Although advances have
been made in the field of static analysis, such as in
detecting metamorphic (Coscia et al., 2023) malware,
the study of the actual behavior enacted by malicious
software requires a more detailed analysis. Dynamic
analysis allows the observation of the behavior of a
malicious sample executed in a simulated and pro-
tected environment, called sandbox. Deep Learning
(DL) exhibited promising results in dynamic analy-
sis tasks, such as identifying malicious files based on
the sequence of Application Programming Interfaces
(APIs) called during its execution, which are repre-
sentative of the exact malicious goal of the running
sample. The results obtained emphasize the effective-
ness of this paradigm in malware classification tasks,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6526-554X
b
https://orcid.org/0009-0004-7954-5296
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7263-4999
especially when different malware families must be
classified, i.e., in multi-class classification problems
(Lu and Shetty, 2021). However, data referring to dif-
ferent classes usually suffer from class imbalance be-
cause malicious samples are scarce for certain fami-
lies, whereas they are plentiful for others (Demirkıran
et al., 2022). Hence, it is desirable to develop DL
models capable of dealing with class skew, i.e., cost-
sensitive approaches that do not require support meth-
ods such as data-level sampling algorithms. In fact,
the latter methods can alter the distribution of the
original data, i.e., the representation of a real-world
scenario. In the domain of DL, Deep Reinforcement
Learning (DRL) has emerged as a promising area to
inspect for the implementation of advanced threat de-
tection approaches, as recent studies highlight its ef-
fectiveness in addressing the most relevant network
intrusion problems (Sewak et al., 2023). Its popularity
grew because of its flexibility in modeling problems
addressed by accurately setting the so-called Markov
Decision Process (MDP). In this regard, the MDP for-
mulation proposed in (Lin et al., 2020) enables DRL
to deal with imbalanced classification problems. Con-
sequently, it is possible to design a DRL classifier ca-
pable of tackling skewed cyber threat detection tasks
(Maci et al., 2023).
342
Maci, A., Urbano, G. and Coscia, A.
Deep Q-Networks for Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware Classification.
DOI: 10.5220/0012303800003648
In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy (ICISSP 2024), pages 342-349
ISBN: 978-989-758-683-5; ISSN: 2184-4356
Copyright © 2024 by Paper published under CC license (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0)

This paper analyzes the performance of several
DRL-based classifiers capable of dealing with unbal-
anced data according to the MDP formulation pre-
sented in (Yang et al., 2022). As DRL agents,
we examine the classic Deep Q-Network (DQN)
model (Mnih et al., 2015) and its double-Q-learning-
based extension, i.e., the Double Deep Q-Network
(DDQN) (Hasselt et al., 2016). Then, each has
been evaluated when equipped with state-of-the-art
DRL techniques, namely, the dueling network design
(Wang et al., 2016), the Prioritized Experience Re-
play (PER) (Schaul et al., 2016), and Noisy Networks
(NoisyNets) for exploration (Fortunato et al., 2019).
The main contributions of this study can be sum-
marized as follows:
• It presents a comprehensive investigation of DRL-
based algorithms capable of tackling the problem
of multi-class malware classification in the case of
unbalanced data.
• It provides a benchmark analysis to highlight the
effectiveness and robustness of the algorithms ex-
amined with respect to the scarcity of samples in
minority classes.
The remainder of this manuscript is organized as
follows. The literature survey related to our study is
discussed in Section 2. Section 3 provides the under-
lying theory of the DRL field and focuses on the main
concepts used in this paper. The formulation of the
MDP tuple pertinent to this study is presented in Sec-
tion 4. Section 5 describes the experimental plan and
discusses the results. Finally, the main findings and
potential future directions are outlined in Section 6.
2 RELATED WORK
2.1 Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware
Classification
The random oversampler (ROS) technique proved to
be the best solution among the approaches compared
in (Alzammam et al., 2020) to address class imbal-
ance. In such an evaluation, the adjusted dataset was
used to train a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
model to classify several malware categories using
three different datasets. In (Akarsh et al., 2019),
the authors propose a combination of two DL algo-
rithms, i.e., a CNN and an Long Short Term Memory
(LSTM), for classifying malware images belonging to
twenty-five different malware families. Furthermore,
the proposed CNN-LSTM cost function is updated to
realize a cost-sensitive approach capable of address-
ing class imbalance, thus driving learning in favor of
minority classes. In (Ding et al., 2020), the prob-
lem of classifying nine different malware families in
an imbalanced dataset is approached by deploying a
self-attention mechanism. In (Catak et al., 2021), an
augmented-CNN based malware classification is pre-
sented. Data augmentation is realized by leveraging
additive noise techniques such as Laplace, Gaussian,
and Poisson noises. Given a specific noise ratio, in-
creasing training samples in such a way addresses
class imbalance and improves the performance of a
CNN in classifying seven different malware families.
In (Lu and Shetty, 2021), the class skew is addressed
using a random undersampler (RUS) strategy. The au-
thors then evaluated the classification performance of
a deep residual network (ResNet-18) by varying the
last layer, i.e., classifying the extracted tensors using
three traditional Machine Learning (ML) models in-
stead of a softmax layer. In (Demirkıran et al., 2022),
the authors address the class skew of the training data
using bootstrap sampling. The adjusted training sets
are then used to fine-tune Bidirectional Encoder Rep-
resentations from Transformers (BERT) and Charac-
ter Architecture with No tokenization In Neural En-
coders (CANINE) pre-trained models. These were
compared with a bagging-based ensemble model pro-
posed by the authors on three different unbalanced
state-of-the-art datasets.
2.2 Deep Reinforcement Learning for
Malware Analysis
In the cyber security domain, several DRL algo-
rithms have been implemented to propose or improve
network malware detection solutions (Sewak et al.,
2023). In (Fang et al., 2019a), a DQN-based approach
is leveraged to select static features for malware de-
tection purposes. In this scenario, the actions per-
formed by the agent select a set of minimal features
to improve the performance of traditional ML clas-
sifiers. Analogously, in (Wu et al., 2023), a DDQN
agent is exploited for feature selection, showing a
significant performance improvement in the Android
malware detection task when shallow learning algo-
rithms are adopted as classifiers. In (Wang et al.,
2019), a DRL agent is trained to stop the execution
of a dynamically analyzed unknown sample to im-
prove the classification accuracy of the analysis. In
(Fang et al., 2019b), a DQN-based approach is used
to evade malware detection techniques. In particular,
the agent initially analyzes the sample to determine
the sequence of actions that lead to malware meta-
morphosis, preserving its malicious objective while
evading the target scanner. Using the policy learned
by the agent, the escaped detector can be strength-
Deep Q-Networks for Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware Classification
343

ened. The same objective is achieved in (Wang et al.,
2020) by employing a modified version of an actor
critic agent to predict when behavior analysis should
be suspended. In (Song et al., 2022), a Reinforcement
Learning (RL)-based framework has been proposed
to generate adversarial malware examples capable of
evading state-of-the-art ML classifiers and antivirus
engines. A similar approach is presented in (Ander-
son et al., 2018), which uses a DQN agent to iden-
tify the set of actions that lead to the generation of
new evasive malware samples. In (Deng et al., 2023),
a DDQN agent is used to detect potentially different
ransomware variants based on static features of the
file header. In (Birman et al., 2022), the authors em-
ploy an actor critic architecture with an experience re-
play agent to optimally schedule the use of classifiers
in the ensemble learning model, converting a single-
step classification problem into sequential decision-
making addressed through DRL.
3 BACKGROUND
In the RL area, an agent learns a policy π taking ac-
tion on an environment through a trial-and-error strat-
egy in discrete time steps. In such a phase, namely
training, the agent gains the ability to perform a de-
sired task by opportunely setting the environment us-
ing the MDP tuple < S, A, f
R
, φ,ζ >, where: S and
A represent the observation and action spaces, re-
spectively; f
R
(a
t
, s
t
) is the reward function yielding
in a scalar R
t
that the environment returns to assess
the effectiveness of the action taken by the agent;
φ : S × A × S → [0, 1] is a probability function, deter-
mining s
t+1
given s
t
and a
t
; ζ ∈ [0,1] is a weighting
parameter, called the discount factor. Training usually
involves many episodes (|E |). During this phase, the
goal is to learn π that can maximize the Q-function
Q(s
t
, a
t
) = E[
∑
∞
j=0
ζ
j
R
t+ j+1
] for each observation (or
state) in S and for each action in A. In some real-
world applications, S × A is very large depending on
the problem faced, leading to the use of estimators for
Q(s
t
, a
t
). For this purpose, DRL involves Deep Neu-
ral Networks (DNNs) so that Q(s
t
, a
t
) ∼ Q(s
t
, a
t
, θ)
with θ DNN weights.
3.1 Deep Q-Network
The DQN (Mnih et al., 2015) represents a classical
DRL algorithm that introduces two novel elements:
(i) a replay memory B that stores the so-called experi-
ence tuples (T =< s
t
, a
t
, s
t+1
, f
R
(s
t
, a
t
), ξ
t
>), where
ξ
t
determines whether s
t
is terminal; (ii) a target net-
work (
ˆ
Q) structured as the main network. This sec-
ond DNN estimates the target value to be compared
with Q(s
t
, a
t
, θ) in the calculation of the loss function
L
DQN
(θ) = E[(y
DQN
t
− Q(s
t
, a
t
, θ))
2
], where:
y
DQN
t
= R
t
+ ζmax
a∈A
ˆ
Q(s
t+1
, a, θ
−
) (1)
Although the target network is equivalent to the
main network, its parameter vector (θ
−
) is updated
with the main network parameters (θ) every τ steps.
In contrast, the main network parameters are updated
using a mini-batch (b) of tuples randomly sampled
from B according to a probability function. However,
DQN suffers from overestimation because action se-
lection and evaluation are not decoupled during the
computation of the target value.
3.2 Double Deep Q-Network
The DDQN algorithm (Hasselt et al., 2016) primar-
ily aims to reduce the overestimation problem en-
countered in DQN. Although the DDQN algorithm
uses the same elements introduced in DQN, it over-
comes overoptimistic value estimations by computing
the target as follows:
y
DDQN
t
= R
t
+ ζ
ˆ
Q(s
t+1
, arg max
a∈A
Q(s
t+1
, a, θ
t
), θ
−
t
)
(2)
Action selection is independent of its evaluation,
since the main network selects the best action in the
next state, whereas the target network estimates the
value of this action.
3.3 Dueling Network
Recall that the Q-function determines whether select-
ing an action is a good decision when the agent is in a
given state. In the field of RL, two other functions can
be introduced: (i) the value V
π
(s) = E
a∼π(s)
[Q
π
(s, a)]
to describe the quality of being in a particular state;
(ii) the advantage A
π
adv
(s, a) = Q
π
(s, a) −V
π
(s) to de-
termine the relative importance of each action. In
(Wang et al., 2016), the authors argued that determin-
ing the value of each action choice was significant in
some states and irrelevant in others. Therefore, they
provided a novel DNN design, known as the dueling
network, which separately computes the value and ad-
vantage functions to derive Q:
Q(s, a, θ, γ, ω) = V (s, θ, ω) + (A
adv
(s, a, θ, γ)−
1
|A|
∑
a
′
∈A
A
adv
(s, a
′
, θ, γ)) (3)
where the last hidden layer of the original DNN
consists of two parallel sub-networks with vector
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
344

parameters ω and γ, so that one outputs a scalar
V (s, θ, ω) and the other outputs a vector of |A| size,
i.e., A
adv
(s, a, θ, γ) (Wang et al., 2016).
3.4 Prioritized Experience Replay
Because of the usage of B in both DQN and DDQN,
stored experiences can be used repeatedly to learn
from. However, some experience tuples (or transi-
tions) can result in a more effective learning pro-
cess than others. In (Schaul et al., 2016), the pri-
oritization of these transitions is achieved by intro-
ducing the PER technique that exploits the temporal
difference (TD) error to assess the importance of a
generic T
i
. For DQN, this can be expressed as δ
DQN
i
=
R
t
+ ζ max
a∈A
ˆ
Q(s
t+1
, a, θ
−
) − Q(s
t
, a
t
, θ). The prior-
ity can be assigned using the following two distinct
strategies: (i) a rank-based method, i.e., ι
i
=
1
rank(t)
;
(ii) a proportional variant, i.e., ι
i
= |δ
i
| + κ, where
κ is a small value that ensures the selection of sam-
ples with a non-zero probability. To correctly sample
each transition, the calculated priority is normalized
by considering the maximum priority of any prior-
ity so far, determining the probability of being sam-
pled P(i) =
ι
ν
i
∑
z
ι
ν
z
where ν defines a trade-off between
taking only transitions with high priority and random
sampling (for ν = 0, the probability distribution de-
generates into uniform sampling). To ensure learn-
ing stability, importance sampling weights are used
so that each transition assumes the following final im-
portance score during sampling w
i
=
1
|B|
·
1
P(i)
β
. β
increases linearly over time to reach the unit value
at the end of the learning. This hyperparameter in-
teracts with the prioritization exponent ν, since in-
creasing both simultaneously intensifies prioritization
while simultaneously correcting importance sampling
more strongly. Thus, w
i
is multiplied by δ
i
, and the
result is fed into the Q-learning update.
3.5 Noisy Networks for Exploration
Typically, the above-cited DRL agents take advan-
tage of the ε-greedy (with the progressive decay of
ε) exploration policy. In particular, instead of rig-
orously following the learned policy, the agent takes
random action with probability ε. In (Fortunato et al.,
2019), an alternative strategy is presented, namely
the NoisyNet, i.e., a method that adds noise to the
last fully-connected DNN layers. Thus, the explo-
ration phase is assisted by the perturbation of the vec-
tor θ
def
= µ + Σ ⊙ χ. Considering a DNN linear layer
(y = wx + q) with d inputs and p outputs, the corre-
sponding noisy linear layer is defined as y = (µ
w
+
σ
w
⊙ χ
w
)x + µ
q
+ σ
q
⊙ χ
q
where: (i) µ
w
, σ
w
∈ R
p×d
and µ
q
, σ
q
∈ R
p
represent the learnable parameters
that generate the set ∆
def
= (µ, Σ); (ii) χ
w
∈ R
p×d
and
χ
q
∈ R
p
are random noise variables. This leads to
an update of the DNN loss function, which becomes
¯
L
D(D)QN
(∆)
def
= E[L
D(D)QN
(θ)]. Consequently, the
optimization considers the parameter ∆ over the noise
χ. For example, in the case of DQN, Eq. (1) becomes:
y
NoisyNet−DQN
t
= R
t
+ ζmax
a∈A
ˆ
Q(s
t+1
, a, ∆
−
, χ
′
) (4)
as well as the main network estimates Q(s
t
, a
t
, χ, ∆).
Note that the main and target DNNs are character-
ized by independent noise; therefore, there is no bias
caused by noise correlation.
4 ENVIRONMENT SETTING
To model the MDP according to the problem ad-
dressed, the formulation proposed in (Yang et al.,
2022) has been exploited that extends the Imbalanced
Classification Markov Decision Process (ICMDP)
presented in (Lin et al., 2020) to the multi-class sce-
nario, so:
• Training data provide the observation space S;
therefore, each training sample represents an ob-
servation s
t
for a specific timestep t. Note that
S ∈ R
m×n
, with m the number of samples within
the training set and n the number of features.
• The action space A consists of all known labels
for classes. Therefore, given K classes, A =
{1, 2, ..., K}, i.e., |A| = K.
• The reward function f
R
represents the main com-
ponent of the proposed cost-sensitive approach
according to the following formula:
f
R
(s
t
, a
t
, l
t
) =
(
λ
t
=
m
−1
k
Λ
, if a
t
= l
t
−λ
t
, otherwise
(5)
where Λ = ||m
−1
1
, m
−1
2
, ..., m
−1
K
||
2
, l
t
refers to the
true label of the observed s
t
and m
k
represents the
number of samples in the k-th class. In this way,
the agent can adjust learning to be more sensitive
to minority classes, as the higher m
k
, the lower λ
t
.
• Finally, according to the definition of S, the states-
transition probability φ is deterministic; thus, the
agent advances from s
t
to s
t+1
, as determined by
the order of the samples within S.
Deep Q-Networks for Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware Classification
345

5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
5.1 Materials and Methods
5.1.1 Dataset
This study uses the dataset proposed in (Catak et al.,
2021). It consists of a set of API call sequences ex-
tracted by analyzing each malicious sample through
the sandbox Cuckoo. Each sequence is associated
with a label that denotes the malware family to which
the sample belongs. First, the data were split into
80% for training and 20% for testing using a strati-
fied holdout strategy. Table 1 reports the number
Table 1: No. training samples per malware family for three
distinct unbalanced scenarios (USs).
Malware family
No. samples
US-1 US-2 US-3
Spyware 665 398 131
Downloader 800 ←
1
←
Trojan 800 ← ←
Worms 800 ← ←
Adware 303 36 ←
Dropper 713 446 179
Virus 800 ← ←
Backdoor 800 ← ←
of training samples for each malware family in the
dataset for three different USs. The original dataset
(US-1) shows that the Adware category represents the
minority class. On the other hand, each family with
800 samples can be considered the majority. To gen-
erate two new test cases, i.e., US-2 and US-3, one-
third of the training samples in the majority classes
are randomly removed from the Adware, Spyware,
and Dropper samples. Each US generated represents
a more complex imbalanced problem because the ra-
tio between samples in minority classes and those in
majority classes decreases for new test cases. Accord-
ing to (de Oliveira and Sassi, 2019), we processed the
generic API sequence so that duplicate calls were re-
moved and n was restricted to 100. Once extracted,
the APIs were converted into distinct integers. Fi-
nally, null values before the 100th column have been
padded with −1.
5.1.2 Metrics
Depending on the problem tackled, a true positive
(TP) represents a correct classification of samples as-
sociated with the positive class, whereas a false posi-
1
The symbol ← indicates that the current cell has the
same value as the left one.
tive (FP) indicates a misclassification of samples be-
longing to the same class. Similarly, correct and in-
correct classifications in the negative class are de-
noted with true negative (TN) and false negative (FN),
respectively. This notation is valid considering a
single class as the reference one at a time; hence,
each computation must refer to a single class com-
pared to the other K −1 for a multi-class classification
problem involving K different classes. According to
(Demirkıran et al., 2022), the appropriate metrics for
the problem at hand are the area under Receiver Op-
erating Characteristic curve (AUC) and the macro F1
score, which assumes that each class has the same im-
pact regardless of its skew.
5.1.3 Setting of the Algorithms Evaluated
This section provides some implementation details of
the DQNs evaluated in this study. In particular, the
source code provided in a public repository
2
was ex-
tended to work with the data typology involved and to
include all the DRL techniques described in Section
3. For the RL part, we leveraged the following hy-
perparameter configuration: the discount rate was set
to ζ = 0.8; the update parameter period τ consisted
of 10
3
steps; when NoisyNet was not used, the ε-
greedy exploration policy was invoked to perform an
action with a decay period of 10
4
and ε
min
= 0.2. In-
stead, for the DL part, the main and target DNNs were
implemented using two hidden layers, each with 512
nodes. The dueling layer consists of: (i) a conv1D
layer that has 64 filters and the kernel size set to 8;
(ii) two fully-connected streams such that one has
a single neuron (to compute V ), while the second
comprises |A| neurons (to compute A
adv
). The units
of each DNN layer are activated by a rectified lin-
ear unit (RELU) function. The PER technique was
implemented using the proportional variant. Then,
we set κ = 10
−2
, ν = 0.6, and β = 0.4. The com-
ponents of NoisyNet were initialized as follows: µ
was derived from a truncated normal distribution; σ
consisted of constant values (set to 0.017); χ com-
prised random values obtained from a uniform distri-
bution. The L
D(D)QN
(θ) (
¯
L
D(D)QN
(∆) for NoisyNet)
is minimized using α = 25 × 10
−5
as the learning
rate and considering |b| = 128 tuples sampled (uni-
formly when PER was not activated) from the replay
buffer (|B | = 5 × 10
4
). Furthermore, training lasted
|E | = 15 × 10
4
, and the Adam optimizer applied gra-
dient descent. Finally, a generic training episode ends
when: (i) m samples have been classified; (ii) minor-
ity samples were incorrectly classified (ξ
t
= 1).
2
https://github.com/Montherapy/Deep-reinforcement-
learning-for-multi-class-imbalanced-classification
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
346
5.2 Results
Table 2 reports the macro-F1 and AUC values
achieved by the generic DRL algorithm. Each eval-
uation differs in whether (✓) or not (✗) the techniques
discussed above are used. The main results can be
summarized as follows:
• The DQN exhibits promising classification per-
formance in its vanilla version. It achieves F1 and
AUC scores equal to 44.6% and 0.68 in US-1, re-
spectively. As expected, performance decreases
with the S size in US-2 and US-3 (see Table 1).
Nevertheless, in US-2, the DQN-based classifier
is the second best performer in terms of macro-
averaged F1 score (41.6%) with respect to all al-
gorithms compared.
• The DDQN performance is similar to that
achieved by the DQN in US-1 and US-3. How-
ever, it underperforms DQN in US-2. In fact, in
this case, it appears to be incapable of learning an
adequate classification policy because AUC = 0.5
indicates a random classifier.
When these are integrated with the other three
DRL techniques, the following effects are observed:
• The PER does not result in improved performance
when adopted singularly. On the contrary, DQN
suffers a 5.4% reduction in the F1 value in the US-
2. A worse trend is recorded for DDQN; in fact,
the adoption of prioritization degrades the classi-
fication performance in US-1 and US-2, resulting
in a classifier unable to distinguish between the
malware families involved.
• The dueling design enhances and stabilizes the
performance of both algorithms even when they
are combined with the PER technique. Specif-
ically, in US-1, the dueling version of DDQN
and DQN combined with PER achieves F1 and
AUC of 48.3% and 0.7, respectively, which rep-
resent the highest scores for all algorithms ana-
lyzed. Likewise, the dueling DQN outperforms
the competitors in both: (i) US-2, achieving F1 =
42.5% and AUC = 0.671; (ii) US-3, achieving F1
= 36.2% and AUC = 0.647. Furthermore, it ob-
tained the second best performance in US-1 with
F1 = 47.9% and AUC = 0.698. Lastly, dueling
DDQN with PER is placed as the third top per-
former in US-2 because of F1 = 41.3% and AUC
= 0.662.
• The NoisyNet causes performance degradation
whenever used as an exploration strategy. This
leads the generic DRL-based classifier to perform
random malware categorization, as highlighted by
the achieved AUC score, which is close to 0.5 in
any case. Similarly, the highest F1 score close to
15% is obtained by the dueling NoisyNet-DQN
with PER for US-2.
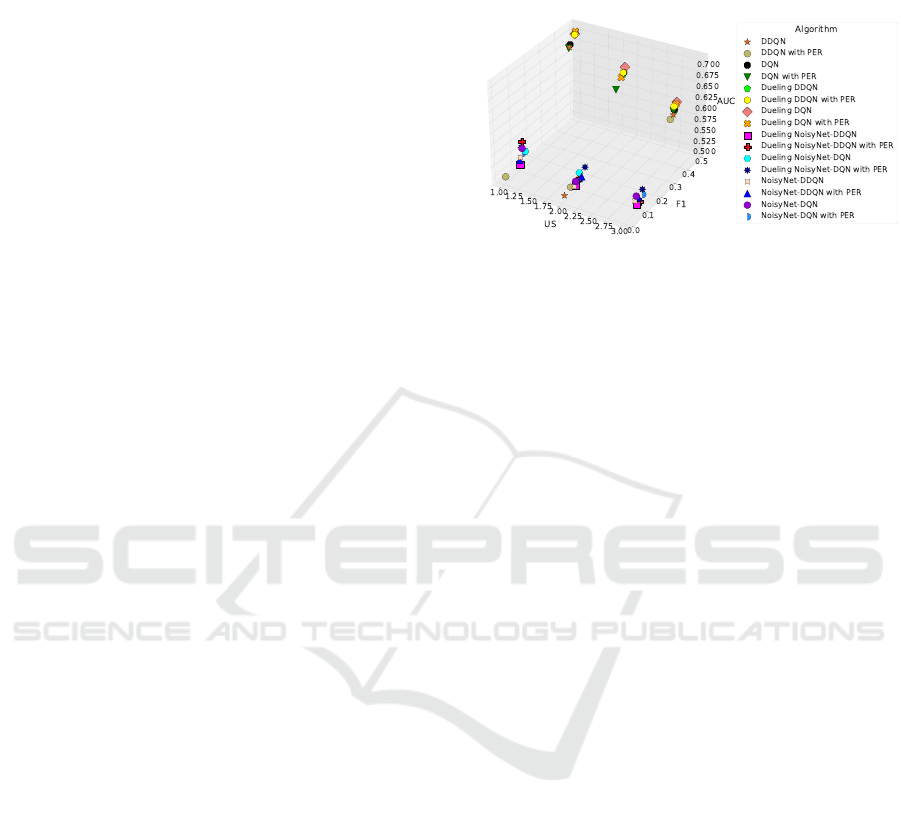
Figure 1: Distribution of the results reported in Table 2.
The overall performance analysis is shown in Fig-
ure 1, which illustrates the algorithmic efficiency,
i.e., the F1 and AUC scores achieved by each DQN
and DDQN configuration per specific US. There is
evidence of two sub-distributions that are, respec-
tively, placed in the two vertical planes of the three-
dimensional space identified by the maximum and
minimum values of F1. Take a look at the three bidi-
mensional scatter plots identified by relating F1 with
AUC. In such a projection, the best performing algo-
rithms are placed in the first quadrant of each plane.
5.2.1 Detailed Analysis
As a consequence of the above discussion, we identi-
fied the three top performers per US to focus on their
ability to address the imbalanced multi-class classi-
fication problem. For this purpose, Figure 2 pro-
vides a detailed problem-specific analysis, showing
the F1 and AUC scores per class achieved by the three
best algorithms for each US. We can list the main
strengths and limitations inferred from such a detailed
analysis as follows:
• Figure 2 is useful for performing a robustness
analysis of each algorithm. Specifically, the ro-
bustness property must be understood as the abil-
ity to continue operating despite a decrease in the
number of samples in the minority class. Based
on our experiments, dueling DQN-based classifier
was found to be robust because it falls within the
three top performers in each of the three USs.
• All algorithms share a key result, that is, the high-
est values of F1 and AUC were obtained for sam-
ples belonging to the Adware family, which effec-
tively represents the minority class. This is true
even for very critical imbalance scenarios, such
as in US-2 and US-3, where the balancing ratio in
training is 0.045.
Deep Q-Networks for Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware Classification
347
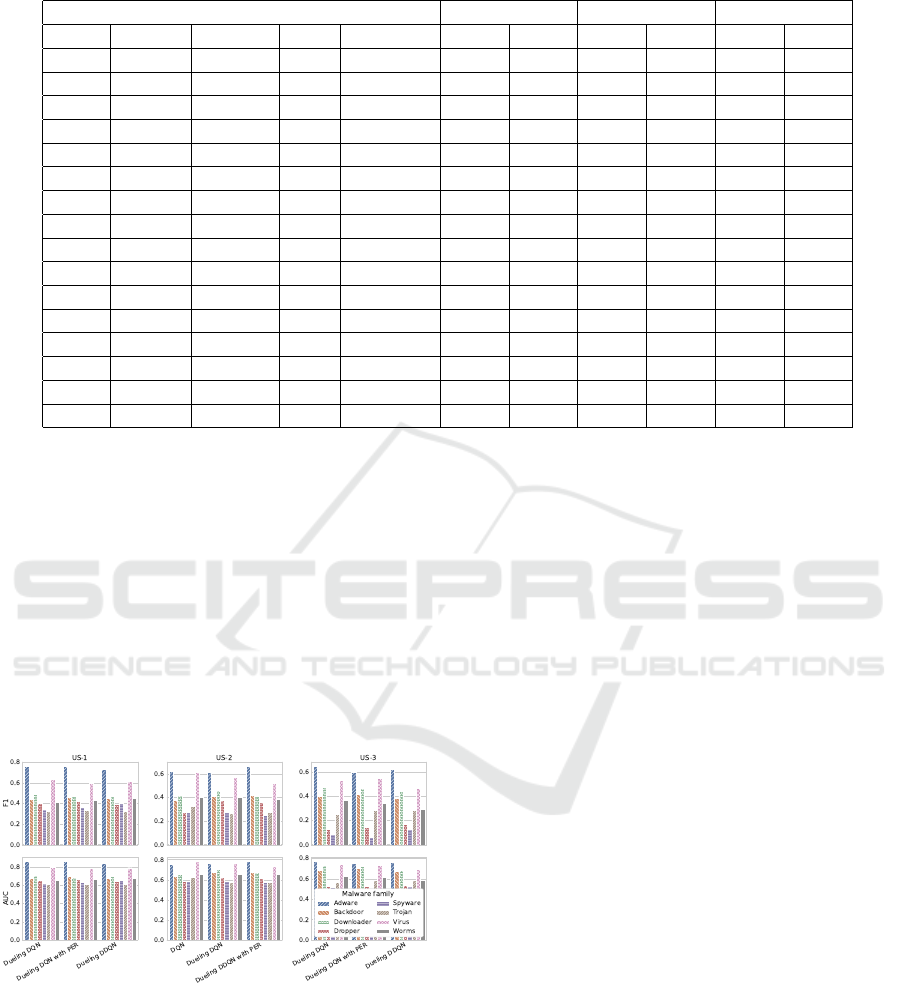
Table 2: Macro F1 score and AUC obtained using each algorithm for different US.
Algorithm US-1 US-2 US-3
DQN DDQN Dueling PER NoisyNet F1 AUC F1 AUC F1 AUC
✓ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✗ 0.446 0.682 0.416 0.661 0.344 0.635
✓ ✗ ✓ ✗ ✗ 0.479 0.698 0.425 0.671 0.362 0.647
✓ ✗ ✗ ✓ ✗ 0.437 0.676 0.362 0.637 0.338 0.634
✓ ✗ ✗ ✗ ✓ 0.119 0.533 0.086 0.509 0.083 0.520
✓ ✗ ✓ ✓ ✗ 0.483 0.703 0.398 0.655 0.357 0.644
✓ ✗ ✓ ✗ ✓ 0.139 0.520 0.111 0.521 0.093 0.500
✓ ✗ ✗ ✓ ✓ 0.119 0.521 0.115 0.505 0.128 0.509
✓ ✗ ✓ ✓ ✓ 0.113 0.537 0.149 0.522 0.125 0.522
✗ ✓ ✗ ✗ ✗ 0.442 0.677 0.013 0.500 0.339 0.625
✗ ✓ ✓ ✗ ✗ 0.483 0.700 0.411 0.658 0.348 0.632
✗ ✓ ✗ ✓ ✗ 0.012 0.500 0.053 0.506 0.317 0.621
✗ ✓ ✗ ✗ ✓ 0.107 0.515 0.076 0.500 0.074 0.512
✗ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✗ 0.478 0.697 0.413 0.662 0.341 0.634
✗ ✓ ✓ ✗ ✓ 0.103 0.500 0.086 0.500 0.087 0.500
✗ ✓ ✗ ✓ ✓ 0.101 0.511 0.126 0.507 0.097 0.513
✗ ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ 0.118 0.549 0.112 0.509 0.108 0.500
• Algorithms appear to be sensitive to a single mi-
nority class (Adware). In fact, the worst perfor-
mance was recorded for the Spyware and Dropper
families, i.e., two other cases of sample availabil-
ity lower than that of the remaining classes. These
poor performances are evident in US-2 and US-
3, which correspond to the undersampling actions
described in Table 1. However, the unsatisfactory
performance on Spyware cannot be uniquely at-
tributed to the availability of samples of that class
in the training set. In fact, the values of F1 and
AUC are comparable to those obtained for the
Trojan malware family, except for US-3.
Figure 2: F1 and AUC scores per class achieved by the three
top performers in each US.
6 CONCLUSION
Malware classification is a crucial task to ensure the
security of information systems. Researchers are ac-
tively searching for detection models that are increas-
ingly efficient and robust to bias due to the unequal
distribution of available data. Accordingly, our study
conducted an in-depth analysis that involved the use
of classical DRL algorithms combined with domain-
specific techniques. Adopting RL allowed the use of
appropriate problem modeling to consider data im-
balance during learning. The experiments performed
showed promising results for the DQN and DDQN
agents equipped with the dueling design. Specifically,
the dueling DQN model exhibited satisfactory clas-
sification performance and robustness to the gradual
reduction of samples within the minority class. Over
existing methods, our contribution represents the first
DRL-based cost-sensitive strategy for the problem at
hand, which does not alter the training data, retain-
ing real-world accuracy. Further research could focus
on ablation studies of the most effective algorithms,
leading to a proper and rigorous tuning of the DNN
hyperparameters could boost the tested DRL agents to
achieve state-of-the-art performance of DL models.
FUNDING
This work was supported in part by the Fondo
Europeo di Sviluppo Regionale Puglia Programma
Operativo Regionale (POR) Puglia 2014-2020-Axis
I-Specific Objective 1a-Action 1.1 (Research and
Development)-Project Title: CyberSecurity and
Security Operation Center (SOC) Product Suite
by BV TECH S.p.A., under Grant CUP/CIG
B93G18000040007.
ICISSP 2024 - 10th International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy
348

REFERENCES
Aboaoja, F. A., Zainal, A., Ghaleb, F. A., Al-rimy, B. A. S.,
Eisa, T. A. E., and Elnour, A. A. H. (2022). Malware
detection issues, challenges, and future directions: A
survey. Applied Sciences, 12(17).
Akarsh, S., Simran, K., Poornachandran, P., Menon, V. K.,
and Soman, K. (2019). Deep learning framework
and visualization for malware classification. In 2019
5th International Conference on Advanced Computing
& Communication Systems (ICACCS), pages 1059–
1063. IEEE.
Alzammam, A., Binsalleeh, H., AsSadhan, B., Kyriakopou-
los, K. G., and Lambotharan, S. (2020). Compara-
tive analysis on imbalanced multi-class classification
for malware samples using cnn. In 2019 International
Conference on Advances in the Emerging Computing
Technologies (AECT), page 1–6. IEEE.
Anderson, H. S., Kharkar, A., Filar, B., Evans, D., and
Roth, P. (2018). Learning to evade static pe machine
learning malware models via reinforcement learning.
arXiv, arXiv:1801.08917.
Birman, Y., Hindi, S., Katz, G., and Shabtai, A. (2022).
Cost-effective ensemble models selection using deep
reinforcement learning. Information Fusion, 77:133–
148.
Catak, F. O., Ahmed, J., Sahinbas, K., and Khand, Z. H.
(2021). Data augmentation based malware detection
using convolutional neural networks. PeerJ Computer
Science, 7:e346.
Coscia, A., Dentamaro, V., Galantucci, S., Maci, A., and
Pirlo, G. (2023). Yamme: a yara-byte-signatures
metamorphic mutation engine. IEEE Transactions on
Information Forensics and Security, 18:4530–4545.
de Oliveira, A. S. and Sassi, R. J. (2019). Behavioral
Malware Detection Using Deep Graph Convolutional
Neural Networks. TechRxiv.
Demirkıran, F., C¸ ayır, A.,
¨
Unal, U., and Da
˘
g, H. (2022). An
ensemble of pre-trained transformer models for imbal-
anced multiclass malware classification. Computers &
Security, 121:102846.
Deng, X., Cen, M., Jiang, M., and Lu, M. (2023). Ran-
somware early detection using deep reinforcement
learning on portable executable header. Cluster Com-
puting, pages 1–15.
Ding, Y., Wang, S., Xing, J., Zhang, X., Qi, Z., Fu, G.,
Qiang, Q., Sun, H., and Zhang, J. (2020). Mal-
ware classification on imbalanced data through self-
attention. In 2020 IEEE 19th International Confer-
ence on Trust, Security and Privacy in Computing and
Communications (TrustCom), page 154–161. IEEE.
Fang, Z., Wang, J., Geng, J., and Kan, X. (2019a). Feature
selection for malware detection based on reinforce-
ment learning. IEEE Access, 7:176177–176187.
Fang, Z., Wang, J., Li, B., Wu, S., Zhou, Y., and Huang, H.
(2019b). Evading anti-malware engines with deep re-
inforcement learning. IEEE Access, 7:48867–48879.
Fortunato, M., Azar, M. G., Piot, B., Menick, J., Osband,
I., Graves, A., Mnih, V., Munos, R., Hassabis, D.,
Pietquin, O., Blundell, C., and Legg, S. (2019). Noisy
networks for exploration. arXiv, arXiv:1706.10295.
Hasselt, H. v., Guez, A., and Silver, D. (2016). Deep re-
inforcement learning with double q-learning. In Pro-
ceedings of the Thirtieth AAAI Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence, volume 30, page 2094–2100. AAAI
Press.
Lin, E., Chen, Q., and Qi, X. (2020). Deep reinforcement
learning for imbalanced classification. Applied Intel-
ligence, 50:2488–2502.
Lu, Y. and Shetty, S. (2021). Multi-class malware classifi-
cation using deep residual network with non-softmax
classifier. In 2021 IEEE 22nd International Confer-
ence on Information Reuse and Integration for Data
Science (IRI), page 201–207. IEEE.
Maci, A., Santorsola, A., Coscia, A., and Iannacone,
A. (2023). Unbalanced web phishing classification
through deep reinforcement learning. Computers,
12(6).
Mnih, V., Kavukcuoglu, K., Silver, D., Rusu, A. A., Ve-
ness, J., Bellemare, M. G., Graves, A., Riedmiller, M.,
Fidjeland, A. K., Ostrovski, G., et al. (2015). Human-
level control through deep reinforcement learning. na-
ture, 518(7540):529–533.
Schaul, T., Quan, J., Antonoglou, I., and Silver, D.
(2016). Prioritized experience replay. arXiv,
arXiv:1511.05952.
Sewak, M., Sahay, S. K., and Rathore, H. (2023). Deep
reinforcement learning in the advanced cybersecurity
threat detection and protection. Information Systems
Frontiers, 25(2):589–611.
Song, W., Li, X., Afroz, S., Garg, D., Kuznetsov, D., and
Yin, H. (2022). Mab-malware: A reinforcement learn-
ing framework for blackbox generation of adversarial
malware. In Proceedings of the 2022 ACM on Asia
Conference on Computer and Communications Secu-
rity, page 990–1003. ACM.
Wang, Y., Stokes, J., and Marinescu, M. (2020). Actor critic
deep reinforcement learning for neural malware con-
trol. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artifi-
cial Intelligence, volume 34, page 1005–1012. Asso-
ciation for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence
(AAAI).
Wang, Y., Stokes, J. W., and Marinescu, M. (2019). Neu-
ral malware control with deep reinforcement learning.
In MILCOM 2019 - 2019 IEEE Military Communica-
tions Conference (MILCOM), page 1–8. IEEE.
Wang, Z., Schaul, T., Hessel, M., van Hasselt, H., Lanctot,
M., and de Freitas, N. (2016). Dueling network archi-
tectures for deep reinforcement learning. In Proceed-
ings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine
Learning, volume 48, page 1995–2003. PMLR.
Wu, Y., Li, M., Zeng, Q., Yang, T., Wang, J., Fang, Z., and
Cheng, L. (2023). Droidrl: Feature selection for an-
droid malware detection with reinforcement learning.
Computers & Security, 128:103126.
Yang, J., El-Bouri, R., O’Donoghue, O., Lachapelle, A. S.,
Soltan, A. A. S., and Clifton, D. A. (2022). Deep re-
inforcement learning for multi-class imbalanced train-
ing. arXiv, arXiv:2205.12070.
Deep Q-Networks for Imbalanced Multi-Class Malware Classification
349
